PHARM: Glucocorticoids and Mineralocorticoids
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
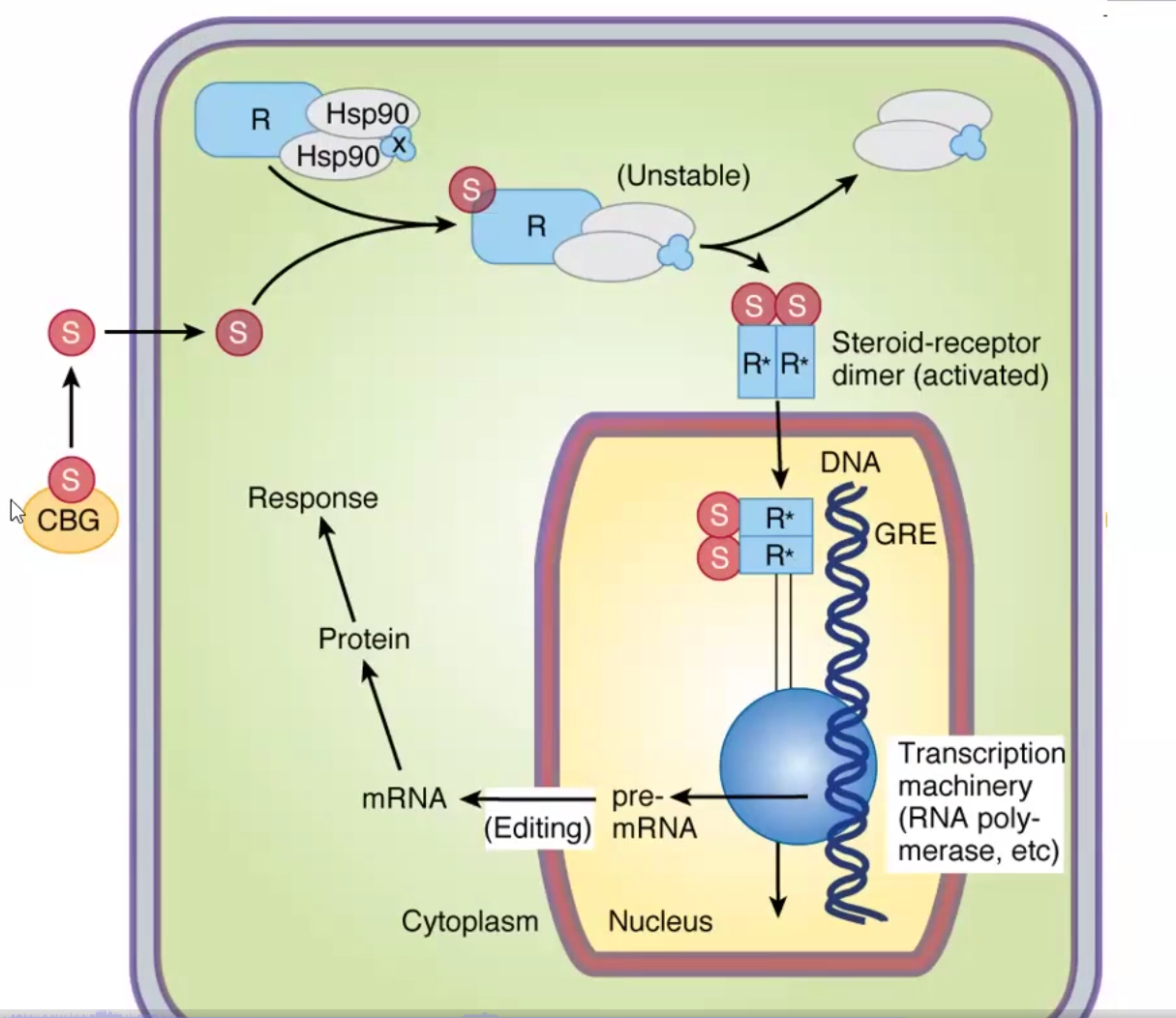
Glucocorticoid Mechanism of Action
Same as other steroids
Passive diffusion into target cells through CBG
Binding to Hsp90 chaperone proteins
Binding of specific cytoplasmic GC receptors
Dimerization and activation of receptor allows to enter nucleus
Alteration of transcription and translation
Hydrocortisone/Cortisol
Physiological effect
Pharmacokinetics
Clinical effects
Physiological effect:
Endocrine/feedback: Rapid suppression of ACTH.
Metabolism: ↑ Gluconeogenesis, ↑ glycogen storage, ↓ glucose uptake → hyperglycemia/diabetes.
Protein/bone: Protein catabolism → ↓ muscle mass; ↓ vitamin D action → osteoporosis.
Fat: Redistribution to face/abdomen (Cushingoid habitus).
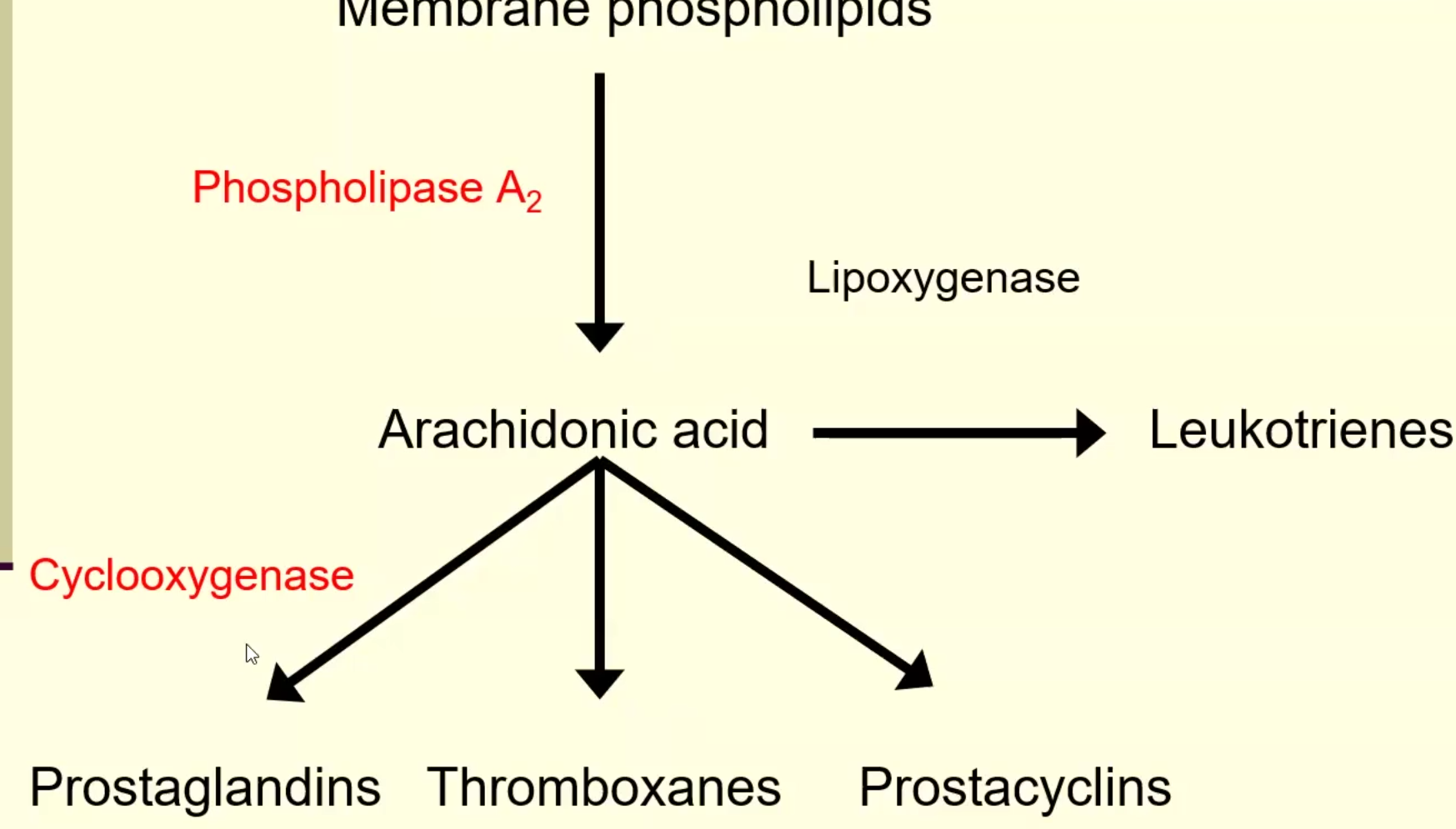
Immune/inflammation: Strong anti-inflammatory & immunosuppressive (↓ PLA₂, ↓ prostaglandins/leukotrienes, ↓ COX-2, ↓ leukocyte activity).
Vascular: ↑ Vasoconstriction; ↓ histamine release.
GI: ↑ Gastric acid/pepsin → peptic ulcers.
Lungs (fetus): ↑ Surfactant production
Pharmacokinetics:
Good oral bioavailability and topically absorbed
HL: 60-90 min
Metabolized by liver and kidney
Clinical effects:
Diagnosis and tx of disturbed adrenal function
Management of inflammatory and immunologic disorders
Tx of allergic rxns
Synthetic Glucocorticoids
Physiological effect
Pharmacokinetics
Clinical effects
Physiological effect: same as natural
Pharmacokinetics:
Rapid and complete oral absorption
Prolonged HL
Decreased mineralocorticoid activity
Types:
Short-medium acting:
Cortisone, Prednisone, Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone
Have mineralocorticoid activity!
Intermediate: Triamcinolone
No mineralocorticoid activity!
Enhanced anti-inflammatory activity, topical and duration
Long-acting: most potent in the market, no mineralocorticoid activity, enhanced topical activity
Dexamethasone: used in differential diagnoses of Addison’s disease:
50% reduction of Cortisol: pituitary adenoma
No effect in cortisol:
Reduced ACTH: adrenal tumor
Increased ACTH: ectopic ACTH-producing tumor in another site, likely lungs
Betamethasone: stimulates fetal surfactant bc it has less plasma binding proteins and is able to cross thru the placenta
Locally acting: Beclomethasone, Budesonide, Ciclesonide, Fluticasone, Flunisolide, Mometasone
Absorbed rapidly and avoid systemic effects/side effects
Used in management of allergic rhinitis, asthma (+beta agonist for bronchodilation) and other inflammatory conditions
Budesonide is used for Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
Fluticasone/Vilanterol is used for COPD and emphysema
Clinical use:
Tx of inflammatory, autoimmune, allergic and hematologic disorders
Organ transplant rejection
Infections -but must be accompanied by antibiotics
Stimulation of fetal lung maturation
Replacement therapy for Cushing’s or adrenalectomy
Addison’s Disease:
1o: hydrocortisone + fludrocortisone (mineralocorticoid)
2o: hydrocortisone and + fludrocortisone if angiotensin II isn’t enough to manage mineralocorticoid secretion
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH): reduced cortisol synthesis makes adrenal glands grow to make up for deficiency
In females, testosterone cannot convert to estradiol therefore there might be genital ambiguity
Tx with GC and MC combo
Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, arteritis, multiple sclerosis
Chemotherapy vomiting
hematological cancers
Adverse effects: Therapy should be tapered down slowly if not u might get cushing’s
Don’t use in heart disease or other conditions that will be worsened by the side effects
Mineralocorticoids/Aldosterone
Physiological effect
Analogs
Clinical use
Physiological effect: synthesized in zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex and regulated by ACTH and Angiotensin II
Same mechanism of action as other steroids
Promotes reabsorption of sodium and excretion of potassium and H+ ions→ overall water retention
Analogs: none
Fludrocortisone: synthetic oral corticosteroid that has both glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid activity; Most prescribed
Used for Addison’s disease, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and adrenalectomy
Adverse Effects:
Hypernatremia, Hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis (due to H+ loss)
Edema and Hypertension
Corticosteroid Antagonists
Physiological effect
Types
Clinical use
Physiological effect: inhibit corticosteroid/mineralocorticoid activity
Adverse effects: hyponatremia, Hyperkalemia, hypotension, menstrual abnormalities
Types:
Spironolactone - mineralocorticoid antagonist
Inhibits renal tubule sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion → Diuretic
Tx of edema and ascites due to hepatic cirrhosis, primary hyperaldosteronism (Conn’s Syndrome)
Eplerenone: selective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist
Diuretic, inhibits Na reabsorption and K excretion
Tx of hypertension, Heart failure
Mifepristone: both glucocorticoid and progesterone receptor antagonist
Tx of hyperglycemia, abortion inducer