Hemo-SLAy-sis - (this one's rough and also bad just btw)
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
hemostasis
____________ = arrest of bleeding; Physiologic response to vascular damage and a mechanism to seal an injured vessel to prevent blood loss
maintain blood in fluid state OR rapid formation of a local plus at site of damage
What are the two main functions of hemostasis? (one in normal and one in abnormal conditions)
formation of platelet plug
what is primary hemostasis?
formation of fibrin-platelet aggregate
what is secondary hemostasis?
dissolution of fibrin-platelet aggregate
what is thrombolysis/fibrinolysis
thrombolysis/fibrinolysis
______________________: dissolution of fibrin-platelet aggregate
vasoconstriction
what is the first step of hemostasis? after injury occurs and the collagen is exposed
platelet adhesion and primary hemostasis
what is step two of hemostasis?
secondary hemostasis
what is step 3 of hemostasis
thrombus and antithrombotic events
what is step 4 of hemolysis
i gotcha
there's some much clearer diagrams on slide 6-9 of these notes on the steps of clot forming that you should look at. But her ppt doesnt have notes and I don't really know how to turn this into a quizlet I'm sorry.
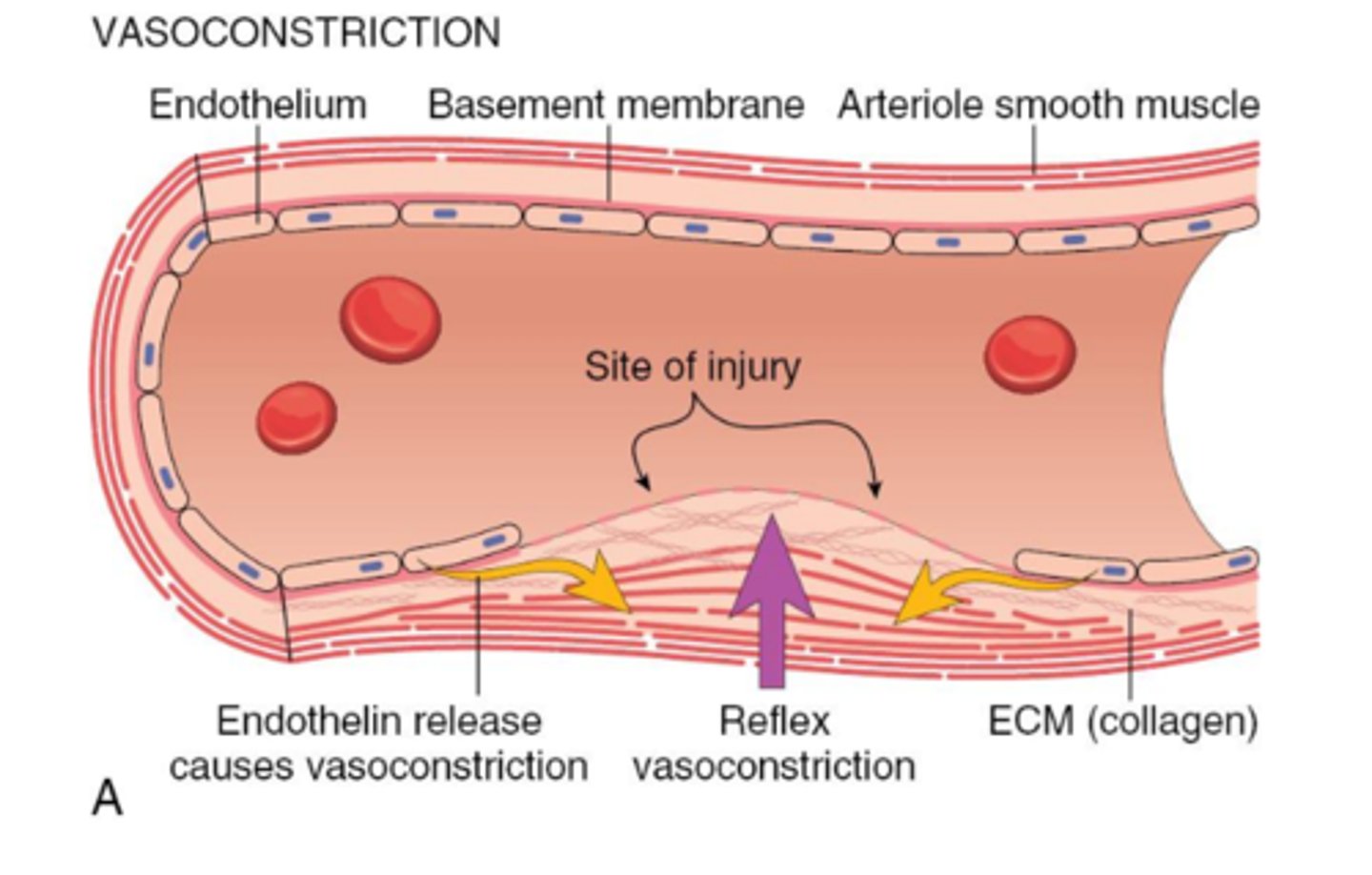
endothelium, platelets, coagulation factors
what are the "cast of characters" of hemostasis?
endothelium
what is the "dynamic interface" of hemostasis?
promotes smooth, nonturbulent flow of blood, vasodilation, antithrombotic, profibrinolytic
What are some of the properties of normal endothelium?
(opposite normal) vasoconstriction, enhance platelet adhesion and aggregation, stimulate coagulation, prothrombotic, antifibrinolytic
what are the properties of injured endothelum?
oxidative stress, hypoxia, inflammation, infectious agents, tissue injury
what can activate endothelium? (what puts it in an injured state)
megakaryocyte
platelets are anucleate cell fragments derived from ____________ circulating in blood
subendothelial collagen, leminin, fibronectin
platelets adhere to exposed _______, _______, -________, etc. but intact endothelium prevents this exposure
coagulation factors, IX, X
platelets provide a surface for the assembly of __________________; specifically _____ and _______
alpha, dense granules
platelets contain cytoplasmic granules split into ____ and ______ groups
PDGF, fibrinogen, factor V, vWF, thrombospondin, platelet factor 4
What are the growth factors in alpha cytoplasmic granules? (1)
And the coagulation factors? (5)
adenine nucleotides, calcium, inorganic phosphates, serotonin
what are the dense granules in the cytoplasmic granules?
coagulation
______________: process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot
intrinsic, extrinsic, common
coagulation is classically organized into _______, ____________, and ________ Pathways
serine protease proenzymes, nonenzymatic proteins, platelet phospholipids, transmembrane cells surface receptors, calcium
coagulation factors can include: (5)
liver, hours to days, proenzymes or zymogens
coag factors are synthesized by the ________
circulate for ___[how long]_____
and require activation to become ________ or ___________
VII, 4-6 hours
which coag factor has the shortest half-life?
II, VII, IX, X
Vitamin K dependent factors
high molecular weight kininogen, prekallikrein, XII, XI, IX, VIII
what is included in the intrinsic pathway?:
_______, _____________, and factors: _____________________
Negatively charges substances (collagen, activated platelets, endotoxin)
contact activation for HMWK, prekallikrein and factors XII and XI are activated by ________________ (like ____________________(3))
factors IX and VIII activate factor X
what marks the start of the common pathway?
When factor III contacts factor VII, IX, X
the extrinsic pathway typically starts when __________________________________, then, this complex can activate factor _____ and factor _____________
tissue factor/factor III
__________________: cell surface glycoprotein expressed on subendothelial tissue
factor VII
___________________: Vit K-dependent, circulating, serine protease
either, factor V, plasma, platelet alpha granules
factor X can be activated by the [intrinsic/extrinsic] pathway and binds to factor _______ which can be found in _______ or within __________________
prothrombinase complex
what is the combination of X-V-Ca2+ complex called?
prothrombin (factor II, thrombin (IIa), thrombin, fibrinogen (factor I), fibrin (Ia), factor XIII, fibrin
prothrombinase complex converts ______________ to _________________
THEN ______________ converts ________ to ___________________.
Finally, ________cross links _____________
(sorry babe, write it out if it helps)
transient vasoconstriction
immediately upon tissue injury, what happens to reduce the volume of blood flowing through the affected areas and brings the endothelial surfaces closer together
collagen, fibronectin, ECM glycoproteins, proteoglycans, von willebrand factor
damage/disruption of the endothelium exposes ________________________(5) and attracts platelets
negatively charged ECM matrix, vWF
Platelets "recognize" endothelial damage by being attracted to the ______________________ and adhering to exposed _______________
shape change, release granules, phospholipid accdivation binds coag factors
when platelets become activated what happens?
platelet plug
Recruitment and aggregation of additional platelets forms a _________________
loosely
the initial fibrinogen bridges [loosely/tightly] link platelets,
platelet contraction, polymerization of fibrinogen to fibrin
_______________ and ___________________ turn the loose fibrinogen bridges into a dense consolidated platelet plug
secondary hemostasis
Mediators from endothelial cells, activated platelets, and the ECM trigger activation of the coagulation cascade and the formation of fibrin for ___________
fibrin
in many cases ________ is necessary for complete hemostasis
extrinsic tenase complex, Xa, intrinsic tenase complex
It is generally believed that the initiation of blood coagulation occurs via the _______________ following tissue injury. However, the sustained generation of factor ______ is dependent upon the ________________ which is 50 times more efficient and not as susceptible to inhibition.
release of factor III, binding of factor XII to negatively charged surface
What is the stimuli in the extrinsic pathway for secondary hemostasis?
And for the intrinsic pathway?
initiation
the release of tissue factor III and the combination of this with factor VII and Ca as well as the activation of factor X and IX BY that TF:VIIa complex is called ____________
extrinsic
initiation is associated with the __________ pathway
Factor V, Ca2+, and phospholipids
now active Factor X (Xa) binds to ___________ , _________ and _________ to form the prothrombinase complex
common
Amplification (Active Factor X (Xa) binds to Factor V, Ca2+,
and phospholipids) is associated with the ___________ pathway
factor Xa
what cleaves prothrombin II into thrombin IIa?
thrombin
what converts fibrinogen I to fibrin Ia?
thrombin
what activates platelets AND factors XI, VIII, V, and XIII
contact activation/binding of factor XII to negative surfaces
what is the stimulus for PROPOGATION
intrinsic
propagation is associated with the _______________ pathway
proenzymes, XII, XI, IX
Conversion of ______________ to active enzymes occurs on platelet surface and we follow the activation cascade
______ → _______ → ________
common
we return to the _____________ pathway for the formation of fibrin
prothrombin (II), thrombin (IIa), thrombin, fibrinogen (I), fibrin (Ia), XIII, thrombin
formation of firbin:
Factor Xa converts ____________ to ______________
__________ cleaves _____________ into ________________
factor __________ is activated by __________ in order to stabilize fibrin.
insoluble
crosslinked fibrin is [soluble/insoluble]
sticky, everything
freshy formed fibrin strands are "_______________" and adhere to _____________________
contracts
over time the fibrin _________ to allow blood to get past and to pull the edges of the damage closer together
fibrinous
The adjective that describes fibrin is ____________________
fibrin
What is this?
platelets are attracted to and adhere to damaged vessel wall and are activated
Quick! give me a one sentence overview of what happens in PRIMARY hemostasis
The plasma coagulation system attracts more platelets and binds them with fibrin. This then contracts and adds more fibrin to make a permanent plug.
And now... give me a two sentence horror story summing up what happens in SECONDARY hemostasis
(super general, this is just cus all the numbers and factors make me lose sight of whats actually happening)
thrombolysis/fibrinolysis
_______________________: Removal/dissolution of fibrin-platelet aggregate (thrombus)
plasminogen
_______________ is responsible for fibrinolysis
- Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), Urokinases, Factor XIIa
- α2-antiplasmin, α2-macroglobin
Plasminogen is activated by ________________
and INactivated by _________________
Thrombin Activatable Fibrinolysis Inhibitor (TAFI), Plasminogen Activator Inhibitors (PAIs)
Fibrinolysis is regulated by ______________ and ___________________
true
true/false: coag factors are CONTINUOUSLY activated and ready to respond, so proteins that inhibit or degrade them are released at sites of injury to limit the hemostatic reactions.
hemostatic, fibrinolytic, anticoagulant
what three pathways must remain balanced during coagulation?
blood flow, liver, spleen
coagulation factors are diluted by the ______________ by removal from the site, and are removed by circulation by _____ and _______
antithrombin III
what is the most potent and most significant coagulation inhibitor
antithrombin III, heparin sulfate, tissue factor pathway inhibitor, protein C-protein S-thrombomodulin system
what are the anticoagulant molecules (4)
heparan sulfate, thrombomodulin
which anticoagulants are endothelial surface members?
Antithrombin III, Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor, Protein C, Protein S
Which anticoagulants are circulating members?
thrombin (IIa), procoagulant, anticoagulant, Xa, VIIa, VIIIa, V
the end result of the anticoagulant system is to convert _____________ from _________________ to _______________ and to inhibit factors ____________ (4)
true!
true/false; thrombin can act as a procoagulant (by cleaving fibrinogen or activating factors V, VIII, XI, XIII and platelets) OR can act as an anticoagulant in high concentrations (DESTROYING factor V and VII and activating protein C)
proinflammatory!
A prothrombic environment is ALSO __________________ because theres a lot of overlap in the mechanisms
II, VII, IX, X
which factors of the coag cascade are Vitamin K dependant?
extrinsic pathway/tissue factor III and VIIfactor IX -VIII
Which members of the coagulation cascade are mainly responsible for initiation coagulation in vivo?
Factor IX/VIII complex
In the cell based model, which is mostly responsible for the sustained generation of Factor Xa during the propagation phase of coagulation?
antithrombin III
what is the most potent and significant coagulation inhibitor