Biochem Exam 4
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what are the 2 main fates of glucose?
storage in glycogen (or reverse rxn: getting glc from glycogen)
convert to CO2 (electrons to NADPH, pentose phosphate pathway)
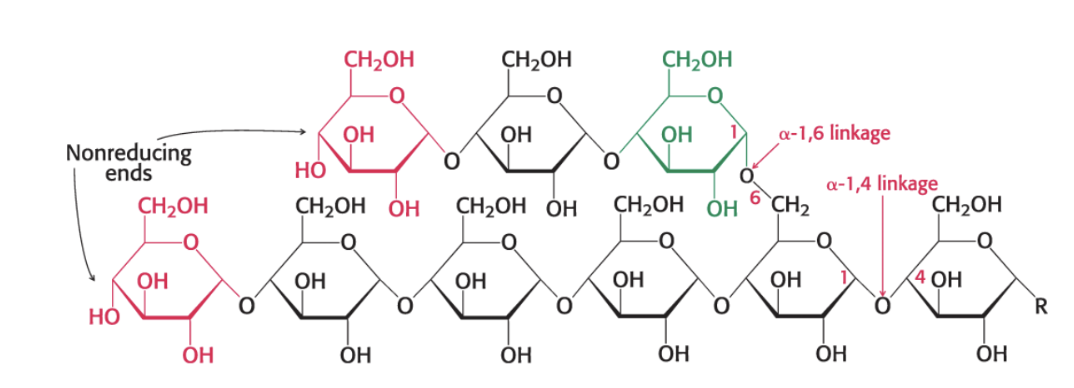
describe glycogen structure
glycogen is composed entirely of glucose units.
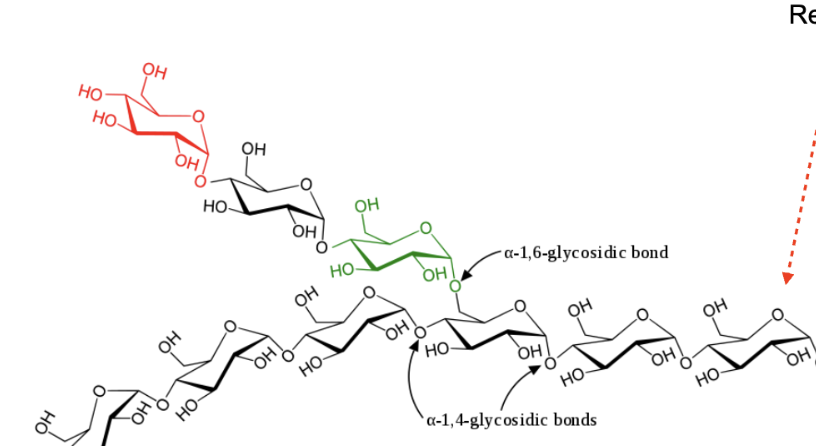
Linear chains joined by alpha 1,4 glycoside bonds. branched chains are alpha 1,6 linkages.
one reducing end per molecule
thousands of nonreducing ends
is glycogen soluble or insoluble in the cytoplasm?
hydroxyl groups on glycogen are free to interact with H2O, so glycogen is soluble in the cytoplasm
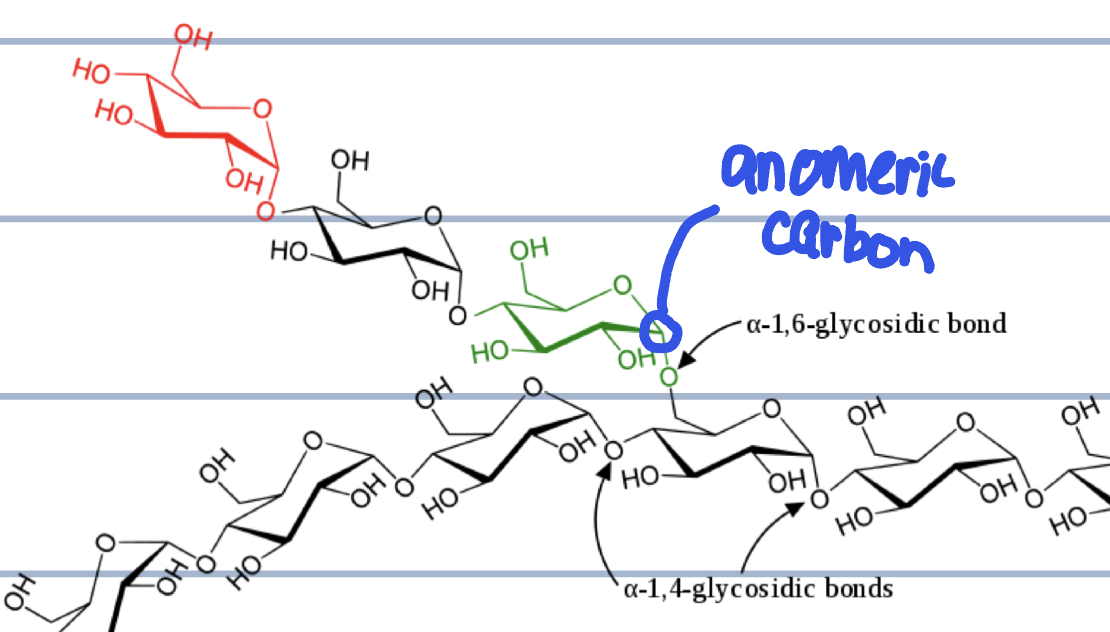
what is the anomeric carbon?
the carbon in a cyclic sugar that was originally the the carbonyl carbon in the open chain form. It is bonded to TWO oxygen atoms (one in the ring and other in the hydroxyl group).
where is the anomeric carbon in this image?
how does glycogen compare to triacylglycerol in terms of energy storage?
glycogen stores LESS chemical energy, because glc units are more oxidized than FA.
how does glycogen provide quick energy release?
glucose units can enter directly into metabolism, which allows for rapid generation of ATp when required. In contrast, fat metabolism takes longer.
by what process is glucose metabolized to generate ATP in the ABSENCE of O2?
lactic acid fermentation
explain briefly how blood glucose levels are regulated in the body
glucose storage in glycogen and its release from the polymer regulates blood glc levels, maintaining a steady supply of glc to tissues that require it for energy (e.g. the brain)
where does glycogen metabolism occur?
in liver cells
what are the 3 fates of glc-6-phosphate after its release from glycogen?
it can go to the muscle for glycolysis to make pyruvate —> lactate
it can go to the liver to make glucose and be released into the blood for use in tissues
it can enter the pentose phosphate pathway to make ribose + NADPH
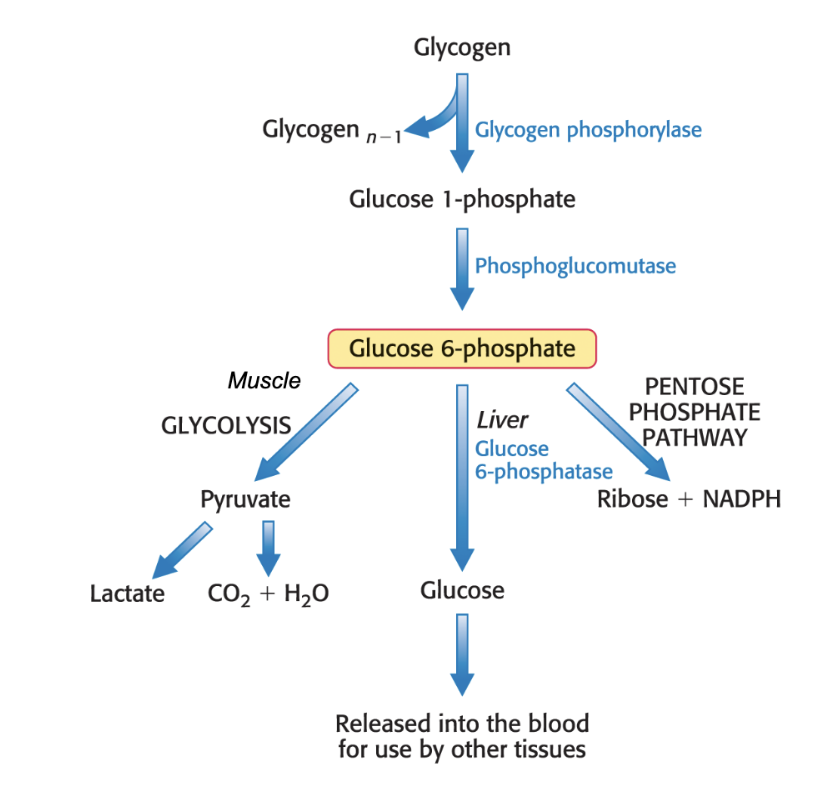
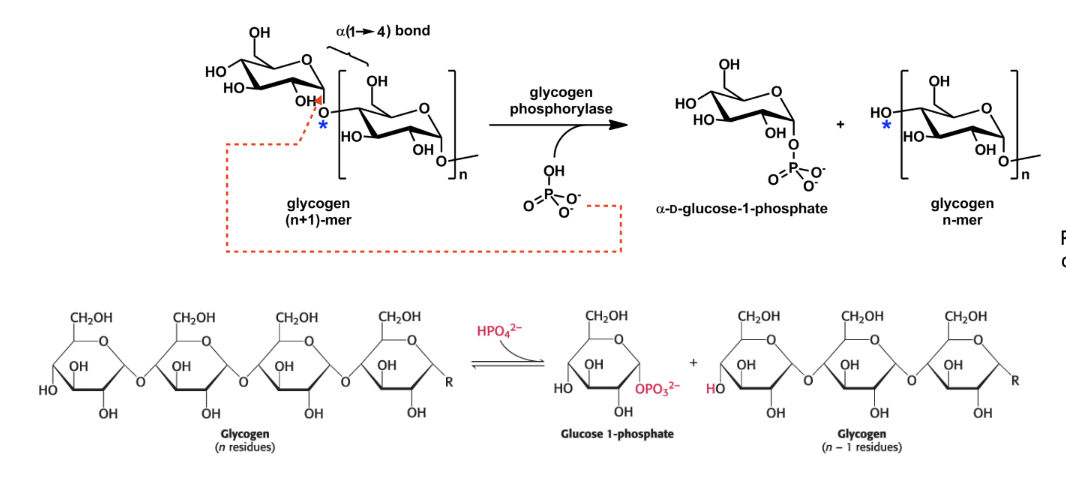
what is phosphorolysis? what enzyme catalyzes this process?
it is the release of glucose units.
catalyzed by glycogen phosphorylase, which inserts phosphate group into an alpha-1,4 glycoside bond at nonreducing end. This releases glc-1-P and shorten the linear chain by 1 glc unit.