SACE STAGE 1 CHEMISTRY UNIT 4 TEST
1/62
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What is the term Miscible?
Miscibility is the term for liquids that can be mixed to forma homogenous substance
What is the term Immmisible?
Substances that cannot mix to form a miscible substance, but form a heterogeneous substance
What type of molecules are miscible
Substances of the similar polarity are Miscible.
What is a solute
Substance being dissolved
What is a solvent
Substance which the solute is being dissolving in.
Molarity
•the number of moles of solute per litre of solution (molL-1)
How are polar substances able to dissolve together?
Because they can interact with secondary bonding
Polar can use Dipole- Dipole interactions/ hydrogen bonding
nonpolar- dispersion forces
Why can substances of the same polarity be Miscible?
Because their secondary forces are weak, they can make a homogenous solution
What is water?
A universal solvent, so can dissolve a wide range of substances. It can disrupt other secondary reactions
Miscibility is determined by
Polarity and Size
Why does size effect Miscibility
Because as the particles increase in size, it is more difficult for the solvent to seperate and surround them.
Dispersion forces occur more so grow bigger as the substance grows, so are harder to break by water.
What is the biggest hydrocarbon that can be dissolved
propanol
What is a polar head?
A polar head is a portion of a non polar molecule that has a polarity
What are emulsions?
mixture of two liquids that are not mutually soluble
What are Emulsifiers?
Substances that have both hydrophilic (polar) and hydrophobic (non polar ) components that help in mixing two immiscible
What is a hydrophobic component?
a water hating component (non polar)
What is a hydrophilic component
water loving (polar
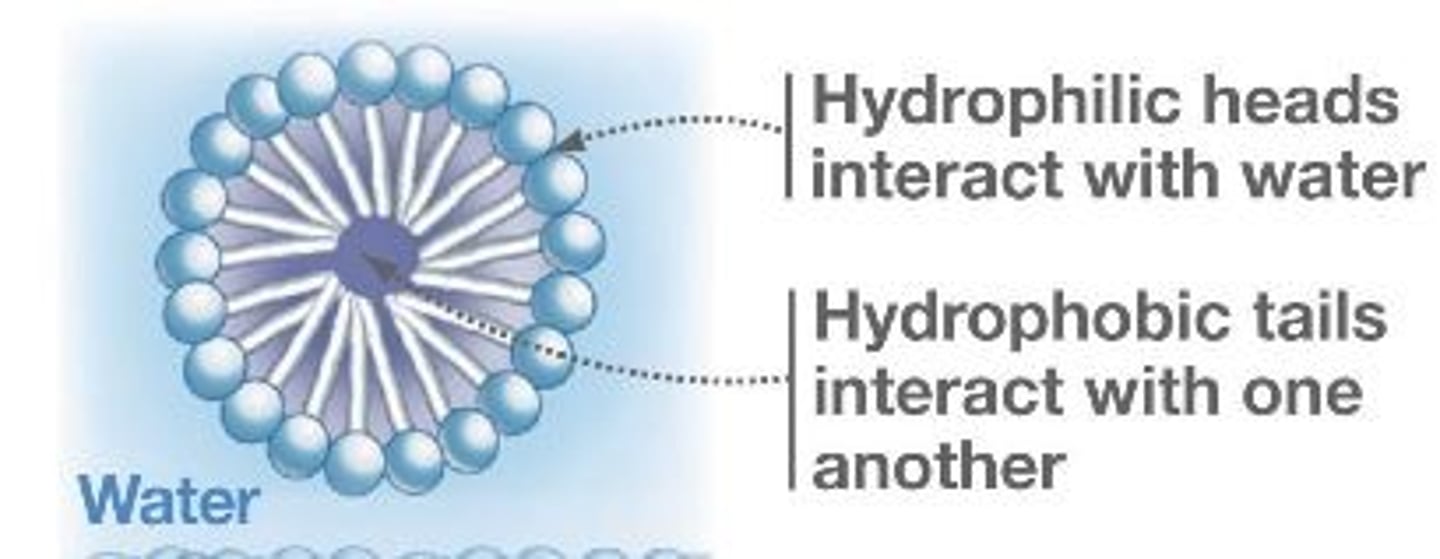
What are micelles?
•The hydrophobic component of the emulsifier interacts with the grease, The hydrophilic component of the emulsifier interacts with the water
The soap and detergent ions surround the droplets of grease forming micelles.
What is an Ion-dipole force?
an attractive force from a polar molecule's dipole to an ion.
What is an example of an ion-dipole force?
Hydration shells
What is a hydration shell?
When an ionic compound is dissolved in water, each ion is surrounded by a sphere of water molecules
Hydrogen atoms from water are attracted to anion, while oxygen atoms of water are directed towards the cation
What is an aqueous state?
where ions have been pulled apart, dissolved in substance, not solid
Ion Dipole bonds are stronger than
Dipole Dipole bonds
Solubility table
picture
how does a precipitate form
When two dissolved substances combine to form a insoluble substance
What is an example of a precipertate reaction?
AgNO₃ (aq) + NaCl (aq) → AgCl (s) ↓ + NaNO₃ (aq)
What are spectator ions?
ions that do not participate in a reaction
What is dissociation?
the process in which an ionic compound separates into ions as it dissolves, it gains energy to do this (not hydration yet, occurs after)
What is a complete ionic equation
It is an equation that shows all the ions in a solution as they exist, and the precipitate
What is a net ionic equation
an equation for a reaction in solution that shows only those particles that are directly involved in the chemical change
How do you calculate the concentration in mol/l
C=n/V(Litres)
concentration of solution (G/L)
C= m(grams)/V(litres)
ppm=
mg/L
ppb=
u/l
percent weight per volume
%w(grams/ v(mL) 100= g/100ml
Calculate missing value for a dilution
c1v1 (Litres) = c2 xv2 (same mol (balancing the equation)
Dilution
Same mol amount of solute doesnt change, but does per L when more added
Dissociation
absorbs energy, to break bonds (endothermic)
Energy required to pull the substance apart
How to Create a standard solution
Weight out the mass of solute needed for the solution
Transfer the mass of solute to a clean beaker (use solvent to remove excess solute from the surface)
Dissolve the solute in appropriate amount of solvent
Transfer the solution from the beaker to the volumetric flask
funnel used to ensure all of the solution is transferred.
Add solvent until the solution is parrallel with the graduation mark at eye level. (bottom of meniscus)
What is a free hydrated cation/ anion called?
Electrolyte
Mass of substance for standard solution- Moles
n=CxV
What is stoichiometry
The calculation of quantities in chemical reactions
Steps of Stoichiometry
1Balance equation
2Determine moles in substances
3Determine mole ration (reactants to product (eg 2:3))
4multiply element 1’s number of moles by the mole ratio to find element 2’s number of moles , 5determine molar mass, determine mass
What is a endothermic reaction?
A reaction that absorbs energy from the surrounds, cooling surroundings
What is an exothermic reaction
energy is released as new chemical bonds are formed in the products, energy is released to the surrounding :heating effect
Enthalpy
Lattice energy- hydration energy
what is a thermochemical equation
a chemical equation that includes the enthalpy change
Calculate the heat energy absorbed or released in a reaction (Q, measured in Joules):
Q= mass (water in g) x temperature change x 4.18 (water capacity)
Determine the molar enthalpy for a substance/solution (measured in kJ/mol):
Q/1000 x n (substance)
What Ions are present in Hard Water?
magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca)
Q=
Mass x Change temperature x 4.18 (for water)
n=
moles
M=
Molar mass
m=
mass
Equation pyramind of m=CV

What are Micelles made up of?
Multiple surfactant molecules that have both a polar head and non polar tail
In Micelles,
there is a polar head, and a non polar tail
How are ionic compounds dissolved in water?
Dissociation and hydration
Dissociation equation
Nacl(s)+ (aq)→ Na+(aq) and Cl-(aq)
Hydration
How is an ionic compound dissolved in water?
The ionic compound firstly dissociates in the water, becoming seperated from the lattice structure, becoming single cation and anion ions. After this, the water surrounds the ions and forms ion dipole bonds, forming a hydration shell around the ion.