unit 1 review
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
what is biotechnology?
study and manipulation of living things or their components (molecules, cells, tissues, organs, etc.) in order to benefit human beings
what is classical biotech?
using living organisms to yield new products or modify foods/other useful products for human use (ex. recombinant DNA, tissue culture, fermentation, etc.)
what is modern biotech?
advancements in classical biotech impacted by developments in the fields of bio, chem, genetics, & microbiology (ex. DNA profiling, genome analysis, DNA cloning, tissue engineering, etc.)
what is the main difference between classical and modern biotech?
traditional: conventional use of living organisms; primarily in agronomy and consumable production
modern: focus on genetic material manipulation; extensive use in medicine, healthcare, & the environment
what is domestication?
process of adapting wild plants and animals for human use; primarily through selective breeding
give examples of domestication in plants/animals.
animals: dogs, cows, horses
plants: corn, wheat, apples
what is fermentation?
metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substances through the action of enzymes; using microorganisms such as yeast or bacteria to other foods
give examples of food products produced through fermentation.
booze (ex. wine, beer, and spirits), bread, cheese, pickles, & yogurt
what are the 3 main modern biotech techniques?
directly using cells (ex. placing yeast into a bioreactor to ferment grapes)
using proteins/enzymes made by cells (ex. isolating antibiotics from bacteria for use in human medicine)
using genetic material inside cell (ex. DNA fingerprinting)
what is gene therapy?
technique that modifies a person's genes to treat or cure disease
what is genetic counseling?
the giving of advice to people concerning the chances of genetic disorders in a future child or themselves
what is pharmacogenetics?
the study of how our genes affect the way we respond to medications
what is the difference between between gene therapy, genetic counseling, and pharmacogenetics?
gene therapy aims to treat genetic disorders by modifying genes; genetic counseling provides information on hereditary risks; pharmacogenetics tailors drug treatments based on an individual's genetic makeup
what is cloning?
somatic cell nuclear transfer; creating a genetically identical copy of something
how is cloning a whole organism similar & different from cloning a single gene?
single genes & DNA are fairly easy to clone, but cloning entire organisms becomes increasingly difficult; entire organism: duplicating the entire DNA of the organism and creating a new individual with the same genetic makeup as the parent; gene: cloning a gene refers to the process of isolating and making copies of a specific gene
what is PCR and its purpose?
polymerase chain reaction; lab technique for rapidly producing (amplifying) millions to billions of copies of a specific segment of DNA, which can then be studied in greater detail
what is gel electrophoresis and its purpose?
lab technique that separates charged molecules like DNA according to size; allows for DNA sample to be easily processed and recovered without causing harm to it
what is in-vitro fertilization (IVF)?
type of fertility treatment where eggs are combined with sperm outside of your body in a lab
how is cloning a whole organism different than IVF?
cloning creates genetically identical organisms by transferring the nucleus of a somatic cell; IVF combines genetic material from egg and sperm donors to create a genetically unique organism
how do you make rDNA with restriction enzymes?
restriction enzymes recognize short DNA sequences and cleave double-stranded DNA at specific sites within or adjacent to these sequences; DNA ligase combines the fragments made and a “vector” (ex. plasmid) can be used to insert a new segment of DNA
how do you make rDNA with CRISPR Cas-9?
design guide RNA sequences for target DNA modifications; combine Cas-9 enzyme with designed gRNA to create CRISPR-Cas9 complex (Cas-( breaks double strand at target sites); deliver CRISPR-Cas9 complex into target cells using methods like transfection or electroporation
how is making rDNA with restriction enzymes similar & different to than with CRISPR Cas-9?
similarities: both methods can be used to insert new genetic material into a host organism
differences:
restriction enzymes: cut DNA at specific recognition sites and is less precise; requires compatible ends for ligation; limited control over site specificity
CRISPR: uses Cas-9 enzyme guided by gRNA to induce targeted DNA breaks; often considered more versatile and precise
what is industrial/environmental biotech?
fermented foods/beverages
genetically engineered proteins for industry
DNA identification/fingerprinting of endangered species
biocatalysts
biopolymers
what is medical/pharmaceutical biotech?
medicines from plants, animals & fungi
medicines from genetically engineered cells
monoclonal & polyclonal antibodies
designer drugs & antidotes
prosthetics & artificial organs/tissues
vaccine & gene therapy
what is agricultural biotech?
breeding of livestock/plant crops
aquaculture & marine biotech
transgenic plants/animals
pharmaceuticals in genetically engineered plant crops
what is diagnostic research biotech?
DNA & protein synthesis/sequencing
DNA fingerprinting
PCR
genetic testing/screening
bioinformatics
why are HeLa cells considered controversial?
original biopsy patient never consented to the use of her retrieved cells for research purposes; medicine using black women for their own benefit
what was the diamond v. chakrabarty case and its significance for biotechnology?
dispute over the patentability of living organisms, particularly chakrabarty's invention; court stated that living organisms (including GMOs) are patentable; established a framework for patent protection in biotechnology
how does the educational requirement vary between technical roles (e.g., laboratory technicians) and more advanced positions (e.g., biotechnologists or researchers)?
more advanced roles require more education
how are the requirements for a professional degree similar & different to requirements of a graduate degree?
similarities: advanced education beyond a bachelor's degree; credentialing for higher expertise
differences:
professional degrees are career-focused for specific professions; graduate degrees emphasize research, theory, and varied career paths
professional degrees: may not require a thesis; emphasis on practical experience; graduate degrees must include research-intensive components
what do each of the colors on the NFPA diamond stand for?
white: special hazard; red: flammability; yellow reactivity; blue: health hazard
what is informed consent?
voluntary agreement to participate in research or medical activities after receiving detailed information about the nature, risks, benefits, & alternatives
how do researchers obtain informed consent?
explain study details, risks, and benefits clearly
allow participants to ask and address concerns
use a written document & provide a copy to participants
how can differences in enzyme function can affect a person’s response to a drug?
genetic differences affect the speed of drug metabolism
enzymatic variations impact the conversion of inactive drugs to active forms
enzymes influence drug absorption and availability in the bloodstream
what are pre-clinical trials? which “phase” is it?
phase 0; drug is tested on human cells/tissues
what is phase 1 of clinical trials?
researchers test new treatment in a small group of people to evaluate safety, dosage, and to identify side effects
what is phase 2 of clinical trials?
product is given to a slightly larger group to test effectiveness and safety
what is phase 3 of clinical trials?
the product is tested in a large group and compared to other drugs/treatments; used to confirm safety and monitor side effects in large populations
what are post-clinical trials? which “phase” is it?
phase 4; studies conducted after clinical trials to monitor long-term safety, effectiveness, and real-world impact of medical interventions
how do the conditions of clinical trials change between phases?
population size increases
earliest trials look at whether a drug is safe or the side effects it causes; later trials aim to test whether a new treatment is better than existing treatments
what is OSHA and its purpose?
occupational safety and health administration; ensures workplace safety by enforcing standards for hazard communication, personal protective equipment, & emergency preparedness
what is the FDA and its purpose?
food and drug administration; ensures public health by regulating safety and efficacy of food, pharmaceuticals, vaccines, & medical devices
what is the EPA and its purpose?
environmental protection agency; safeguards human health and the environment by enforcing regulations, conducting research, & developing policies to prevent pollution and address environmental issues
what is USDA and its purpose?
united states department of agriculture; oversees agriculture, food safety, & rural development to promote production, ensure safety, & protect natural resources
what is an IRB and its purpose?
institutional review boards; provide protection for human research participants through advance and periodic independent review of the ethical acceptability of proposals for human research
what is IACUC and its purpose?
institutional animal care & use committee; ensures the highest animal welfare standards and accurate scientific research in projects involving vertebrate animal testing through supervision, coordination, training, guidance, and review

identify the safety pictogram.
acute toxicity

identify the safety pictogram.
irritant

identify the safety pictogram.
flammable
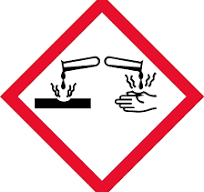
identify the safety pictogram.
corrosive

identify the safety pictogram.
oxidizer

identify the safety pictogram.
health hazard

identify the safety pictogram.
environmental hazard

identify the safety pictogram.
gas under compression
what are right to know laws?
employers must provide workers with basic information about the hazardous materials with which they work
describe the rights/responsibilities of employers towards their employees and the communities within which they operate as defined by the right-to-know laws.
employers must provide a safe and healthy workplace, ensure equal employment opportunities, inform employees about workplace hazards (RTK laws), and minimize their environmental impact