Lecture 11 Pt. 2: Biosynthesis of Amino Acids, Nucleotides, and Related Molecules
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Nitrogen is found in many things including…?
cofactors
hormones
neurotransmitters
pigments
defence chemicals
What percent of the atmosphere is nitrogen?
80%
Non-useful form of nitrogen is what?
very stable
very difficult to reduce
N2 is chemically…?
inert
N2 and O2 → ?
NO via lightning
N2 and H2 → ?
NH3 via industrial processes
requires:
T>400 C and P>200 atm
Some organisms can fix N2 to useful forms, this includes?
single-celled prokaryotes i.e., archaea
proteobacteria with legumes → symbiosis with plants
spirochetes with termites → symbiosis with animals
How are these organims able to transform N2 to useful forms?
enzymes that overcome high activation energy
binding and hydrolyzing ATP
Chemical transformations maintain what with respect to nitrogen?
balance between N2 and biologically useful forms of nitrogen
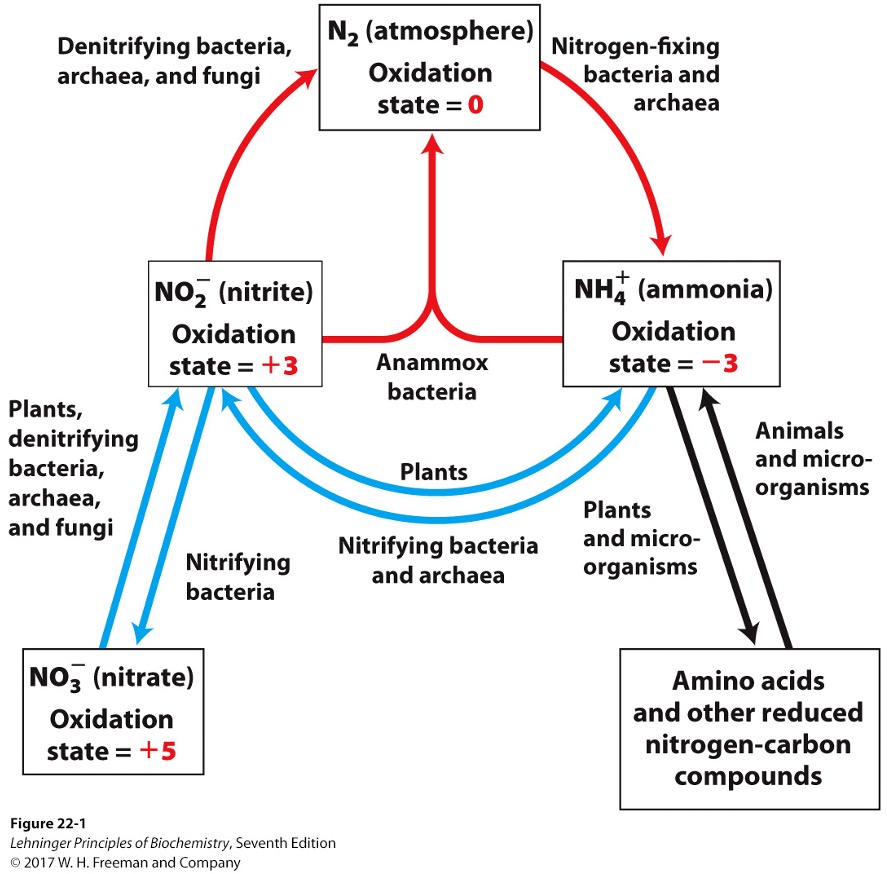
Key steps of the nitrogen cycle
fixation
nitrification
assimilation
denitrification
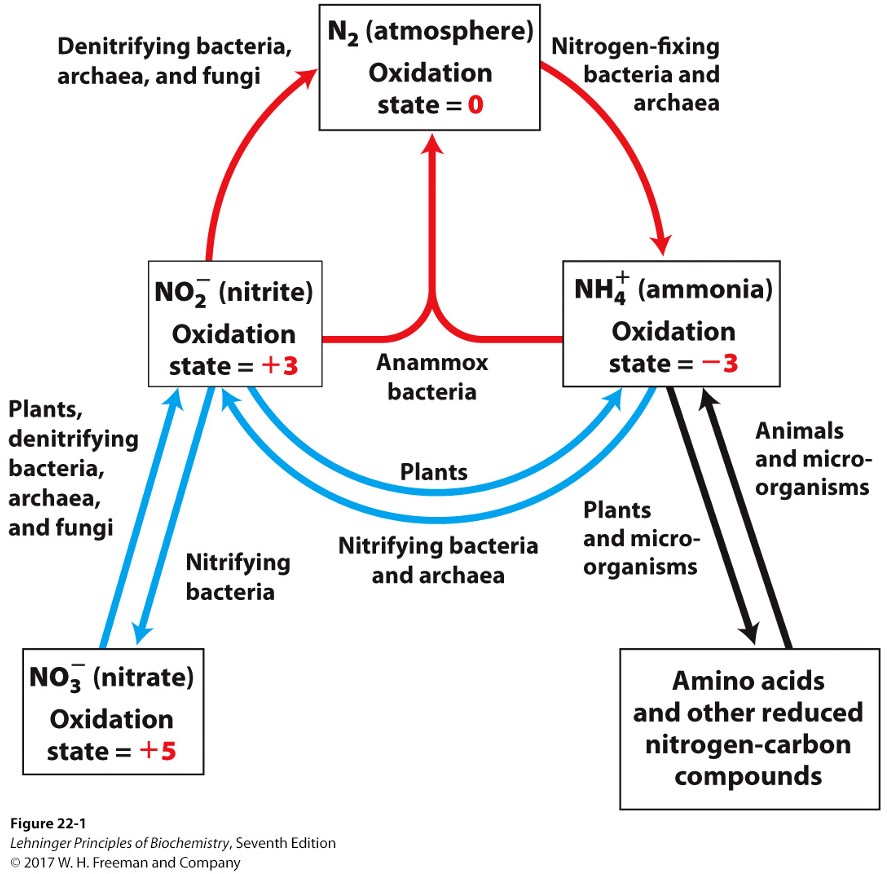
Fixation
bacteria reduce N2 to NH3/NH4+
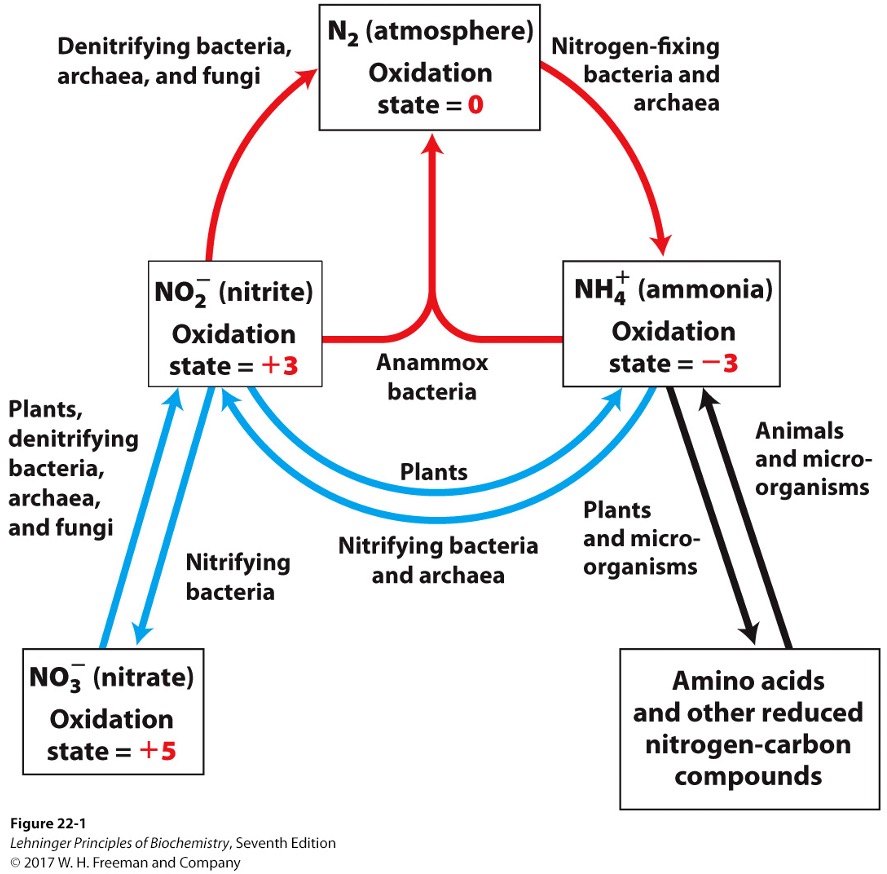
Nitrification
bacteria oxidize ammonia into nitrite (NO2-) and nitrate (NO3-)
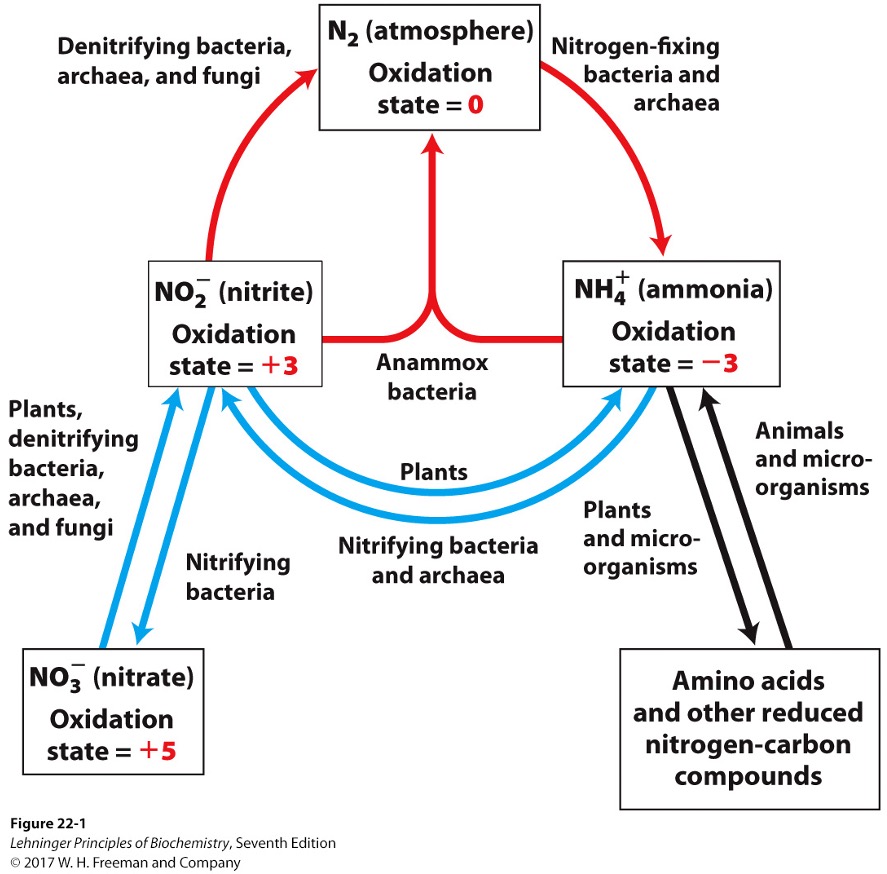
Assimilation
plants and microorganisms reduce NO2- and NO3- to NH3
via nitrite reductases and nitrate reductases
What are the 3 key points of assimilation?
NH3 incorporated into amino acids
organisms die returning NH3 to soil
nitrifying bacteria again convert NH3 to nitrite and nitrate
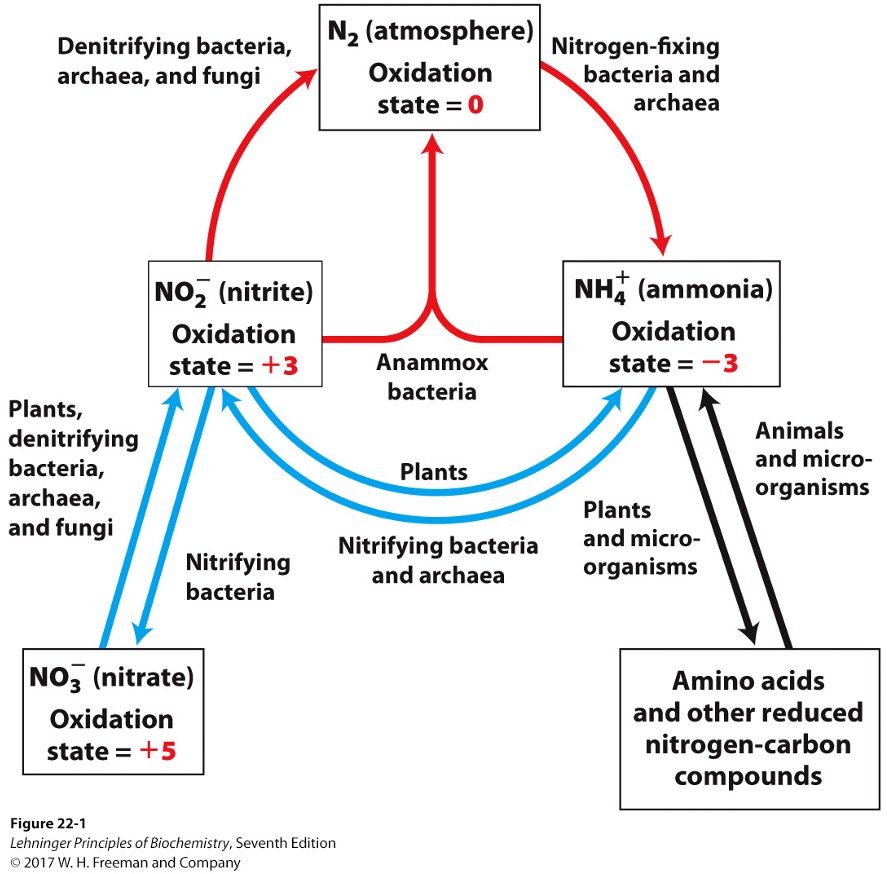
Denitrification
nitrate is reduced to N2 under anaerobic conditions
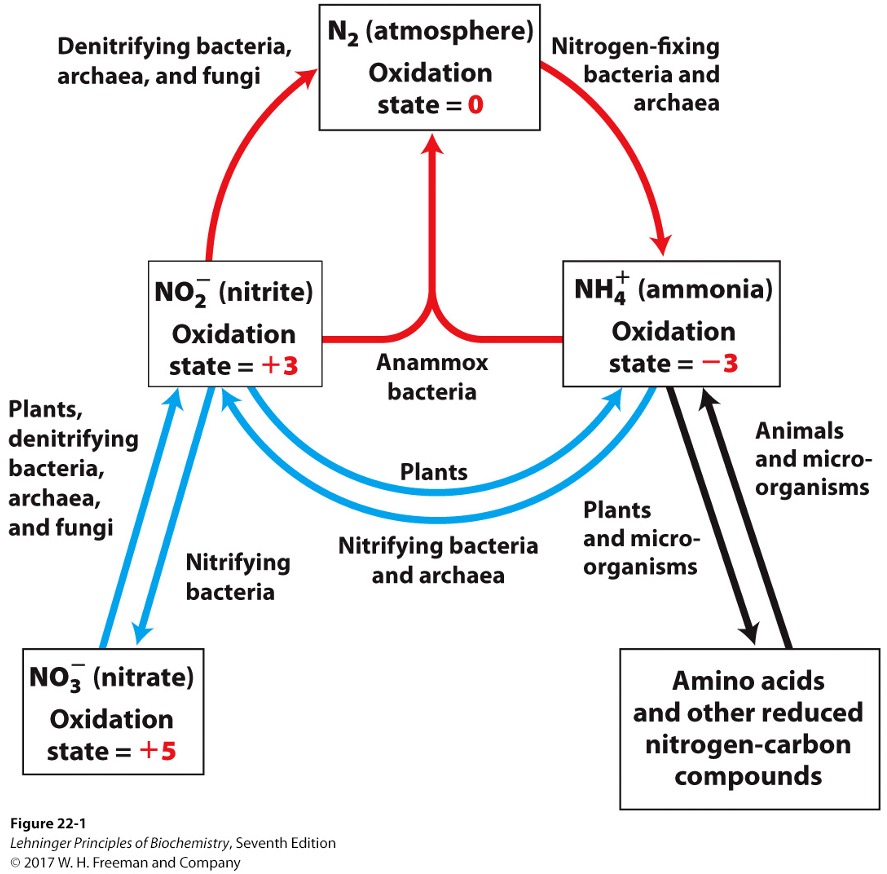
In the nitrogen cycle, what is the ultimate electron acceptor?
NO3- instead of O2
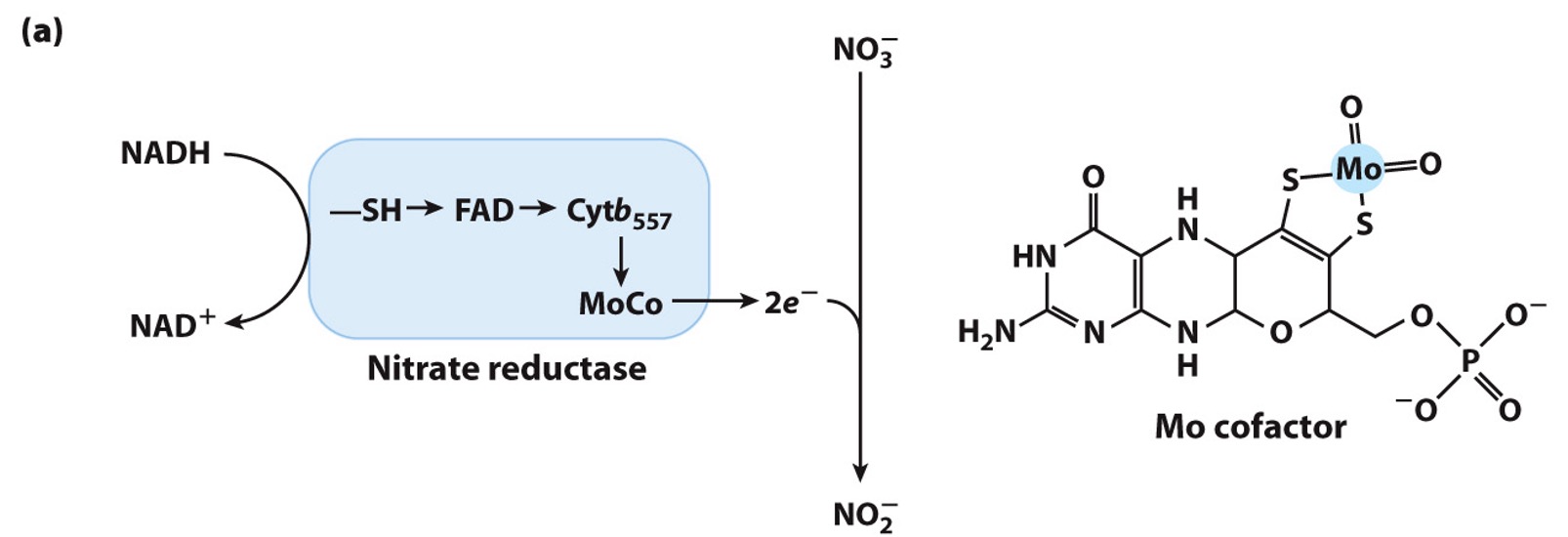
Nitrate reductase
large soluble protein
contains Mo cofactor
catalyzes 2e- reduction of NO3- to NO2-
NADH → e- donor
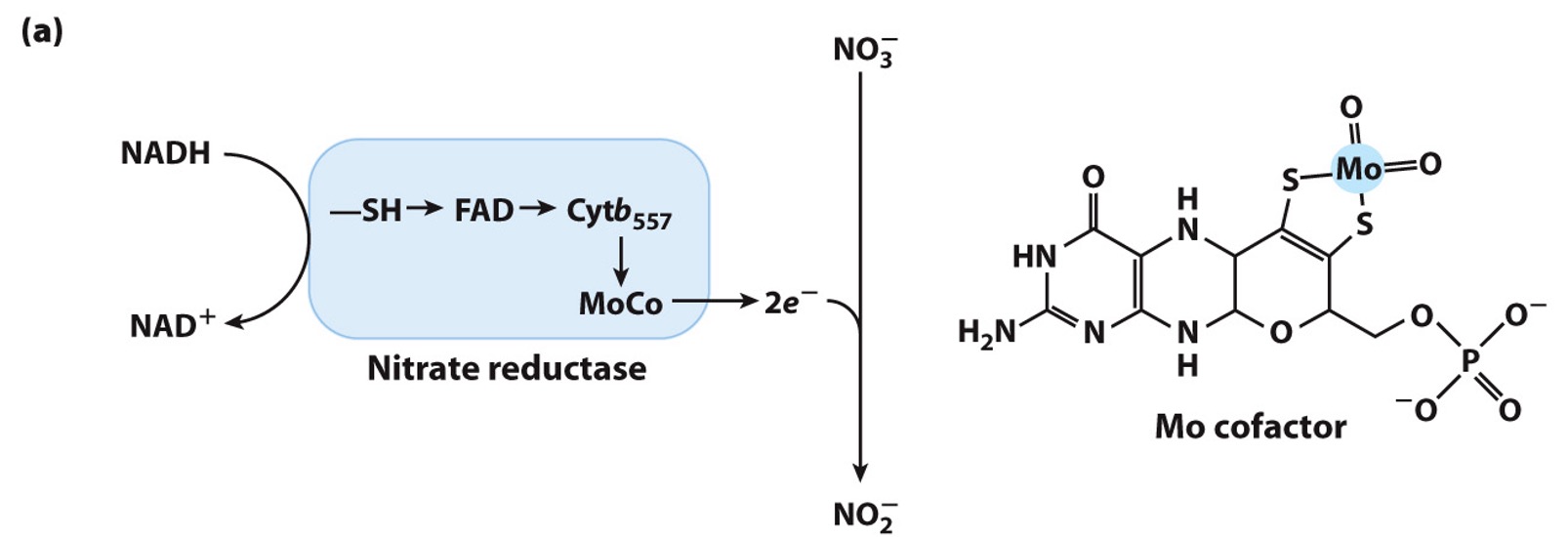
NO3- + 2 e- → ?
NO2-
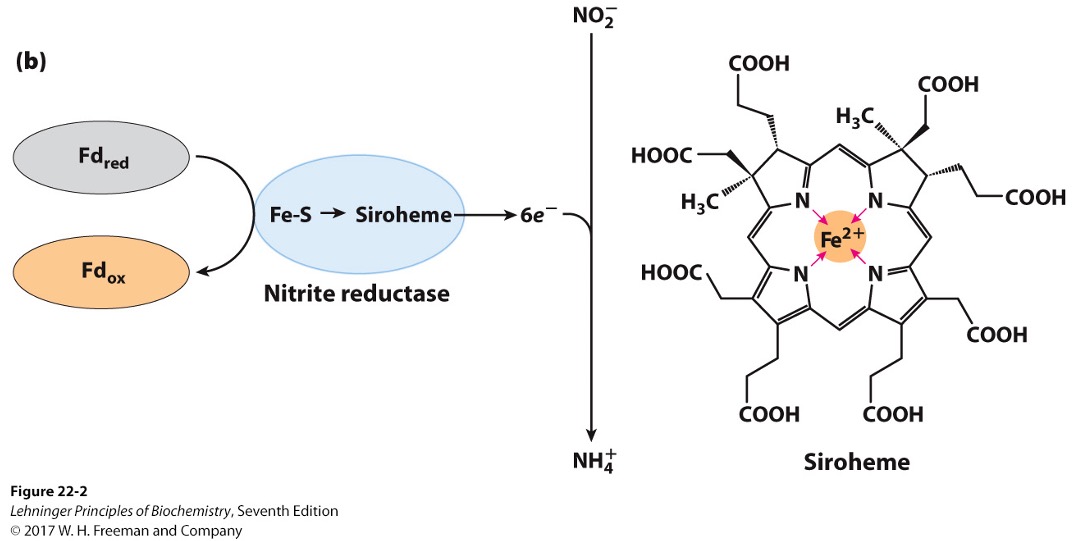
Nitrite reductase
converts products of nitrate reductase into NH4+
found in chloroplasts in plants
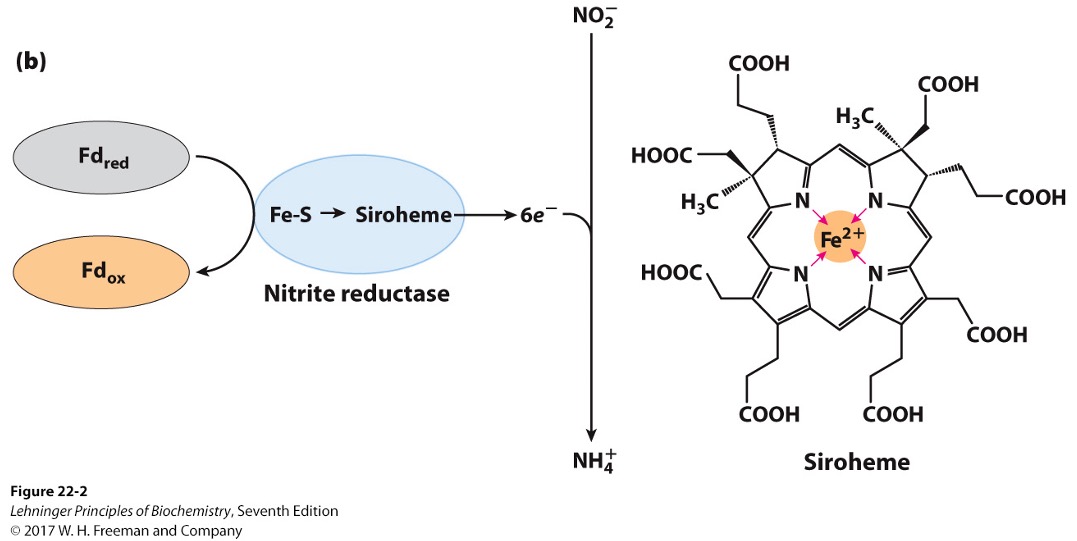
NO2- + 6e- → ?
NH4+
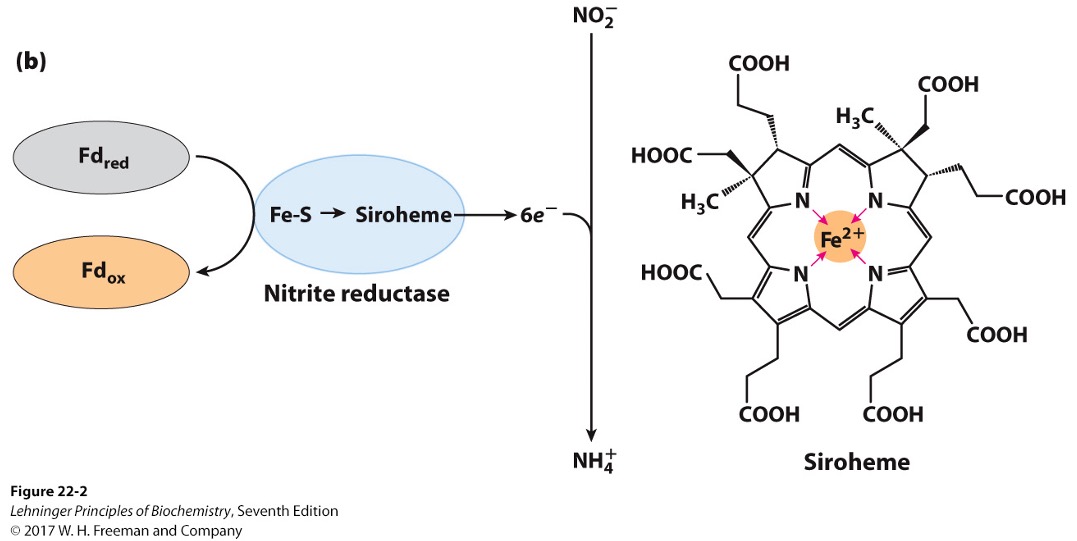
Siroheme
prosthetic group involved in electron transfer for assimilation via nitrite reductase