Muscular System
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
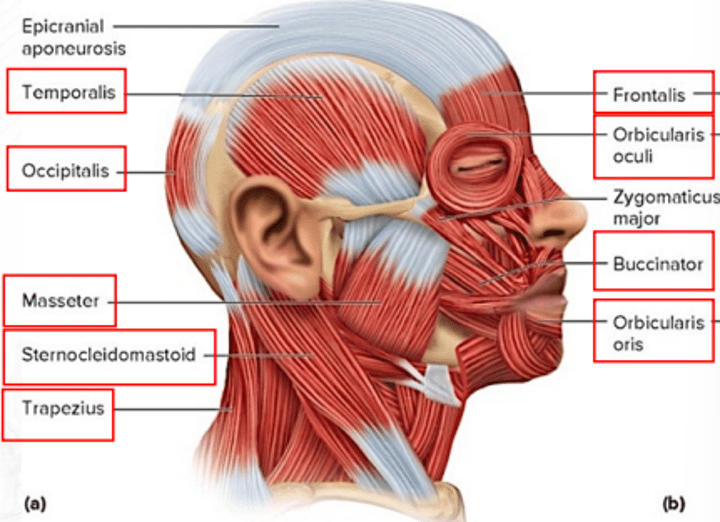
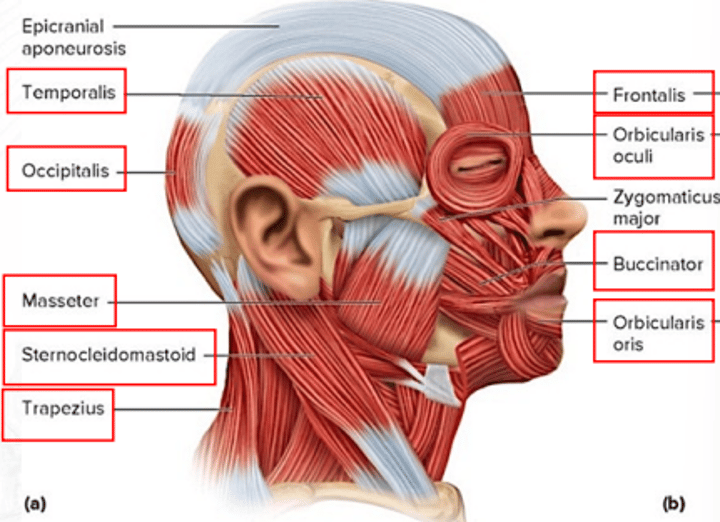
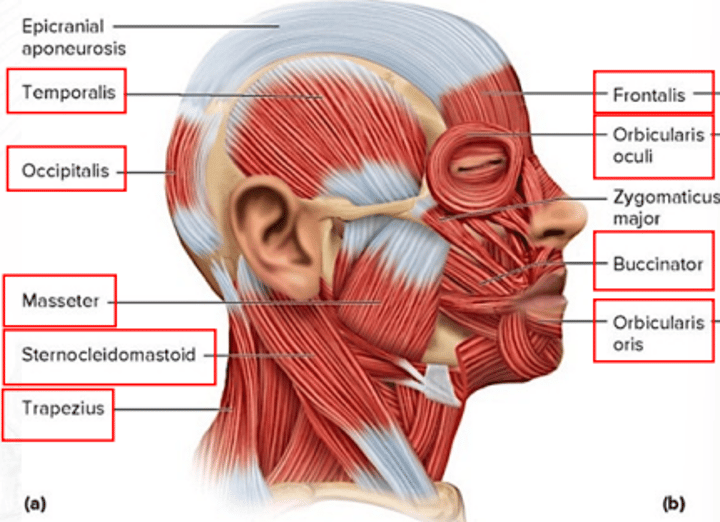
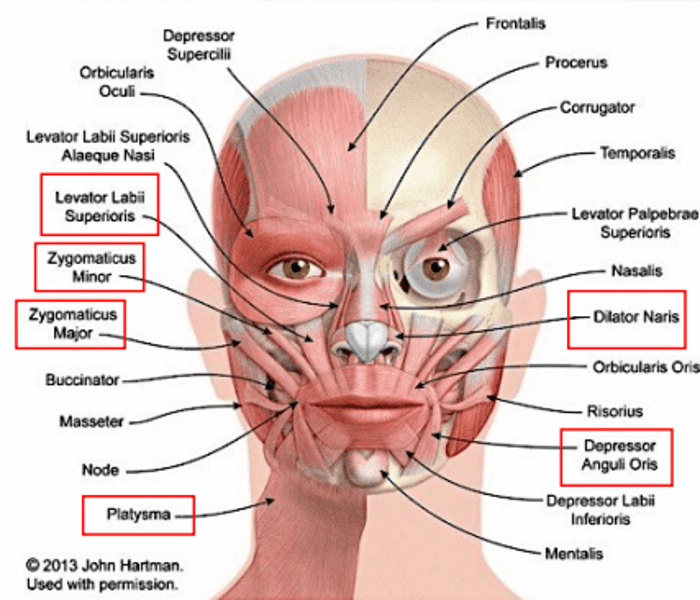
frontalis
draws scalp anteriorly; raises eyebrows; wrinkles forehead
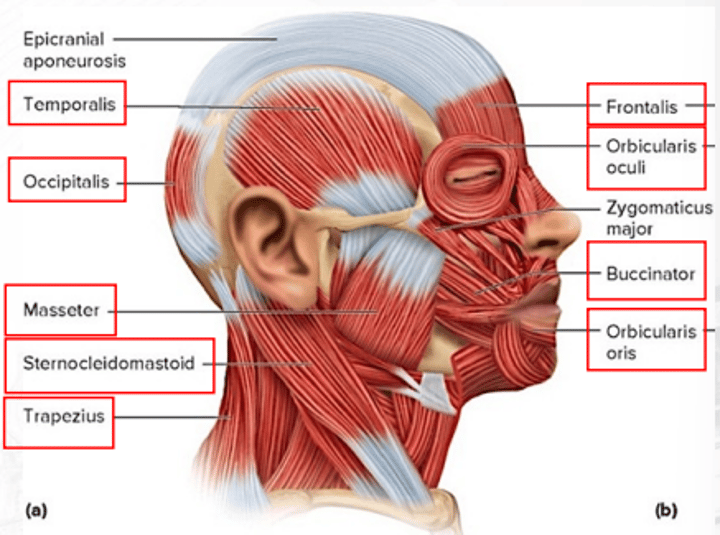
temporalis
for mastication; elevates mandible and closes the jaw
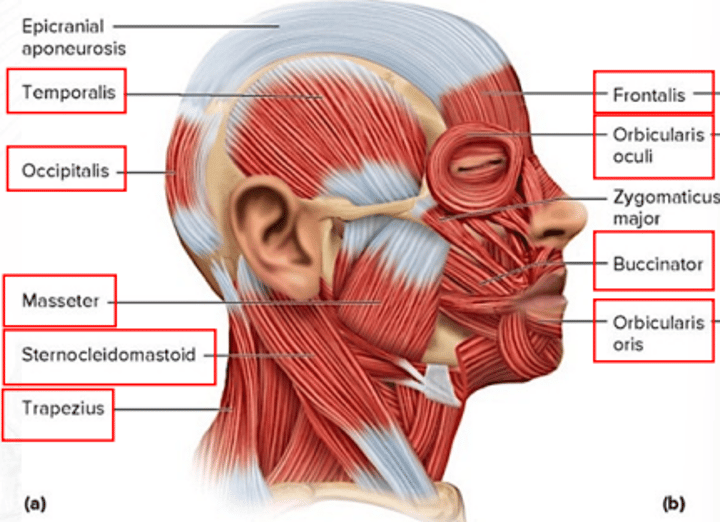
orbicularis oris
closes the mouth and puckers the lips
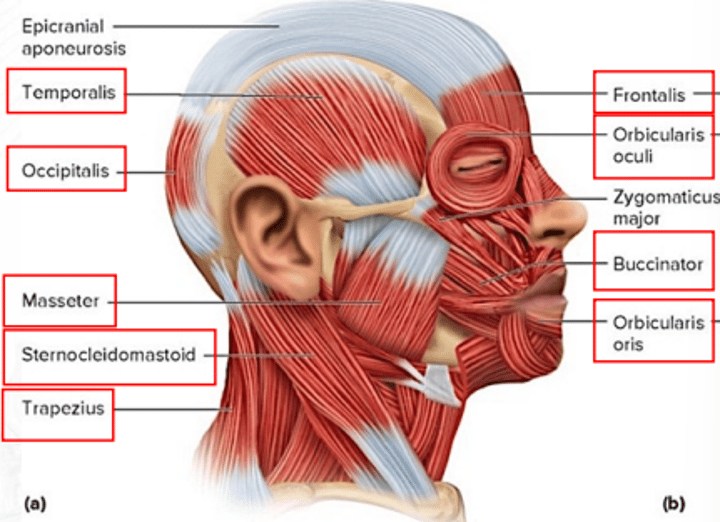
orbicularis oculi
closes the eye
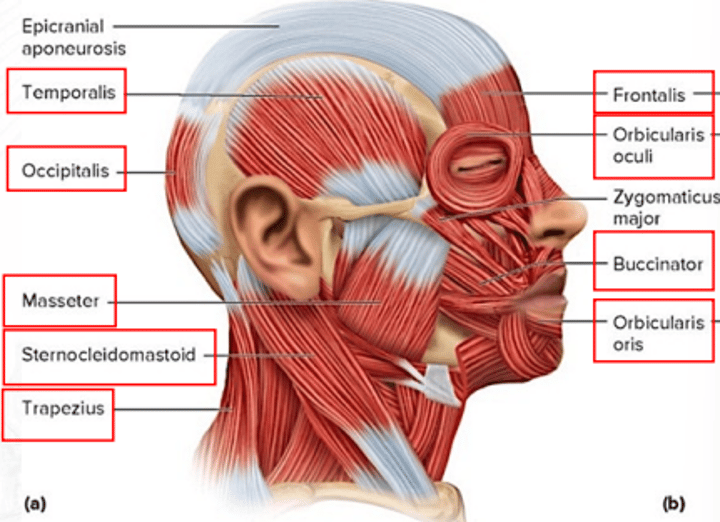
sternocleidomastoid
both muscles: flex head; one muscle: rotates head toward the opposite shoulder
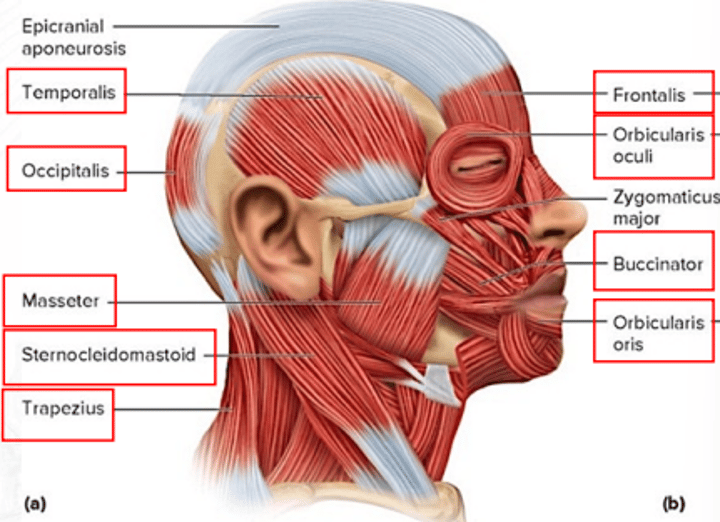
trapezius
extends the head and rotates the scapula
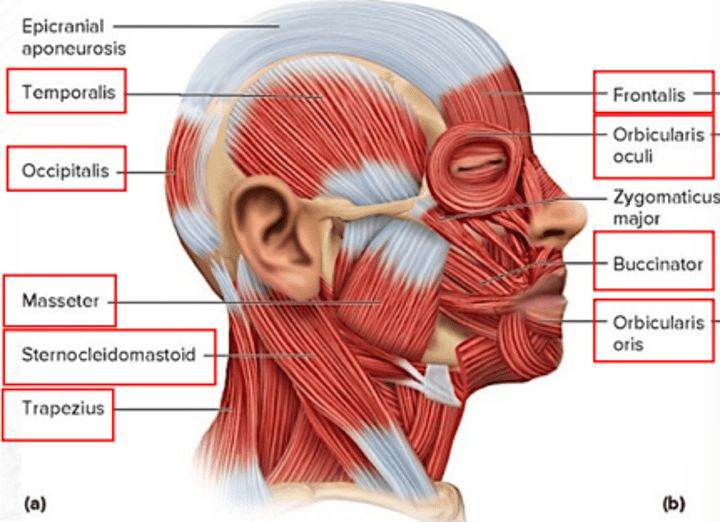
medial pterygoid
raises the jaw
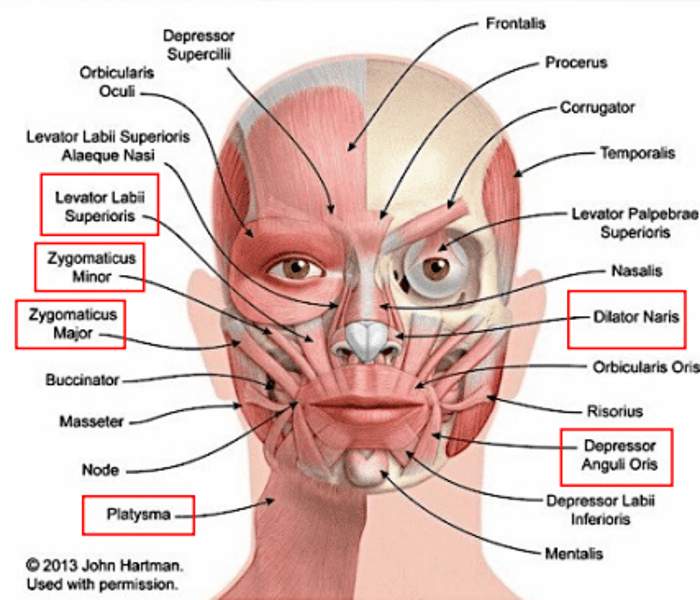
platysma
depresses the mandible
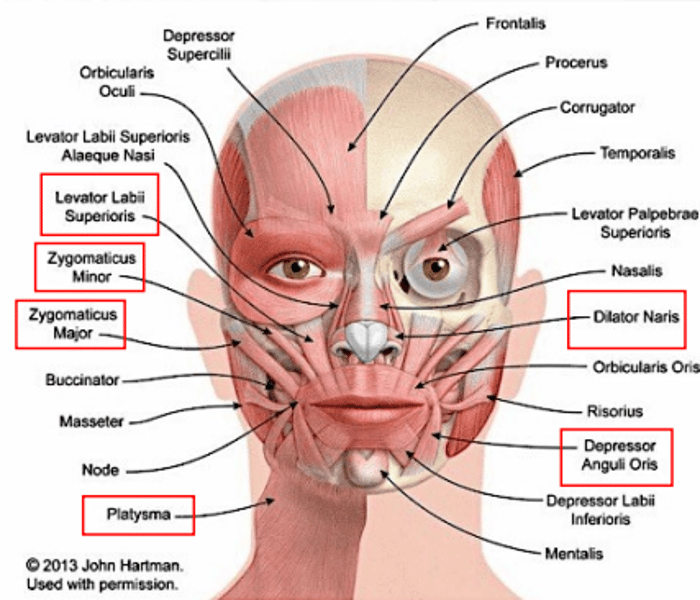
trapezius
extends head and scapula
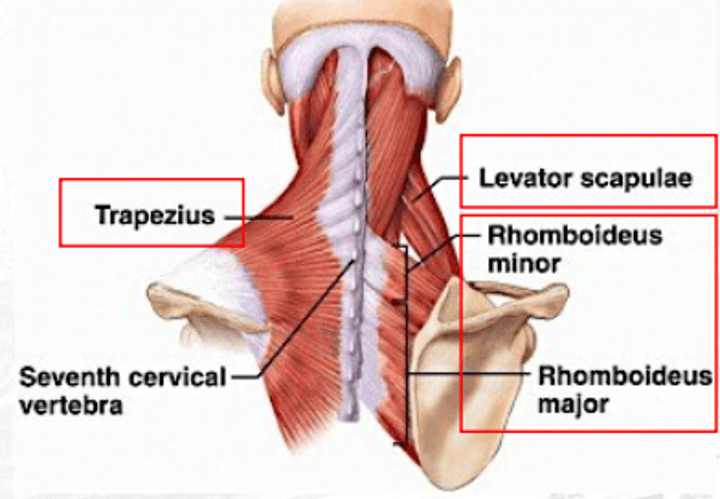
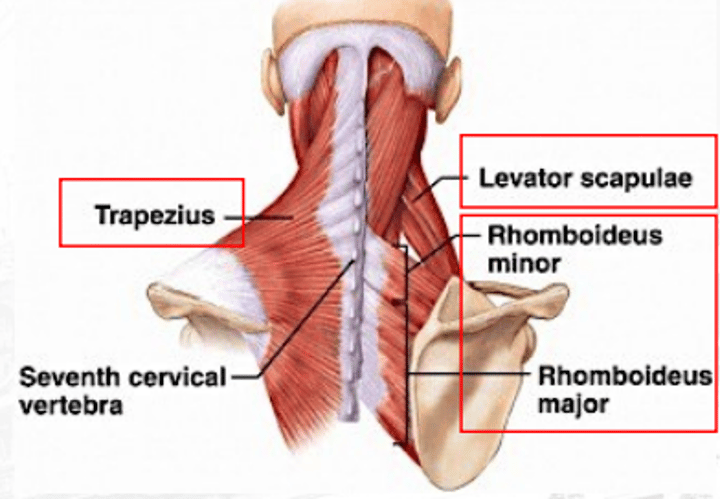
levator scapula
raises scapula
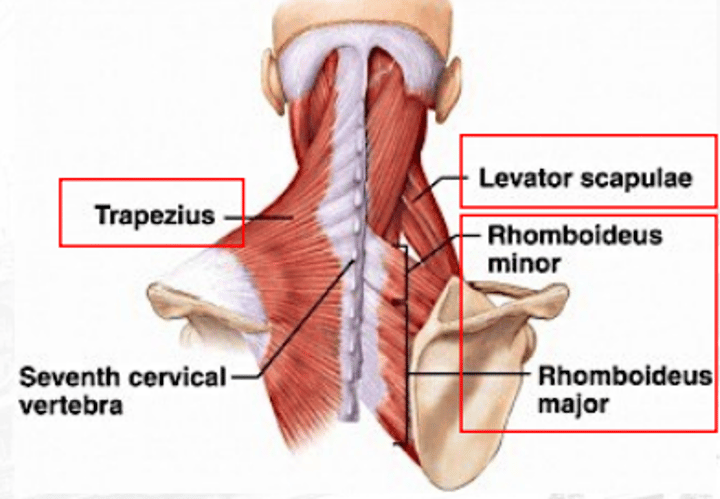
rhomboideus
retracts the scapula
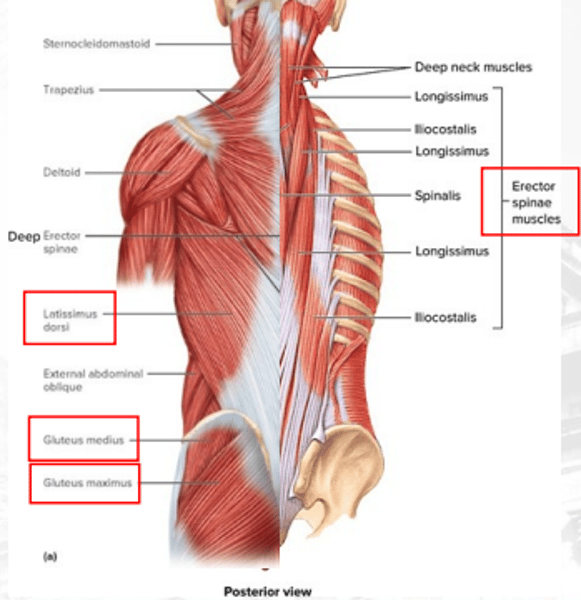
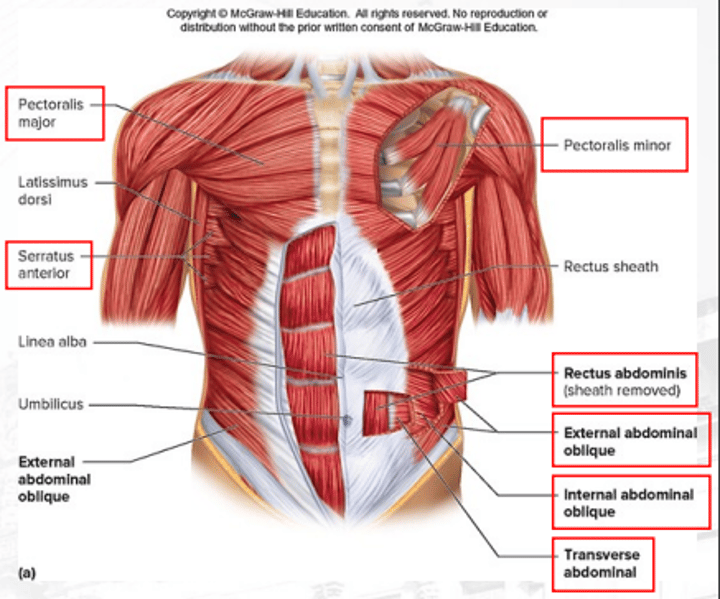
Latissimus dorsi
extends the shoulders and adducts arm
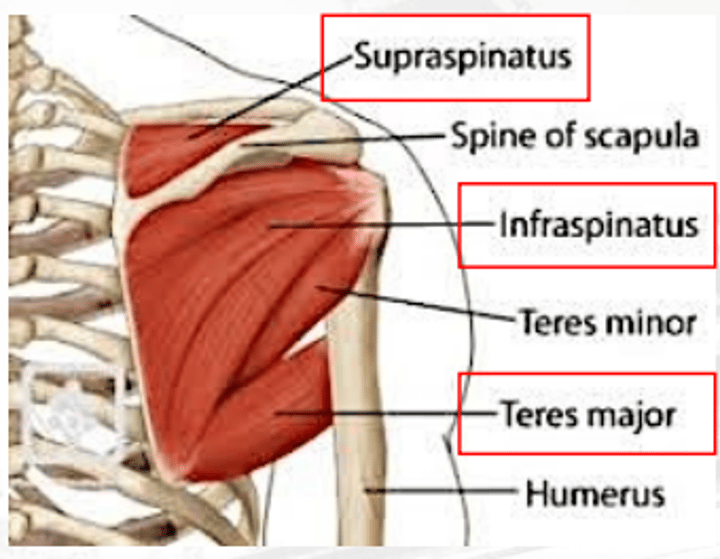
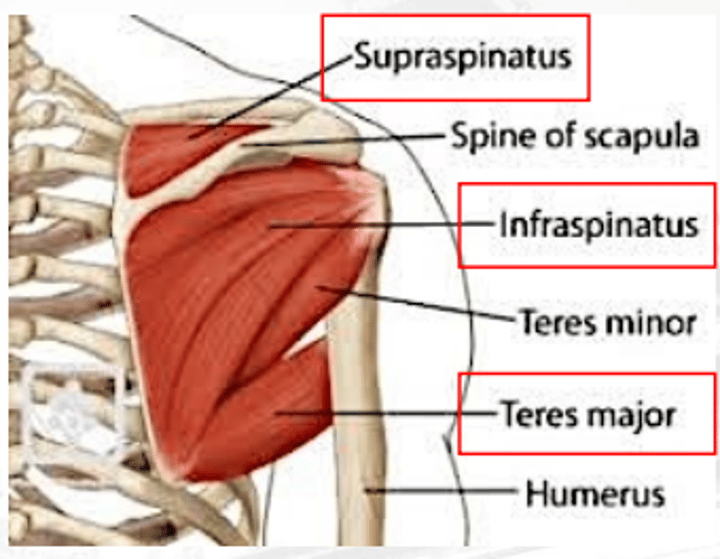
teres major
extends the shoulders
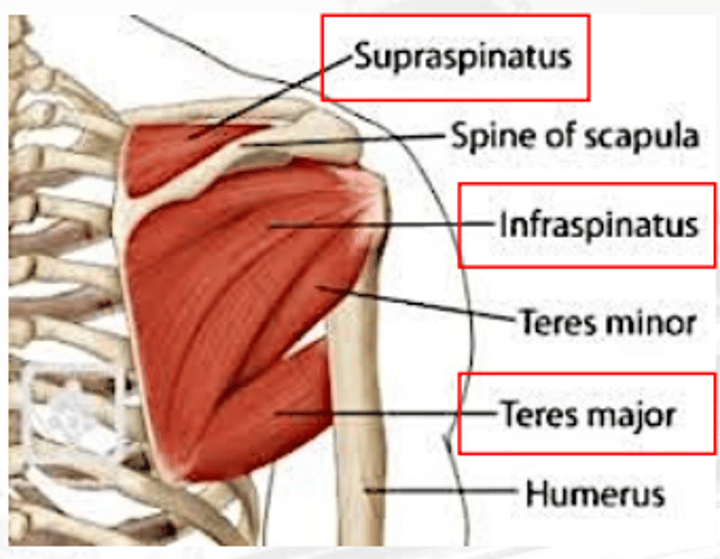
infraspinatus
extends and rotates arm
external intercostals
expand the thorax
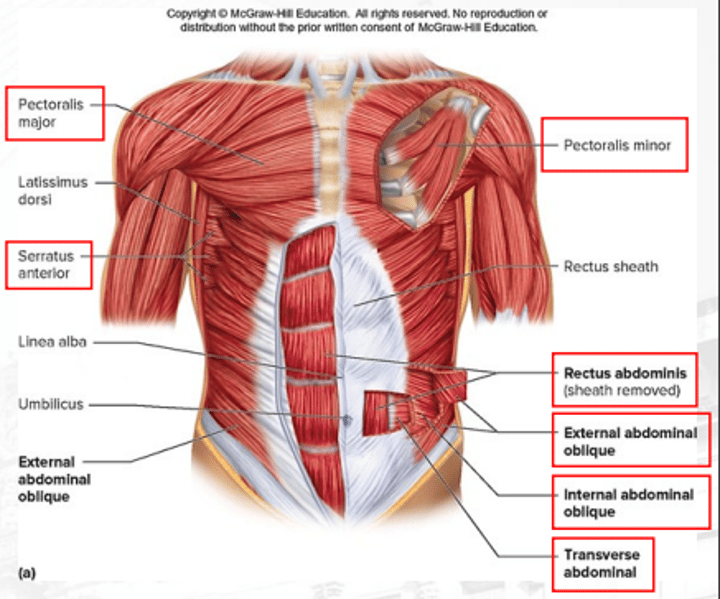
pectoralis minor
depresses the scapula
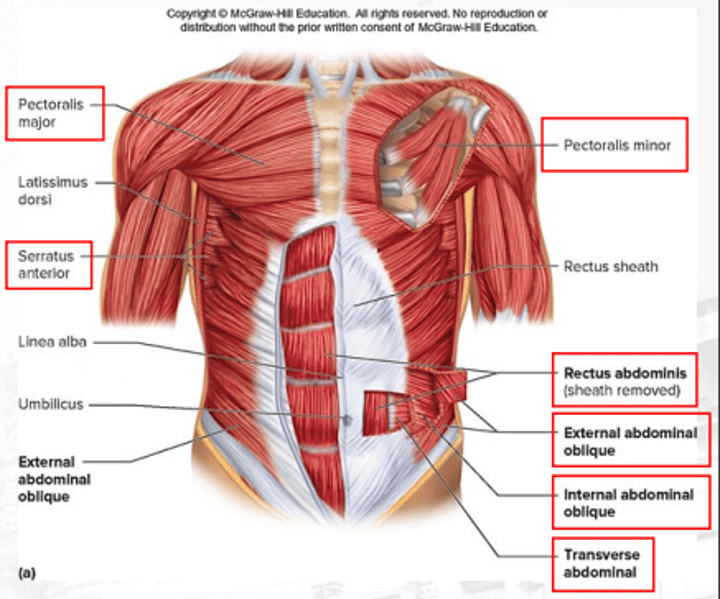
serratus anterior
protracts the scapula
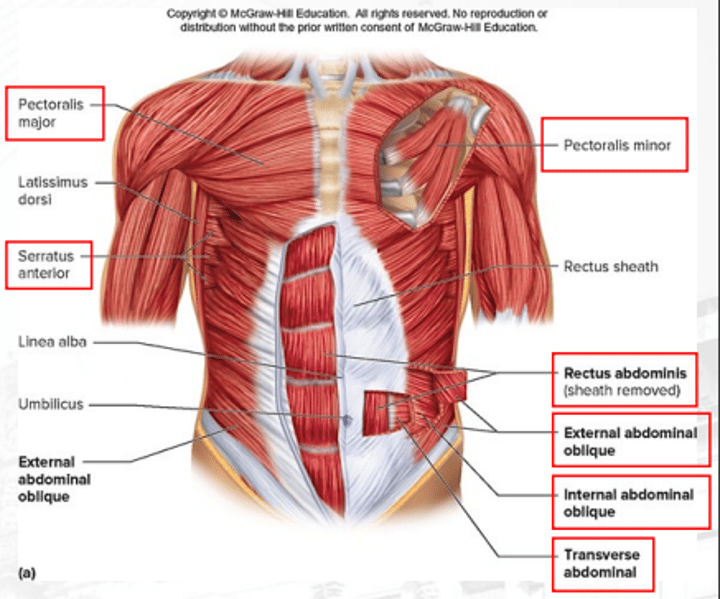
internal abdominal obliques
compresses the abdomen (deep)
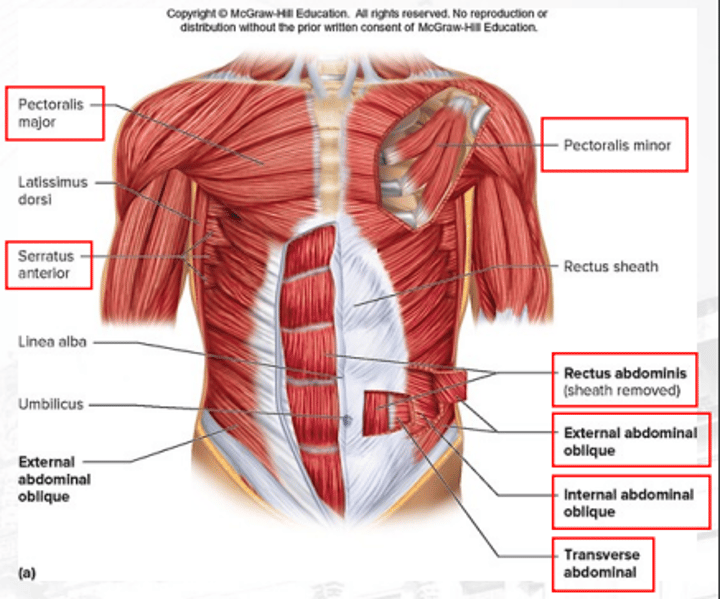
rectus abdominis
flexes vertebral and column increases the pressure of the abdomen
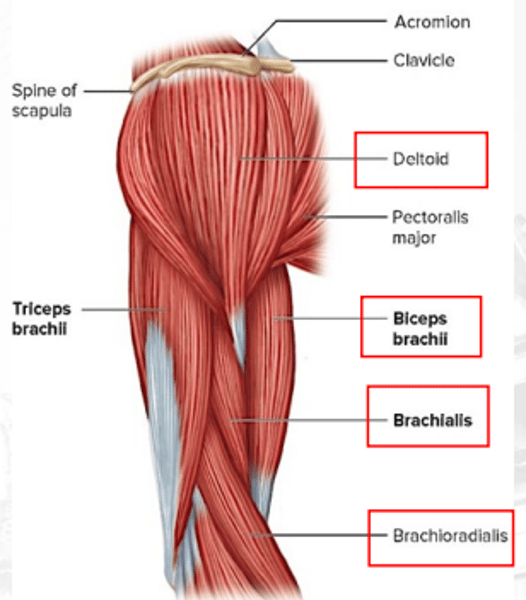
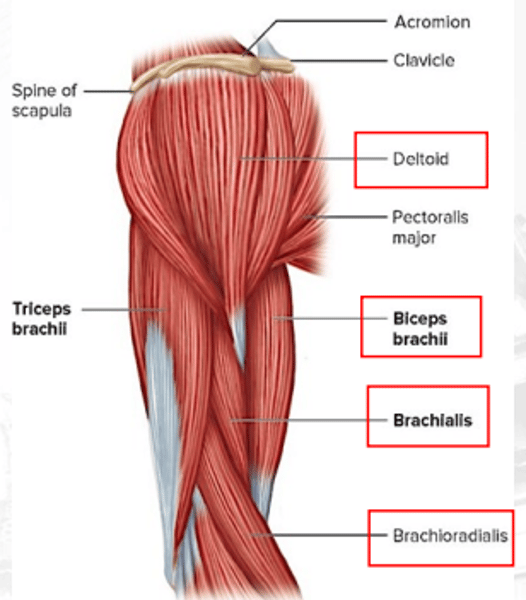
deltoid
abducts the arm; flexes and extends shoulders
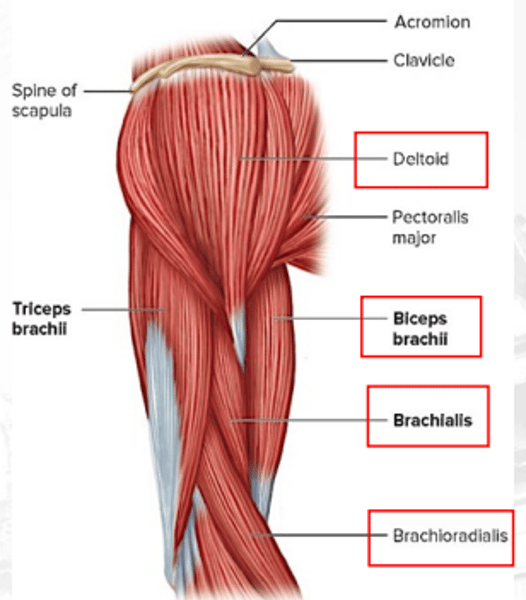
biceps brachii
flexes the elbow and supinates the arm
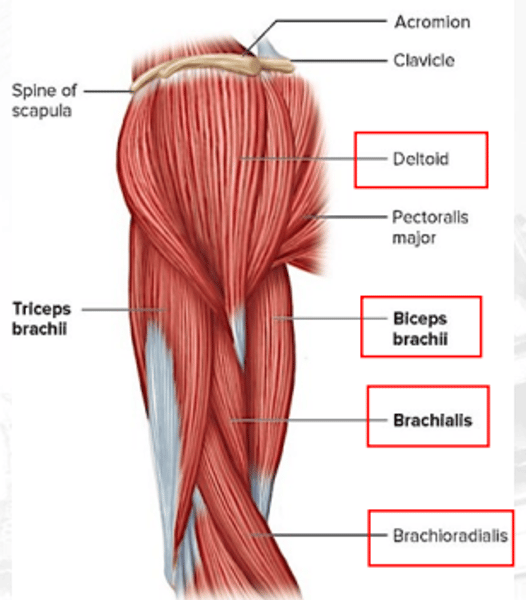
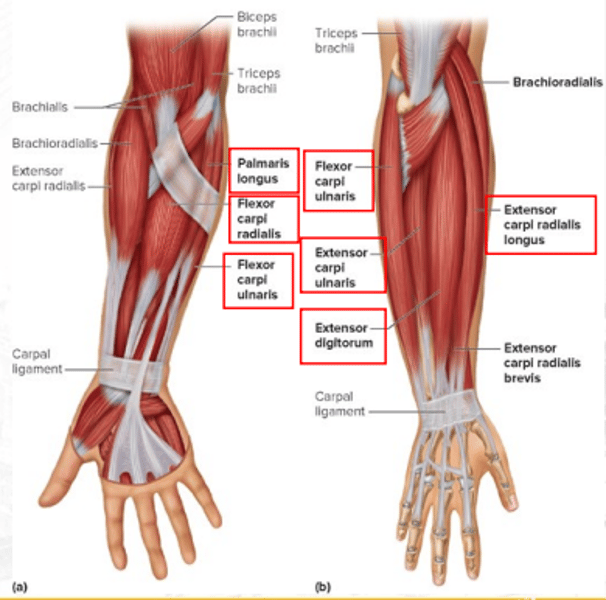
brachioradialis
flexes forearm (synergist of brachialis)
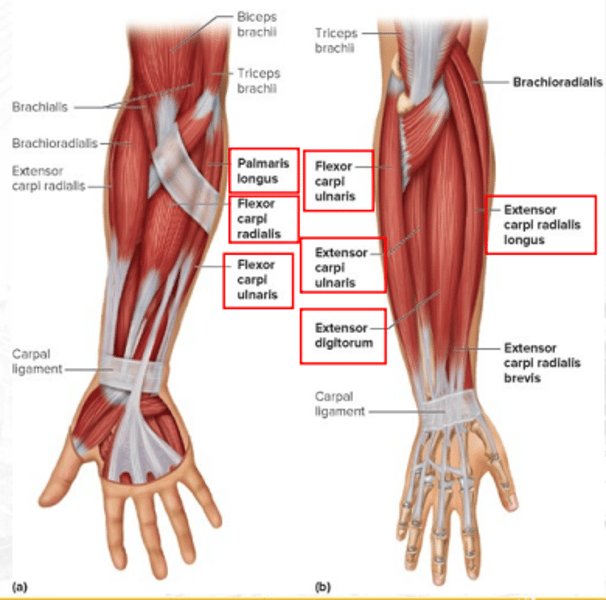
extensor carpi radialis longus
extends and abducts the wrist
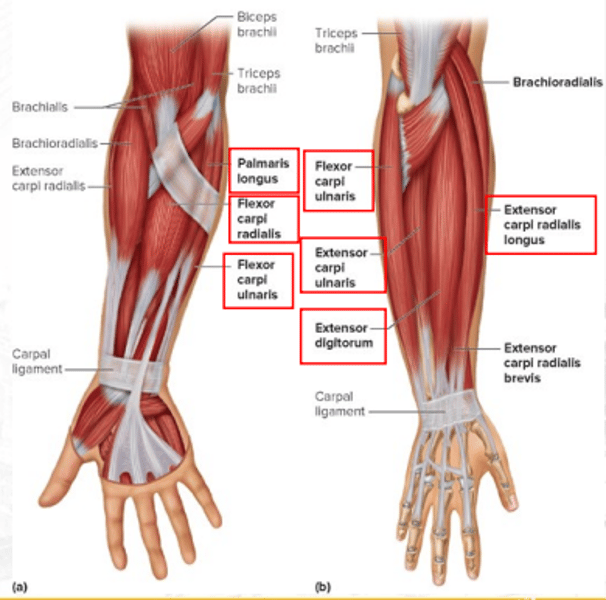
extensor digitorum
extends fingers and flares or adducts fingers
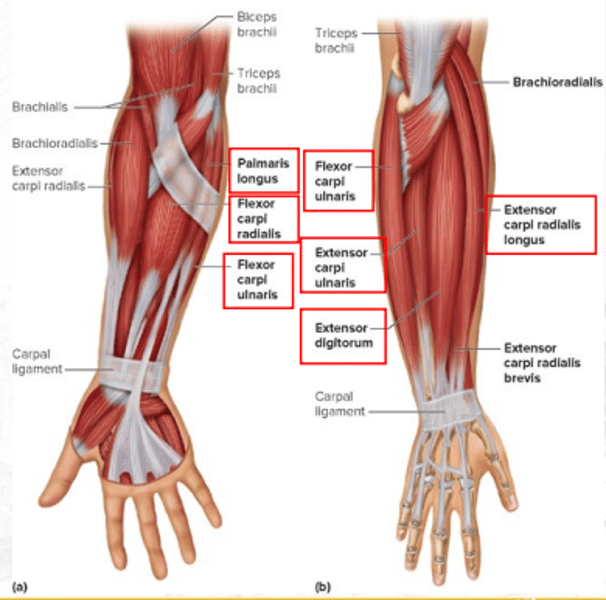
flexor carpi ulnaris
flexes and adducts the hand at wrist joint
pronator teres
pronates the forearm
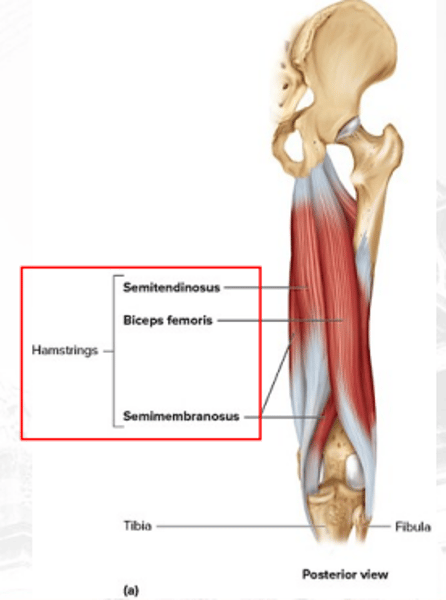
biceps femoris
extends the thigh and laterally flexes the knee
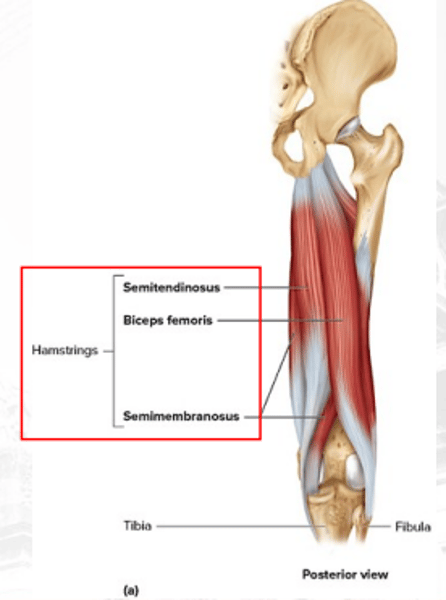
semitendinosus
extends the thigh, flexes the knee, and rotates the leg medially
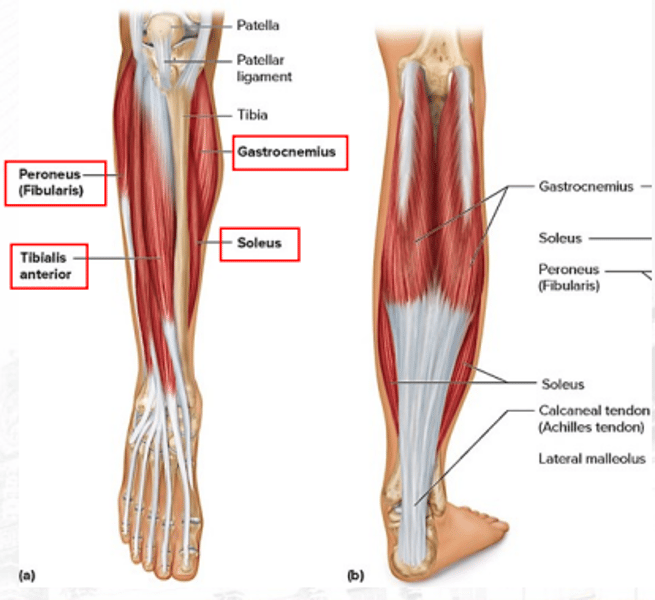
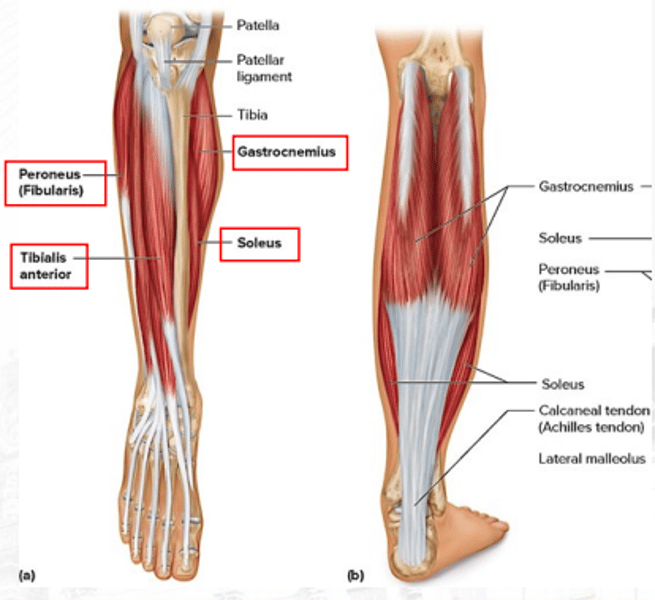
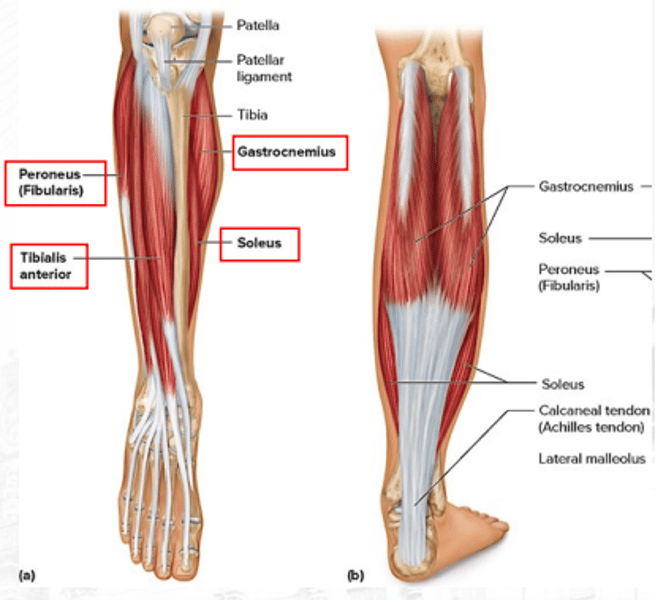
gastrocnemius
plantar flexes the foot (bigger)
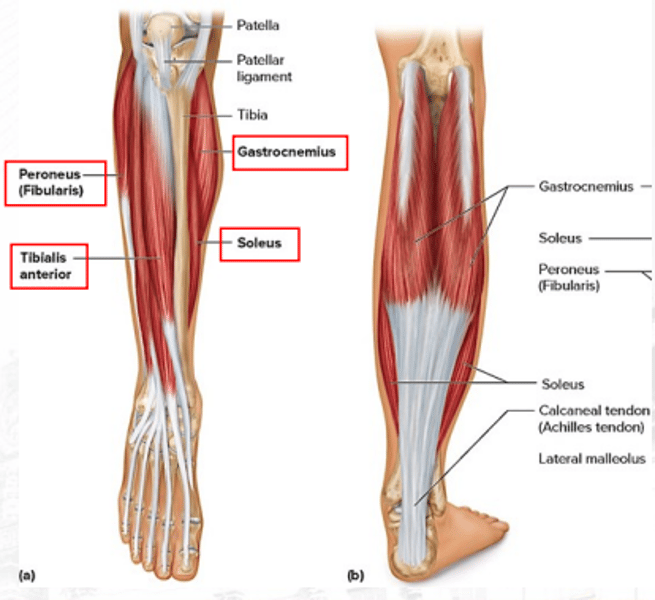
soleus
plantar flexes the foot (smaller)
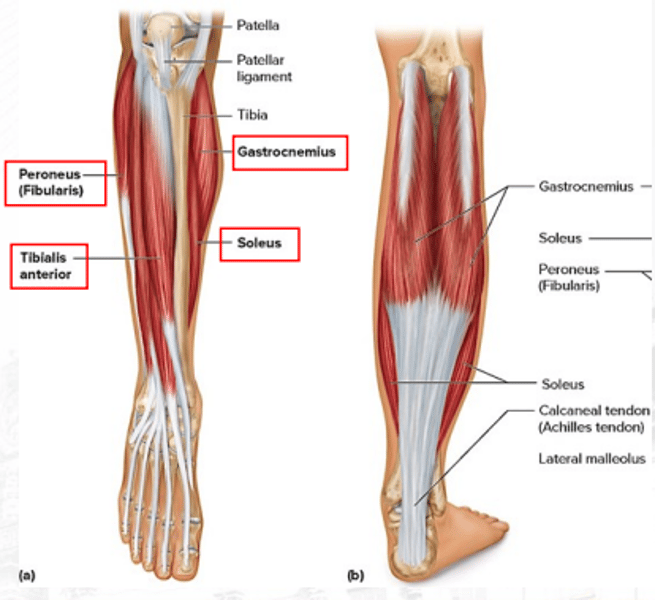
extensor digitorum longus
dorsiflexes the foot
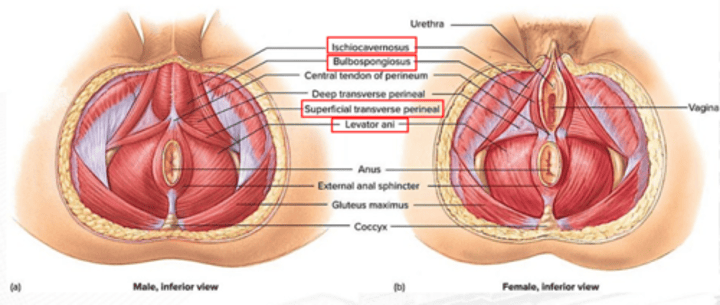
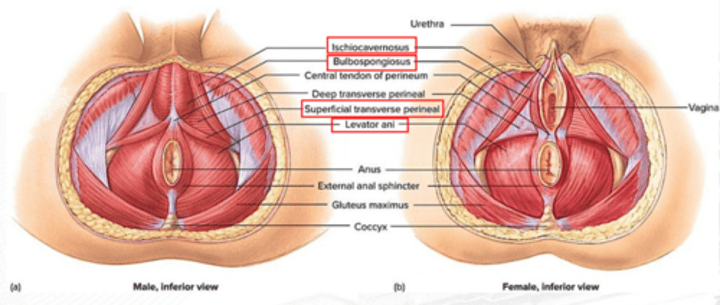
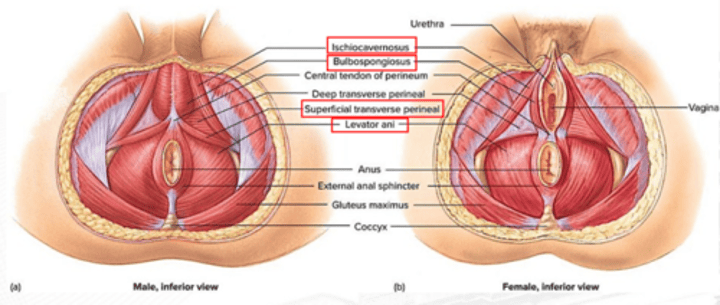
levator ani
constricts the anus, urethra, and vagina; resists increased intra-abdominal pressure; and supports fetal head during childbirth
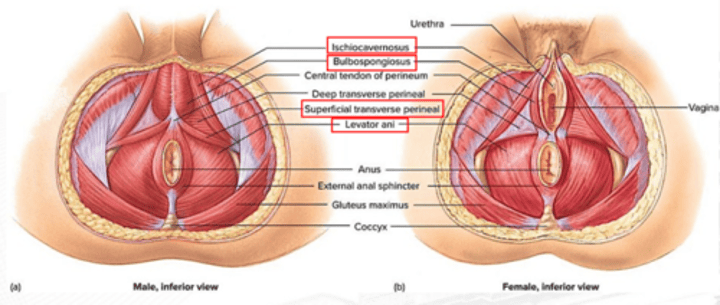
ischiocavernosus
erection
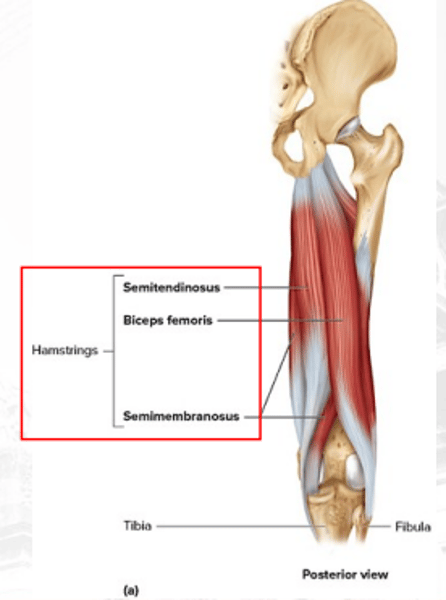
•Biceps femoris
•Semitendinosus
•Semimembranosus
hamstring muscles
1.movement
2.maintain posture
3.respiration
4.production of body heat
5.communication
6.heart beat
7.contraction of organs and vessels
functions of the muscular system
intrinsic muscle
refers to a muscle having its origin and insertion located in the same body region
extrinsic muscle
refers to a muscle having its origin in a different body region and the insertion
fixator
a muscle that holds an origin stable for another muscle
synergists
muscles that have the same action
extension
action that bends a part of the body posteriorly
abduction
movement of a part of the body away from the midline
retraction
movement that brings part of the body backward
plantar flexion
position of standing on tiptoes with the heels off the floor
inversion
position in which the soles of the feet are together, facing each other
eversion
position in which the soles of the feet point away from each other
rotation
the act of spinning on an axis
circumduction
the act of making a circle with part of the body
pronation
rotation that turns the palms down
elevation
the act of closing the jaw or raising the shoulders
occipitalis
draws scalp posteriorly
buccinator
for mastication; compresses cheeks (as in blowing or whistling)
masseter
for mastication; raises jaw
levator labii superioris
elevates the upper lip
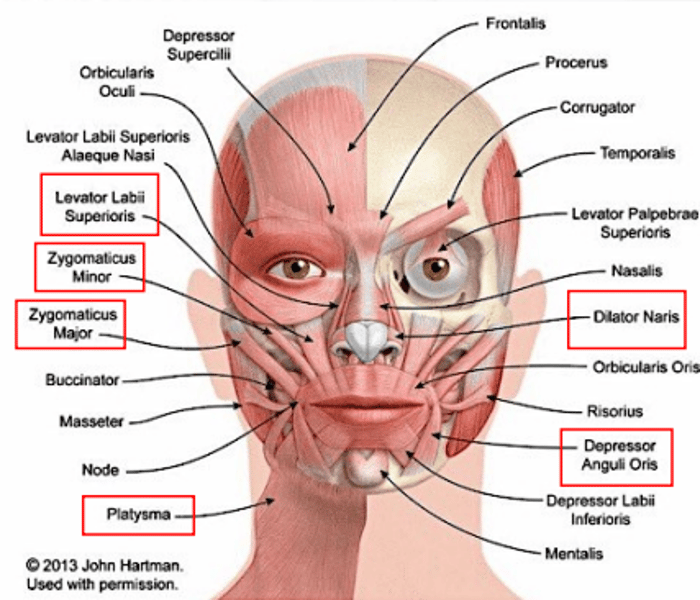
zygomaticus major
raises the angle of the mouth (as in smiling)
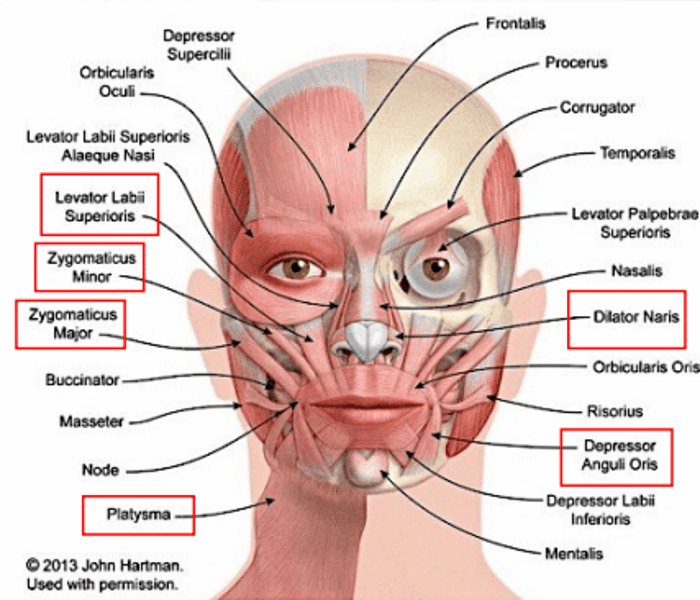
zygomaticus minor
elevates the upper lip and exposes maxillary teeth
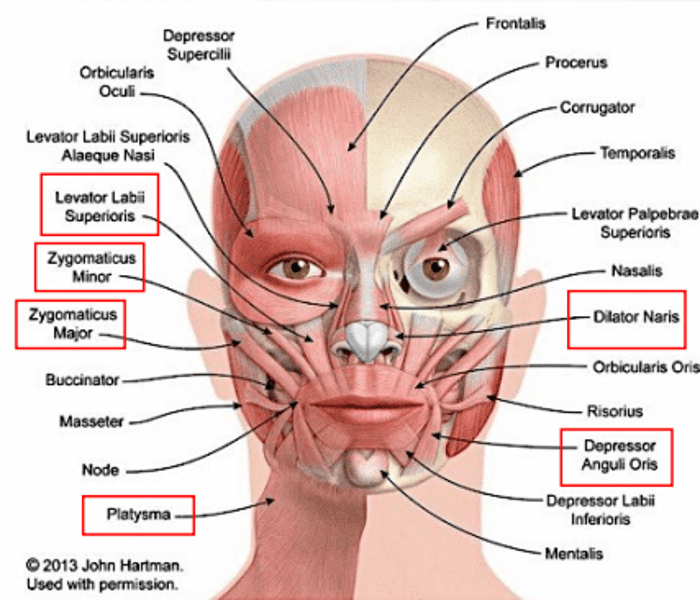
depressor anguli oris
depresses the angle of the mouth
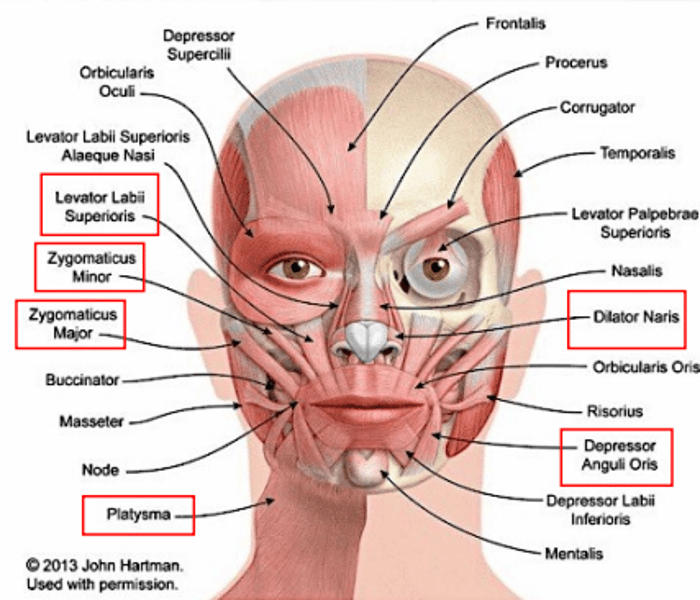
lateral pterygoid
lowers the jaw
gluteus medius
abducts the thigh and medially rotates it
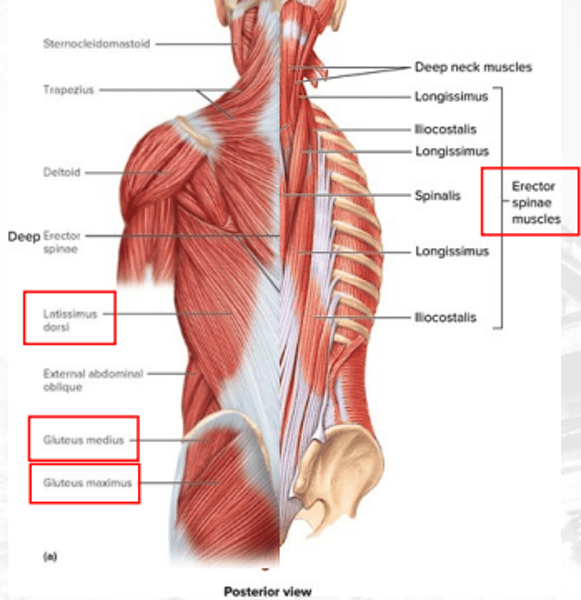
gluteus maximus
facilitates extension at hip joint
supraspinatus
abducts the arm
internal intercostals
compress the thorax
pectoralis major
controls the movement of the arm; adducts and medially rotates arm
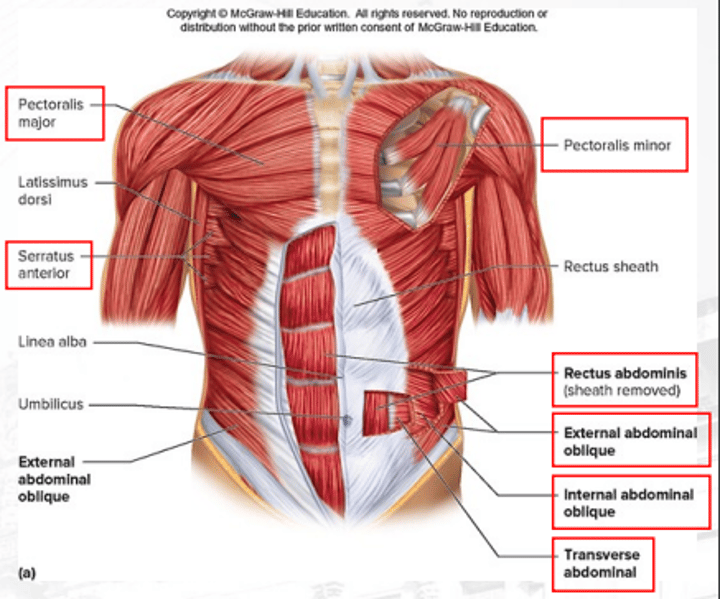
external abdominal obliques
compresses the abdomen (superficial)
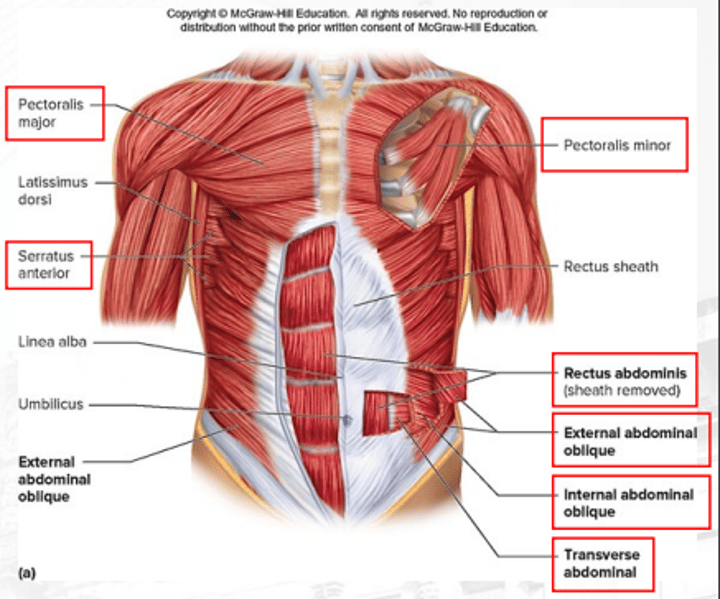
transverse abdominal
compresses the abdomen
brachialis
flexes arm
extensor carpi ulnaris
extends and adducts the wrist
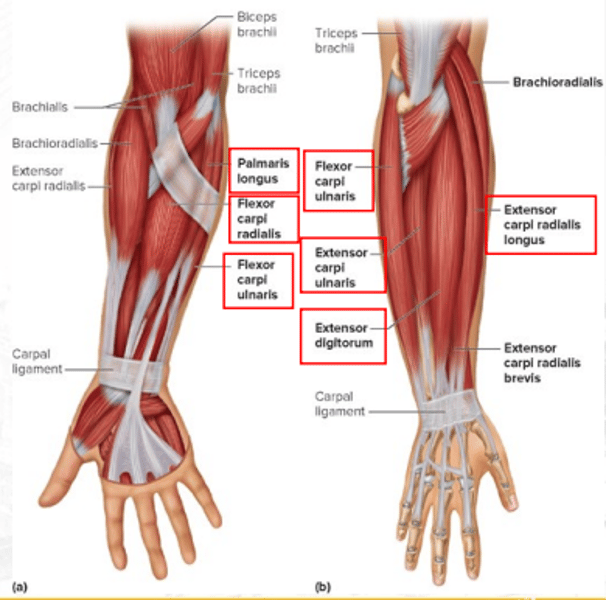
palmaris longus
weakly flexes the hand at wrist joint
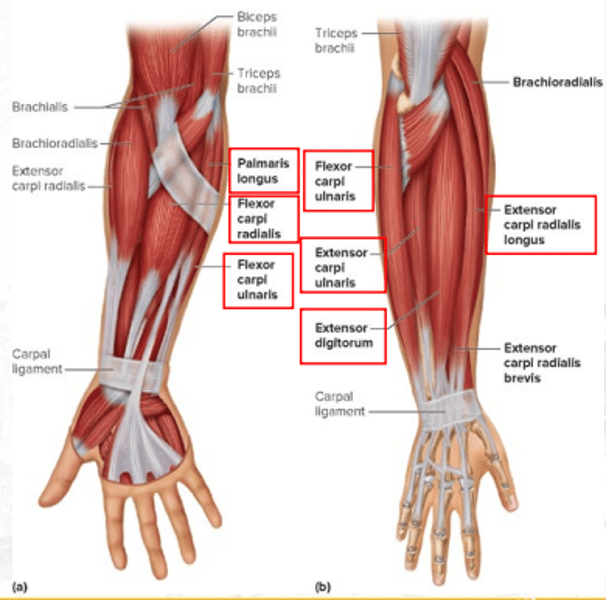
flexor carpi radialis
flexes the wrist and abducts the hand
semimembranosus
extends the thigh, flexes the knee, and rotates the leg medially (deep)
peroneus/fibularis
plantar flexes the foot and everts the foot
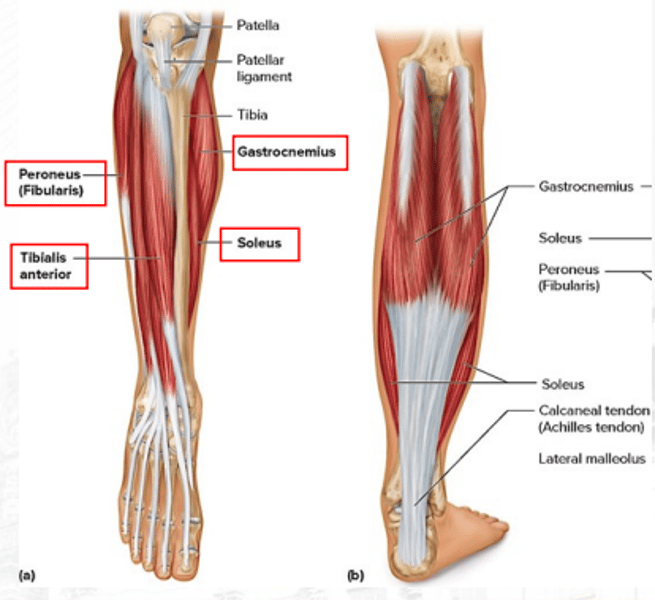
tibialis anterior
dorsiflexes the foot (prime mover) and inverts the foot
plantaris
plantar flexes the foot and flexes leg at the knee joint
bulbospongiosus
Male: aids in urine and semen expulsion, and erection of penis; Females: constricts vaginal orifice, and assists in the erection of the clitoris
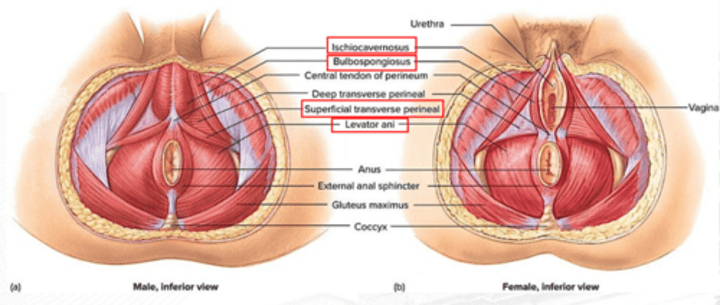
superficial transverse perineus
stabilizes central tendon of perineum
coccygeus
supports pelvic viscera; resists intra-abdominal pressure; and pulls coccyx anteriorly after defecation or childbirth
erector spinae
•iliocostalis
•longissimus
•spinalis
maintains erect posture of the vertebral column
scalenes
•scalenus anterior
•scalenus medius
•scalenus posterior
raise the ribs and expand the thorax
•scalenus anterior
•scalenus medius
•scalenus posterior
scalenes
•iliocostalis
•longissimus
•spinalis
erector spinae muscles
prime mover
the main muscle of the synergists that performs the action
antagonist
a muscle that has an opposing action
flexion
action that bends a part of the body anteriorly, such as flexing the elbow
adduction
movement of a part of the body toward the midline
protraction
movement that brings part of the body forward
lateral excursion
movement of the jaw laterally to either side
medial excursion
movement of the jaw back to the midline
dorsiflexion
position of standing on the heels with the toes pointing up off the floor
supination
rotation that turns the palms up
opposition
the act of bringing the thumb to the palm
reposition
the act of taking the thumb away from the palm
depression
the act of opening the jaw or lowering the shoulders