Exam 1 Review
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
according to Mihlay Csikszentmijalyi, in what respect are all creative people unanimous?
they all love what they do
true/false: creativity is only for a select few
false: all people can further develop their creativity
what are Tim O’Brian’s five ideas for creative problem solving?
list and counter list: before you do anything, list the first 5 ideas that come to mind, then write 5 approaches that are the opposite. look and see if any make sense or maybe combinations of the two
use both sides of your brain: approach the problem first analytically, then look at it from an emotional point of view
convene a panel of experts: you can either gather experts to brainstorm or create an imaginary panel and ask yourself what they would do
be a consultant: approach the problem as if you were a hired consultant
ask children: when you ask a child, you have just tapped into nearly limitless imagination
what are Judith Bell’s steps to jump-start creativity?
Look at what your retail competition is doing
Compare your ideas with those from your own company’s presentations
Innovate: instead of just copying, put your own spin on things
What is the SCAMPER model?
S - Substitute: exchange one expected element of a visual idea for another
C - Combine
A - Adapt: take an item intended for one use and adapt its purpose to suit your needs
M - Modify, minify, magnify: magnifying and minifying some elements can provide an imaginative counterpoint to otherwise routine presentations
P - Put to other uses: use an item in a different way
E - Eliminate: quit while you are ahead, don’t overuse an idea
R - Reverse, rearrange: rearrange the normal order (large/small, front/back)
what is cross-merchandising?
refers to moving merchandise across traditional department or classification lines to combine elements in a single department or display
what is a prototype?
the original model on which later types are based
who was the very well known Creative Director at Tiffany & Co.?
Gene Moore
What was Gene Moore’s signature style?
he would juxtapose unrelated items, such as a diamond on a piece of lettuce, a brooch embedded in a watermelon made of gumdrops or diamond studded snowflake pins with cut-out paper snowflakes
who was the very well known creative director for Barneys New York?
Simon Doonan
what are some sources for idea development?
community events and local traditions
books and movies
current events
New York Times Style sections
Wall Street Journal
USA Today Snapshots
What is a flagship store?
a store that displays the highest ideals of a company’s brand image. every detail from the fitting room hooks to floor coverings reflect the company’s brand.
What is an Idea Stopper?
according to Karl Albrecht, author of The Creative Corporation, it is a critical statement (verbal bullet) that shoots down creative ideas
what five characteristics does Karl Albrecht cite, that make the difference for innovative and creative thinking?
Mental flexibility: being free of preconceived interpretations and fixed opinions
Option thinking: willingness to give problems further thought and having a reluctance to jump on the first idea that seem to be a solution
Big-picture thinking: taking the “helicopter view” and rising above the landscape of everyday ideas to see al the factors involved at once
Skill in explaining and selling ideas: being able to develop a concept and connect the facts and ideas involved so that others can understand and accept them
Intellectual courage: willingness to advocate an idea or a course of action that you believe in, but which is unpopular with your peers
how do you build and sustain in a creative work environment?
be an idea helper, not an idea stopper
voice you ideas
employ the 5 characteristics that Karl Albrecht lists for creative and innovative thinking
what is visual merchandising?
the process of promoting the sales of products by producing mental images that urge potential customers to make purchases
how does visual merchandising support sales?
merchandise is displayed and signed so effectively that it can sell itself
what is a mom-and-pop store?
refers to the days when many retailers were family businesses and they often lived in apartments above the store. today, it refers to a small, independent retailer
what is a promotional mix?
a combination of communication tools — advertising, in-store marketing, special events, and personal selling — that tells targeted customers about a store and its merchandise
how does visual merchandising support retail strategies?
visual merchandisers make advertised promises of pleasant and productive shopping experience come true
they carry out a store’s promotional selling strategies by:
designing and executing window and interior displays that support advertising goals
installing promotional signing for in-store selling
producing workable departmental layouts and interior decor
devising merchandise fixture layouts for day-to-day operations
how does visual merchandising communicate with customers?
assures that every tangible aspect of the store sends a unique merchandise message to the shoppers
what are atmospherics?
a word coined by retailers to describe the elements (lighting effects, sound levels, aromas, etc.) that appeal to our five senses and contribute to the overall environment of a store
what is a target market?
an identified (targeted) segment of the population that research indicates is a good “fit” for a retailer’s product or service offerings. this is the group at which the retailer aims all the store’s promotional communication efforts.
what are strip malls?
made up of side-by-side stores with parking lots immediately outside their doors. some have enclosed walkways, but they are not configured under one large roof as conventional covered malls are
what is a brand image?
the retailer’s identity in shoppers’ minds
it is a combination of a tangible and intangible factors that describe what a shopper thinks about his or her relationship with a favorite store
also describes how the store acts towards its customers
it encompasses not only merchandise brands and types but also store environment, reputation, and service.
in some cases, the retailer employs the store’s name or another exclusive title on its private-label merchandise
how do chain stores stretch their brand image?
when a store expands their offerings, projecting their brand onto various products
retail chain stores can even introduce new products that are exclusive to different store locations
the key is to maintain its core brand image
what are some retail trends?
emphasizing interiors: changed from focus on dramatic window display to open back displays that allow the passer-by to view the inside of the store
consumer interaction with merchandise: visual merchandisers found new ways to bring the customer in touch with the product by creating more functional fixtures and furnishings, they changed the layout to facilitate interaction between customer and merchandise, incorporated signing to direct traffic and inform about products on self-service fixtures, and placed graphics on the walls set the mood and explained lifestyles
nonstore retail: there is less need for visual merchandising with internet shopping
what does layering mean?
including multiple sensory elements to achieve a particular atmosphere for the store environment - simultaneous use of sight, sounds, touch, taste, and smell
layers of atmospherics can alter the perception of time for shoppers, encouraging them to become so comfortable and pleasantly stimulated in the shopping environment that time becomes less important than it might otherwise have been
they browse longer, see and touch more products and become more inclined to make purchases
define composition
the placement and arrangement of the elements in a display; it means balancing various elements in an artful format
what are the design elements?
color
texture (pattern)
shape
line (direction)
what are the design principles?
unity/harmony
rhythm/repetition
balance
emphasis
proportion
what are color schemes or color harmonies based on?
complementary schemes
split-complementary schemes
double-complementary schemes
triadic schemes
analogous schemes
monochromatic schemes
what is a complementary color scheme?
a color scheme that consists of two colors that are directly opposite each other on the color wheel
what is a split-complementary color scheme?
a color scheme that consists of three colors -one central color plus the two colors on either side of its complement
what is a double-complementary color scheme?
a color scheme that consists of four colors - two colors plus their complements
what is a triadic color scheme?
a color scheme that consists of three colors that are equidistant from one another on the color wheel
what is an analogous color scheme?
a color scheme where (color families) consist of two or more colors that are next to each other (adjacent) on the color wheel
what is a monochromatic color scheme?
a color scheme that consists of a single color in different values and intensities (more white or gray blended into the basic color)
what is a color story?
a color-coordinated or color keyed product grouping that shows how to use a season’s trend colors
what are the seven common color groups?
brights
pastels
midtones
jeweltones
muted/dusty
earthtones
neutrals
what is color intensity?
the degree of saturation of a color
what are some practical guidelines for merchandising by color?
divide the colors of product groups according to their color intensity
combine the colors within each group to create color schemes. colors of same intensity blend together harmoniously
do not combine colors from the various groups together, except for neutrals
what are color systems?
systematic systems that are created by designers who interpret, create, forecast, and select colors for manufactured products
created for the use of color as it applies to the profitable marketing of goods and services
what is balance?
can be defined as an equality of optical weight and importance that creates a unified presentation
what is optical weight?
how important, large, or heavy an object appears to be versus how much it really weighs or how large it is in actual scale
what is a face-out?
a piece of hardware for hanging merchandise so that the full front of the item is visible
can be a straight arm or a slanted arm for a “waterfall” effect
name two types of balance
formal balance (symmetrical balance) and informal balance (asymmetrical balance)
what is rhythm?
can be defined as a sense of visual movement from item to item and element to element in a single display or presentation of an entire department
this movement can come as a result of the effects of lines, shapes, or colors as well as varying heights, lines, and forms used in the overall display’s desing
does not require mechanical animation
what do diagonal lines add?
activity and movement
what is proportion?
proportion can be defined as a relationship between the apparent size, mass, scale, or optical weight of two or more objects
What is open sell?
fixturing that makes most merchandise (even items traditionally kept in locked cases) accessible to shoppers without the assistance of salespeople
what is texture?
refers to both visual and tactile surface characteristics
contrasts of this element in store decor determine overall environmental “mood” and can influence the appearance of merchandise as well
can absorb or reflect light, providing contrasts that enhance that features of merchandise and invite a shopper to touch merchandise
what is harmony?
an “artful” element, creating visible unity
it is careful selecting of complementary, interwoven elements that create a unified whole
what is emphasis?
it indicates which features of the merchandise you will highlight
this depends on what you want to communicate to the customer
you can use surprise, colors, signing, lighting, graphics, and strategic placement on fixtures to create this
what is a planogram?
drawings that show how merchandise and selling fixtures should be placed on selling floors, wall sections, or freestanding displays and window displays
planning tools that make it possible to communicate consistent store layout and decor directives to multiple locations thereby creating a strong retailer identity
what are leaselines?
the boundary line where store space begins and a mall’s common area ends
merchandise tables and other selling fixtures will feature items that have been purchased in depth; such items are of placed here
name six store layouts
grid layout
free-flow layout
racetrack layout
soft aisle layout
minimal floor layout
combination floor layout
what is a grid layout?
a linear design for a selling floor where fixtures are arranged to form vertical and horizontal aisles throughout the store
what is a free-flow layout?
a layout that has selling fixtures arranged in loosely grouped, informal, nonlinear formations to encourage browsing
what is a racetrack layout?
a layout that exposes shoppers to a great deal of merchandise as they follow a perimeter traffic aisle with departments on the right and left side of the circular, square, rectangular, or oval path
what is a soft aisle layout?
a layout where fixtures are arranged in groups, creating natural aisles without any change in the floor covering to designate a separate aisle space
what is a minimal floor layout?
a layout, almost gallery-like in its simplicity, that shows small selections of handcrafted or very exclusive merchandise
what is a combination floor layout?
a layout that employs the best features of several selling floor layouts in an overall plan that suits a retailer’s specific strategy
what do merchants base their floor layout moves on?
sales data from previous years, so they can evaluate dollar results
what is a sight line?
in store presentations, it refers to the area a person can see from a particular vantage point - the view at the end of an aisle or at the top or bottom of an escalator
where should a retailer place current season merchandise?
in the first third of the store; this is prime selling space for products the customers are currently seeking
what are adjacencies?
thoughtfully planned layouts that position same “end use” products next to eachother
where should a retailer place preseason merchandise?
in the very early stage, it will be placed towards the back and then moved up in the front third of the selling space as the apparel becomes more appropriate
what is the fashion cycle?
a bell-shaped curve that drives sales and departmental presentations
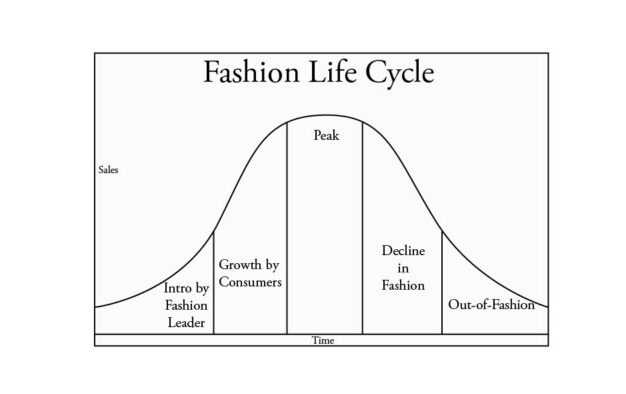
how does a retailer test the merchandise? (relate it to the fashion cycle)
buyers introduce small quantities to the department to see how shoppers will respond. at this point it is in the beginning of the fashion cycle that represents “incoming” or “test”. as shopper react, the merchandise is either cleared out, signaling a poor response, or reordered
if reordered, the item is expected to rise in popularity and offered at regular price. it is now in the pre-peak area of the cycle. as sales increase, the item will peak. at this point the popularity with customers is established and sales are brisk. when everybody who wanted the items has made their purchase, sales diminish. this is the post-peak stage. the merchandise is marked down and eventually cleared out of the department.
what are the five types of fixtures?
conventional metal fixtures
furniture fixtures
“found” fixtures
vendor fixtures
custom fixtures
what are the three categories of fixtues?
Capacity fixtures
Feature fixtures
Signature fixtures
what are capacity fixtures?
fixtures that hold a large quantity of merchandise, usually showing a single style in several colors and in a complete range of sizes
what are feature fixtures?
fixtures that are designed to hold fewer items and are used to highlight category groups or smaller coordinate groups
what are signature fixtures?
fixtures that are attention getting, one-of-a-kind units positioned at the entrance to a store or department to reflect the store’s brand image
what are two challenges a store must balance when considering fixtures and furnishing?
Aesthetics
Cost
What is a round rack?
a capacity fixture fabricated in several diameters and adjustable heights for stocking basic apparel items
what are superquads?
a four-armed capacity fixture with an adjustable height feature for showing items purchased in depth or to hold coordinate grouping of pants, skirts, blouses, sweaters or jackets
what is a gondola?
a versatile four-sided capacity fixture that may be shelved for folding or stackable products; it is occasionally set with garment rods to show apparel on hangers
the end of the gondola is called
the endcap
what are the guidelines for using fashion cubes?
Arrange BOYGBV colors vertically and work from left to right. If stock quantities are too low to support an entire vertical column, use vertical colorization in at least the top two or three cubes that are most visible in the department
size the cubes with the smallest size at the top moving down to the largest
what is a two-way fixture?
also called a T-stand
a two-armed hanging fixture used to feature small quantities of trend apparel or test merchandise
what is a four-way fixture?
also called a costumer
features a hanging coordinate group or a small quantity (24 to 48 items) of separates presented as coordinated outfits
what is slatwall?
a wall system of horizontal backer panels with evenly spaced slots that accept brackets and display accessories with special fittings
what is a gridwall?
a wall system of metal wire, which accepts brackets and display accessories with special fittings
what is a waterfall?
an angled display arm affixed to a wall standard, slatwall or gridwall system, a T-stand (two-way or four-way) or other selling floor fixture to show a cascade of hanging merchandise
what is a straight arm?
a perpendicular display arm affixed to a wall standard, slatwall, or gridwall system of a T-stand or other selling floor fixture to show a small quantity of hanging merchandise
what kind of fixtures hold key items?
those that hold large quantities of products, such as tables and round racks
what is the single most important fixture in the retail industry?
a table: its low key profile makes it an ideal introductory fixture to a department
what is way-finding?
a term used by architects to describe any tools that help customers to “find their way” through the store
signs positioned in highly visible areas - on walls or hanging from the ceiling - are examples of these strategies
what is the purpose of interior walls?
to guide traffic and separate merchandising departments
what is an outrigger?
types of non-permanent wall dividers
decorative or functional elements mounted to a wall at right angles in order to define, separate, and from categories of merchandise presented on shelves or display fixtures
what is retrofitting?
the act of adding architectural features, fixtures or other elements after the original structure is completed
why would retrofitting or outriggers be used in store design?
to break up a wall space into clearly defined functions
how is wall signing is especially useful?
indicating brand, size, gender, or category of merchandise
what is a soffit?
a long ledge, permanent arch, or box reaching down from a store’s ceiling to its top shelves or usable wall space
often used to mask non-decorative (functional) lighting fixtures
how many types of balance should be employed in a wall presentation?
one
how many types of fixtures should be employed in a wall presentation?
at least two or three
what are colorways?
the assorted colors or groups of colors a manufacturer has chosen for its line of fashion products
what is the primary function of wall dividers?
separating a long wall into shorter, clearly defined sections
may be permanent or semi-permanent