Geo 004 final Study Guide
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
4 A's of mitigation
avoid
accept
anticipate
alter
Levees
a natural or artificial wall that blocks water from going where we don't want it to go
stages of tornadoes
wall cloud
tendril (comes down and spins fast)
tornado forms
jet streams
fast wind from west to east
influences weather
water phases
solid, liquid, gas
how are thunderstorms form?
warm air is brought to the atmosphere
water vapor condenses and releases energy (heat)
how do hurricanes happen?
warm moist air rises up and form clouds and clump together
air goes down forming the hurricane spinning counterclock wise
pyrolysis
gas release from wood (makes fire stronger)
atmosphere circulation
comes from the sun’s energy not hitting the earth evenly
do hurricanes last on land?
nope, they lose power because they are powered by warm waters
where does the sand of a beach come from?
the land
swash zones
waves that goes in and out/ back and forth
coastal erosion
the lost of sand and rock on a beach (increased by El Nino)
wave refraction
shallow parts slow down and deep parts move fast (wave curves)
headlands make waves into shallow water waves and keep deep water waves the same
headlands focuses wave energy, which allows the waves to transport to transport more sand
groin
structure that goes out into the ocean and causes sand to be deposited
sand is eroded on the other side
which is more dangerous tsunamis or earthquakes?
tsunamis
how to classify mass movement
how much water they contain
how rapidly they move
what happens to the speed of tsunamis when it reaches the shore?
it slows down
how are waves characterized?
wavelength and wave height
most waves are formed by winds
tidal bore
fast tides that are similar to tsunamis
tidal range
difference b/t high and low tides
¼ moon = lowest
full moon = highest
how to alter mass movements
by adding channels to sheer material out of populated areas
cut and fill techinque
cut into a slope and fill in
this is to build house on hills
potentially dangerous
difference b/t flows and slides
flows move down like liquids
slides maintain there shape as they slide down
flow types
earth, mud, and debris flows
traditional slides
a landslide or mass movement where material moves down a slope
rotational slides or slumps
Rotational slide along a curved failure surface.
what contributes to mass movements?
Water, and the type of material
what happens when streams have too much discharge
they tend to erode their channel therefore shallowing its gradient
longshore drift
wave process that carries sediment (sand) along a beach
man made beach structures
seawalls
breakwaters
jetties/groins
seawalls
Protect cliffs but starve beaches of sediment
breakwaters
structure put on the water to protect the beach Reduce wave energy but alter sediment deposition
jetties
entrances for harbors
Trap sediment on one side, causing erosion downdrift
beach renourishment
addition of sand to beaches to combat erosion, temporary & costs a lot
Effects of Water
Water reduces friction, adds weight, and weakens materials and can cause slides or flows
landslide features
Head scarp (top fracture)
head (upper slide mass)
toe (lower debris pile)
Clay vs. Hard Rock
Clay is weak, prone to sliding when wet; hard rock is stronger but can fail if fractured or undercut
wavelength
the distance between two corresponding points on a wave, crests and troughs
Dams
Store water to control floods but alter ecosystems and sediment transport
where do mass movements occur?
Steep slopes, loose sediment, fractured rock, areas with heavy rainfall or seismic activity.
the relationship between gravity and friction
Gravity drives mass movements; friction resists.
Slope angle, material strength, and water content determine stability all contribute to this relationship
period
time it takes to get b/t wavelengths
speed
how fast the wave goes
height
how high the wave gets
earthflows
super slow flows that resemble fluids
rockfalls
move fast
are dry
formed when water freezes, expands and makes rocks detach from steep slopes
subsidences
sinking of the ground due to material seeping into the earth like groundwater
like a sinkhole
beaches
they have rocks under the sand
sand moves because of waves
rocks resurface
summers (sandy) & winters (rocky/erosion)
water movement in the ocean
rotates in circles (wave orbitals)
Major rivers in the U.S
Mississippi
Colorado
Missouri
Ohio
Columbia
Watersheds
area of land where water drains to for ex. river or lake
Discharge
Volume of water flowing per unit time (ex. sec)
there is more discharge at the end of a river
sediment load
stuff carried by rivers
ways rivers can flow
braided
straight
meandering (these causes rivers to shift)
types of floods
flash floods
regional floods
catastrophic floods
flash floods
rapid onset. often in small streams, does not last long
regional floods
widespread, prolonged flooding affecting large rivers
catastrophic floods
rare, massive events like dam breaches or glacial outbursts
recurrence interval
time b/t floods of a given magnitude for ex. 100 yr floods
floodplains
low-lying areas adjacent to river (flood a lot)
how do people interact with floods
moving or elevating their buildings
stream challenlization (this controls flooding but can cause erosion)
Levees
tsunamis
made of multiple waves
can be caused by earthquakes at subduction zones, landslides, and eruptions
low amplitude and long wavelength
can be detected by D.A.R.T
creeps
slow gradual movement of soil downhill (they have some water in it)
caused by expansion and contraction of the ground
can move houses
photosynthesis and fire
fire is just the reverse of the process of photosynthesis
how does lightning happen?
upper part of cloud is (+)
lower part of cloud is & ground (-)
how does air flow?
from high to low pressure
hanging and foot walls
hanging (over head)
foot (you can walk on it)
what caused the magnetic field around earth?
the rotation of the outer core (Liquid)
Contour interval
the vertical distance in elevation b/t adjacent contour lines
what are the different kinds of volcanoes?
spreading center fissure
shield volcanoes
stratovolcanoes
super volcanoes
flood basalts
Spreading center fissure volcanoes
no silicon dioxide (peaceful eruptions)
very wide
navigational maps
like google or apple maps
what are maps used for?
location, data, and understanding geography
Love Waves
side to side motion
one of the last to arrive but cause the most shaking)
Rayleigh Waves
up and down motion that feels like a ocean wave
one of the last to arrive and cause the most shaking
natural hazard
it is a natural process that threatens humanity in some way either life, economic development etc
if it has happened before it can probably happen again
natural disaster
natural process that has happened and affected humans
basic map elements
Scales
Legend
X & Y axis
Color, etc.
numeric scale
NO UNITS
tells you the distance on the map relative to the distance it is in real life
ex: 1 mi equals 100,000 inches or whatever unit
graphical scale
a small ruler that can be used to convert distances covered on a map to real-world distances
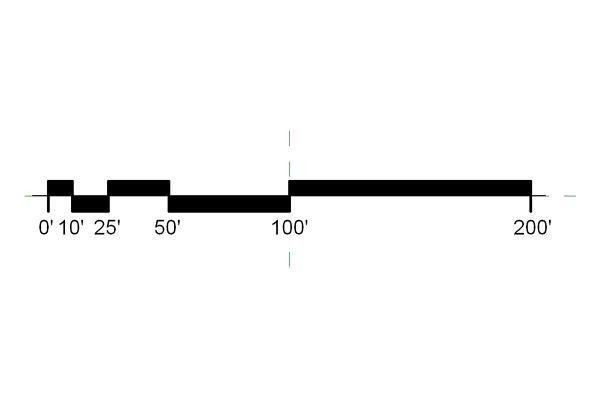
verbal scale
expresses distance in words
ex: 3 inch equals 10 miles
small scale
`relatively zoomed out
has less detail
large scale
relatively zoomed in
more details
topographic map
shows you elevation along with longitude and latitude
longitude
east or west
goes -180 to 180
middle is called the prime meridian (0 degrees)
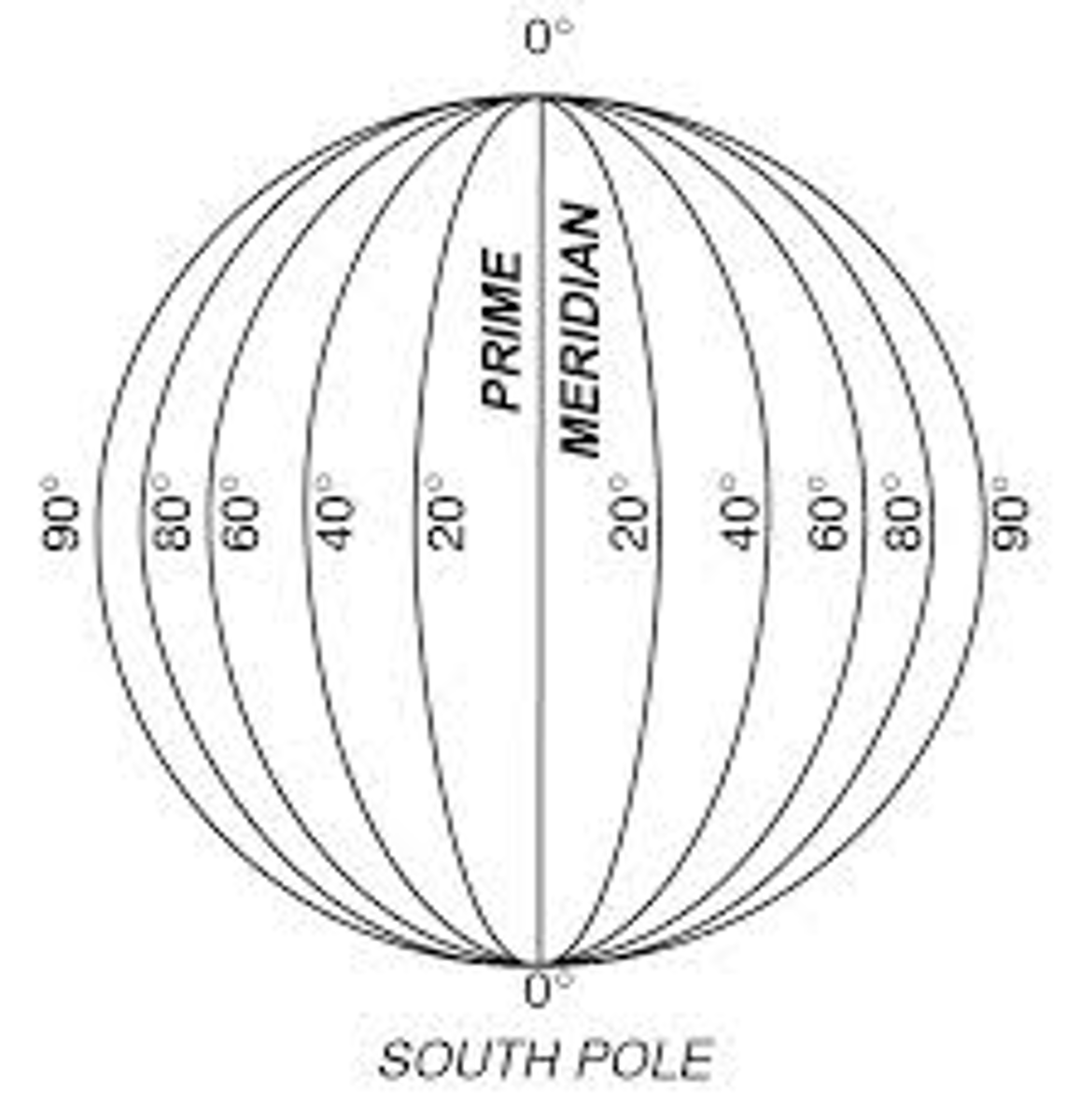
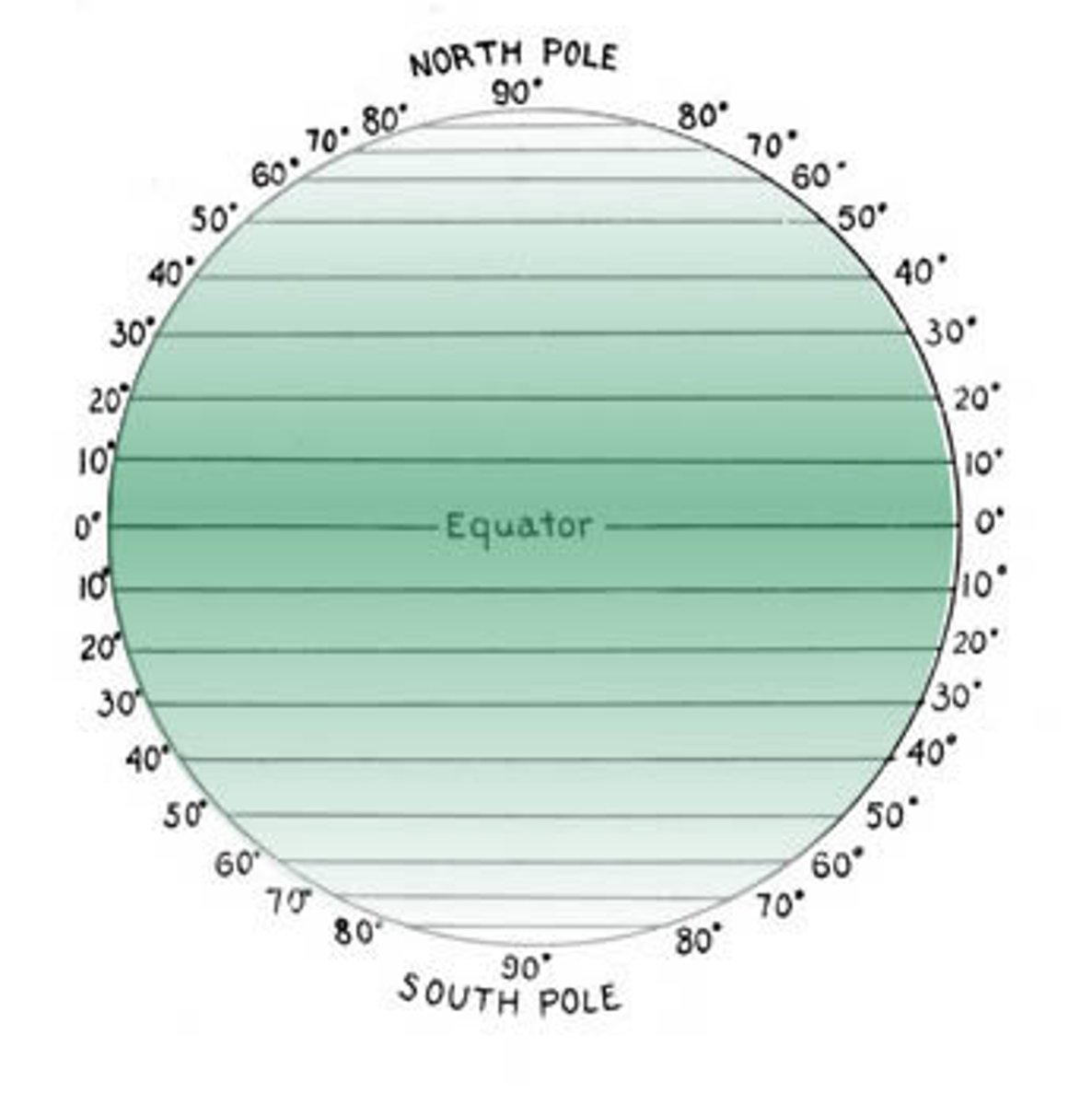
latitude
North to South
equator is 0 degrees
goes from -90 to 90
chemical layers (the one we learned in middle school)
crust (2 types)
mantle (heavy dense rock)
core (iron)
sorted by density, heaviest elements near center
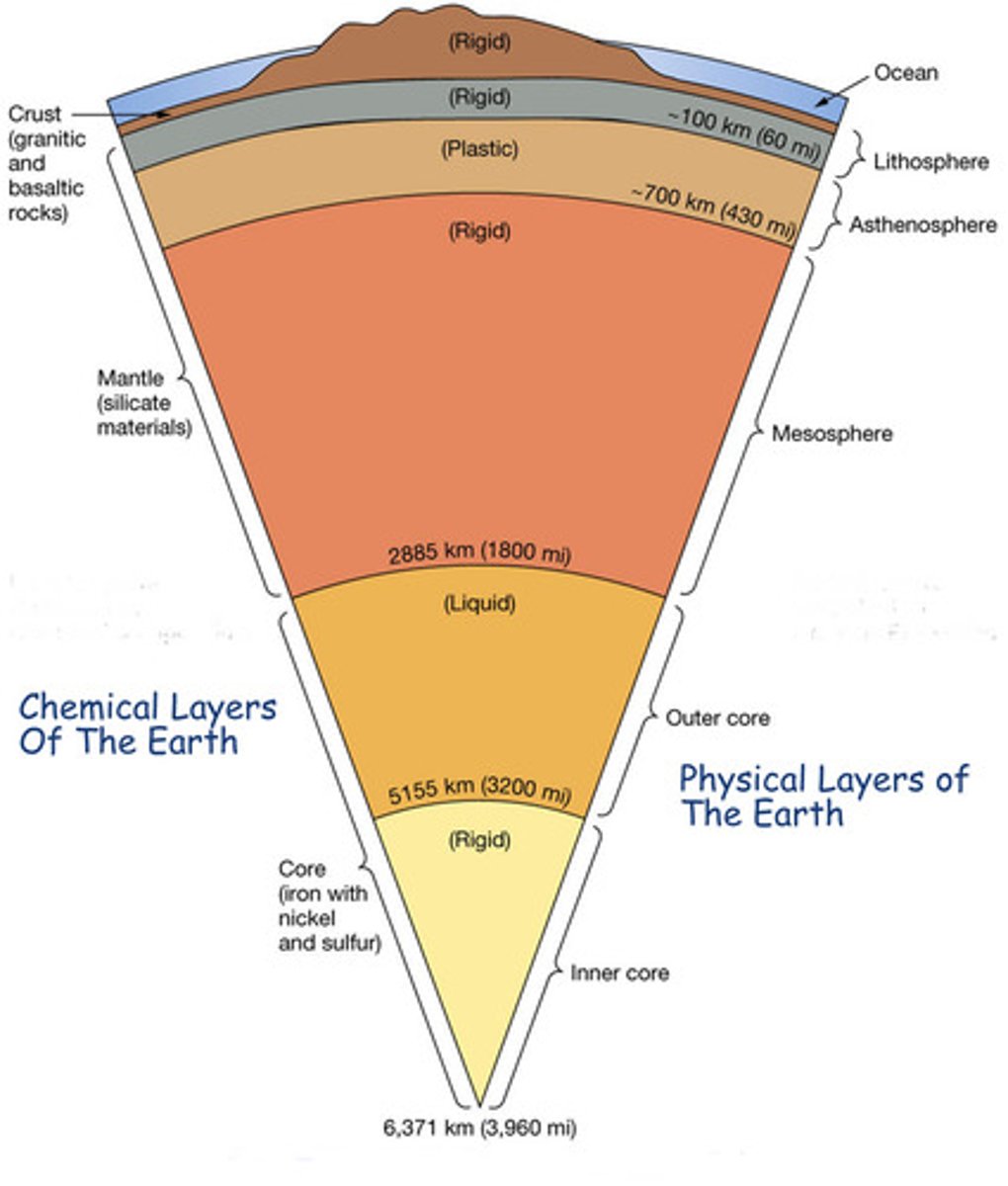
mechanical layers
lithosphere (rocky)
asthenosphere (plastic)
mesosphere (rigid)
outer core (liquid)
inner core (solid)
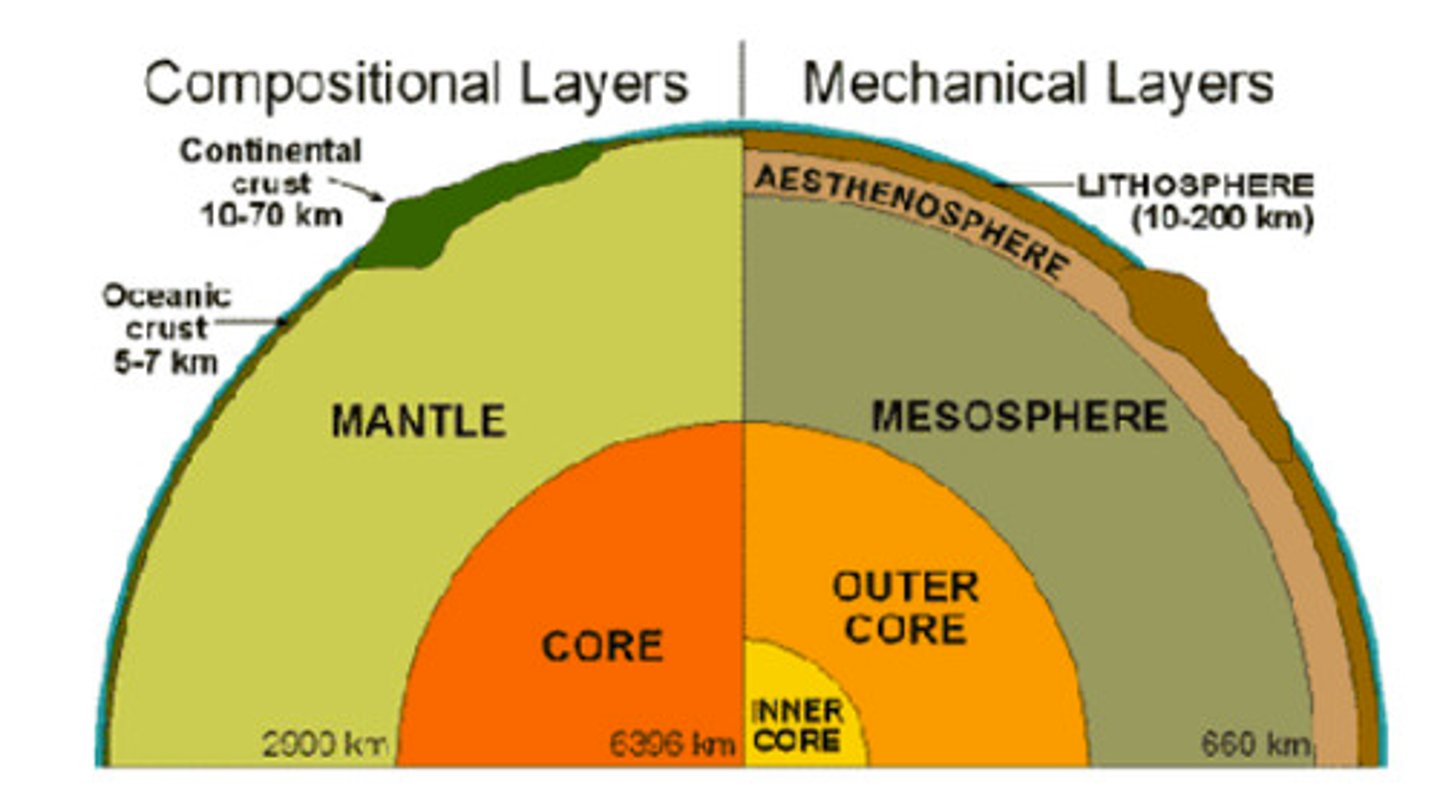
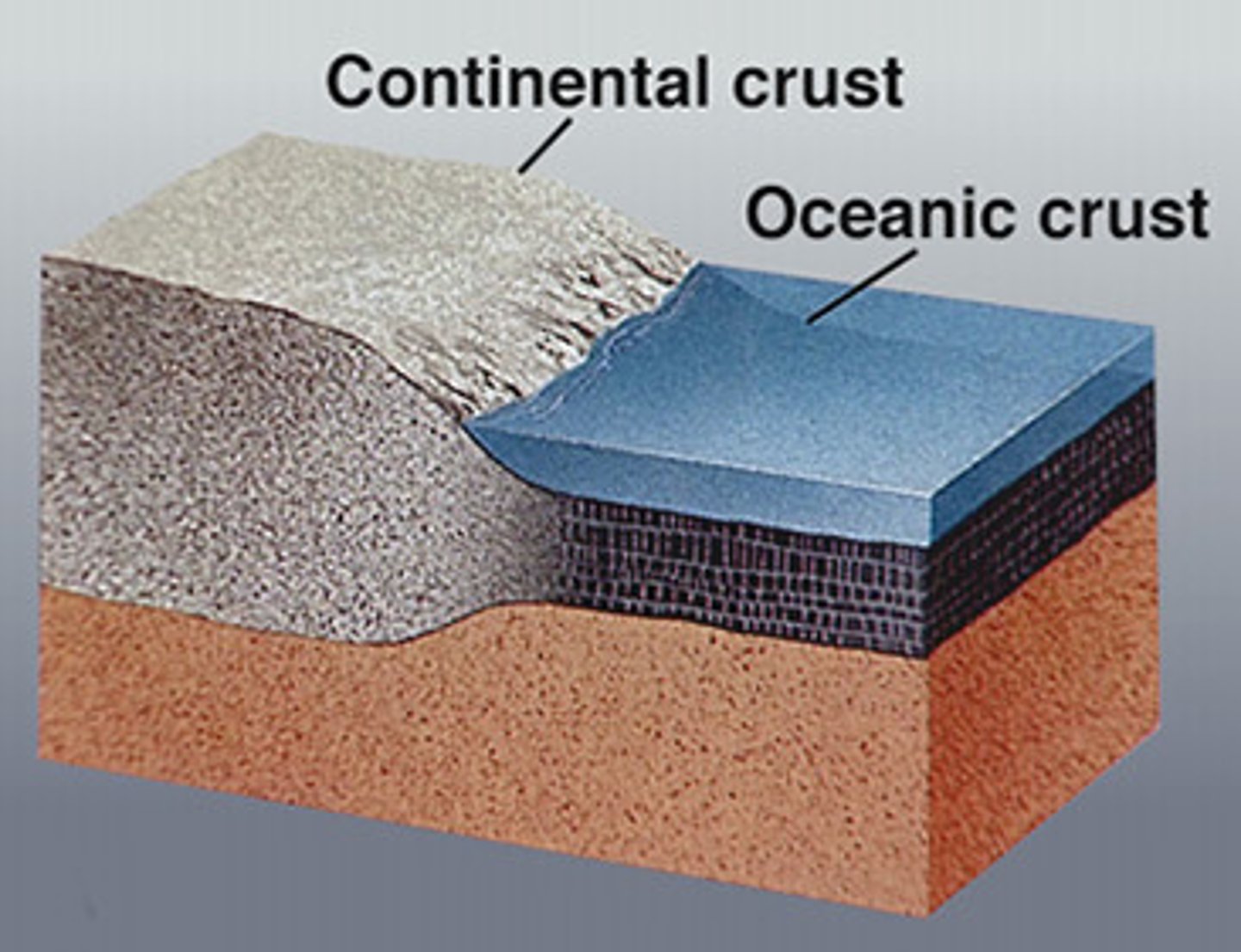
oceanic crust
Earths crust located under the ocean
usually thinner
more dense than the other crust
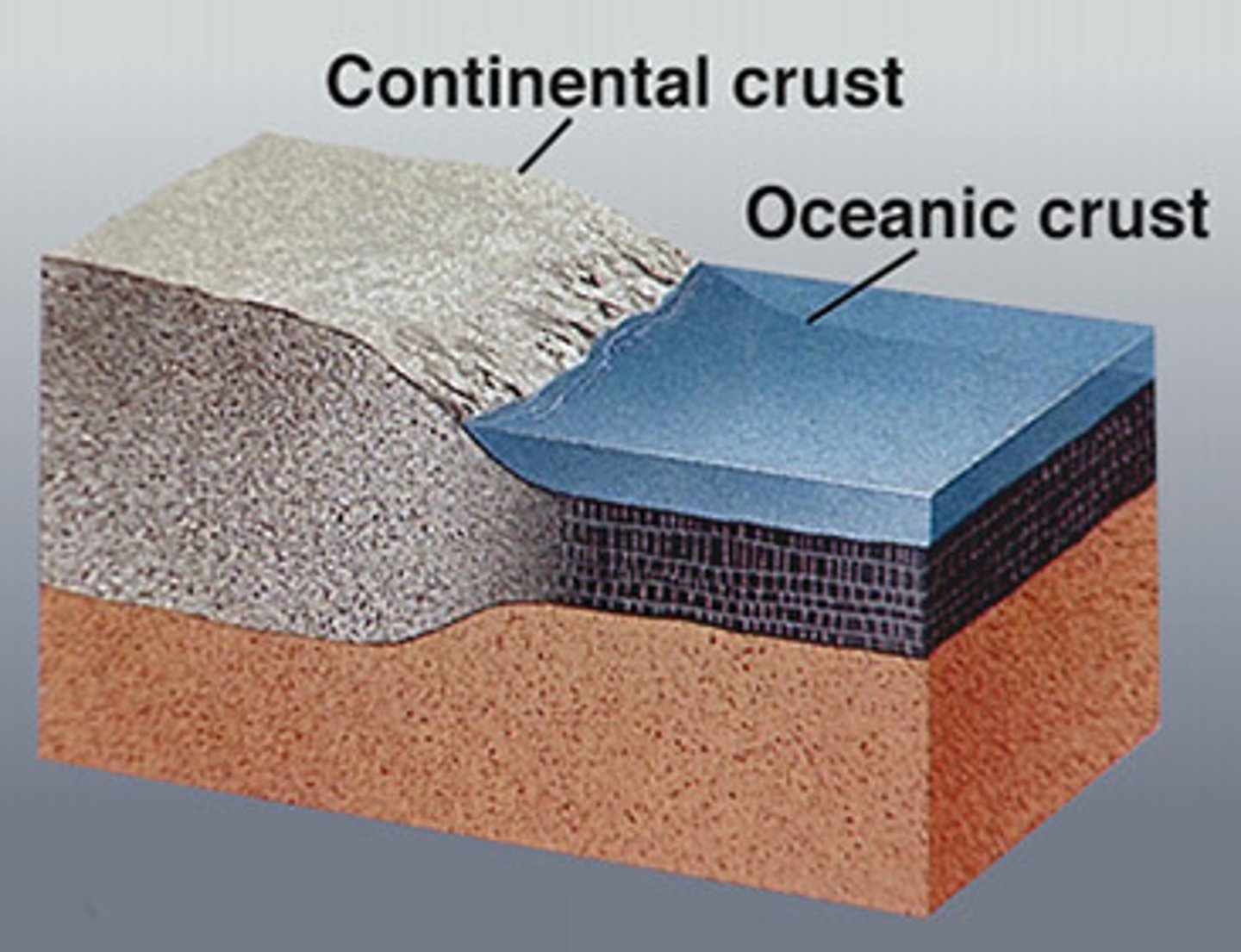
continental crust
The portion of the earth's crust
primarily contains granite
less dense than other crust
usually thicker
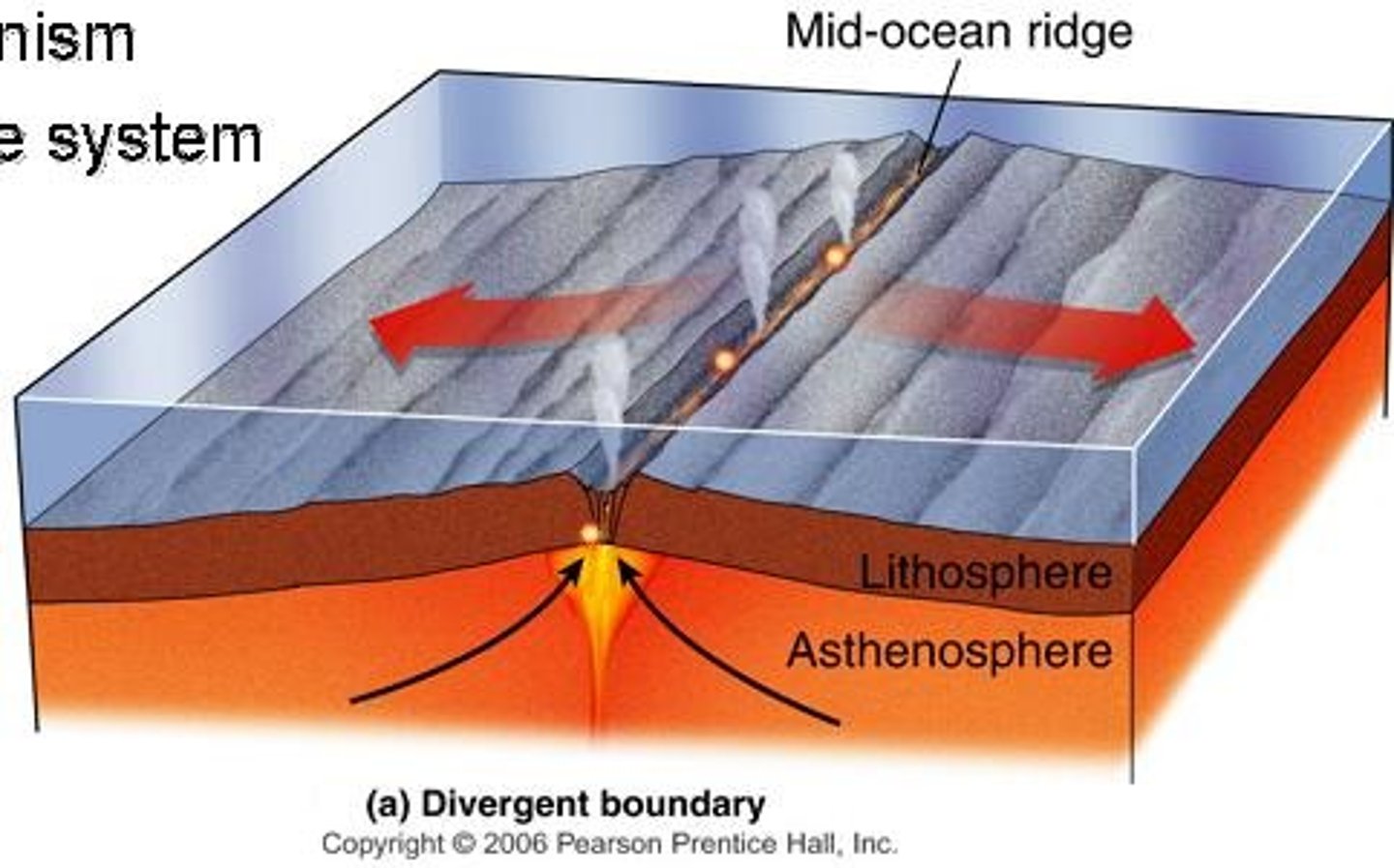
divergent plate boundaries
pull apart from each other
spreading center
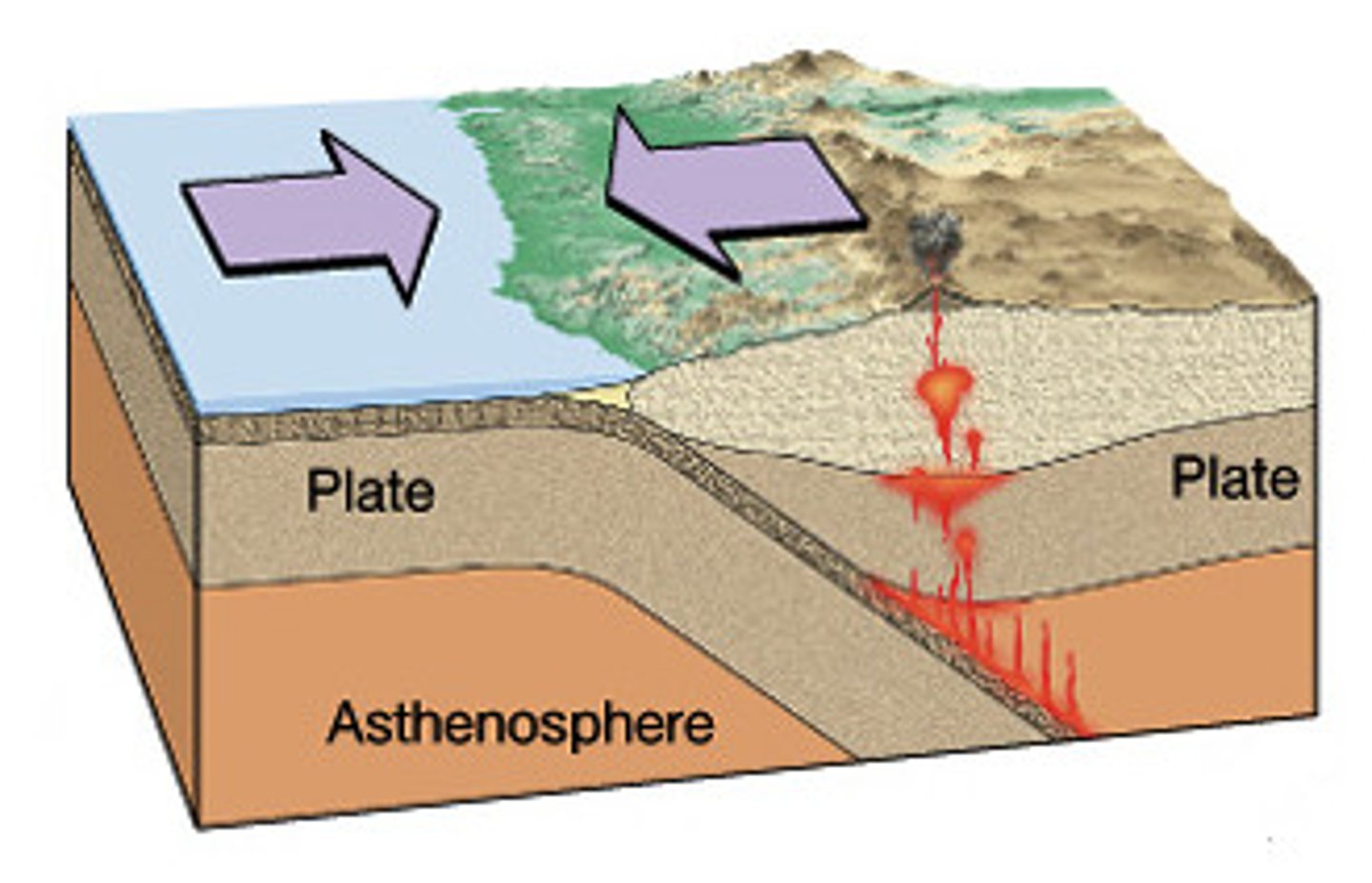
convergent plate boundaries
2 plates coming together
subduction zone
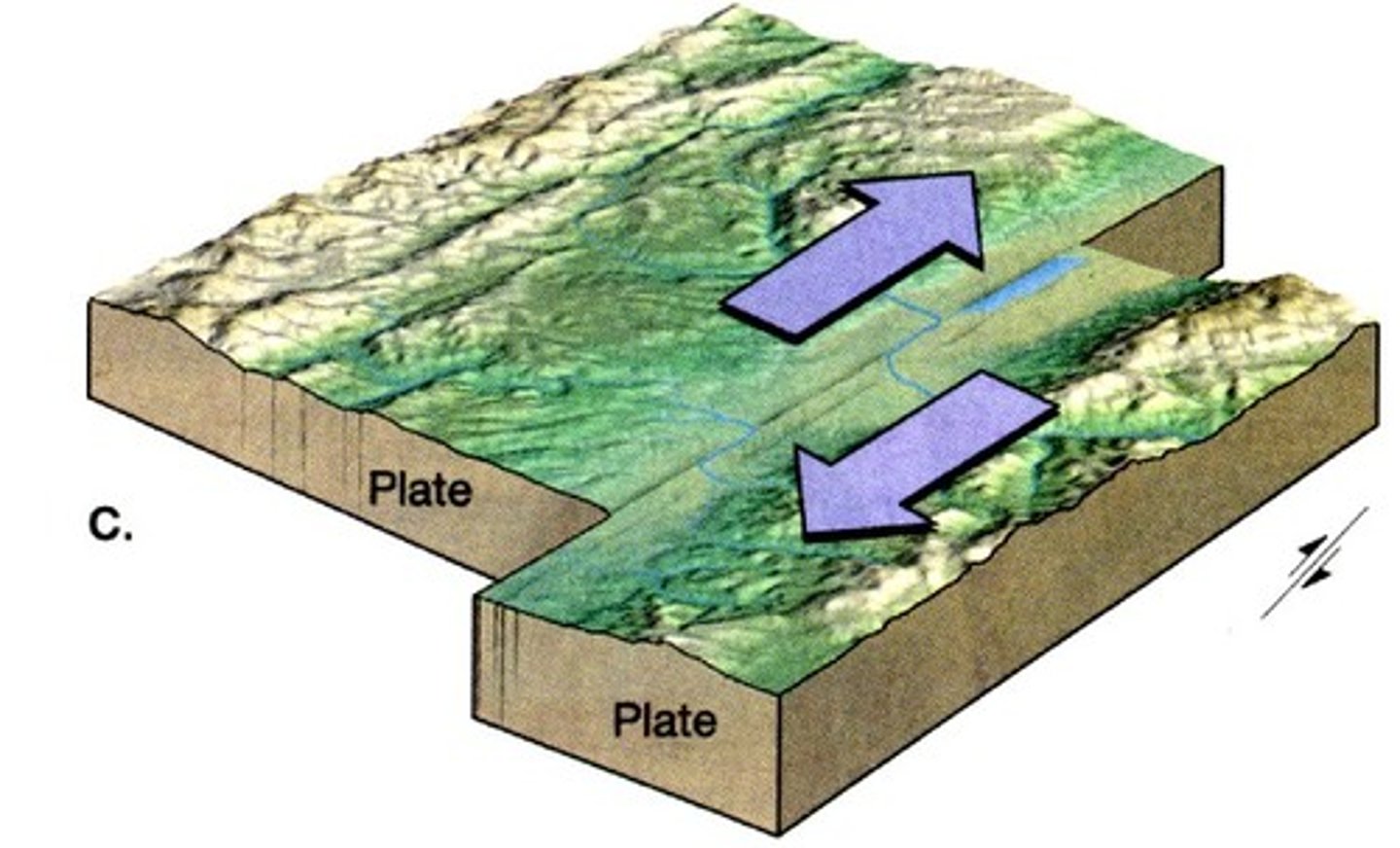
transform plate boundaries
slide past each other
Evidence for plate tectonics
shape of continents
rocks of mountain belts
climate indicators and fossils
earthquakes, volcanoes, and hot spot volcanism
seafloor magnetization
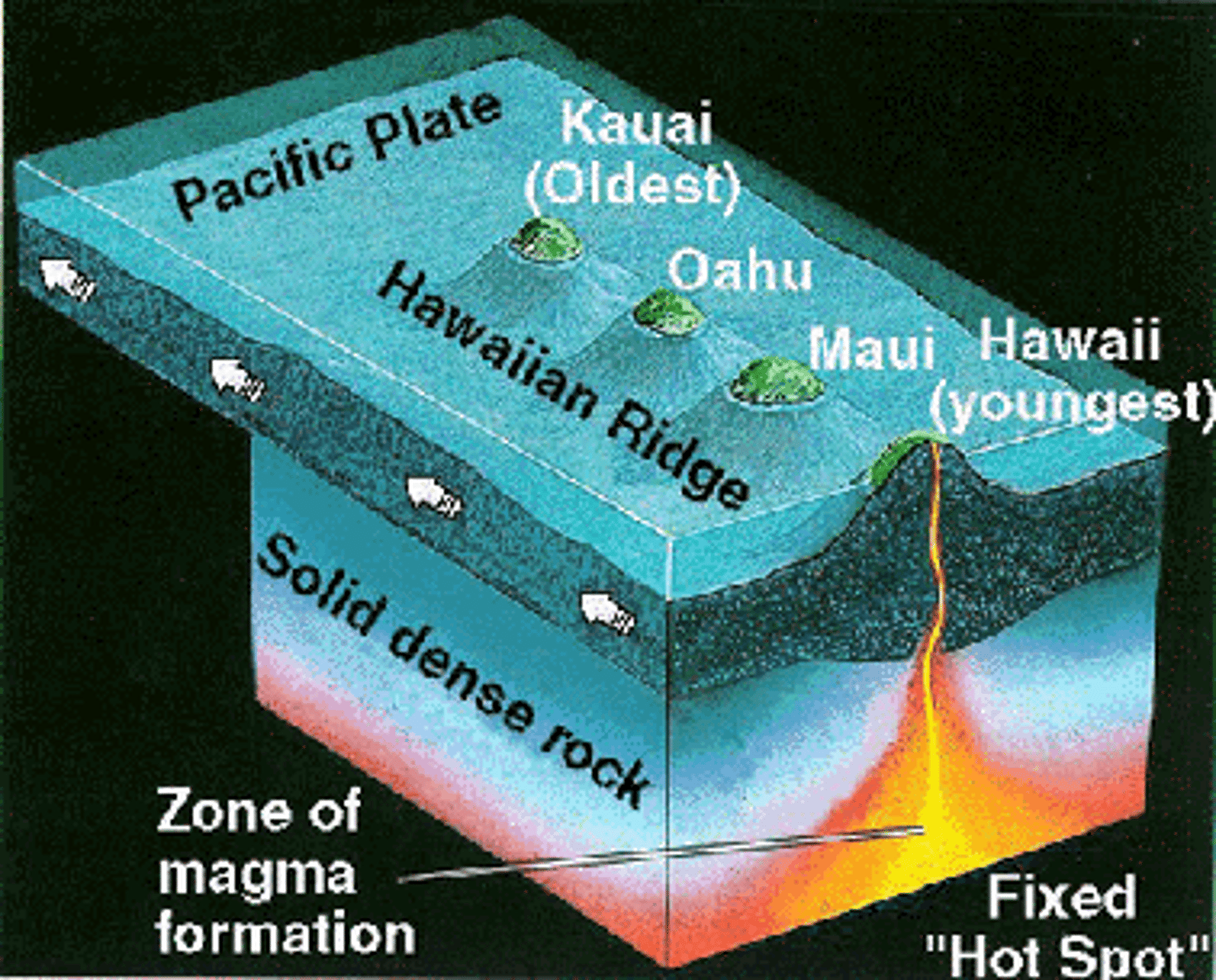
hot spot volcanoes
starts off with hot material that starts on surface and over time, as hot spot stays stationary, plate moves over hot spot (kills old volcano and makes a new one)
3 V's of volcano hazards
viscosity
volatiles
volume
viscosity
A liquid's resistance to flowing
higher viscosity is caused by silicon dioxide
more viscosity (worse eruption)

volume
size of magma chamber
more magma=more erupted material
volatiles
dissolved gas in fluids