Basics of xray
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
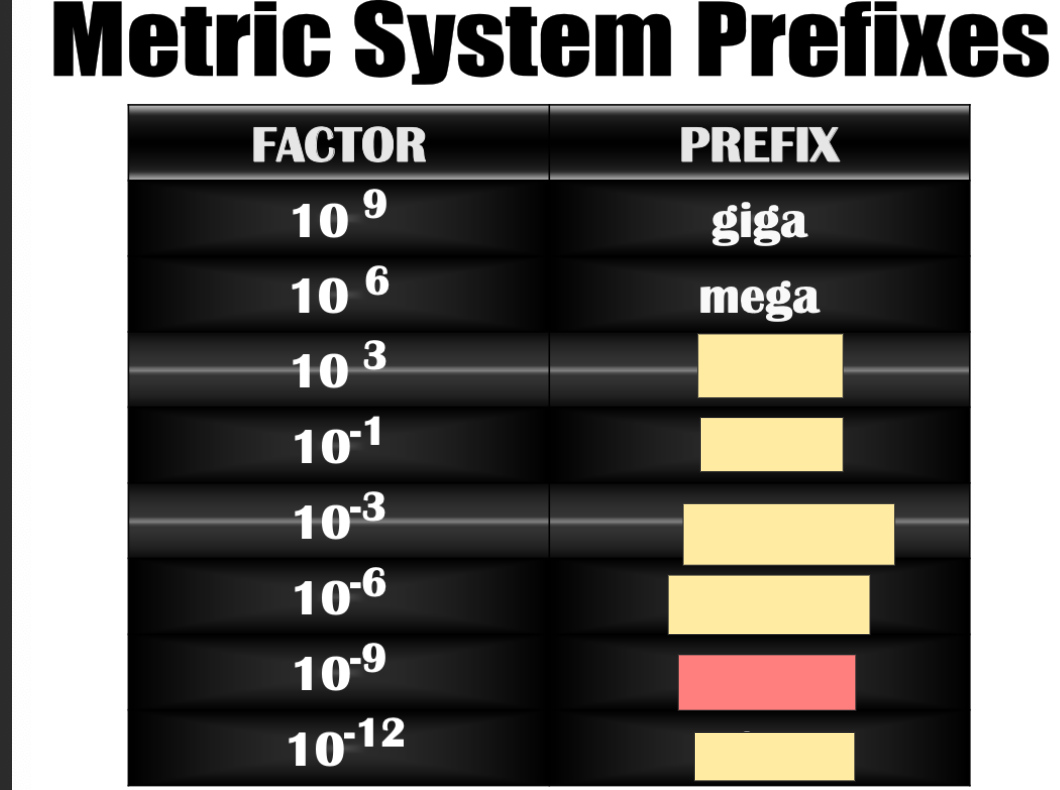
Nano
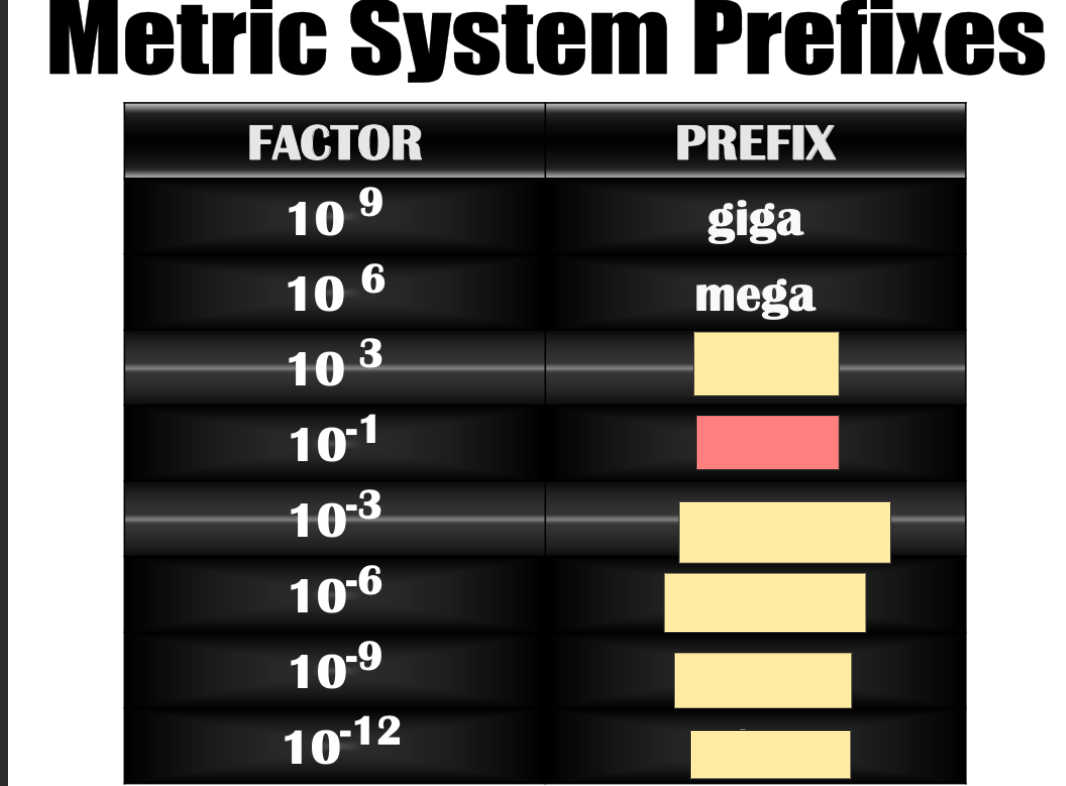
deci
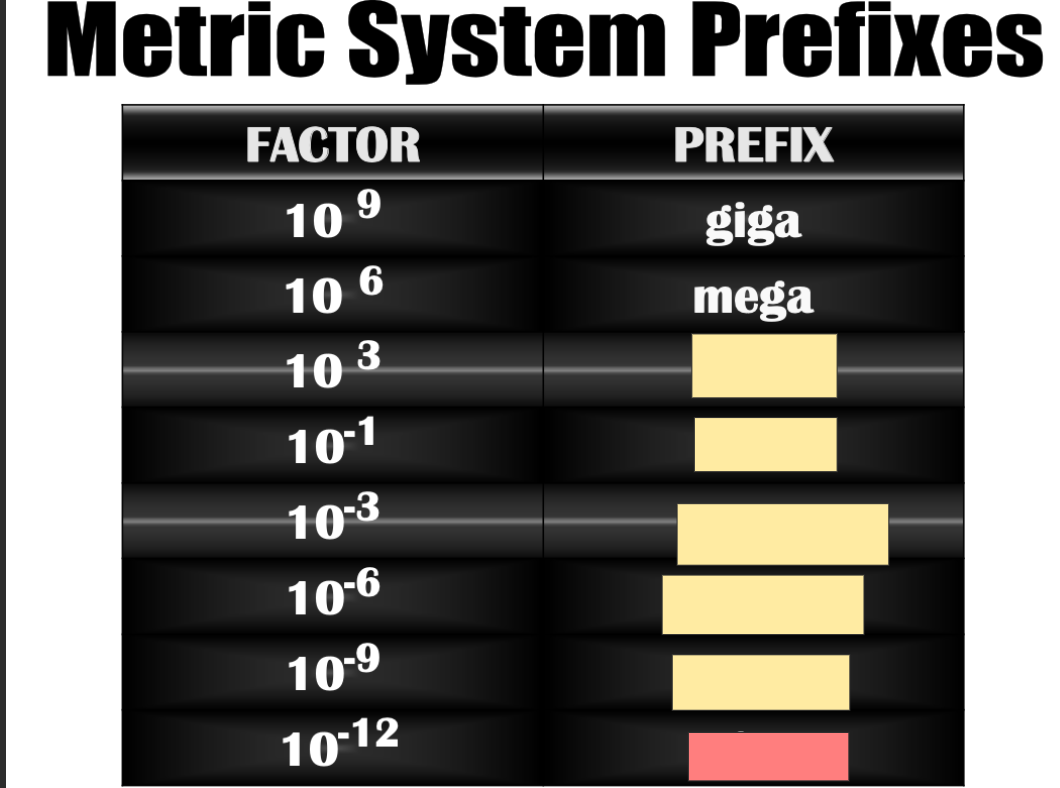
pico
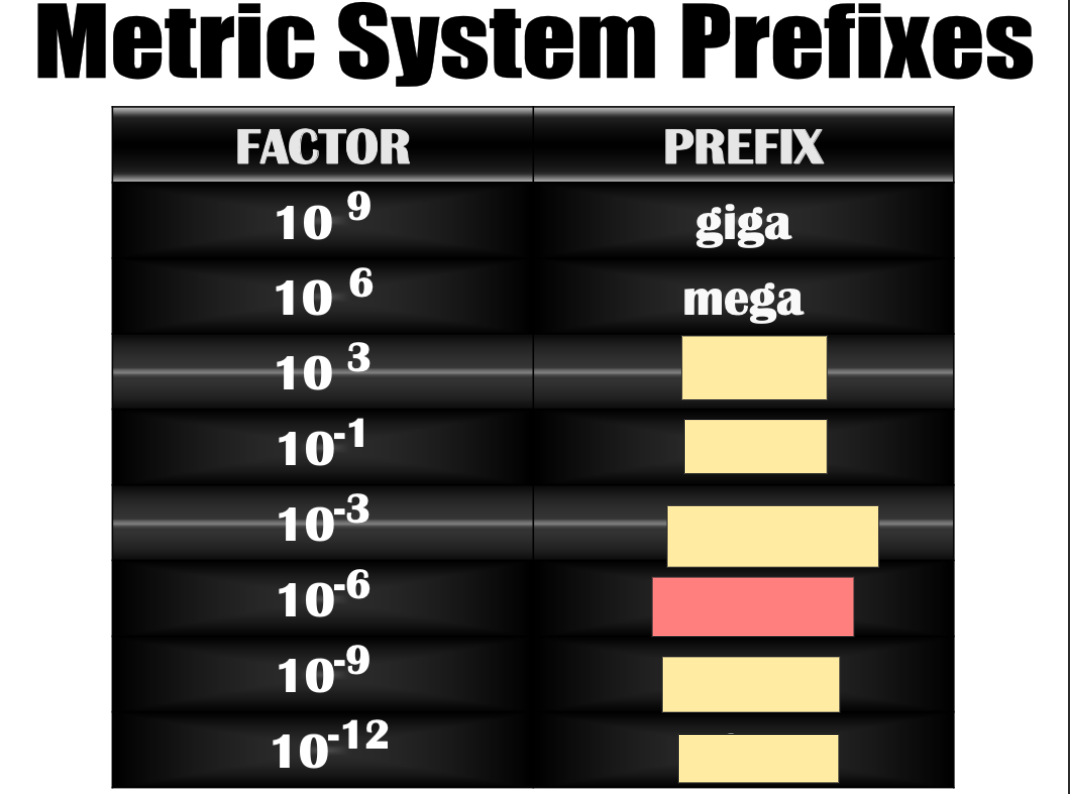
micro
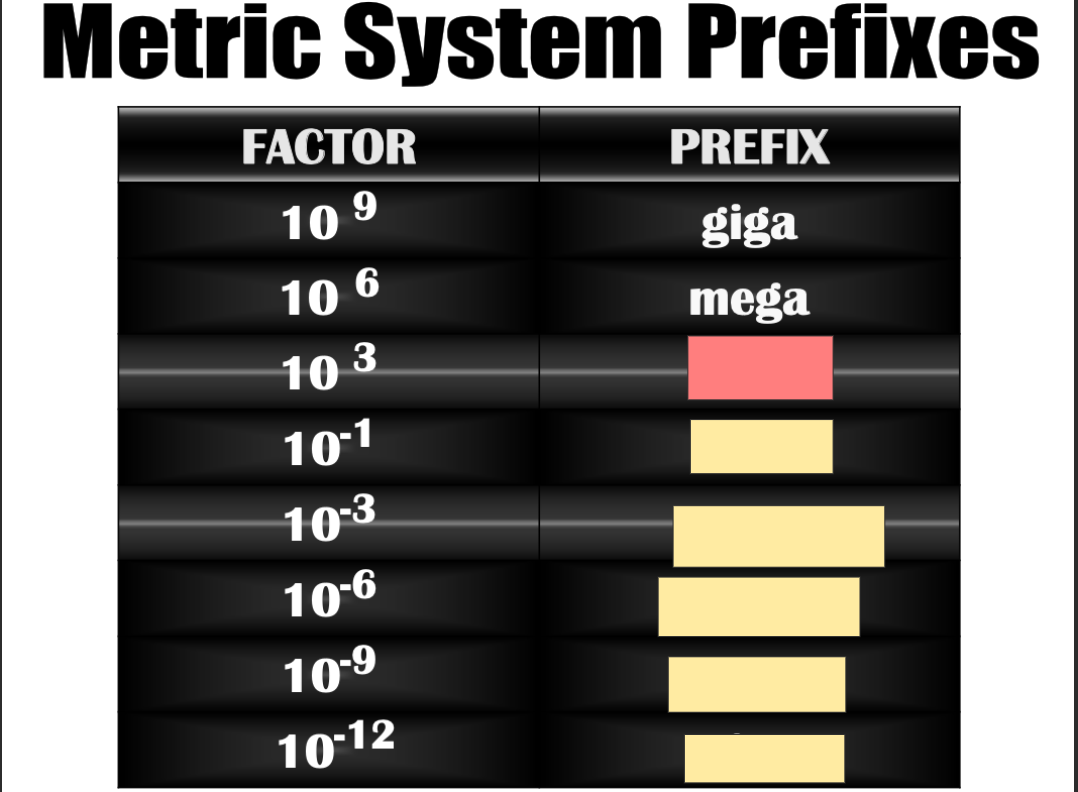
kilo
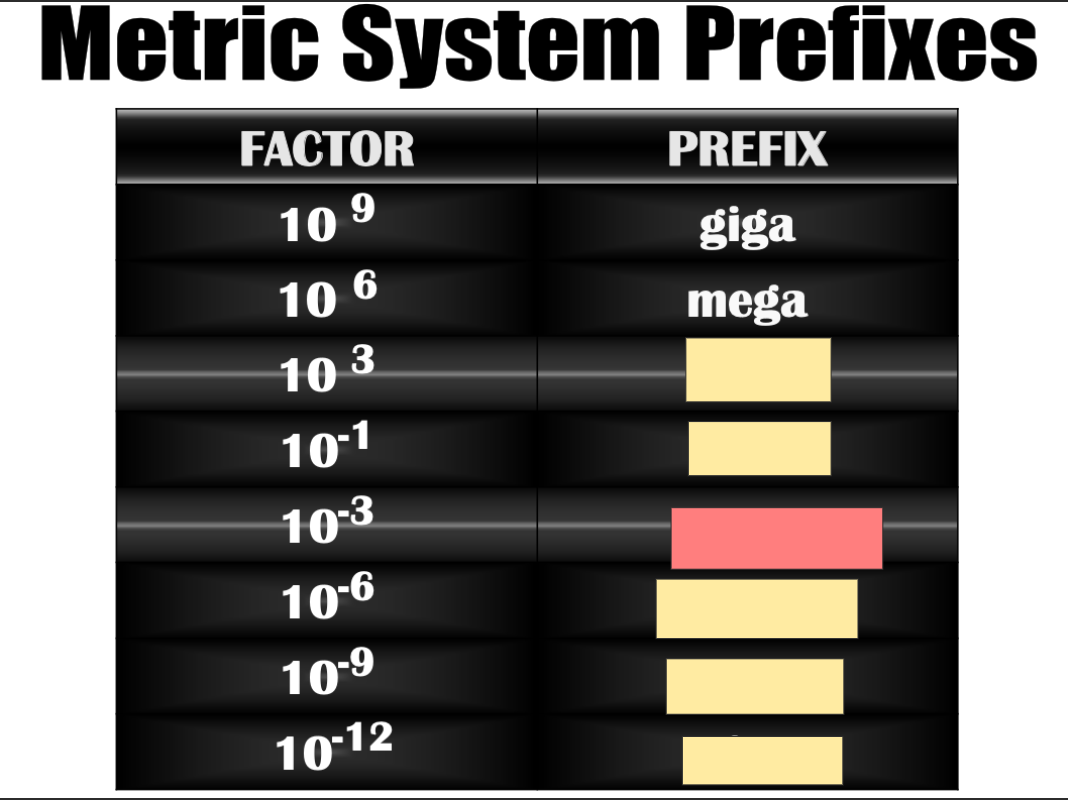
mili
A changing magnetic field produces a [...]
A changing electric field produces a [...]
transient electric field
transient magnetic field
This is the principle of induction
A wire carrying current experiences a [...]
magnetic field
[...]
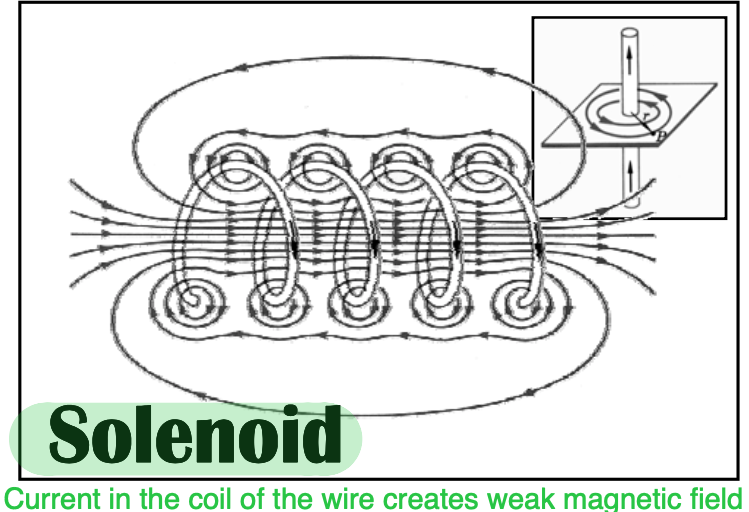
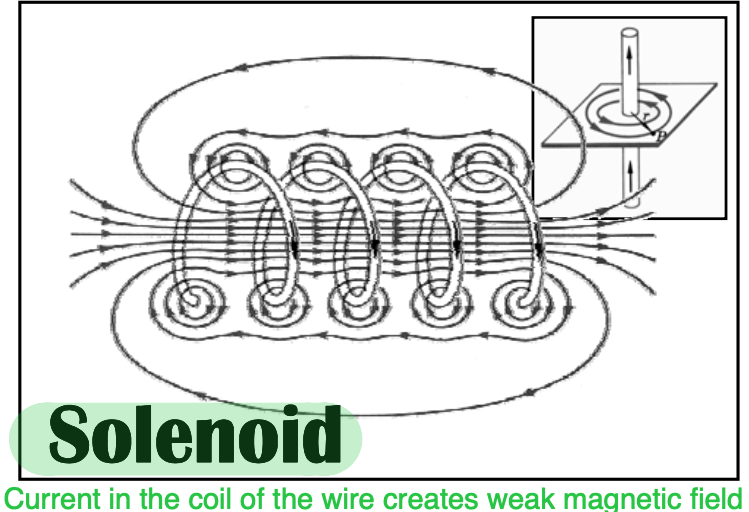
If iron core placed in center of solenoid, magnetic field much more intense
electromagnet
![<p>What is the purpose of this image?</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fb09d0ec-f9d3-4117-b521-739d9fc4b98a.png)
What is the purpose of this image?
[...]
[...]
A change in current (+ or -) influence magnetic field
When the swith opens or closes, see bumps in magnetic field
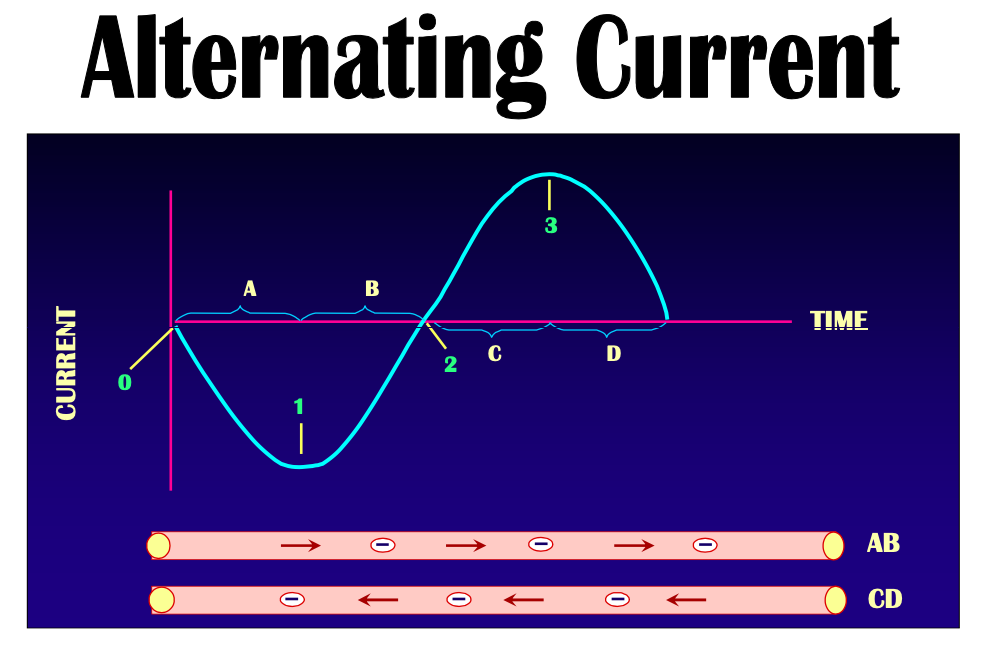
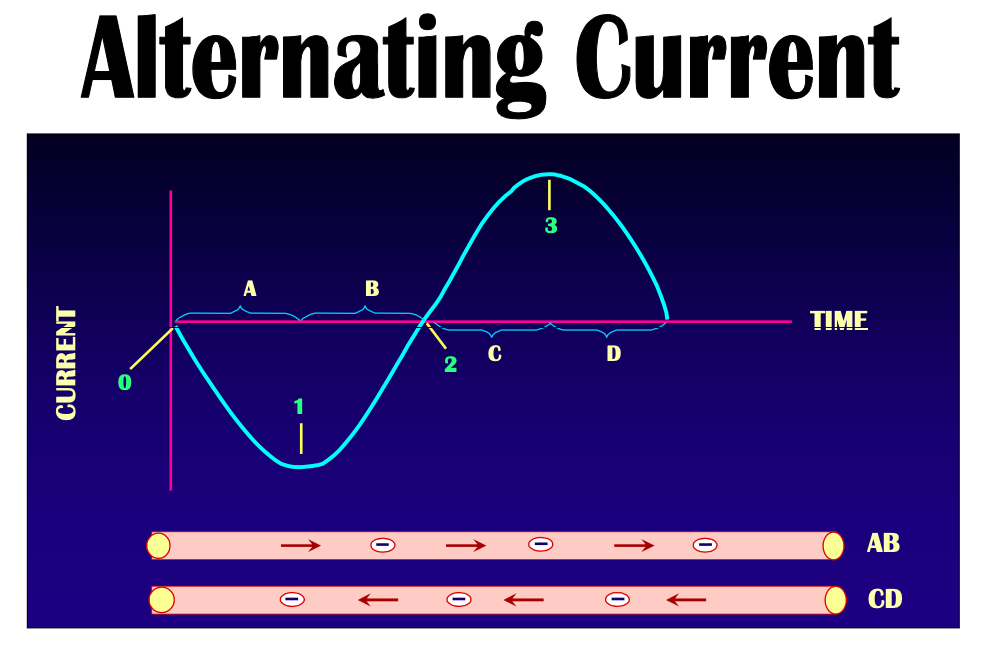
2 types of current
[...]: flow of electrons in one direction
[...]: flow in alternating opposite directions
Direct current
Alternating current
2 types of electricity
[...]: electric charges at rest
Units: Coulombs
[...]: moving electric charges
Units: Amperes
Static
Current
2 types of electricity
Static: electric charges at rest
Units: [...]
Current: moving electric charges
Units: [...]
Coulombs
Amperes
Alternating current: flow in alternating opposite directions
Pulse
One pulse is from negative to positive (or vice versa)
[how many pulses are in an AC current?]
AC goes in opposite directions so one cycle has 2 pulses
As wavelengths decrease, frequency [increase or decrease?]
increase
Atom
Atomic number (Z) = [...]
Atomic Mass = [...]
number of protons
number of protons + number of neutrons
Atom
[...] = number of protons
[...] = number of protons + number of neutrons
Atomic number (Z)
Atomic Mass
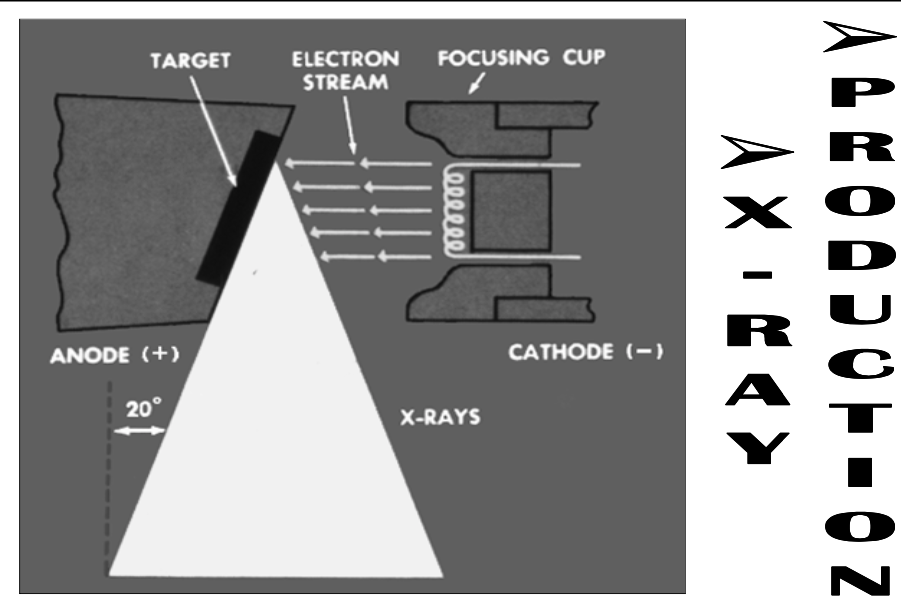
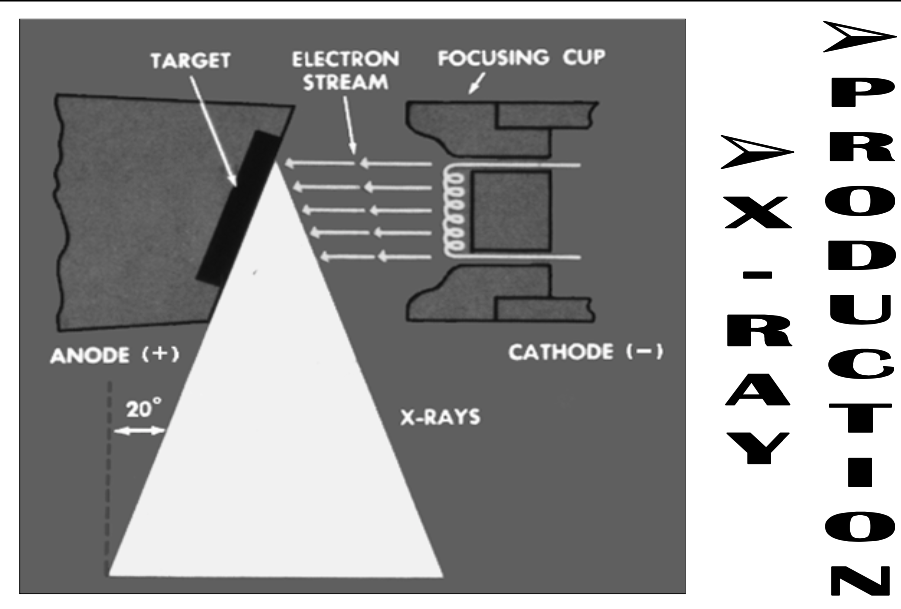
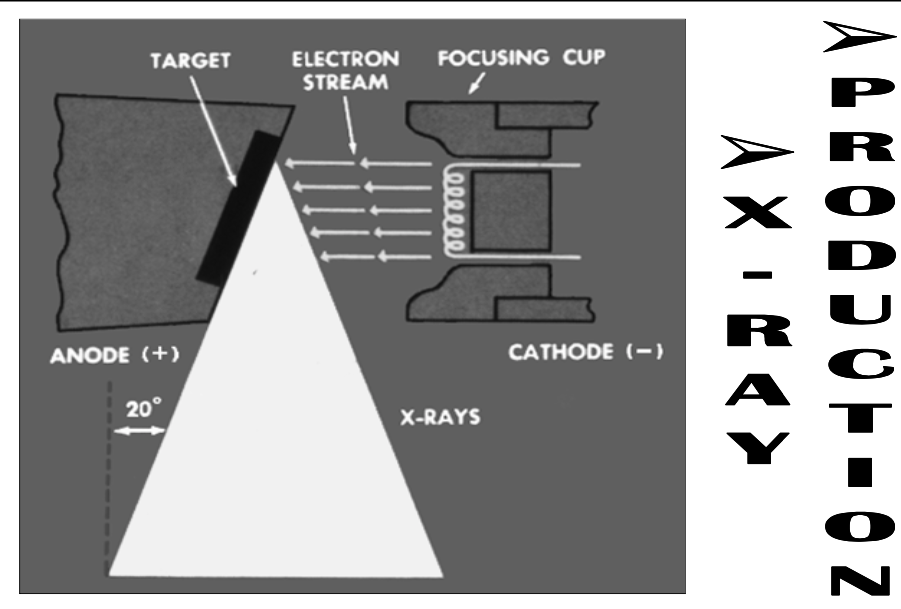
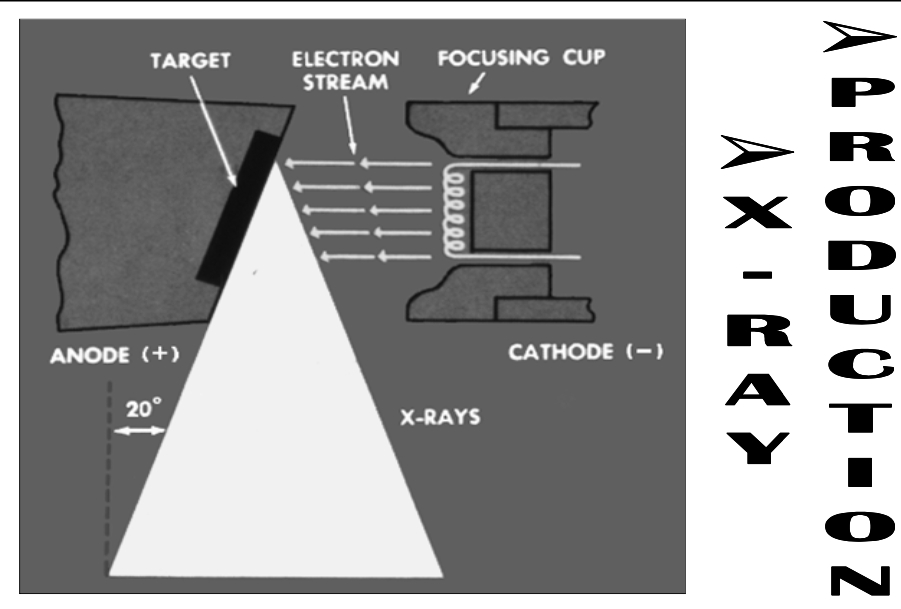
Basic X-Ray Generation
[step 1?]
[step 2?]
High KE electrons interact with target atoms to produce photons in x-ray wavelength
Electrons are conducted away & complete the circuit
Current is flowing and since it is a high voltage area, current needs be low in mA
Electrons thermionically “boil off” filament embedded in the cathode
Negatively charged electrons are shot at positive anode tungsten target by the strong potential difference
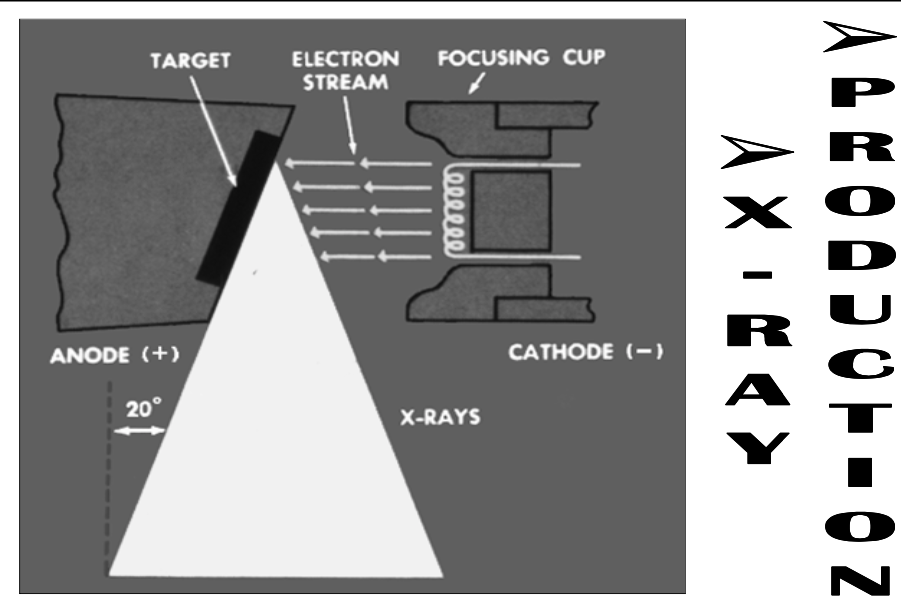
Basic X-Ray Generation
Electrons thermionically “boil off” filament embedded in the cathode
Negatively charged electrons are shot at positive anode tungsten target by the strong potential difference
High KE electrons interact with target atoms to produce photons in x-ray wavelength
Electrons are conducted away & complete the circuit
[What unit is it in?]
Current is flowing and since it is a high voltage area, current needs be low in mA
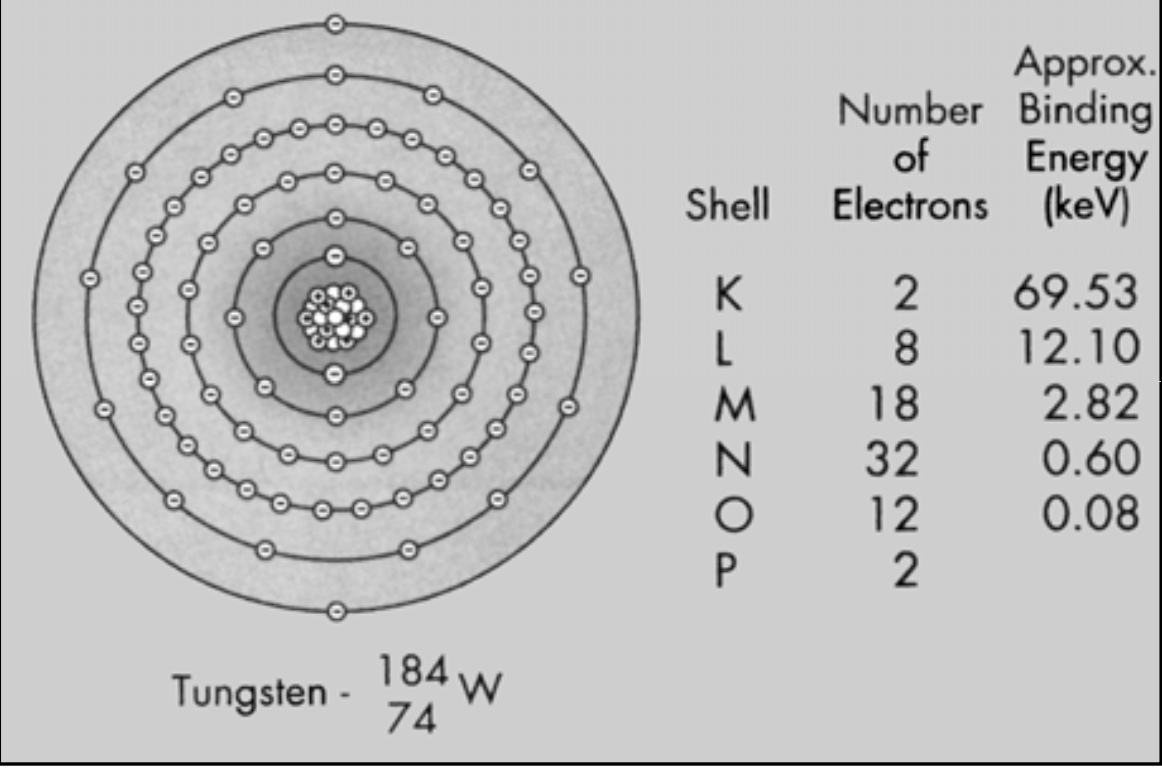
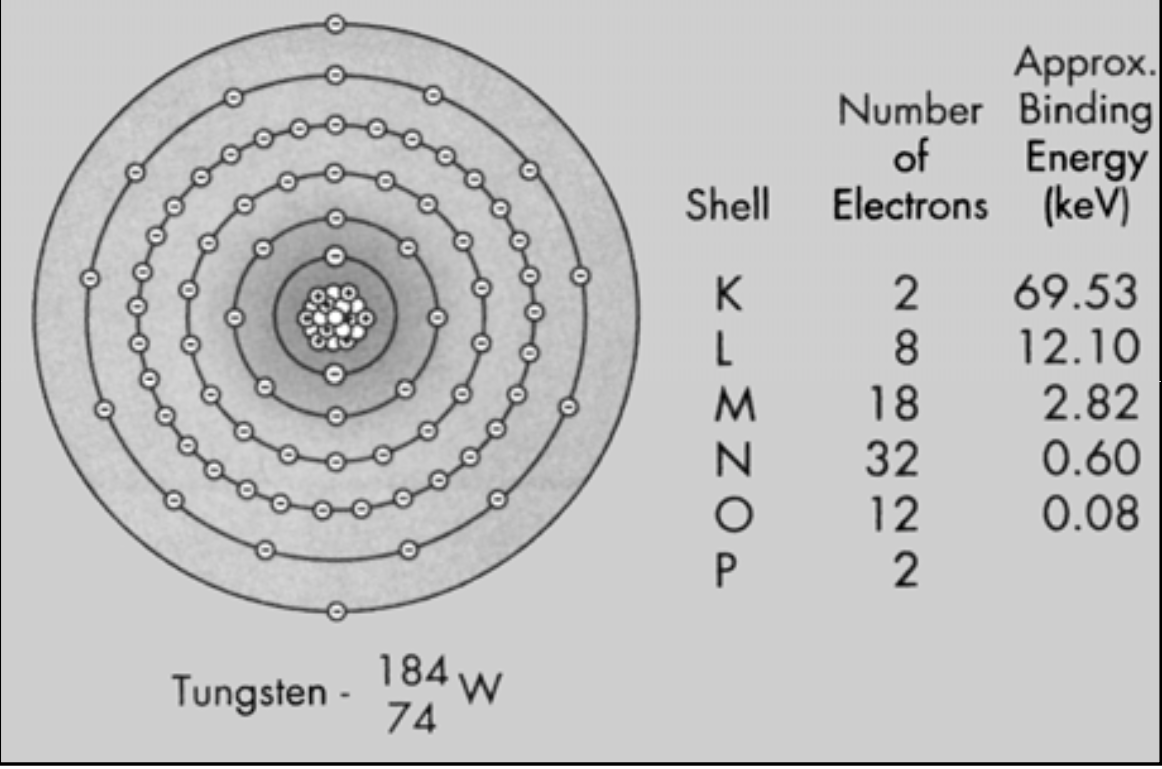
Binding Energy (BE): the amount of energy that electrons have in each shell
[Higher or lower?] BE if closer to nucleus
Higher the atomic number, the tighter the K shell electrons are bound
Higher
The higher the BE, the harder it is to separate the electron (freeing an electron requires equal or more energy than the BE)
Outer shells like O and P have a really low BE (so its easy to pry those electrons away) but inner shells (like K) have a high BE
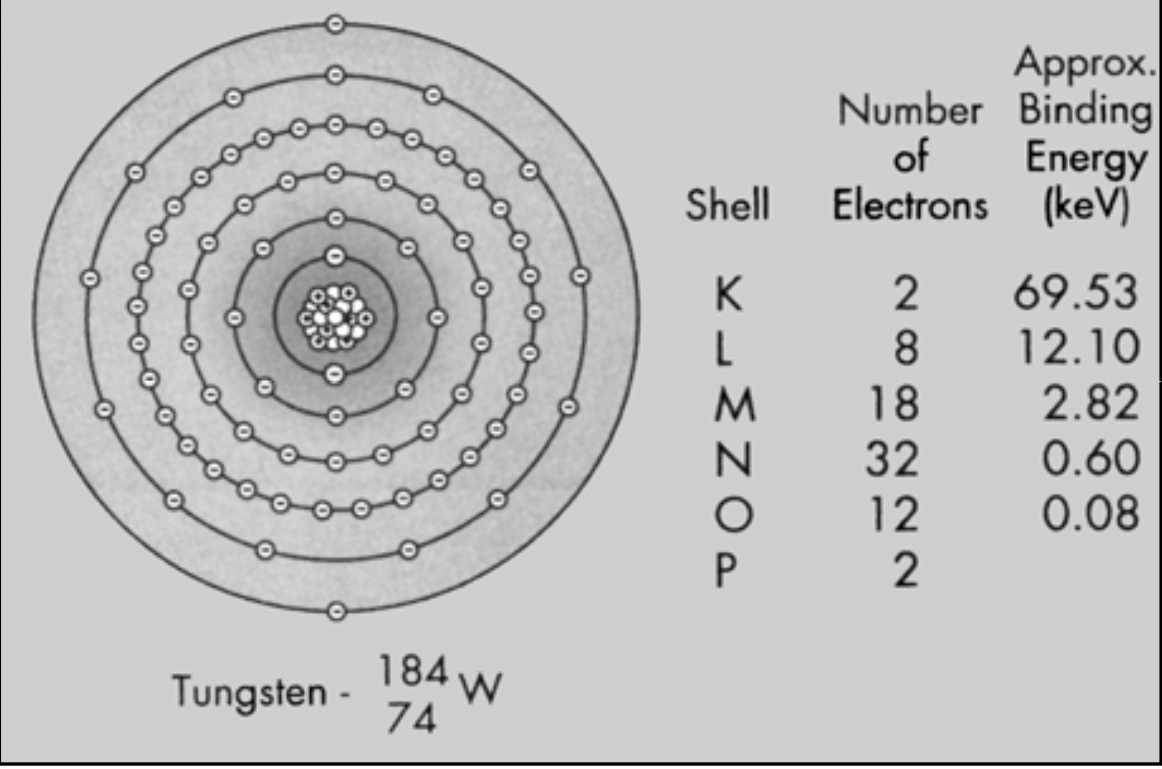
Binding Energy (BE): the amount of energy that electrons have in each shell
Higher BE if closer to nucleus
[Higher or lower?] the atomic number, the tighter the K shell electrons are bound
Higher
The higher the BE, the harder it is to separate the electron (freeing an electron requires equal or more energy than the BE)
Outer shells like O and P have a really low BE (so its easy to pry those electrons away) but inner shells (like K) have a high BE
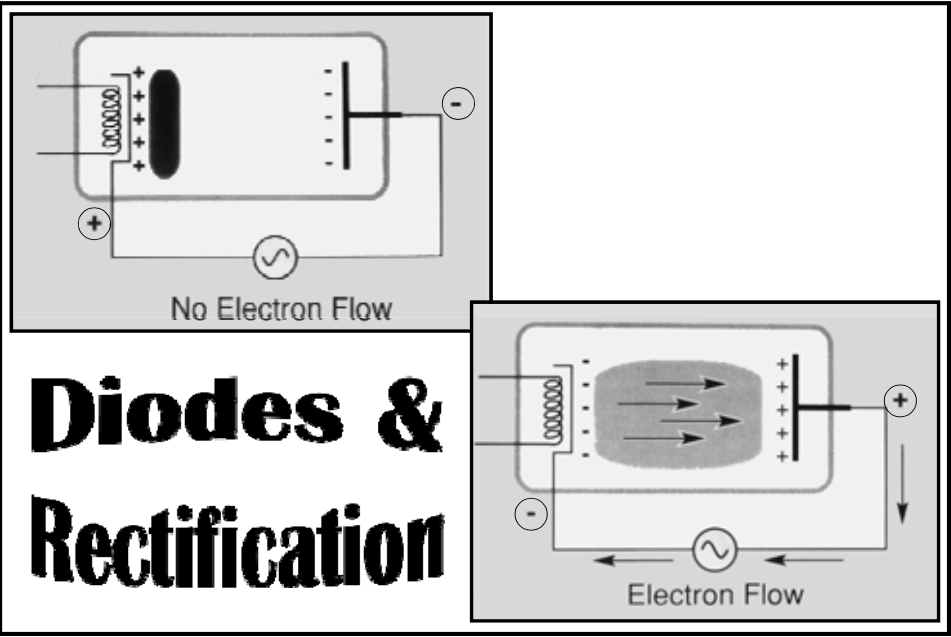
Current Rectification
Diodes only allow flow in [how many directions?]
one direction
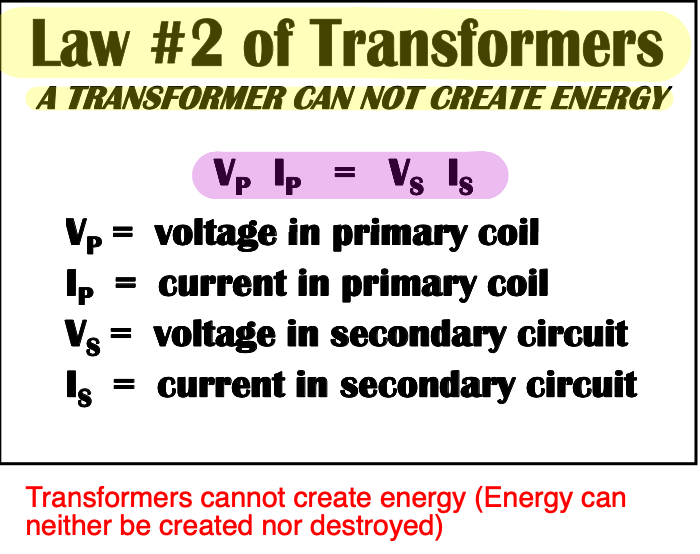
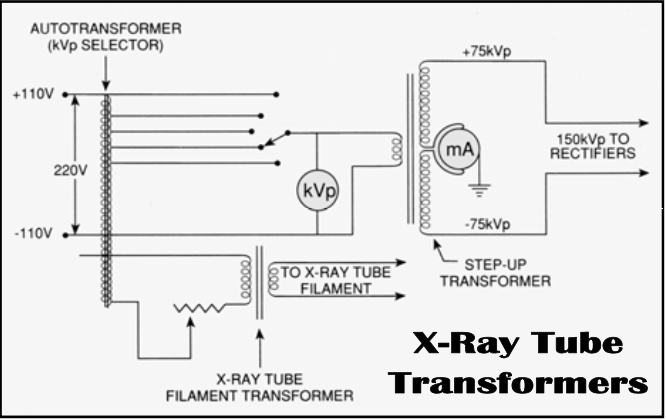
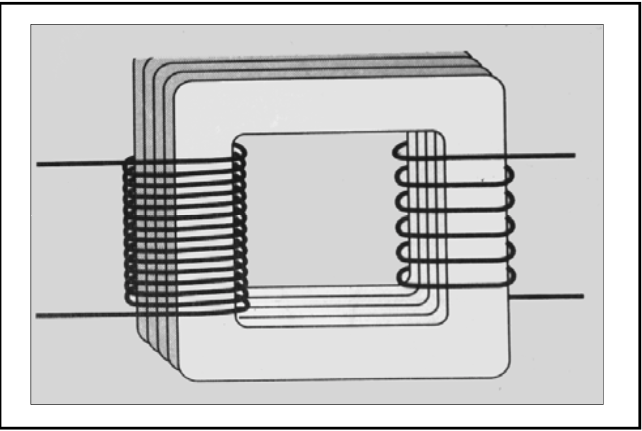
Describe the second law of transformers?
[...]
[...]
If voltage is increased in primary, it is at the expense of current in the primary
power in the primary equals the power in the secondary
VI = P (watts)
Explain why X-Rays can be dangerous, in terms of the ionizing radiation.
[...]
Energy is always transferred to any material with which it interacts
Since high energy EM can ionize atoms (disrupt DNA), there are safety concerns
IF there is an interaction, energy is transferred (likely disrupting DNA)
But if the X-Ray passes through without interaction, there no energy transferred and everything is okay (no harm, no foul)
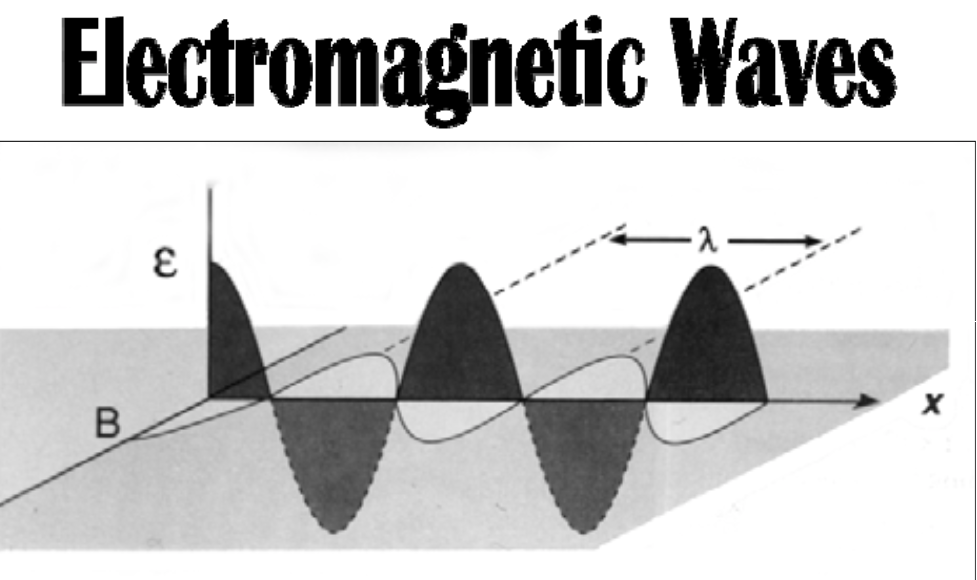
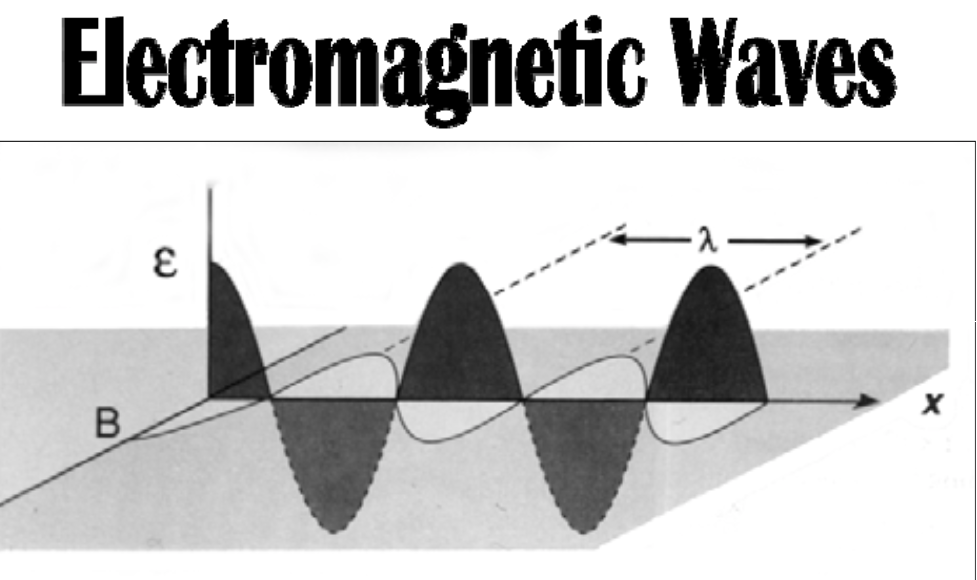
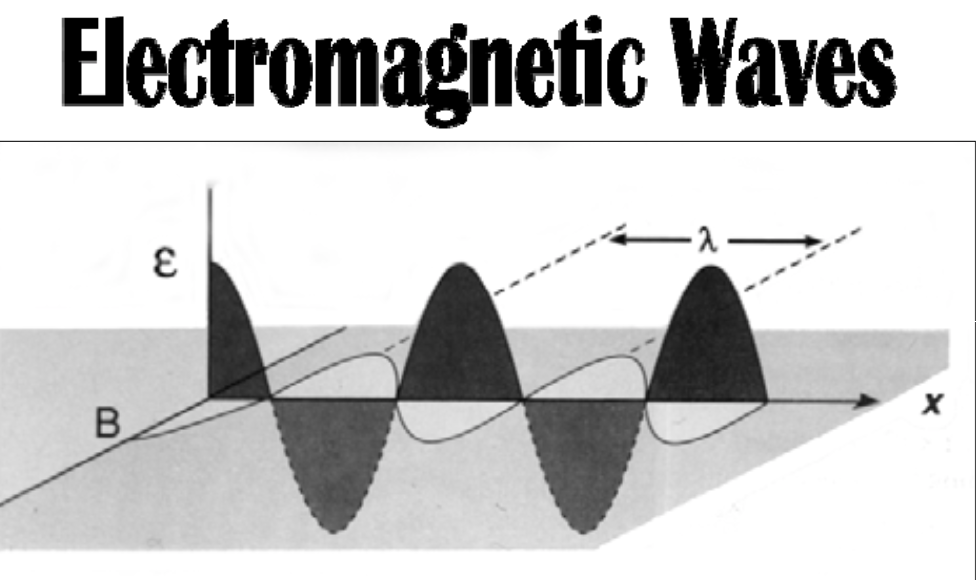
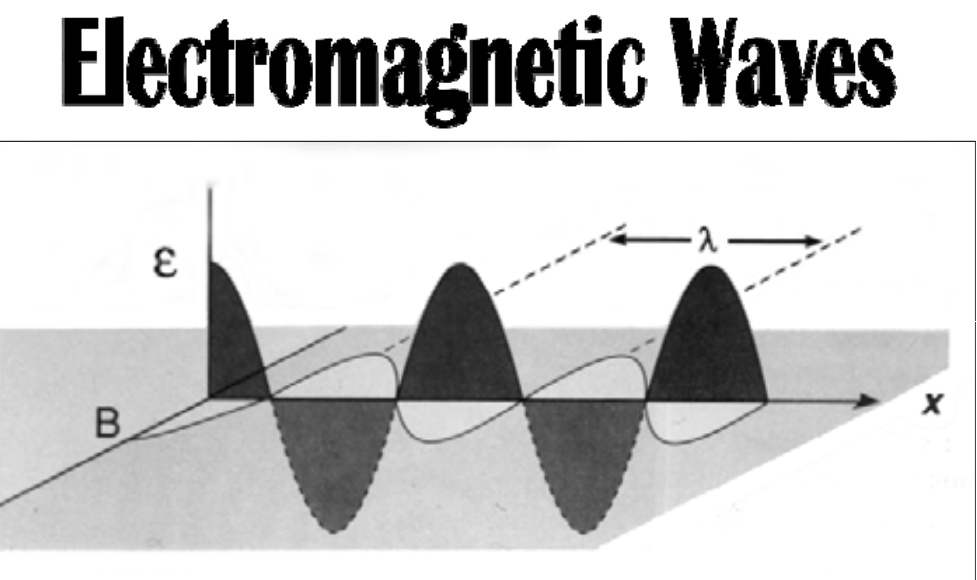
Frequency: number of waves passing per second
SI unit: [...]
1 Hz = 1 cycle per second
Hertz (Hz)
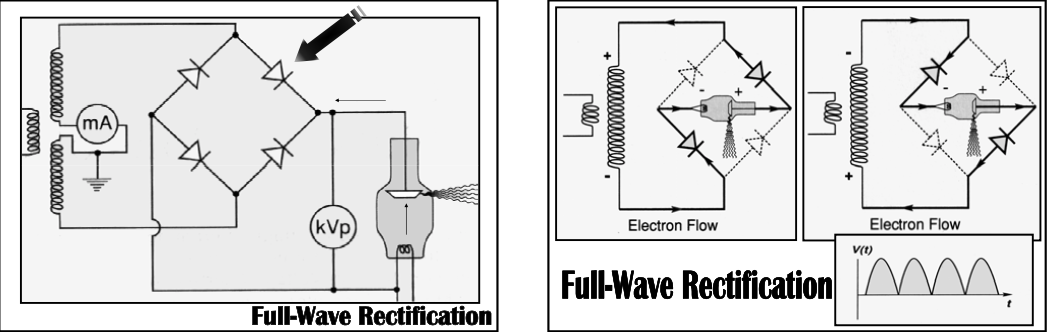
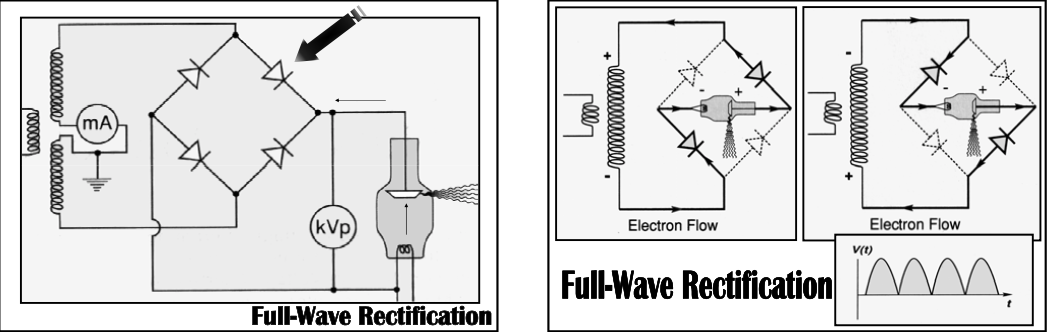
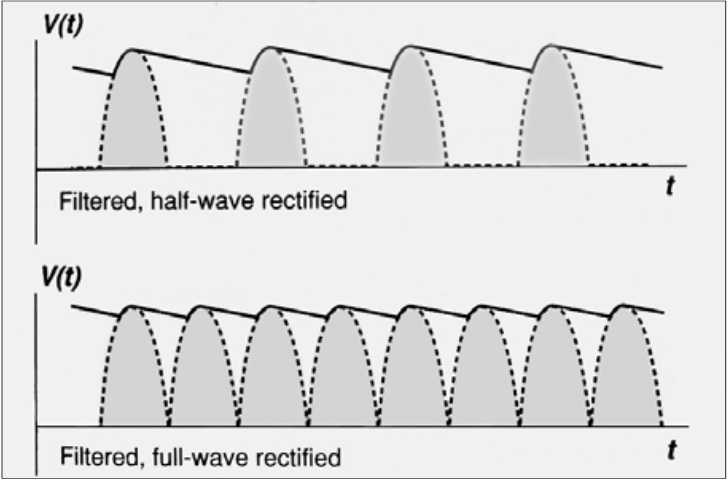
Full Wave Rectification
Accomplished by [...]
a diode bridge, formed by 4 diodes
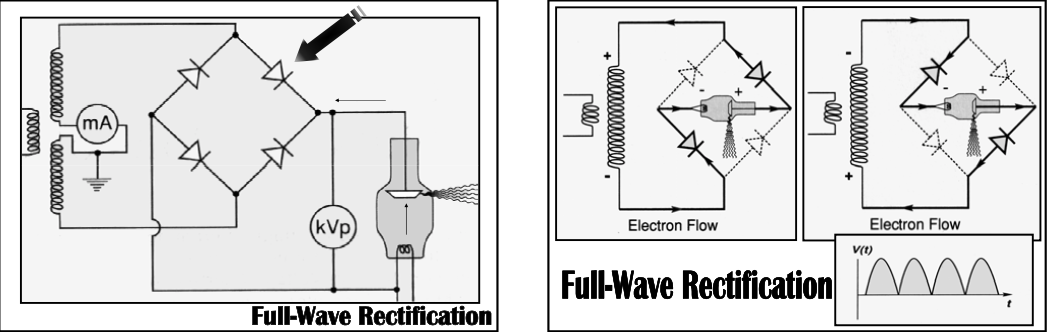
Full Wave Rectification
Disadvantages
[...]
[...]
Tube pulsates and anode receives rapidly varying amounts of energy
Intensity of x-ray beam varies. Consequently, quality of beam varies over each half cycle
increased patient dose via "soft radiation"
Full Wave Rectification
[What parts of the alternative voltage] are used to produce x-rays
Converts alternate current to direct current
Both halves of the alternative voltage
Generally no more than [...] electrons in the outermost shell
8
![<p><span>How does additional phases affect ripple factors? </span></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/32a7c58c-51d4-48a5-a6f6-00ef1e1c49e6.png)
How does additional phases affect ripple factors?
[...]
Additional phases results in low ripple factors which means better image quality but also more expensive
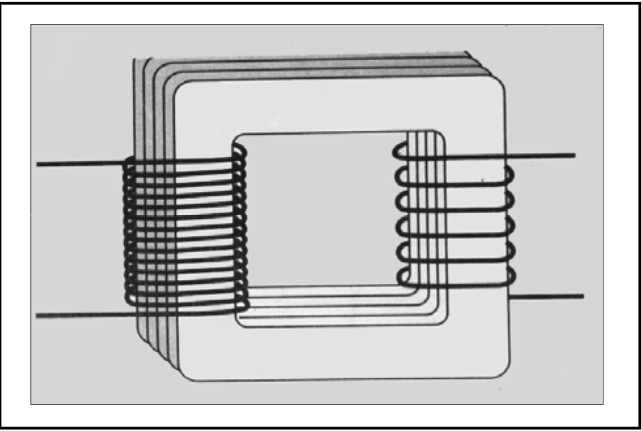
How does the secondary coil recieve current?
[...]
Rapidly changing electric fields in the primary coil induce rapidly changing magnetic fields
The rapidly changing magnetic fields in turn induce rapidly changing electric fields in the secondary coil
Induced EMF's
Current flow thru one coil can cause [...] in a 2nd coil wrapped around the same iron core or rod
mutual inductance
Basis of the transformer
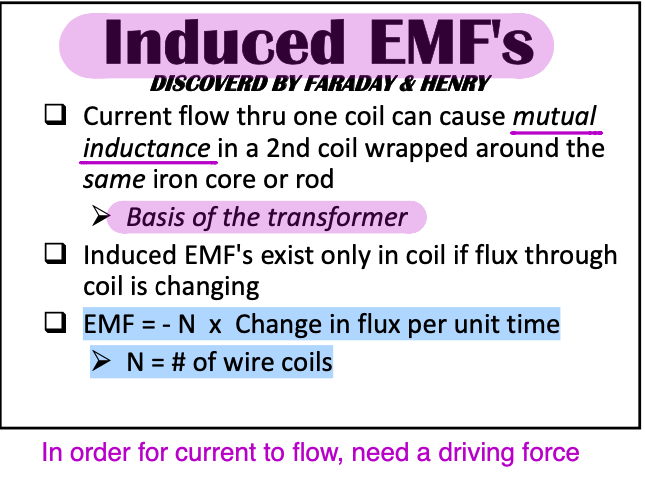
Induced EMF's
EMF= [...] x [...]
Number of wires x Change in flux per unit time
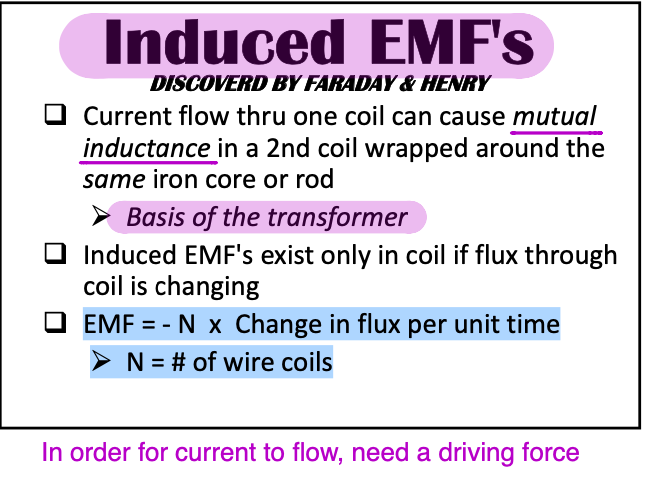
Ionizing Radiation: X-Ray electromagnetic radiation energy range
Can penetrate matter
Causes some material to [...]
Reacts with [...] of film
fluoresce
silver halide
X-Rays have enough energy to cause atoms to ionize (gain or lose electrons)
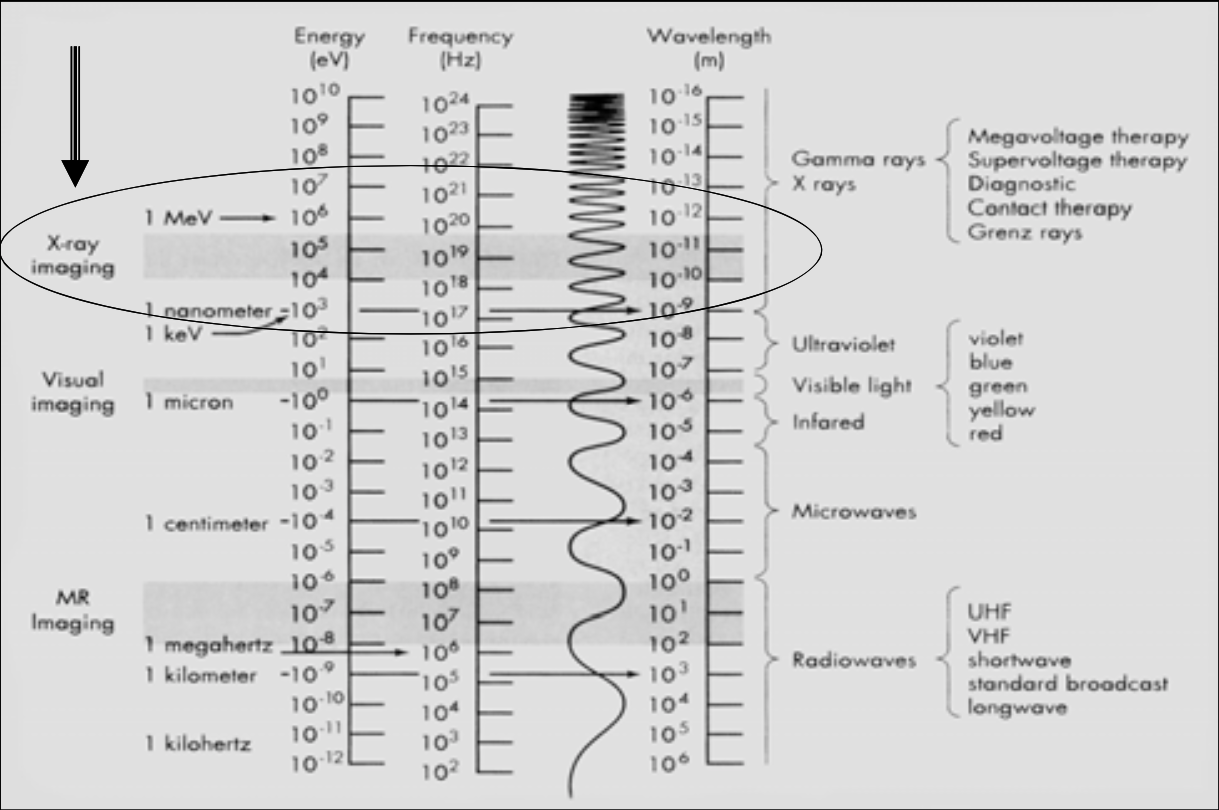
Ripple Factor
Half-wave
Unfiltered – [...]%
Filtered – [...]%
Full-wave
Unfiltered – [...]%
Filtered – [...]%
100%
20%
100%
9%
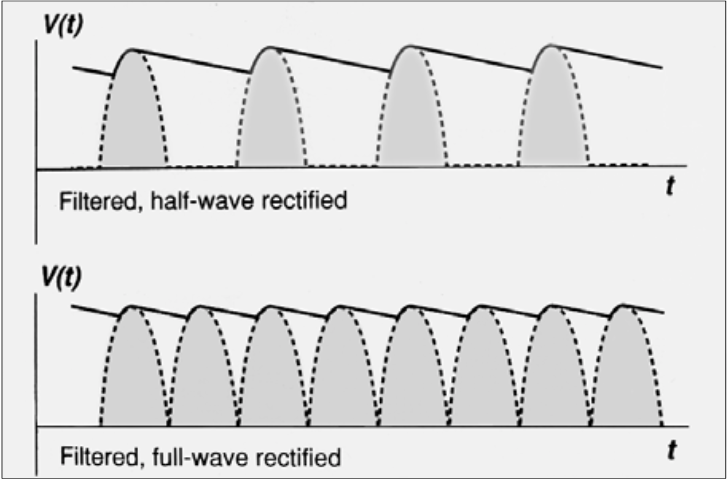
Secondary Coil
If there are more coils in the secondary coil, then it is a [step up or step down]
If there are less coils in the secondary coil, then it is a [step up or step down]
step up transformer
step down transformer
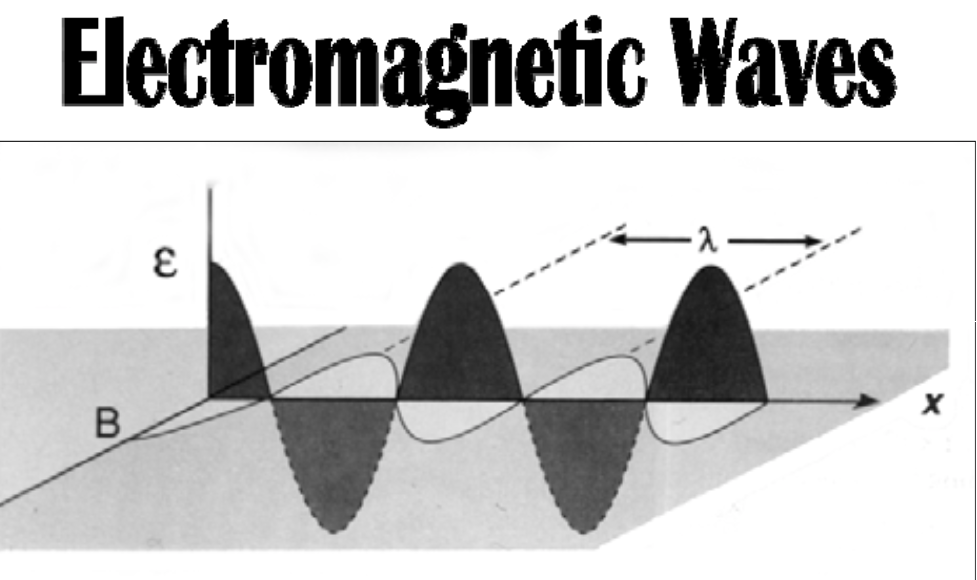
Sinusoidal (in the form of the sine curve) electric and magnetic fields are [...] to each other
perpendicular
Step down transformer
Has less coils in the secondary coils than the primary coil
[Function?]
Used to heat filament

Step up transformers
Has more coils in the secondary coil than the primary coil
[Where is it used?]
Used in the electron accelerating part of the x-ray tube
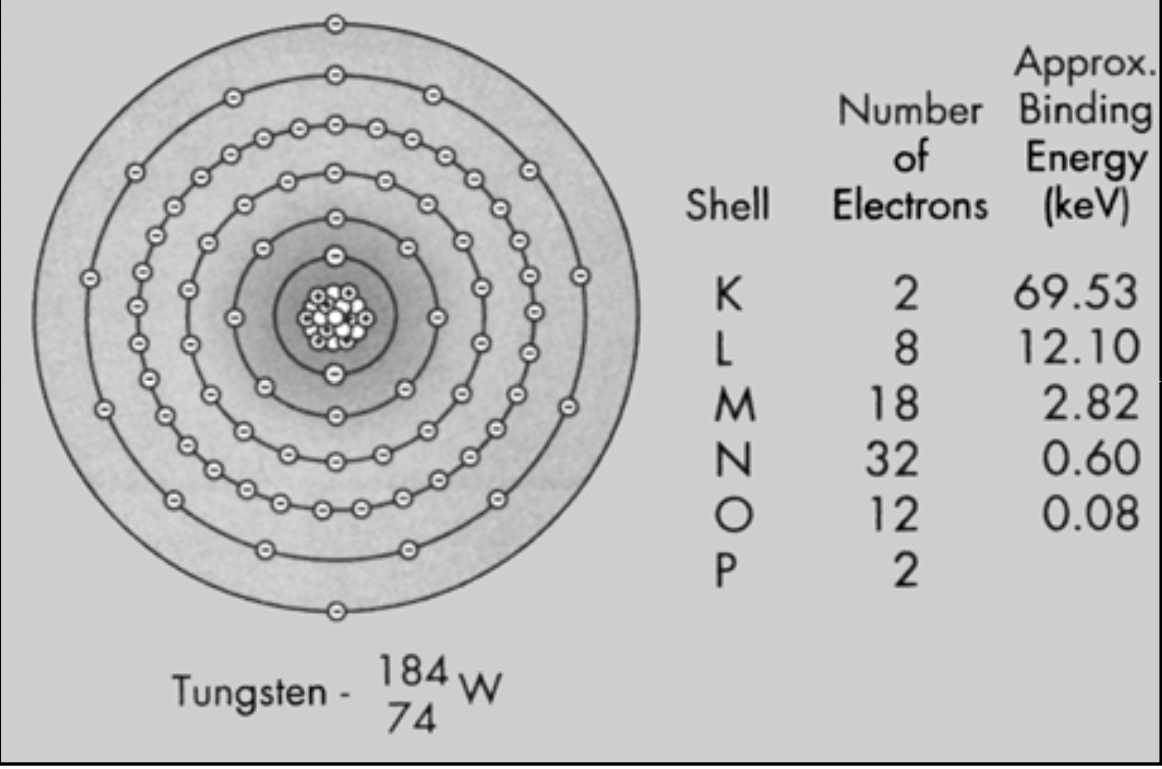
Tungsten
Atomic number = [...] (so number of protons is also [...])
Atomic mass = [...] (so 110 neutrons)
74
74
184
Wave-Particle Duality
EM radiation has wavelike properties and particle properties
Particles are called [...]
Energy of a photon can be calculated via following equation
Energy = h x frequency where h = Planck’s constant
photons
Wave-Particle Duality
EM radiation has wavelike properties and particle properties
Particles are called photons
Energy of a photon can be calculated via following equation
Energy = [...] x [...] where h = Planck’s constant
h x frequency
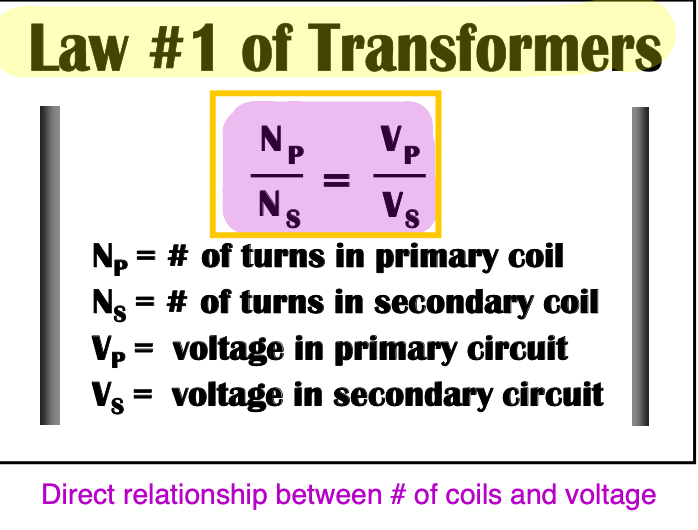
What is the first law of transformers?
[...]
Ratio of number of turns is equivalent to the ratio of voltage in the circuits
What's the difference between half-wave rectification & full-wave rectification?
[...]

Why can AC current not be used with X-Rays?
[...]
Not safe & produces poor images
AC cannot be used in an X-Ray tube bc its pulsating
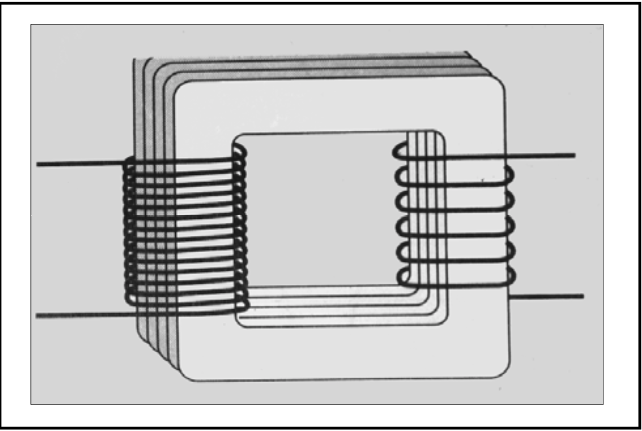
Why can't direct currents be used in a transformer?
[...]
A rapidly changing electric field is required to induce a magnetic field
X-Ray Generator
Function
[...]
Accomplished by a transformer
[...]
Rectified by diodes
Must transform voltage from 115 to that 40 – 150 kVp that is required
Must convert alternating current (from the wall plug) into direct current
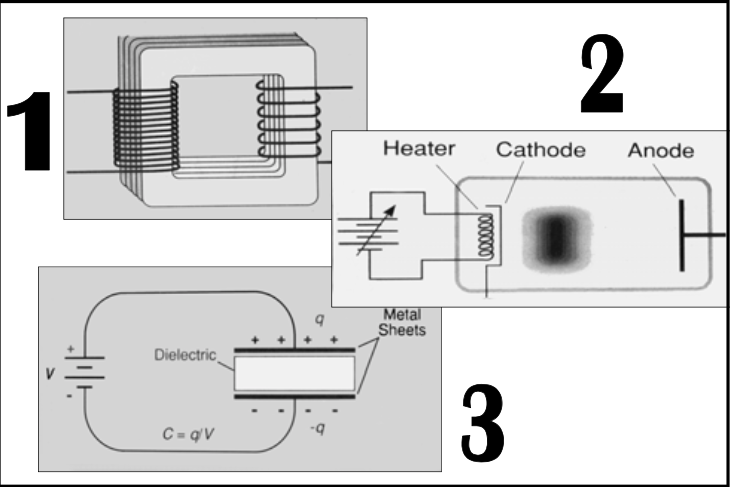
X-Ray Generator
Function
Must transform voltage from 115 to that 40 – 150 kVp that is required
Accomplished by a [...]
Must convert alternating current (from the wall plug) into direct current
Rectified by [...]
transformer
diodes
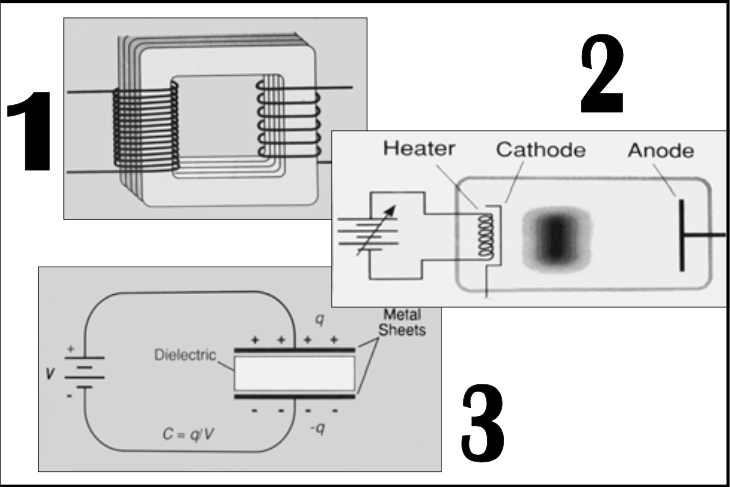
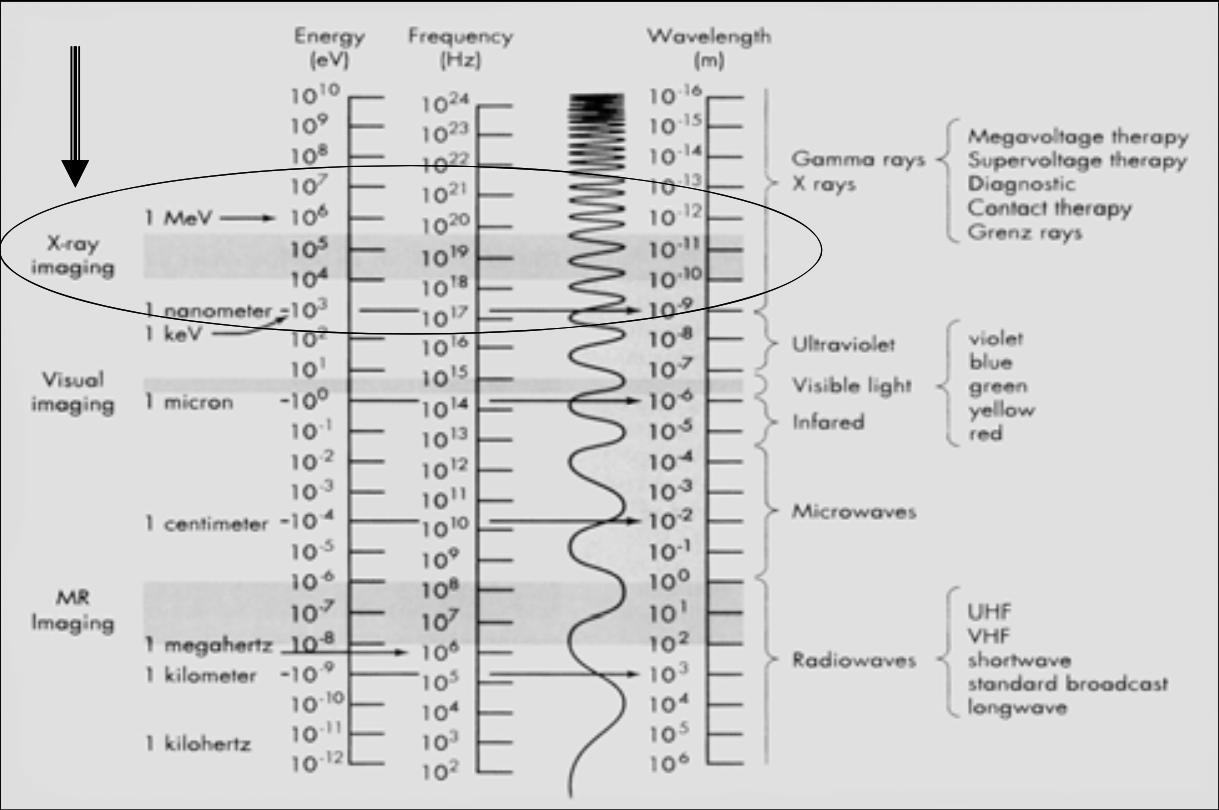
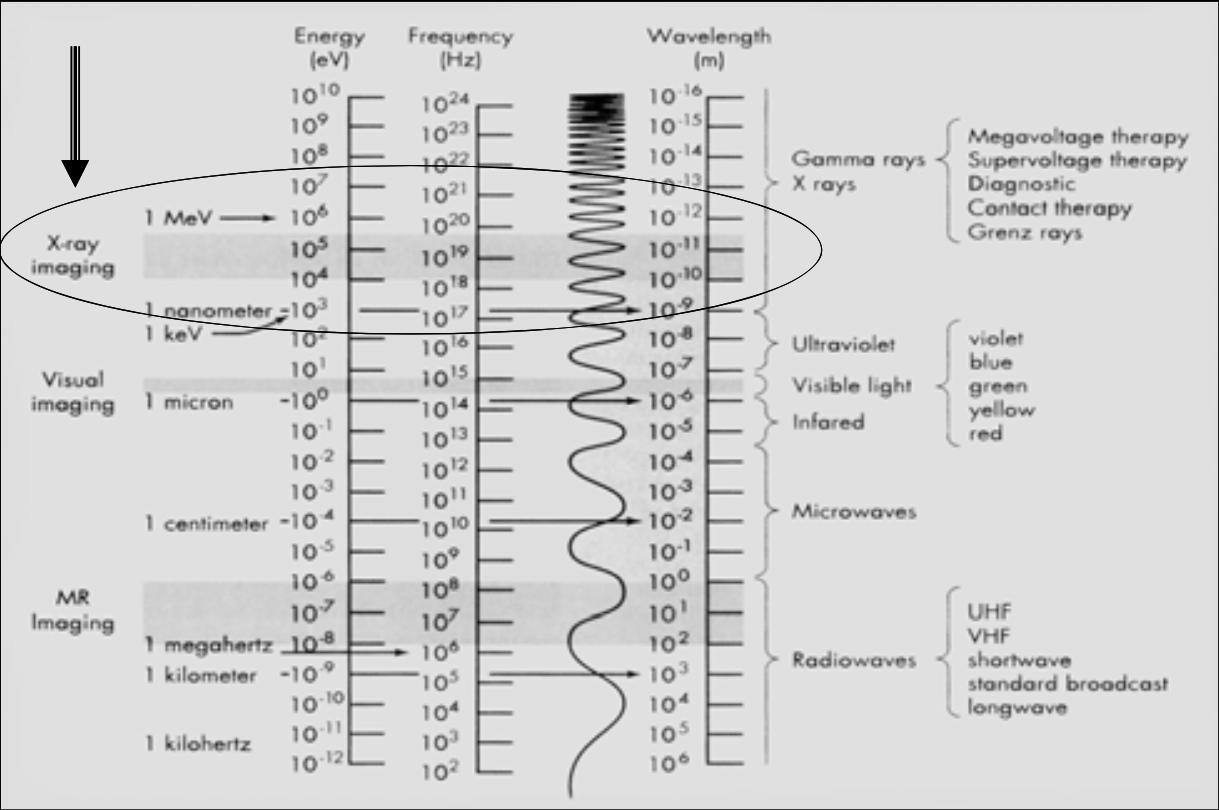
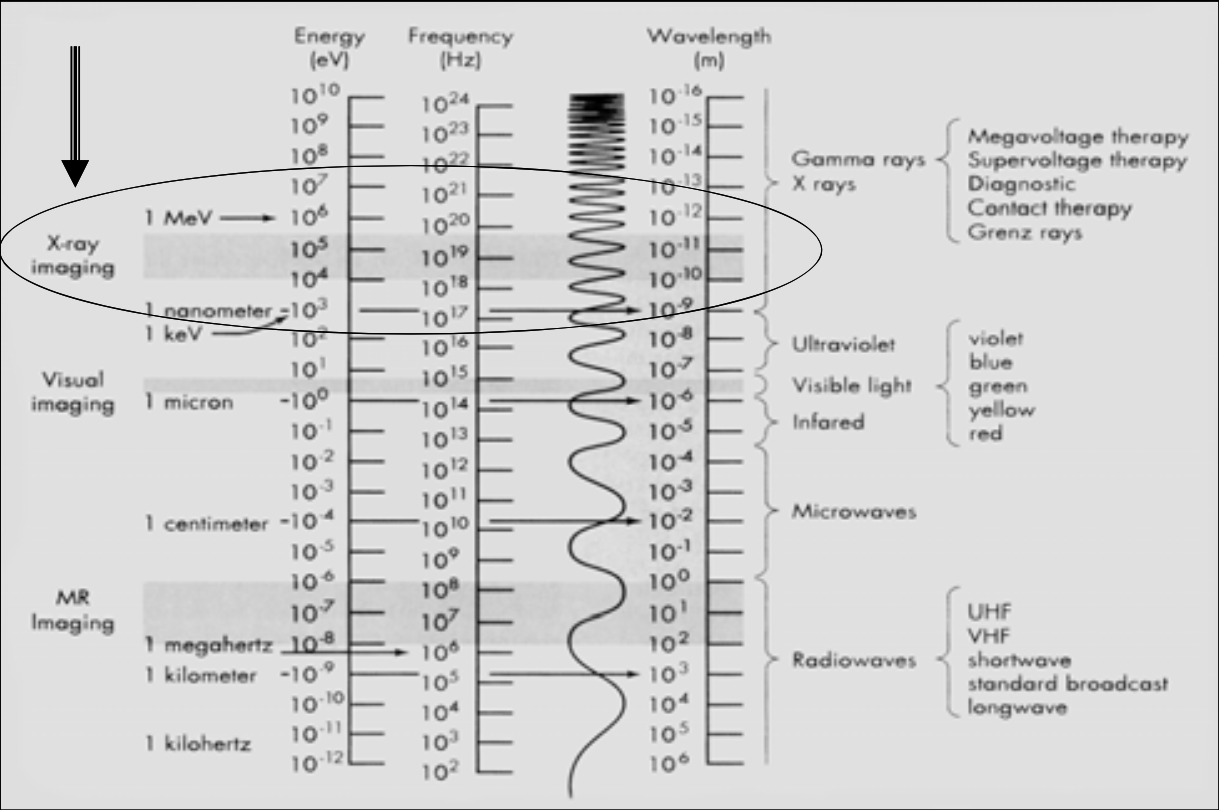
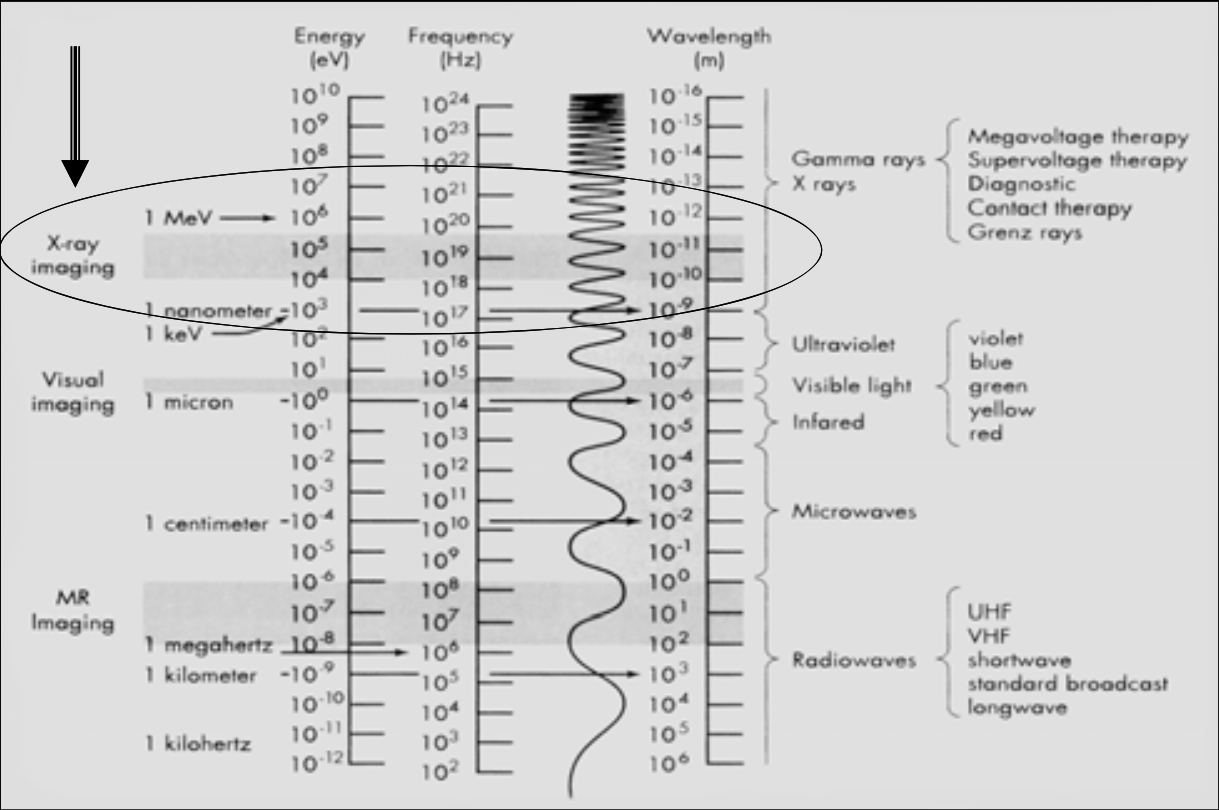
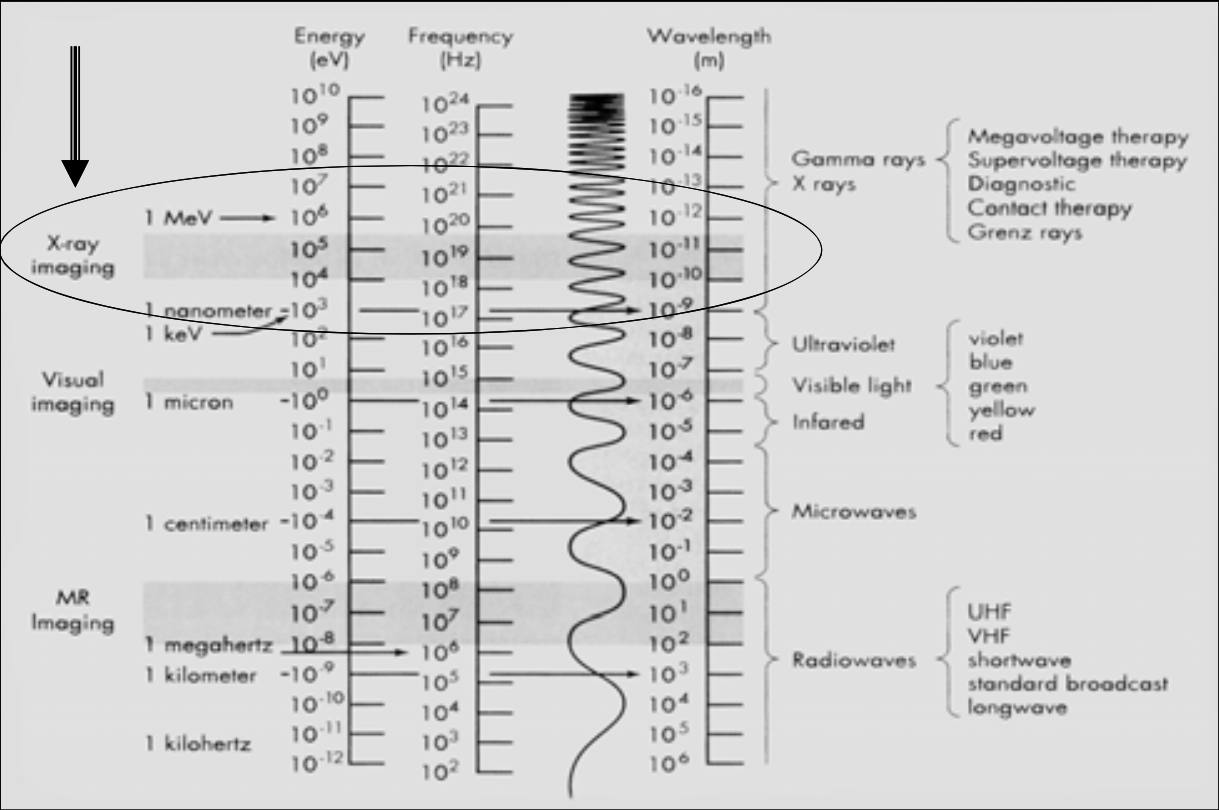
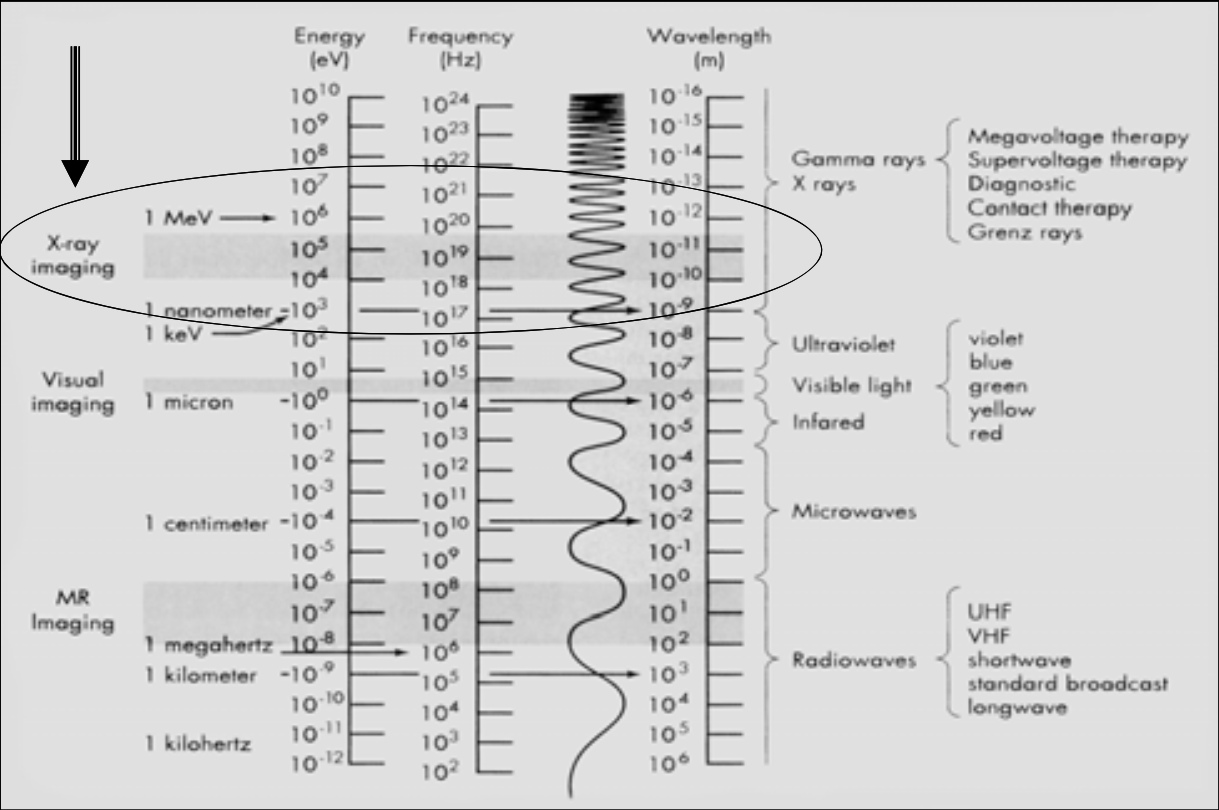
X-ray imaging is between [...] and [...] energy (eV)
This range is called the ionizing radiation (the high energy EM can ionize matter)
104 and 105
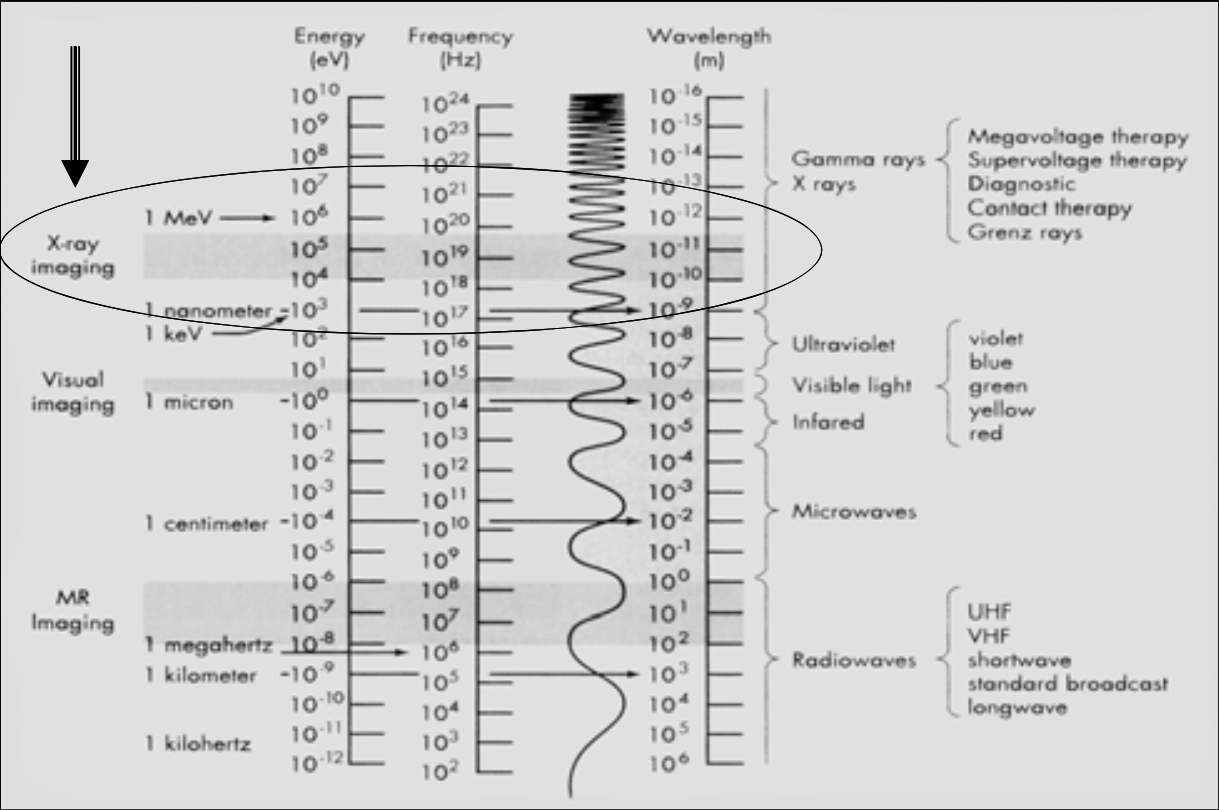
X-Ray Machine 3 basic components
[...]
[...]
[...]
X-Ray Generator
X-Ray Tube
Control Panel
X-Ray production
Cathode is a [step up or step down] transformer that generates electrons
Anode is a [step up or step down] transformer that accelerates electrons
Responsible for potential difference between cathode & anode??
step down
step up
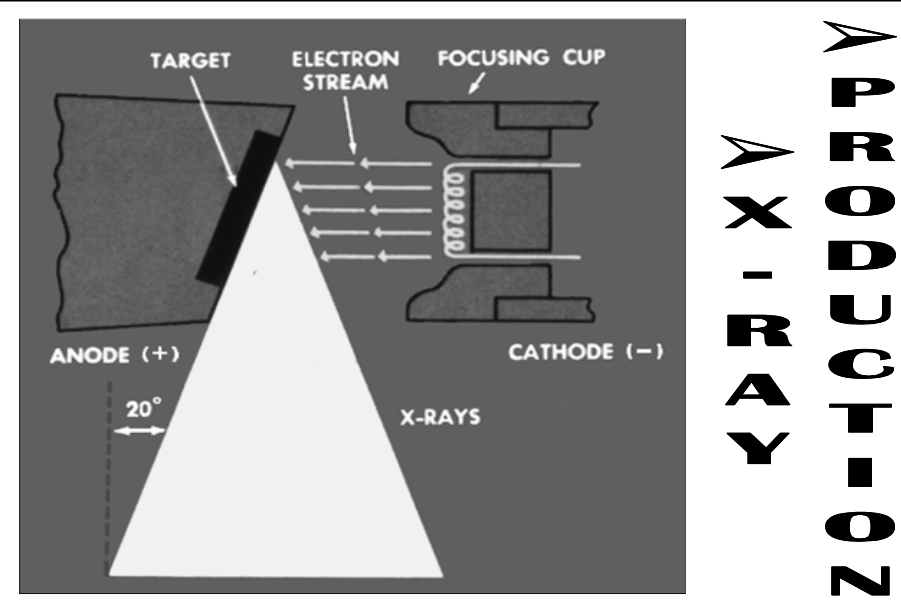
X-Ray production
[...] is a step down transformer that generates electrons
[...] is a step up transformer that accelerates electrons
Responsible for potential difference between cathode & anode??
Cathode
Anode
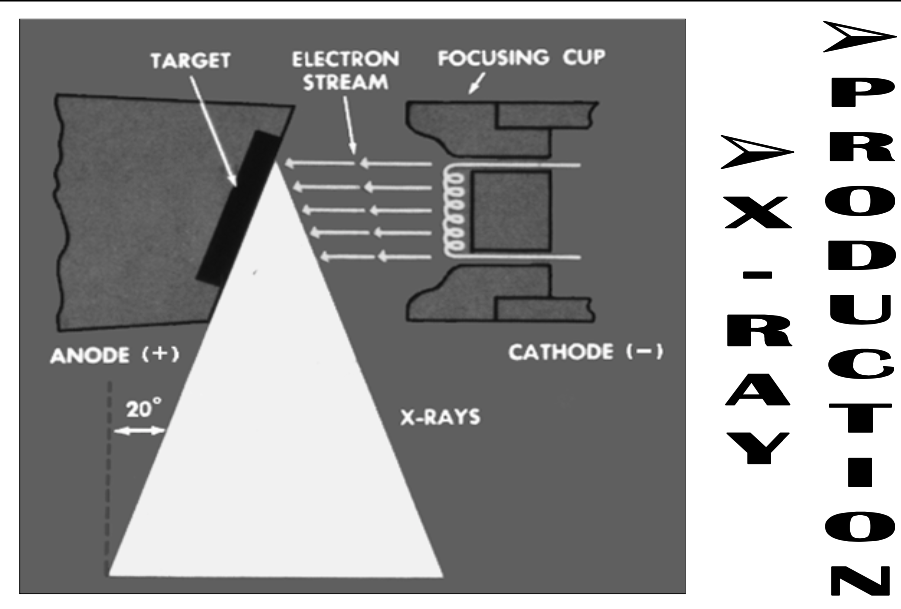
X-Ray Tube Head
[Positive or negative?] charged tungsten cathode
Coiled filament within the cathode
[Positive or negative?] charged copper anode
With embedded tungsten target
Negatively
Positively
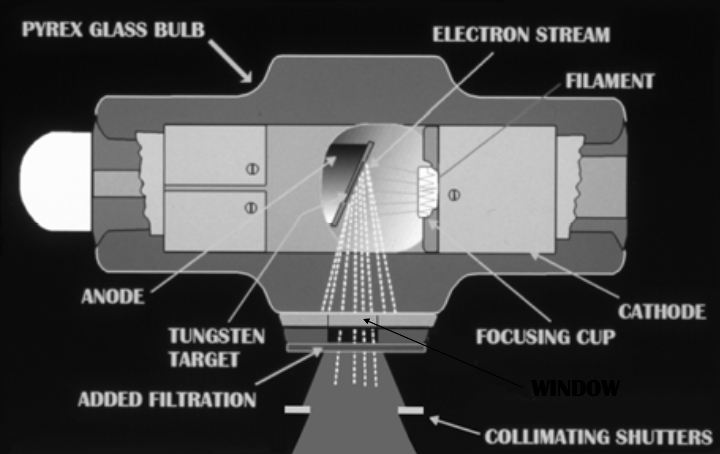
X-Ray Tube Head
Negatively charged [which element] cathode
Coiled filament within the cathode
Positively charged [which element] anode
With embedded tungsten target
tungsten
copper
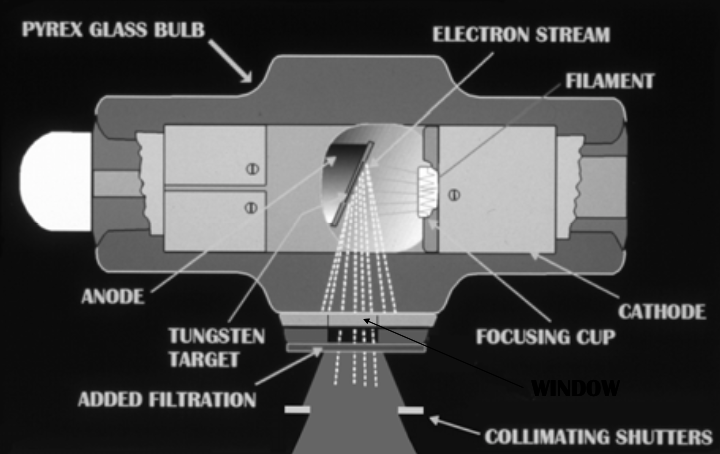
X-Ray Tube Head
Negatively charged tungsten cathode
[what's found within it?]
Positively charged copper anode
[what's found within it?]
Coiled filament within the cathode
With embedded tungsten target
[...]: the amount of energy that electrons have in each shell
Binding Energy (BE)
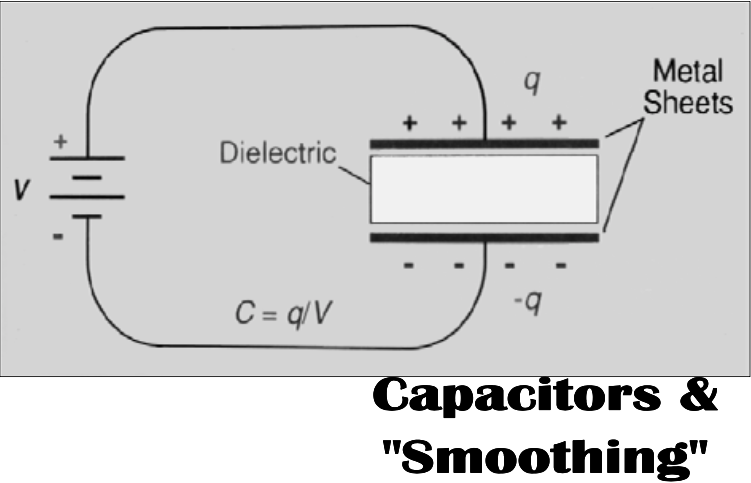
[...]
Way to store energy
Builds up energy when the circuit is closed
Quickly discharges when it senses dropping voltage in the tubes
Capacitors
[...] anytime electric charges are made to accelerate
EM radiation
[...]: process whereby atom gains or loses electrons (typically from outer shell)
Positive ions = cations
Negative ions = anions
Ionization
X-Rays have enough energy to cause atoms to ionize (gain or lose electrons)
Ionization: process whereby atom gains or loses electrons (typically from outer shell)
Positive ions = [...]
Negative ions = [...]
cations
Anions
X-Rays have enough energy to cause atoms to ionize (gain or lose electrons)
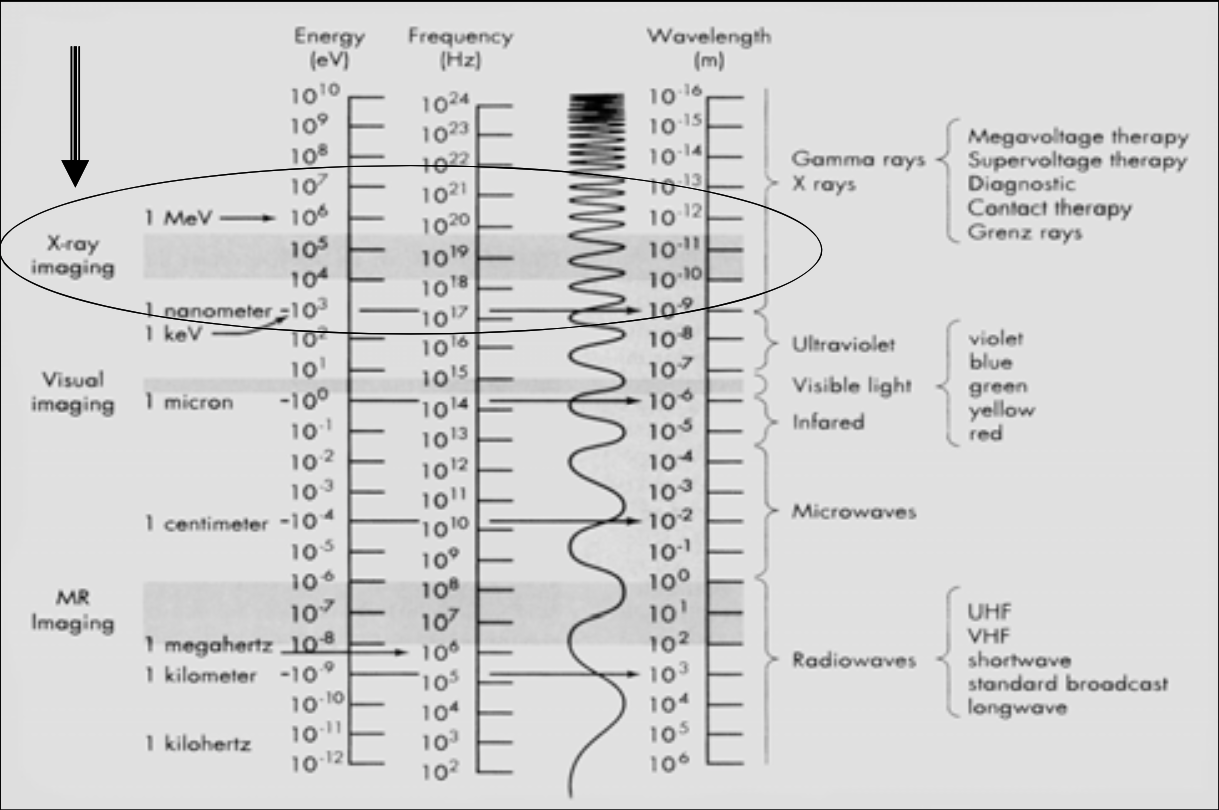
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong>: X-Ray electromagnetic radiation energy range </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cc2202f7-9653-4629-9cf3-524071019a89.png)
[...]: X-Ray electromagnetic radiation energy range
Ionizing Radiation
[Primary or secondary] Coil = whatever is plugged into the wall or battery
Primary
[...]
Atom & molecules can only exist in certain energy states & changing states requires energy
Ionized – when an atom or molecule changes its state (requires energy)
Quantum Theory
[...]: variation in the voltage across the x-ray tube, expressed as a percentage of its maximum value
Ripple Factor
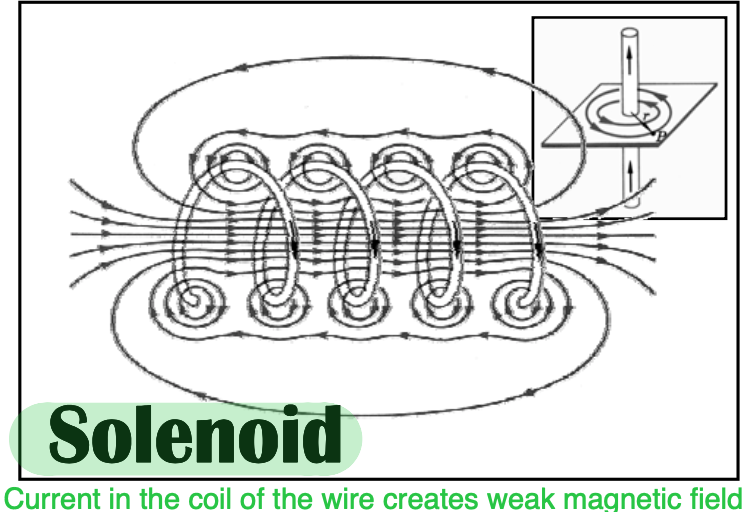
[...]
Coils generate heat, forming an electron cloud and a positive and a large negative at the other end
Electrons move in a clockwise fashion and electricity flows through the current & converts it to a direct current
Simple Vacuum Diode System
[...]
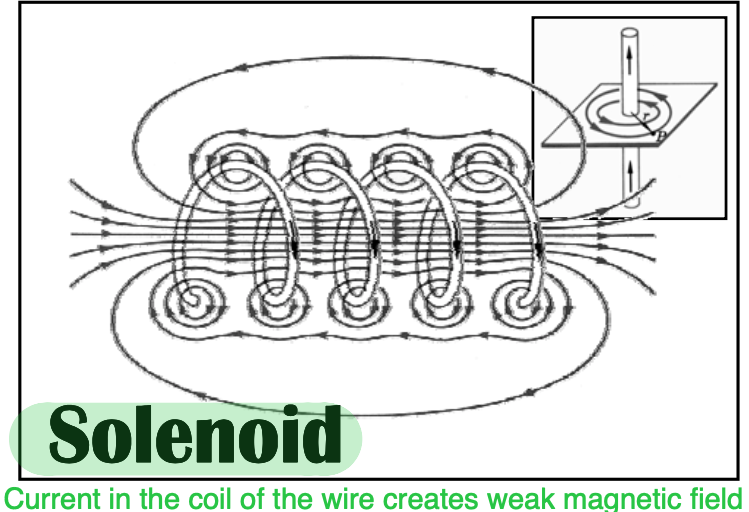
current in coil of wire creates weak magnetic field
solenoid
[...] x [...] = velocity (c)
Changing = wavelength & frequency
Constant = speed is the speed of light (constant for EM waves)
C = 3e8 m/s
Wavelength x Frequency
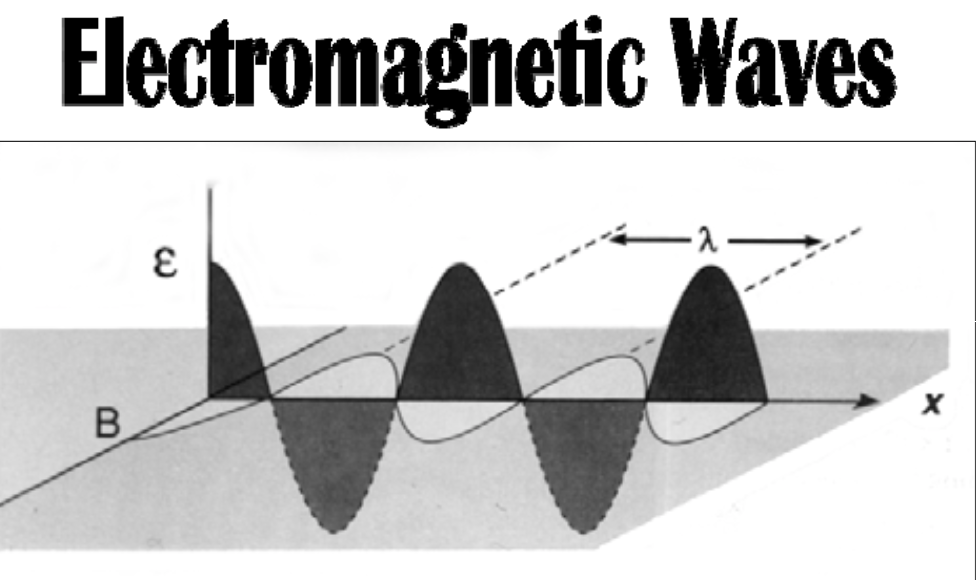
Wavelength x Frequency = velocity (c)
Changing = [...]
Constant = [...]
C = 3e8 m/s
wavelength & frequency
speed is the speed of light (constant for EM waves)
[...]
Supplies electric power to the x-ray tube
Begins with wall plug (115 V)
Filament heating requires ~10 V
X-Ray Generator
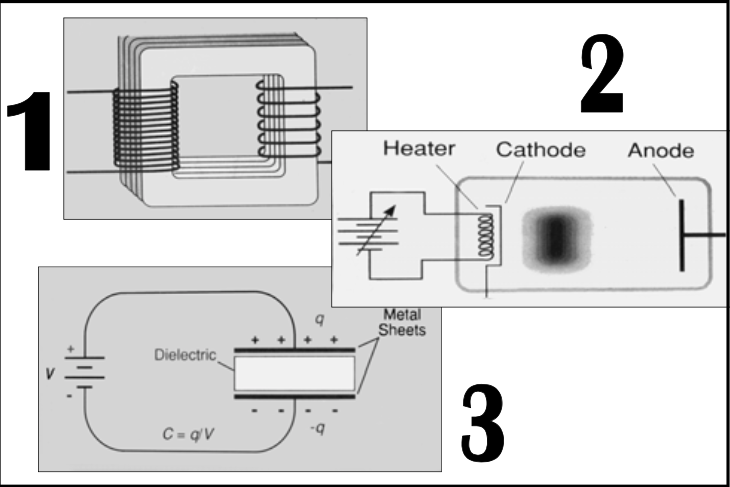
X-Ray Generator
Supplies electric power to the x-ray tube
Begins with wall plug (115 V)
[...] requires ~10 V
Filament heating
Electrons all acquire the same KE or velocity (half the speed of light) --> [...]
Travels a very short distance (b/w cathode & anode): 1 to 3 cm
Photons are comprised of varied energies (different wavelengths) --> [...]
monochromatic
polyenergetic
[...] --> monochromatic
Travels a very short distance (b/w cathode & anode): 1 to 3 cm
[...] --> polyenergetic
Electrons all acquire the same KE or velocity (half the speed of light)
Photons are comprised of varied energies (different wavelengths)
Electrons all acquire the same KE or velocity (half the speed of light) --> monochromatic
Travels a very short distance (b/w cathode & anode): [what's the distance?]
Photons are comprised of varied energies (different wavelengths) --> polyenergetic
1 to 3 cm