Lecture 1: Atypical Bacteria: Mycobacteria, mycoplasma, legionella
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Atypical bacteria
lacking a typical cell wall or being intracellular, which makes them resistant to certain antibiotics like penicillin
what are types of atypical bacteria ?
Mycobacterium and Atypical pneumonias
Mycobacteria characteristics
Slow growing bacilli, mycolic acid, and is acid fast bacilli (AFB)
Mycobacteria: Slow growing bacilli
aerobic to microaerophilic so it needs oxygen or little oxygens and doubling time is 18-24 hours so its slow growing
Mycobacteria: Mycolic Acid
Key virulence factor, its a rich cell wall with thick hydrophobic waxy long fatty acid that prevents gram staining
Mycobacteria Species
M. tuberculosis complex (MTC)
M. leprae and M. lepromatosis
Mycobacteria Tuberculosis (Mtb)
Human respiratory tract bacterial pathogen and causes 2 diseases: Pulmonary TB and Extrapulmonary TB
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
most common disease but can disseminate from lung to other parts of the body
Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis
infections outside the respiratory tract in the gastrointestinal tract, bones, joints, nervous system, lymph nodes, genitourinary tract, and skin
Mycobacteria Tuberculosis Reservoir
Humans are the only known b/c its a obligate human parasite, “white plague”, and deadliest infectious disease worldwide now
Obligate human parasite
requires a living host to survive and complete its life cycle
Mycobacteria: Pulmonary Tuberculosis transmission
via inhalation of infectious air droplets emitted from a person
After infection, 3 possible clinical outcomes of Mycobacteria Tuberculosis
infection is eliminated, it turns out to latent tuberculosis, or active tuberculosis disease
Tuberculosis
disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Once in the body tuberculosis (TB) can be
Inactive tuberculosis - Latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI)
Active tuberculosis - Tuberculosis disease
Tuberculosis occurs more often
In people with weakened immune systems like very young, very old, and immunocompromised HIV
Symptoms of Active TB
Chronic, productive coughing, or bloody sputum
Other common symptoms are fever, weight loss, fatigue, and can disseminate from lungs to other body parts
AIDS
Active TB number one killer for people with
Risk Factors for TB Today for Mtb
Recent airborne exposure to mycobacteria tuberculosis like close contact with a person with active tuberculosis or works/lives in a area with high tuberculosis rates or weakened immune systems
Mycobacteria Tuberculosis Detection
Tuberculin skin test by injection (of PPD) and evaluation of injection site but it cant distinguish between latent or active infections
Diagnosis of active Tuberculosis based on
Abnormal chest radiograph, acid fast bacilli in sputum, and DNA detection tests (NAATs)
Treatment of tuberculosis
Both Active Tuberculosis and Latent Tuberculosis infection are curable with multi-drug antimicrobial therapy
Active Tuberculosis treatment
6 – 9 months of 4-drug regimen (isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol); more added if multidrug resistant (MDR-TB)
Latent Tuberculosis infection Treatment
3 – 6 mon prophylactic preventable antibiotics (TST Positive (+PPD) w/no signs or symptoms of active TB)
Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB)
a form of tuberculosis infection caused by bacteria that are resistant to at least two of the first-line drugs used to treat TB: isoniazid (INH) and rifampin.
Mycobacteria tuberculosis – Prevention
BCG Vaccination but only works for kids
Infection control
Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) Vaccination
derived from a live strain of Mycobacterium bovis that is used to protect against tuberculosis
Mycobacterium leprae characteristics
Slow growing obligate intracellular AFB and invades skin macrophages and schwann cells (found in pns)
Mycobacterium leprae: Slow growing obligate intracellular AFB
Longest doubling time of all known bacteria but grows optimally at cooler temps (30-35C) and strictly depends on living inside a host to survive
Hansen disease aka leprosy
Caused by the organism Mycobacterium leprae and needs cooler temps (30-35) for growth
Mycobacterium Leprae – Hansen’s Disease
Chronic, granulomatous disease (like TB), chronic infection results in inflammatory nodules (granulomas) in the skins and peripheral nerves
Hansen’s Disease results in
inflammatory damage to the peripheral nerves and skin tissues of the extremities, eyes, nose, respiratory mucosa
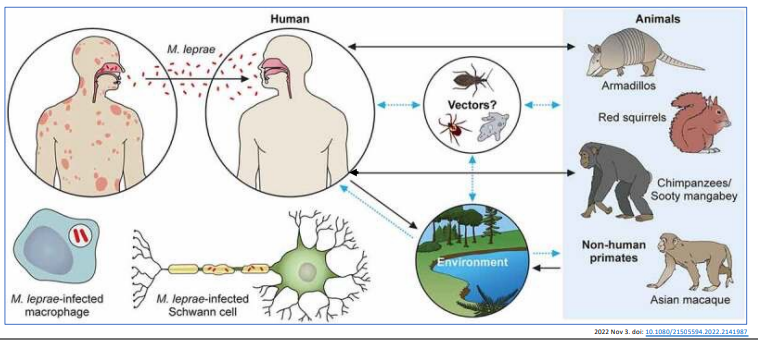
M. leprae - Transmission
Used to be spread person to person by inhalation of infectious respiratory droplets but recently shows zoonotic origin by armadillos
Mycobacterium leprae infects
~95% of people have a natural immunity to the disease (large genetic component to susceptibility)
M. leprae – treatment
Antibiotics is %100 cure, without antibiotic can lead to chronic inflammation
Mycobacterium Leprae – Risk Factors
Living near leprosy endemics, close contact with infected humans/animals, and having specific immune system defects
Mycobacterium leprae – Disease Signs/Symptoms
subtle, occur slowly (usually over years), begin in cooler areas of the body (e.g., hands, feet, face, and knees)
Mycobacterium leprae – Diagnosis 3 criteria
Hypopigmented or reddish skin patches
thickened peripheral nerves
AFB detected on skin smears or biopsy
Mycobacterium leprae – Prevention
Avoid contact infected untreated people and avoid armadillos zoonotic and no vaccines yet
Pneumonia
infection of the lung/lower respiratory tract
Atypical
distinguished from classical bacterial pneumonia by clinical findings and lack of response to typical antibiotics used for classical pneumonia
Atypical pneumonia (AKA walking pneumonia)
Symptoms often milder, slower to develop 1 – 4 weeks after infection, and more persistent than those of typical pneumonia
Species of Atypical Pneumonia
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Chlamydia pneumoniae
Legionella pneumophila
Mycoplasma pneumoniae characteristics
One of the smallest free-living bacteria, no cell wall, and limited metabolic and biosynthetic capabilities
Mycoplasma pneumoniae: No cell wall
able to do cellular polymorphism, prevents gram stain, is naturally resistant to many, and is susceptible to desiccation
Mycoplasma pneumoniae: Limited metabolic and biosynthetic capabilities
Small genomes so depends on tight adherence to human respiratory epithelium and escapes host immune response by intracellular localization
Mycoplasma pneumoniae virulence factor
Produces hydrogen peroxide which causes cytopathic effect to airway epithelium and results in persistent cough
Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infected
Community-acquired upper and lower respiratory tract disease in children and adults worldwide
Mycoplasma pneumoniae – Transmission
person to person through respiratory droplets and incubation period is 2-3 weeks
Mycoplasma pneumoniae – Signs and Symptom
Illness is typically mild with symptoms that get worse over a period of 1 to 4 weeks
Fatigue, headache, low grade fever, sore throat, cough, and chest pain
Mycoplasma pneumoniae – Treatment
Most people recover from mild disease without treatment (or diagnosis)
can be treated with antibiotics
Mycoplasma pneumoniae – prevention
There is no vaccine and infection is not protective against re-infection
Legionella pneumophila characteristic
Non-encapsulated, motile, environmental gram negative bacilli
Legionella pneumophila location
Widespread in nature; reside in surface and drinking water
Legionella pneumophila: Facultative intracellular parasite
Able to live and reproduce inside or outside cells, they invade and replicate inside amoebae in environment and macrophages in humans - intracellular lifestyle
Legionella pneumophila is most
important atypical pneumonia pathogen in terms of disease severity and primarily respiratory infections
Legionella pneumophila – Transmission
By inhalation of contaminated aerosols like water
Person to person transmission is rare
Legionella pneumophila – Infection
Begins in lower respiratory tract where bacteria multiply intracellularly in alveolar macrophages
Can be sporadic or epidemic
Legionnaire’s disease caused by
Organism Legionella Pneumophila
Legionnaire’s disease
Most severe type of atypical pneumonia, most people exposed don’t become ill, and risk factors are old, lung disease, and smoking history
Two diseases caused by Legionella infection
Legionnaire’s disease (most common)
Pontiac fever
Legionellosis: Pontiac Fever
Less common and milder respiratory infection and symptoms resemble acute influenza (fever, headache, severe muscle aches)
Legionella pneumophila – Diagnosis
Chest X-ray exam, urine test for legionella antigens, NAATs, and analysis of blood samples
Legionella pneumophila – Treatment and prevention
Antibiotics and avoid smoking
4 Atypical Bacterial Pathogen
1.Mycobacteria: Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium leprae
2.Atypical pneumonias: Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Legionella pneumophila