Digestive System
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
172 Terms
Ingestion
Complex foods taken into the GI tract
Motility
A number of GI movements resulting from muscular contraction
Digestion
Group of processes that break complex nutrients into simpler ones
Secretion
ØRelease of digestive juices and hormones that facilitate digestion
Absorption
ØMovement of digested nutrients into the internal environment of the body
Regulation
ØNeural, hormonal, and other mechanisms that regulate digestive activity
called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal (GI) tract
Irregular tube
Principle structure of digestive system: Irregular tube called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal (GI) tract and accessory organs of digestion
Transfers nutrients, water, and electrolytes from food into the body’s internal environment.
•Motility
•Secretion
•Digestion
•Absorption
The digestive system performs four basic digestive processes:
common hepatitic duct
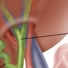
alimentary canal
another name for gastrointestinal tract
cystic duct

§Salivary Glands.
§Liver.
§Gall Bladder.
§Pancreas.
Accessory Organs:
common bile duct

roof
Formed by hard palate and soft palate
hard palate
parts of maxillary and palatine bones
soft palate,
arch-shaped muscle separating mouth from pharynx
Uvula
: Downward projection of soft palate
Floor
Formed by tongue and its muscles
Papillae
Small elevations on mucosa of tongue
Lingual frenulum
Fold of mucous membrane that helps anchor tongue to floor of mouth
sensory analysis, mechanical processing, lubrication, limited digestionm
Accomplishments in the Oral Cavity
•Crown
•Neck
•Root
ØThree main parts of teeth
enamel
which covers the crown, is hardest tissue in body
20 teeth
deciduous or baby teeth
32
permanent teeth #
6 ; 17 and 24
ØAverage age to cut first permanent tooth ___ years old; set complete usually between _________years old
6; 30
ØAverage age cutting first tooth ___ months old; set complete at ___ months old
Serous-type saliva:
ØWatery and contains enzymes (salivary amylase) but no mucus
•Produced by serous-type secretory cells
Mucous-type saliva
ØThick, slippery and contains mucus but no enzymes
•Lubricates food during mastication
•Produced by mucus-type secretory cells
One pair of parotid glands
One pair of sublingual glands
One pair of submandibular glands
- 3 pairs of salivary glands
Parotid glands
ØLargest salivary glands
ØProduces serous type saliva
ØMumps (viral infection):
Infection of parotids
Submandibular glands
ØMixed gland: Produces both serous-type and mucous-type saliva
ØLocated below mandibular angle
Sublingual glands
ØProduce only mucous-type saliva
Approximately 1 Litre/day
pH 6.0-8.0
Hypotonic
99% H2O
1% solutes:
• Electrolytes: (ions such as Na+, K+, Cl-, PO4-2 (phosphate), HCO3 (bicarbonate), thiocyanate).
• Metabolic wastes: (urea, uric acid)
• proteins:
Composition of Saliva
Mucins
these are glycoproteins secreted and converted into mucus
Salivary amylase
starts digestion of carbohydrates in the mouth
Salivary lipase:
starts digestion of lipids in the mouth
Lysozyme
this is antibacterial enzyme
IgA
these are antibodies that prevent antigens from attaching to mucus membrane
Lactoferrin
: this is a protein that inhibits growth of many microorganisms by removing iron
moistens and lubricates food, digestion of polysacchardies by amylase, dissolves food, antibacterial actions
functions of saliva
Pharynx
is a tubelike structure made of muscle and lined with mucus membrane.
Pharynx
is a tubelike structure made of muscle and lined with mucus membrane.
Pharynx
A common passageway for solid food, liquids, and air
ØNasopharynx
ØOropharynx
ØLaryngopharynx
Three anatomic components
Oropharynx
most involved segment in digestive process of swallowing or deglutition [pharynx]
cerebrum
voluntary
brainstem
“deglutition center” of ___________ (involuntary)
Pharynx
Food passes through oropharynx and laryngopharynx to esophagus
Pharyngeal muscles
_________ assist in swallowing
Swallowing
is the movement of food from the mouth through the pharynx and esophagus into the stomach.
- The oral phase (buccal phase), Pharyngeal and esophageal phases (involuntary):
3 phases of swallowing
the swallowing center
- The respiratory center of the medulla is directly inhibited by __________ for the very brief time that it takes to swallow.
The upper esophageal sphincter (UES)
relaxes and the pharyngeal muscles contract to push the bolus of food down into the esophagus.
esophagus
is a muscular, mucus-lined tube.
Esophagus
It is about 25 cm (10 inches) long.
Upper esophageal sphincter (UES)
ØHelps prevent air from entering tube during respiration
ØLES
normally prevents backflow of acidic stomach contents.
LES or cardiac sphincter
ØFood enters stomach by passing through ______________
Stomach
lies in the upper part of the abdominal cavity.
fundus, body, and pylorus.
Three divisions of stomach:
large sausage
ØExpands after large meal; about size of ______________ when empty
Pyloric sphincter
muscle closes opening between pylorus (lower part of stomach) and duodenum
pylorus
(lower part of stomach)
pylorus
gatekeeper
fundus
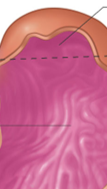
body
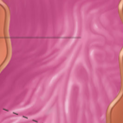
mucus pespinogen and HCl
what does body secret
antrum
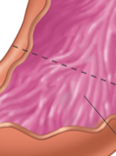
gastrin, pepsinogen, mucus
what does antrum secrete
stomach wall
many smooth msucle fibers; produce churning movements
stomach lining
mucuos membrane; many microscopic glands that secrete gastric juice and hcl into stomach
persitalsis
churning movements
simple columnar epithelial cell
cell the lines the mucosa
pepsinogen
cheif cell secretes waht
mucous
mucous cells secrete what
HCl and intrinsic factor
parietal cell secretes what
secretes gastrin
enteroendocrine cell
mucosa— submucosa——muscularis—-serosa
order from inside to outch
§Bulk storage of undigested food
§Mechanical digestion due to churning (agitate or turn)
§Chemical Digestion due to acid and enzymes
§Production of intrinsic factor (IF)
§Needed for absorption vitamin B12
§Very little absorption
Accomplishments in the Stomach
2-3L a day
gastric juice
•HCl
•
•Activates Pepsinogen
•Aids Iron Absorption
•Kills Bacteria
•Pepsinogen
•Initiates Protein Digestion
•IF
•Required for Vit B12 Absorption (in terminal Ileum)
3
musuclaris of stomach how many layers
lamina propia
connective tissue layer in the mucosa
Small Intestine wall
ØContains smooth muscle fibers that contract to produce peristalsis and segmentation movements
Villi
microscopic finger-shaped projections from surface of mucosa into intestinal cavity
Villi
contain blood and lymph capillaries
small intestine lining
ØMucous membrane with villi
plicae
– folds which are covered in villi: finger-like projections
plicae
•are covered in microvilli
•are responsible for the absorption of nutrients into the body
plicae
•contain blood vessels and lacteals
•blood vessels
collect sugar and amino acids
lacteals
•collect lipids
Intestinal Wall:
•greatly increase the surface area for absorption
longitudinal and circular muscle
muscularis layers in small intestine
Small Intestine
•Is 3 m to 11 m in length