(h) chemical tests
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
test for hydrogen (2.44)
place a lit splint into a test tube. if the test tube is filled with hydrogen, it will produce a ‘squeaky pop’ and the splint will go out
test for oxygen (2.44)
place a glowing (recently extinguished) splint into a test tube. if the test tube is filled with oxygen, the splint will relight
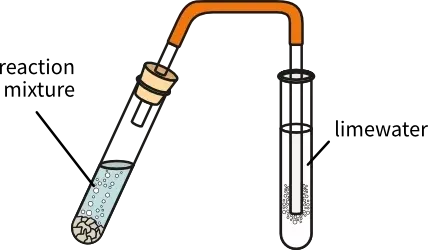
test for carbon dioxide (2.44)
bubble the gas into limewater. if the limewater turns cloudy, the gas is carbon dioxide
test for ammonia (2.44)
ammonia smells really bad!!! (pungent) hold a damp piece of red litmus paper over a test tube. if the test tube is filled with ammonia gas, the litmus paper will turn blue
test for chlorine (2.44)
hold a damp piece of blue litmus paper over a test tube. if the test tube is filled with chlorine gas, the litmus paper will get bleached
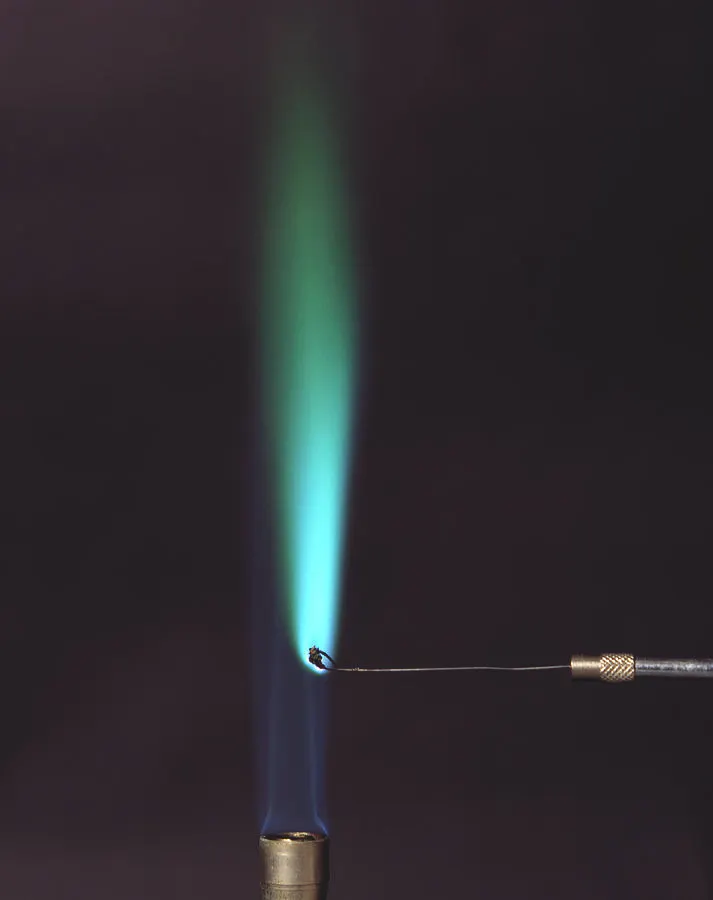
how to carry out a flame test (2.45)
1) use a platinum or nichrome wire (used due to their high melting points and that they are inert) and dip it into hydrochloric acid to clean it
2) the wire should be dipped into the salt you are testing to make some salt stick to the end
3) the wire should then be held in a blue bunsen burner flame
4) observe the colour
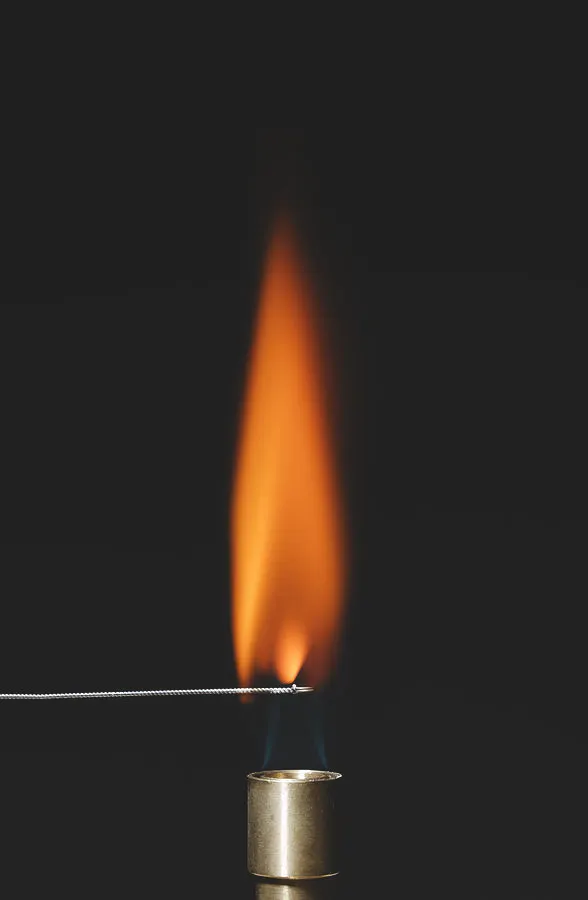
flame test colour for Li+ (lithium) (2.46)
red

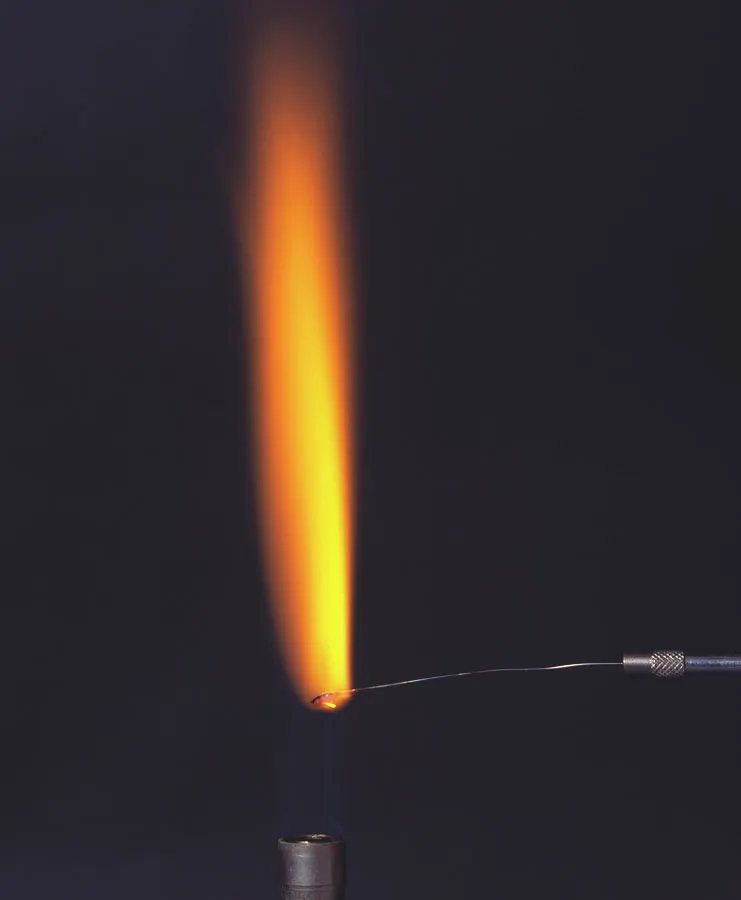
flame test colour for Na+ (sodium) (2.46)
yellow

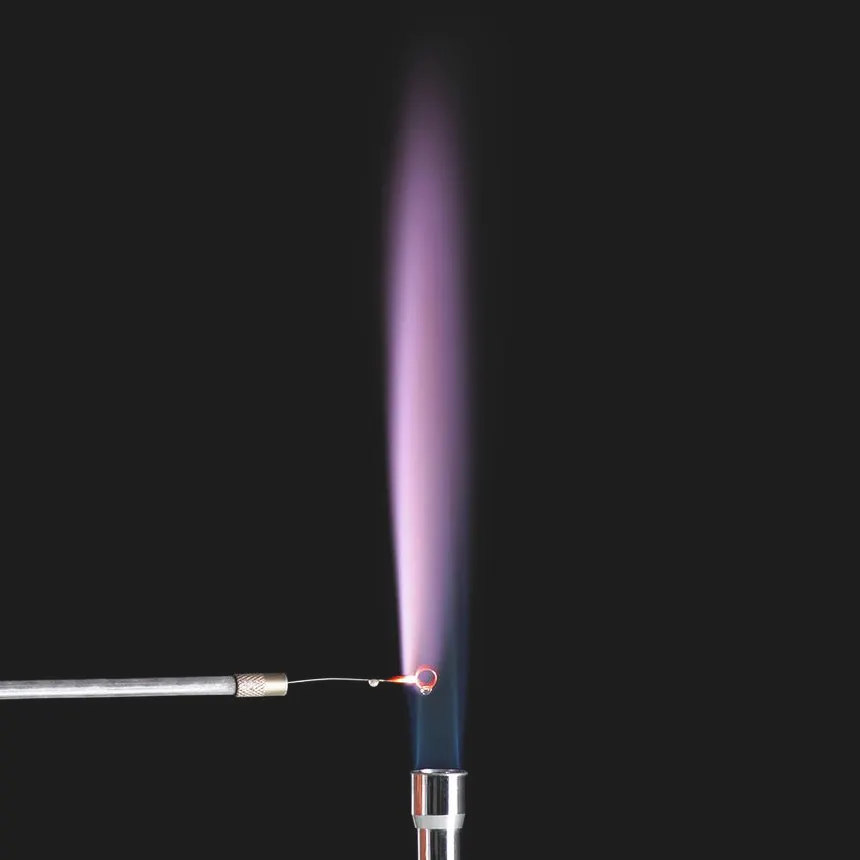
flame test colour for K+ (potassium) (2.46)
lilac

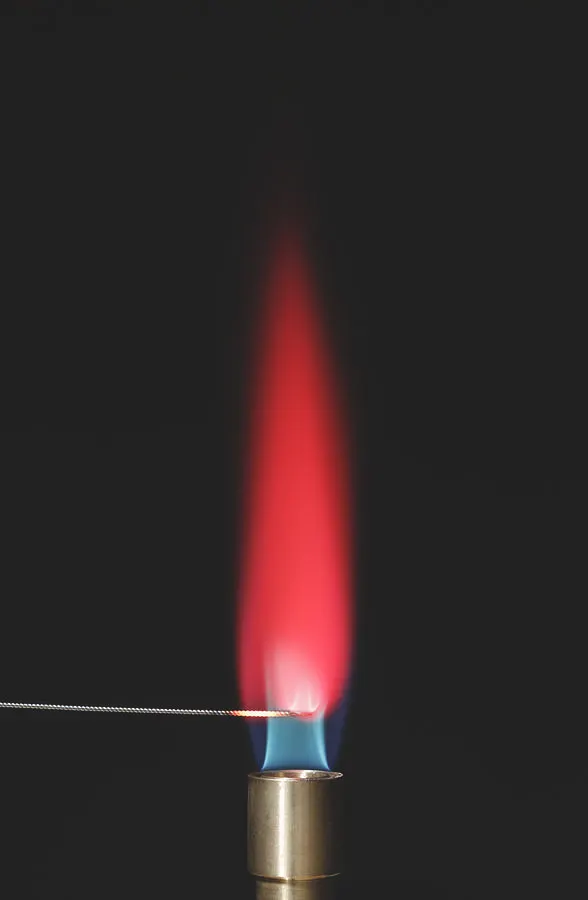
flame test colour for Ca2+ (calcium) (2.46)
orange-red

flame test colour for Cu2+ (copper) (2.46)
blue-green

test for cation NH4+ (ammonium) (2.47)
1) add some NaOH (sodium hydroxide)
2) heat gently, which will produce ammonia gas
3) follow the steps to detect ammonia gas (will turn damp red litmus blue)
test for cations Cu2+, Fe2+ and Fe3+ (2.47)
add NaOH (sodium hydroxide)
Cu2+: will produce a blue precipitate
Fe2+: will produce a green precipitate
Fe3+: will produce a brown precipitate
test for anion Cl-, Br- and I- (2.48)
(milk, cream, butter)
add silver nitrate
Cl-: white precipitate (milk)
Br-: cream precipitate (cream)
I-: yellow precipitate (butter)
test for anion SO42- (2.48)
add hydrochloric acid and barium nitrate. if there are sulfate ions present, a white precipitate will form
test for anion CO32- (2.48)
add hydrochloric acid to the solution, forming bubbles. bubble these through limewater. if the limewater goes cloudy, there are CO32- anions present.
test for water (2.49)
when water is mixed with anhydrous copper (II) sulfate, which is a white powder, it will turn into hydrated copper (II) sulfate, which is blue.
test to prove purity of water (2.50)
heat the liquid over a bunsen burner with a thermometer in it. if the boiling point is exactly 100°C, the water is pure