Food Safety: A Guide for Ontario's Food Handlers
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for Food Safety Review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
A food premise is: _.
A place that prepares and/or sells food.
Safe Cooking & Reheating Temperatures of Hazardous Food
The minimum internal temperature required to effectively kill harmful bacteria in food, ensuring it is safe for consumption.
How to ensure safe temperatures for hazardous food
have a chart with necessary minimum heat for different types of hazardous food, use a clean and sanitized food thermometer to check internal temperatures, make sure the item reads as the desired heat for 15 seconds. Make sure to calibrate your thermometer often.
cooking and reheating temp for whole poultry
82°C (180°F) for cooking. 74°C (165°F) for reheating
cooking and reheating temp for ground poultry, poultry products and poultry pieces.
74°C (165°F) for both cooking and reheating
cooking and reheating temp for food mixtures containing poultry, eggs, meat, fish or other hazardous food
74°C (165°F) for both cooking and reheating
cooking and reheating temp for pork, pork product, and ground meat other than ground poultry
71°C (160°F) for both cooking and reheating
cooking and reheating temp for fish
70°C (160°F) for both cooking and reheating
cooking and reheating temp for seafood
70°C (158°F) for both cooking and reheating
How to recalibrate a food thermometer
To recalibrate most food thermometers, immerse it in ice water for 30 seconds and adjust to 32°F (0°C) or place it in boiling water and adjust to 212°F (100°C), ensuring accuracy for safe cooking. If you have a digital thermometer there should be a “reset” button, if this doesn’t work contact a technician.
A food handler is
a person who prepares, handles, or serves food in a food premise.
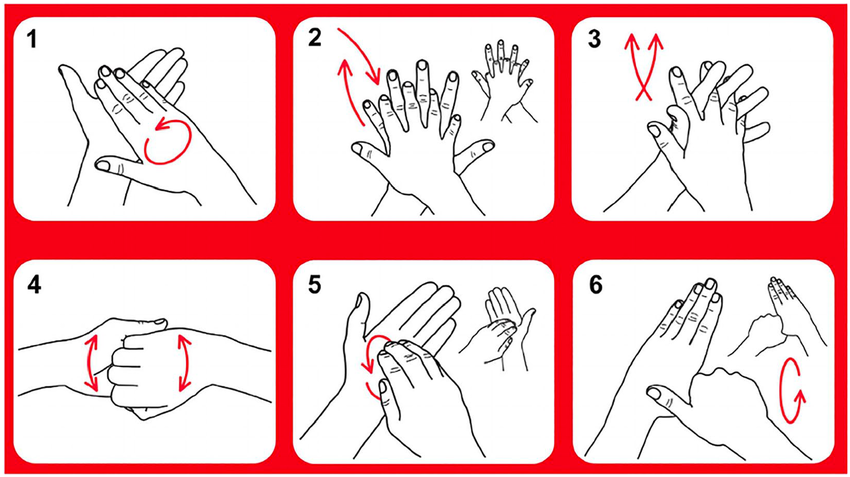
six step hand washing method
Wash palms of hands.
Wash between fingers at back of hands.
Wash between fingers palm to palm.
Wash palm area.
Pay particular attention to thumb area and thumb join
Wash finger tips paying particular attention to nails and dry hands well with clean disposable towel discarding correctly.

Three compartment sink dishwashing method:
Scrape, sort, and pre-rinse before washing
Wash with warm water and detergent solution capable of removing grease.
Rinse with clean water that is at least 43°C (110°F).
Sanitize with clean warm water.
Soak for at least 45 seconds in one of the following:
24°C (75°F) water with 100ppm chlorine.
24°C (75°F) water with 200ppm quaternary ammonium.
or 77°C (170°F) water only.Air Dry, do not towel dry.
The three main causes of foodborne illness are:
biological, chemical, and physical hazards.
Chemical foodborne illness is also called
food poisoning
if you see a pest such as a mouse or cockroach during the daytime it means:
there is likely already an imbedded infestation and corrective actions are necessary to address the issue.
Three types of biological foodborne illness:
bacteria, viruses, and parasites
What part(s) of the government regulate the food service industry.
The food service industry is regulated by legislation at all three levels of government (federal, provincial, and municipal).
The _ has the power to seize, destroy, and order closure of a premise.
The medical officer of health or a Public Health Inspector.
During inspections, Public Health Inspectors look for _.
Unsafe food handling practices,
issues of non-compliance with regulations
investigation of foodborne illnesses,
investigation of consumer complaints,
action needed on food recalls, fires, floods, and emergencies.
signs of pests
Municipal by-laws are enforced by _.
Municipal by-law enforcement officers.
A foodborne illness _.
Occurs when something you eat or drink makes you sick.
the three types of chemical food poisoning are:
Metal, intentional additives, incidental additives.
How metal can cause food poisoning
Metal can cause food poisoning when contaminated food or drink is ingested. This can occur through exposure to heavy metals like lead or cadmium or when food is improperly packaged. Food items with high acidity can cause metal to break down and cause chemicals to leech into the good.
What does epipen stand for:
epinephrine autoinjector: a device sed to treat severe (Anaphylactic) allergic reactions.
The most dangerous allergic reaction that can occur quickly and can be life-threatening is _.
Anaphylaxis.
The Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) has identified the following foods and additives as most frequently associated with causing an allergic reaction: _.
Eggs,
peanuts,
sesame seeds,
sulphites,
wheat & triticale,
milk,
fish,
crustaceans and molluscs,
soybeans,
mustard,
tree nuts.
If a customer has an allergic reaction, _.
Immediately call 911 or your local emergency service.
Both ___ and ___ should be aware of introducing allergen or other contamination.
Kitchen and service (wait) staff
There are six main types of microorganisms: _.
Viruses
protozoa,
parasites,
yeasts,
mould,
bacteria.
_ are the most common way that viruses get into food.
Human hands.
The best way to control the spread of parasites is _.
Thorough cooking.
Consider the key factors of __ and __ that support microbial growth.
Time and Temperature.
The danger zone is between what temperatures.
4°C (40°F) and 60°C (140°F)
what is the “danger zone”
The temperature range in which bacteria and pathogens can grow rapidly,
Potentially hazardous foods include __.
Moist foods with a pH above 4.5,
dairy products,
meat,
fish,
poultry and eggs,
some raw vegetables and fruit.
_ is the most effective way to slow the growth of bacteria in food.
Temperature control.
The basic sequence of food preparation is __.
Receiving and storage,
freezing,
thawing,
refrigeration,
food preparation,
cooking,
hot and cold holding,
cooling,
reheating.
It is important to take steps to minimize bacteria growth by __.
Thawing foods safely,
monitor freezer and refrigerator temperatures,
minimize time spent in the danger zone,
use different safe temperatures for cooking meats.
Any water used in food premises must be from a _ water supply.
Potable.
Once you’ve inspected shipped food and decided to accept it, _ to keep the food and workers safe.
Remove staples, nails or other fasteners from packages.
Use the _ rule to ensure food is used in the right order.
First in, first out (FIFO).
Cross-contamination happens in three ways: _.
Food to food,
equipment to food,
people to food.
__ may carry pathogens.
Dirty clothing.
___, when done correctly, is the single most effective way to prevent the spread of communicable diseases.
Handwashing.
Keeping your food premises __ isn’t only about it looking good. It is also to __
Clean and sanitized, control microorganisms and keep your food and customers safe.
The best defense is __ and __.
Cleaning and sanitizing.
Always __ before __ .
Clean before sanitizing.
__ give off a strong oily odour and their feces looks like large grains of pepper.
Cockroaches.
Food premises operators should rely on certified pest control services and emphasize integrated pest management practices that minimize the reliance on __.
Pest Management System. PMS
HACCP stands for __
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point
The seven principles of HACCP are __.
Conduct a hazard analysis,
determine the Critical Control Points (CCPs),
establish critical limit(s),
establish a system to monitor control of the CCPs,
establish the corrective action,
establish procedures for verification,
establish documentation.