CH 24
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
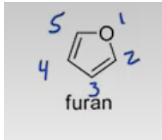
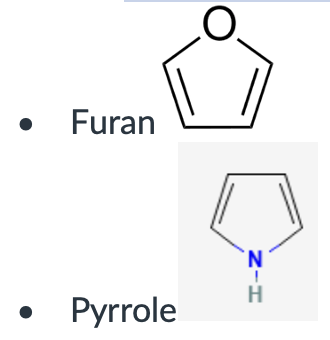
Furan
pyrrole
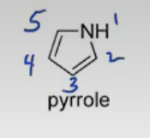
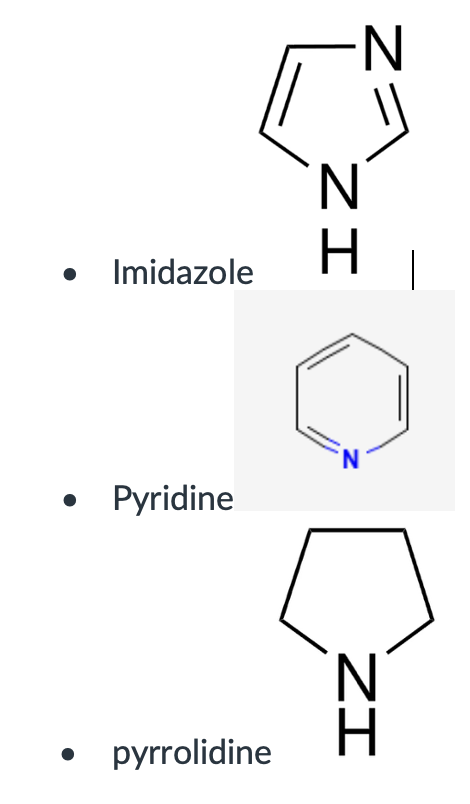
Imidazole
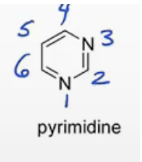
Pyridine
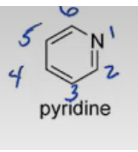
Pyrrolidine
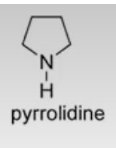
Purine
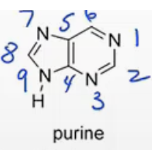
Pyrimidine
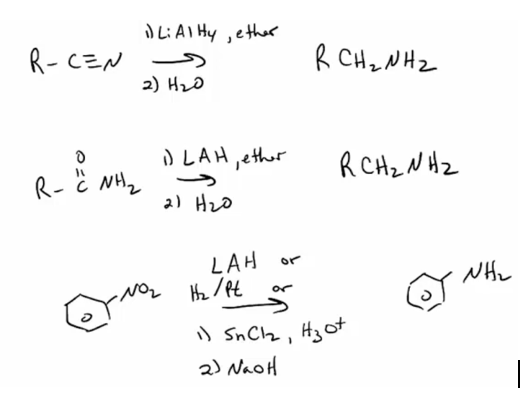
1. Prepare amines by reduction of azide, nitrile, nitro, or amide. (You do not need to know mechanisms for azide, nitrile or nitro reduction. You should know the mechanism of the LiAlH4 reduction of amides.)
1. Provide products and a mechanism for the acylation of ammonia, primary amines, or secondary amines.
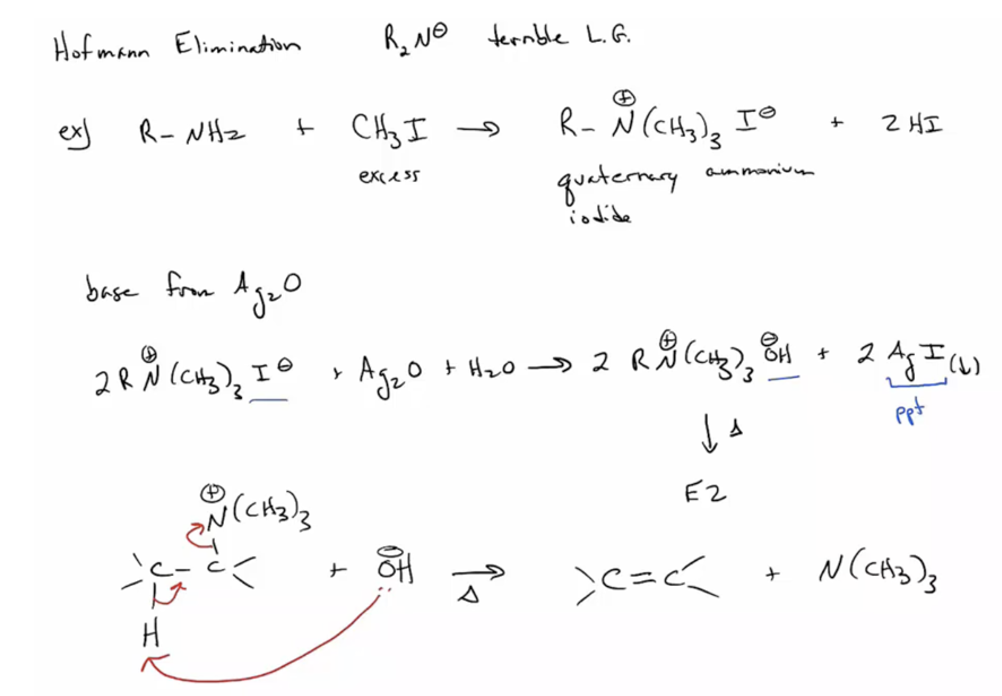
1. Provide products and a mechanism (E2) for the Hofmann elimination. Hofmann elimination takes advantage of over-alkylation.
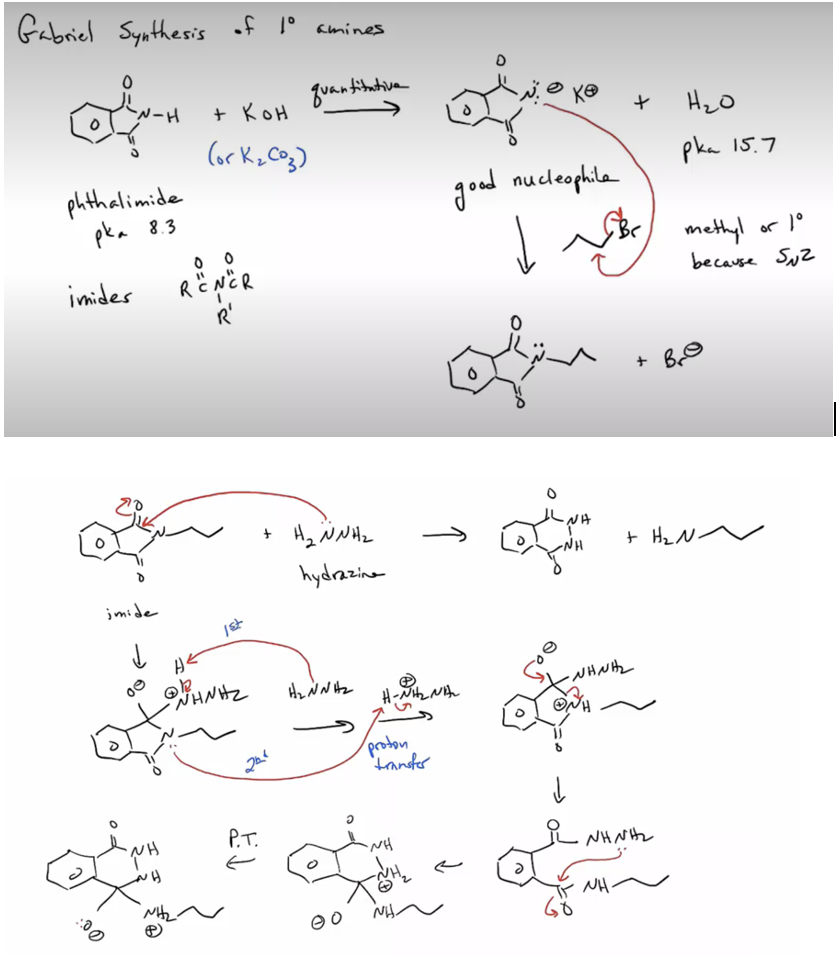
Provide products and a mechanism for the Gabriel synthesis of primary amines
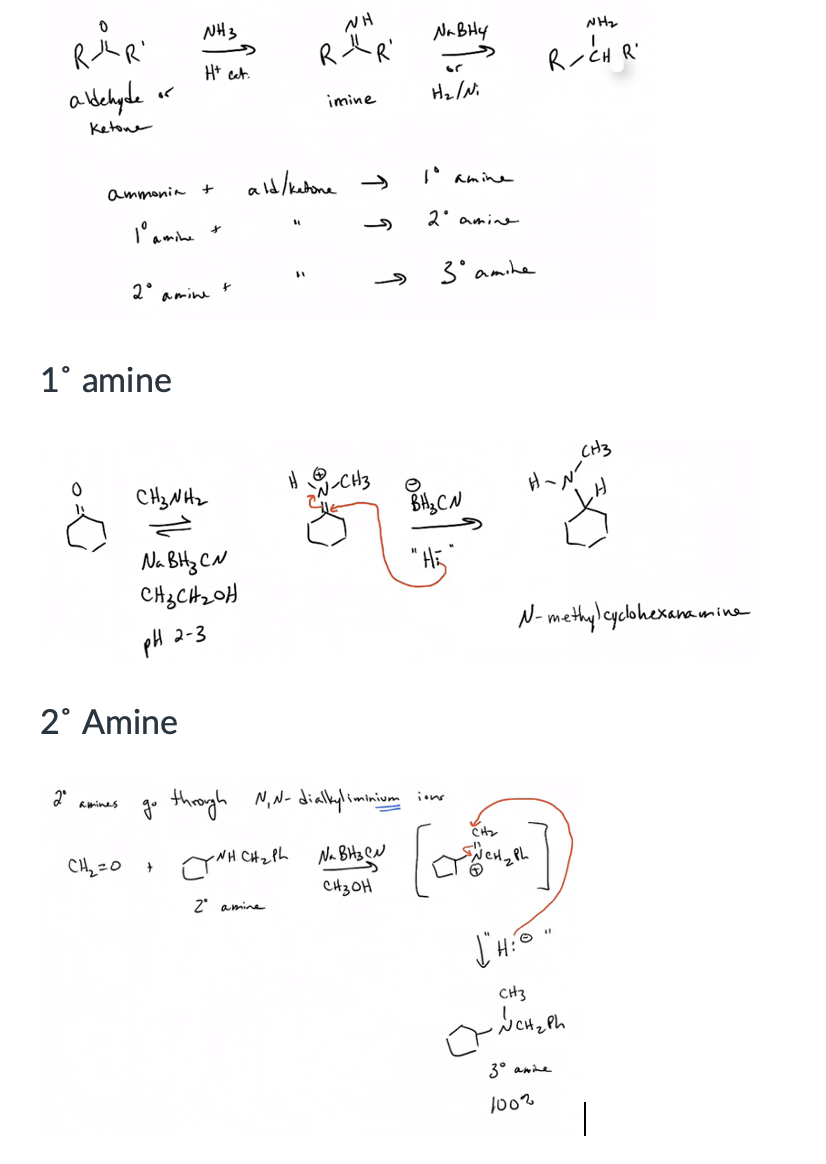
Prepare amines by the reductive amination of aldehydes or ketones
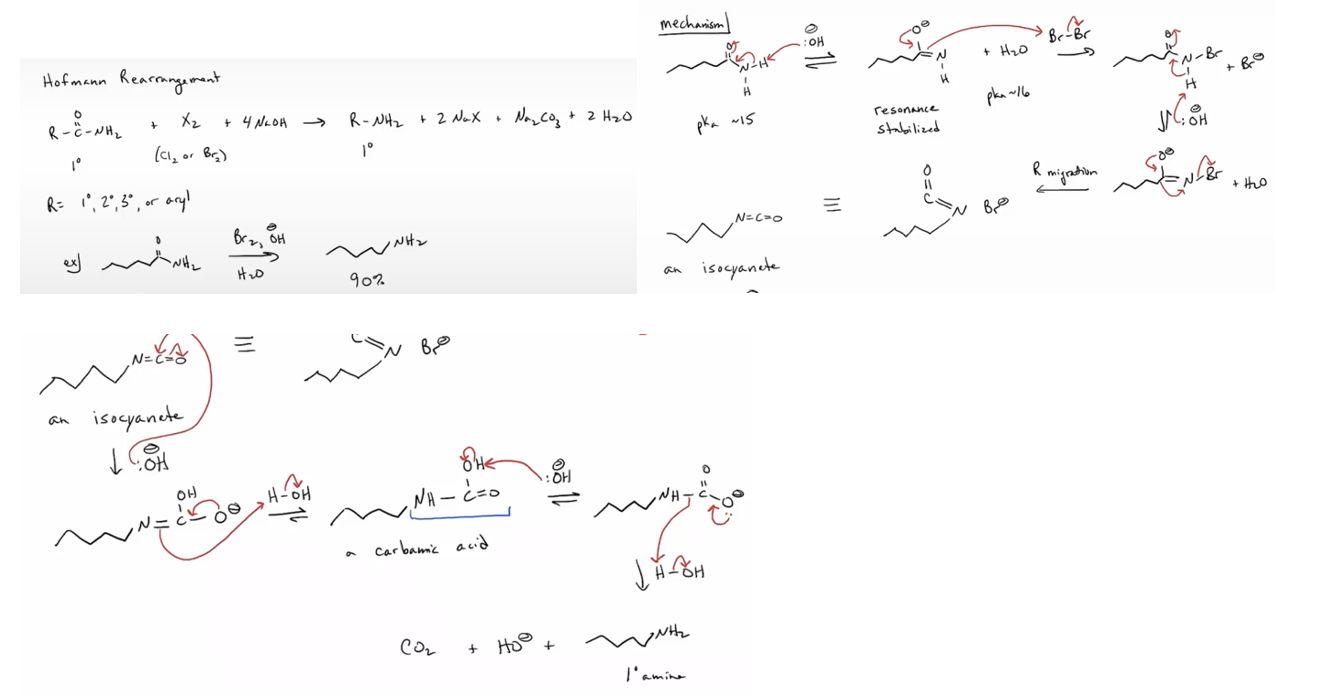
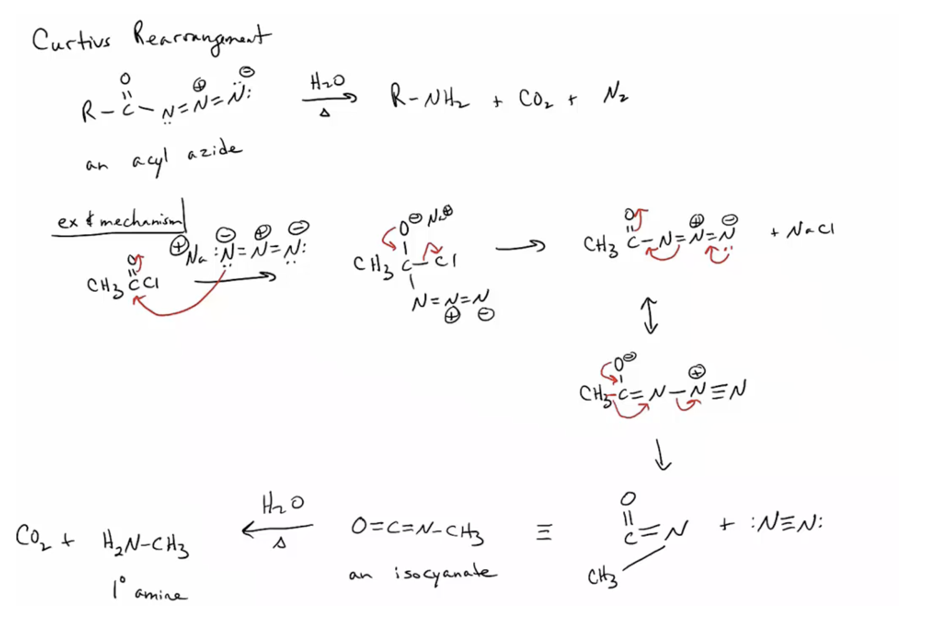
Prepare primary amines by the Hofmann and Curtius rearrangemen
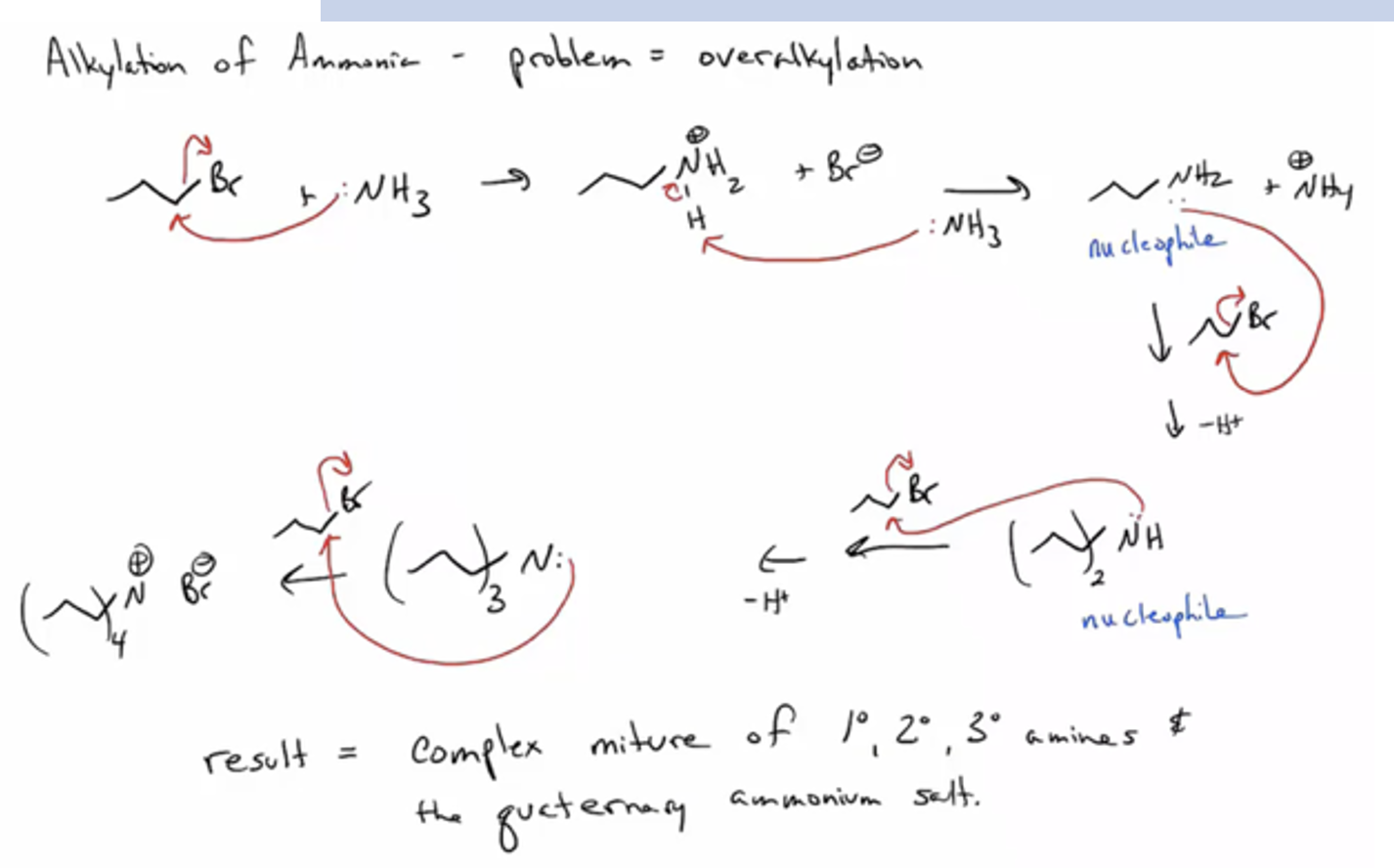
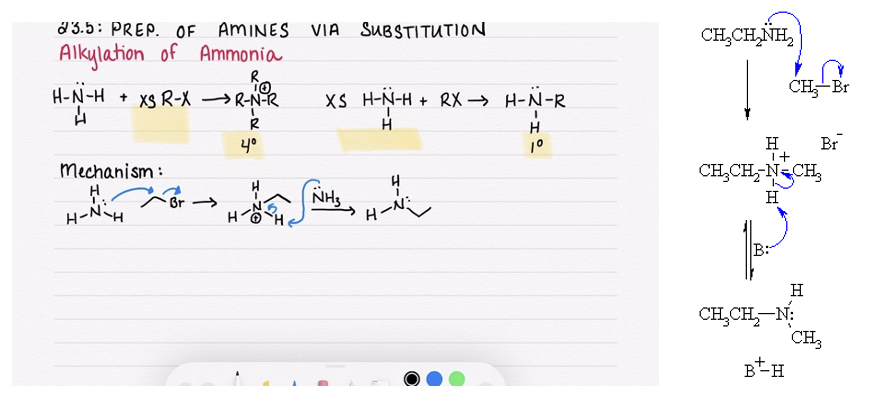
alkylation of ammonia or amines
1. Synthesize aryl amines by the addition an –NO2 group to the ring (by electrophilic aromatic substitution) followed by reduction to an –NH2 group. (24.8 See also 16.2.)
HNO3 + H2SO4
Fe HCl
synthesis of the nitrosyl cation (NO+)
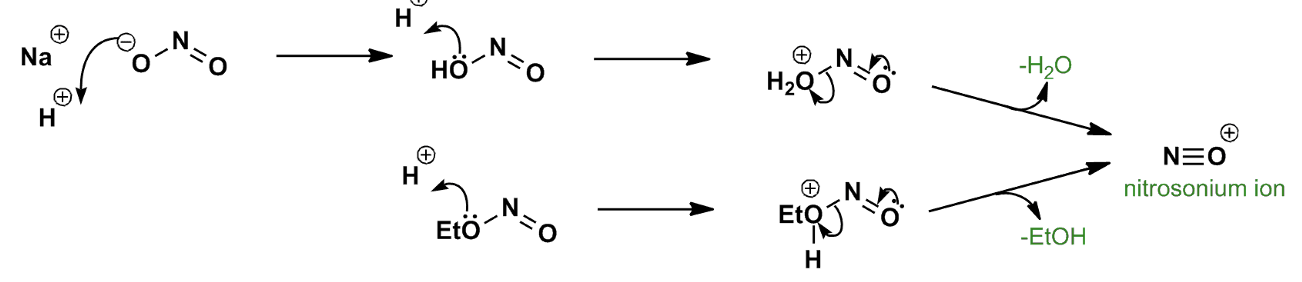
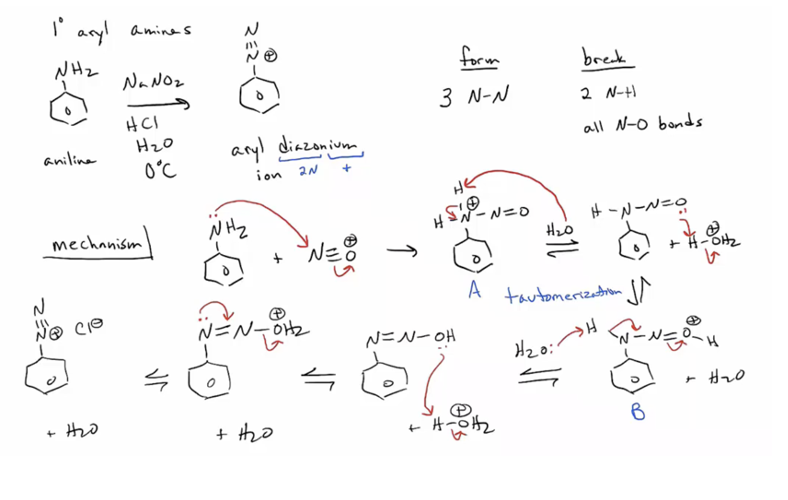
1. Form aryl diazonium salts from a variety of aromatic rings. (Ar-H to ArNO2 to ArNH2 to Ar-+NN)
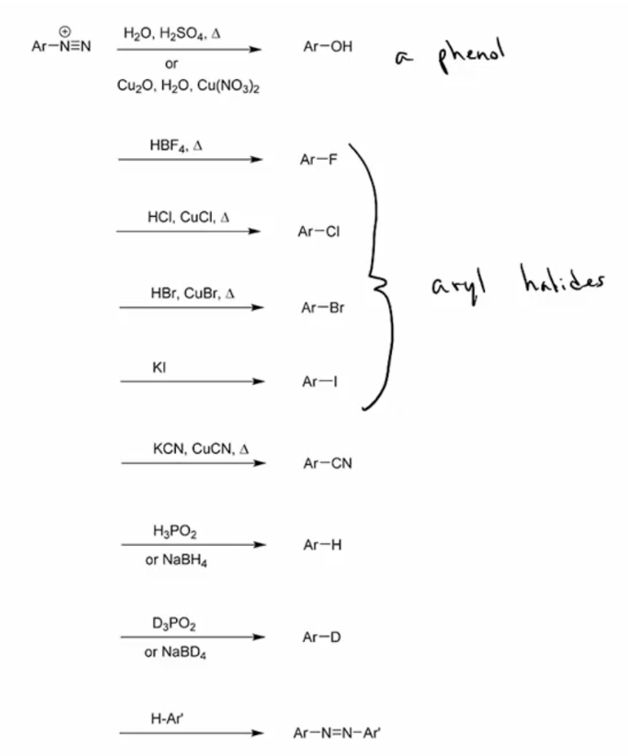
1. Convert aryl diazonium ions into phenols, aryl halides, aryl cyanides, Ar-D (using D3PO2 or NaBD4) or back to Ar-H (using H3PO2 or NaBH4). (You do not need to know mechanisms for these conversions.)
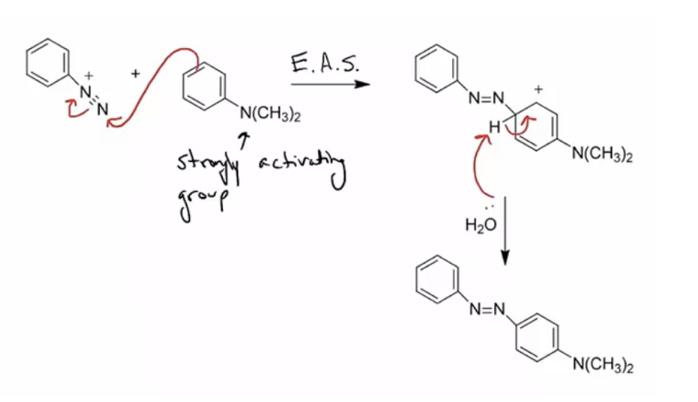
1. Provide products and a mechanism for the azo coupling reaction. (An aryl diazonium ion is the electrophile for an electrophilic aromatic substitution.)
furan, pyrrole, imidazole, pyridine, pyrrolidine.
1. Predict the products of pyrrole with an electrophile.