AP Biology Unit 2 Terms
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
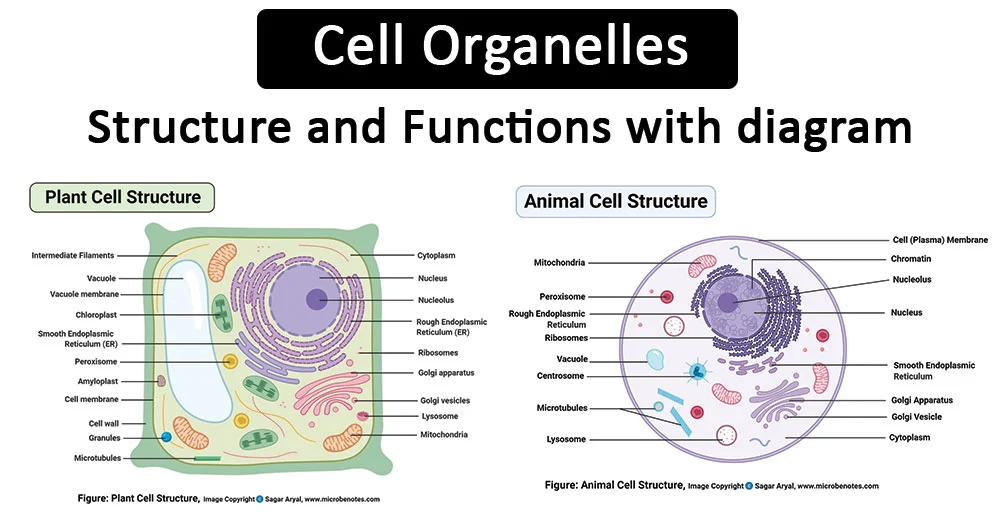
Organelle
Structures within a living cell.
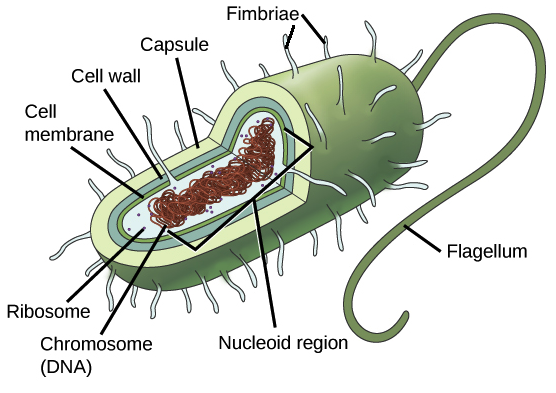
Prokaryotic
Usually unicellular organisms; simple cells w/ no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles.
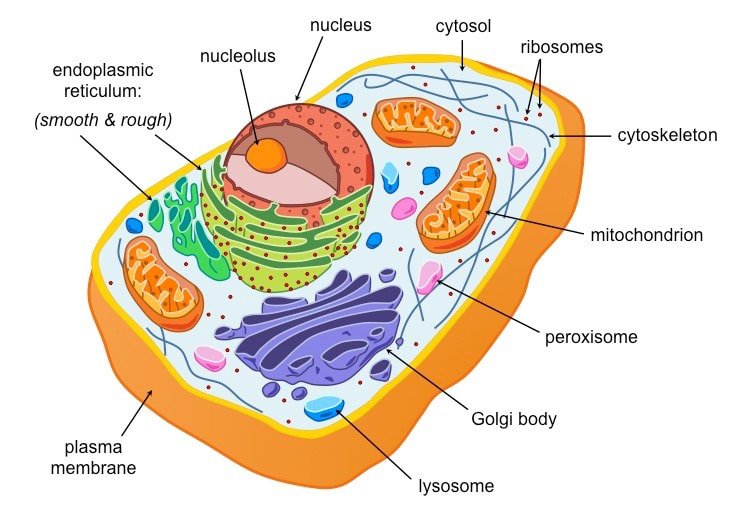
Eukaryotic
Usually multicellular organisms; has nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
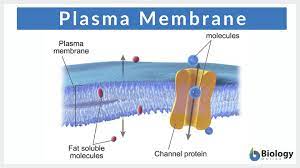
Plasma Membrane
Protects cell and controls what goes in/out of the cell.
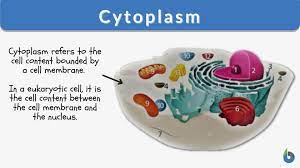
Cytoplasm
Area inside the cell that surrounds the other organelle
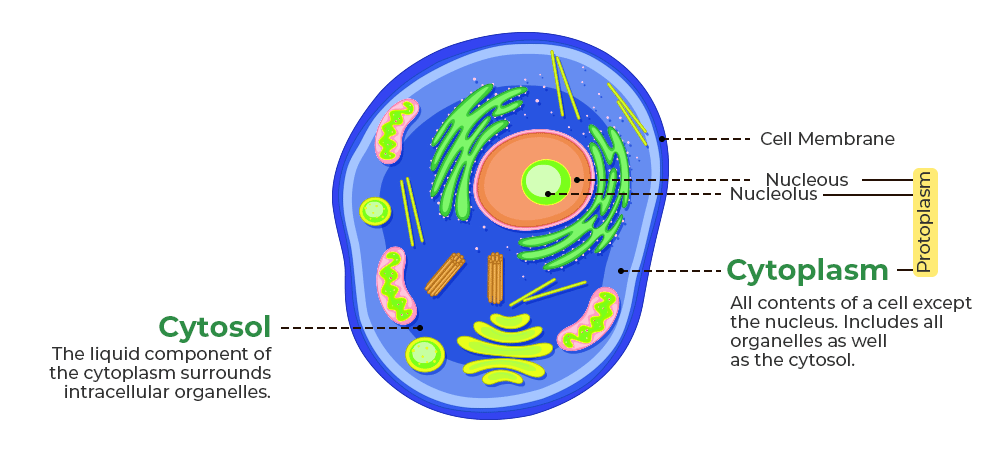
Cytosol
Semifluid substance ("jelly") inside the cell.
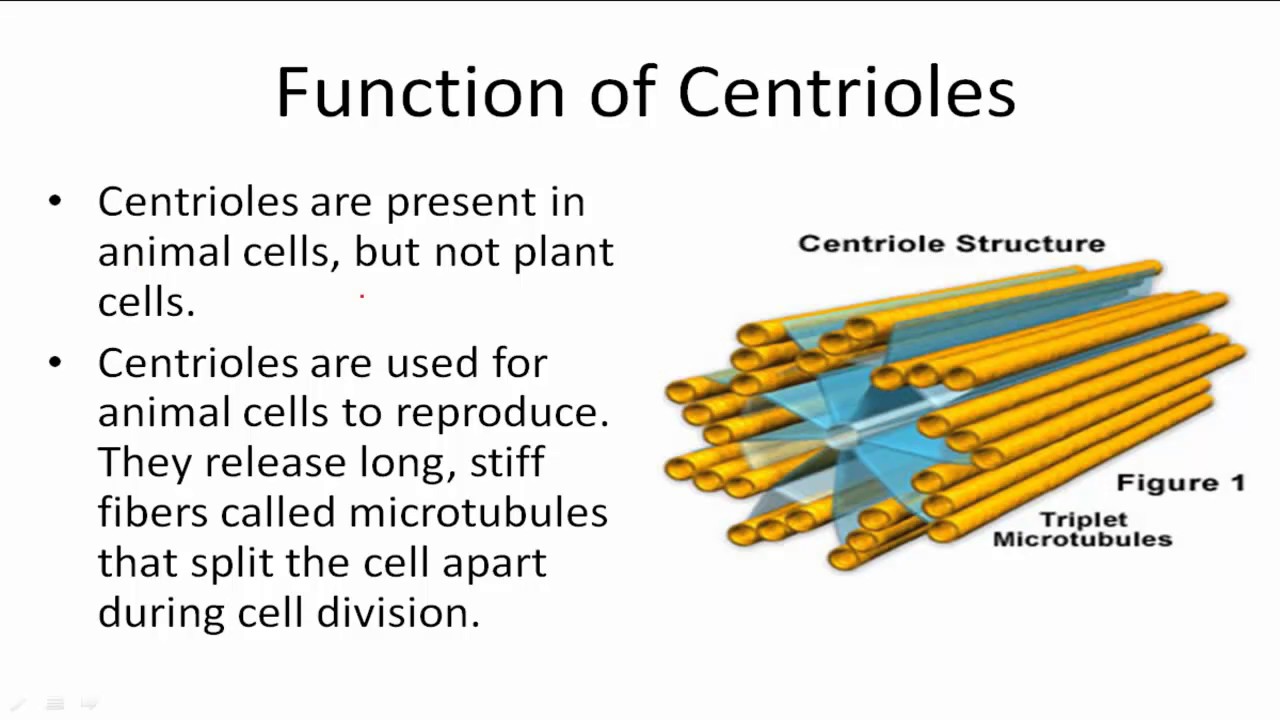
Centrioles
Helps cell split during cell division.
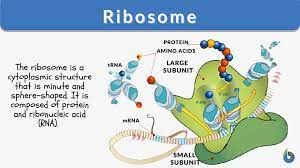
Ribosome
Creates proteins.
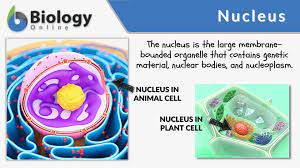
Nucleus
"Brain" of the cell that holds DNA in chromosomes.
Nuclear Membrane (Envelope)
Protects nucleus.
Nucleolus
Creates ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
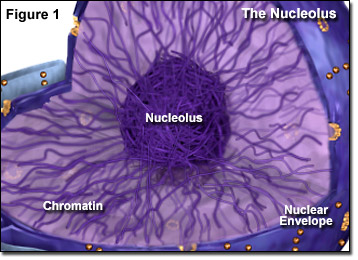
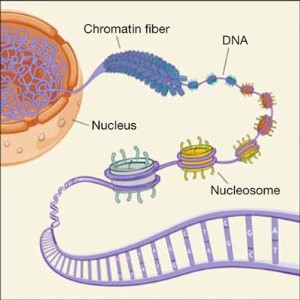
Chromatin/Chromosome/Chromatid
Carries genetic information.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Makes proteins and transport them to the golgi via vesicles -> proteins become enzymes to help stomach or lysosomes, or become part of the membrane.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Synthesizes (makes) lipids, detoxifies the cell, and metabolizes carbohydrates.
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies, sorts, packs, and ships proteins to where they need to go (exocytosis).
Mitochondria
Powerhouse = makes energy as ATP.
Cell Wall
Protects plant cells from water pressure (turgor).
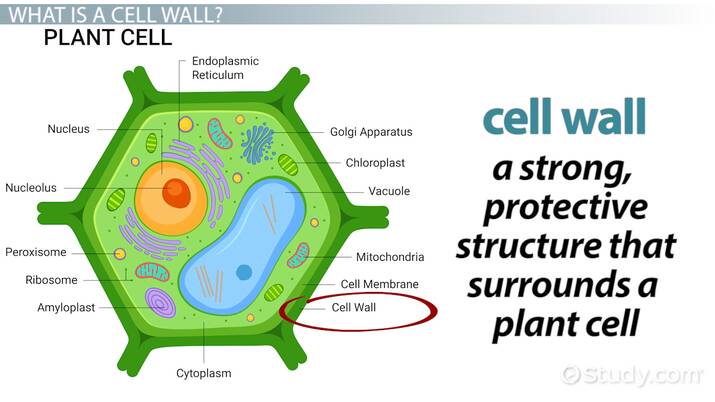
Vacuole
Storage of waste/water/food, water control.
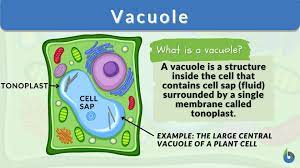
Chloroplast
Photosynthesis = creates sugar (chemical energy) from solar energy (light) and uses it to create energy.
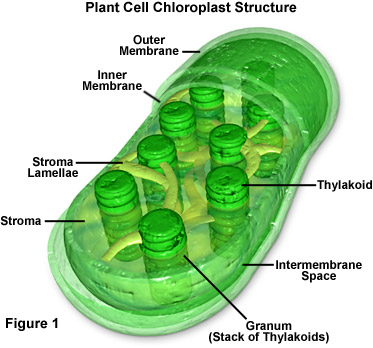
Metabolism
Total chemical process to change food into energy (including breaking down and building molecules).
Selective Permeability
Ability to regulate what substances go in and out of the cell.
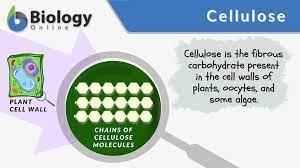
Cellulose
Provides structure to plant cell walls.
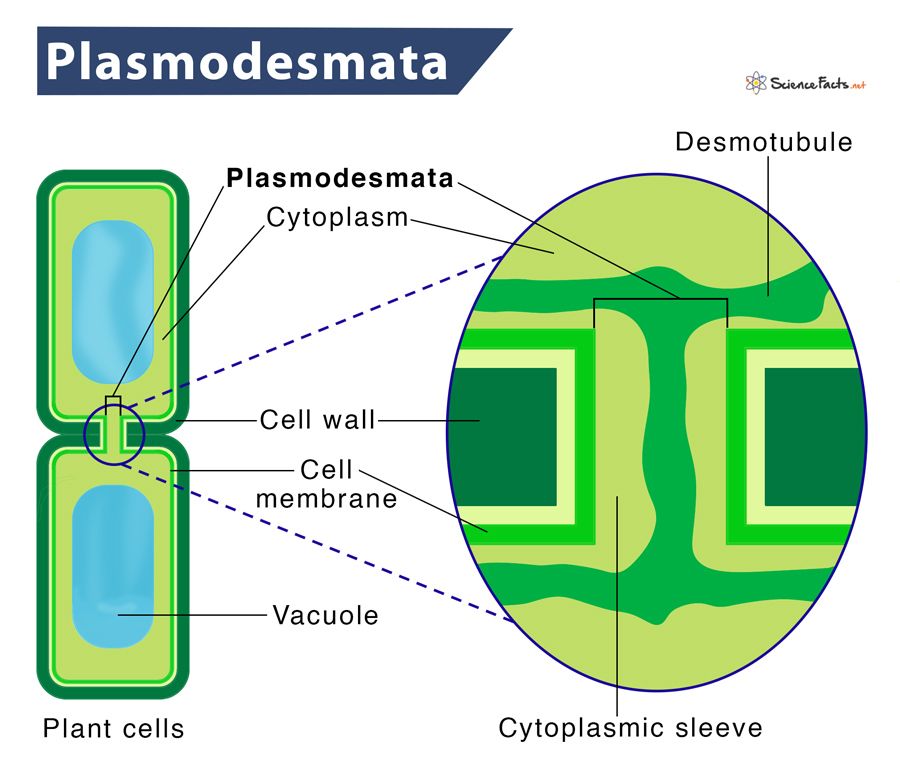
Plasmodesmata
Holes that connect adjacent cells to control water and molecule movement.
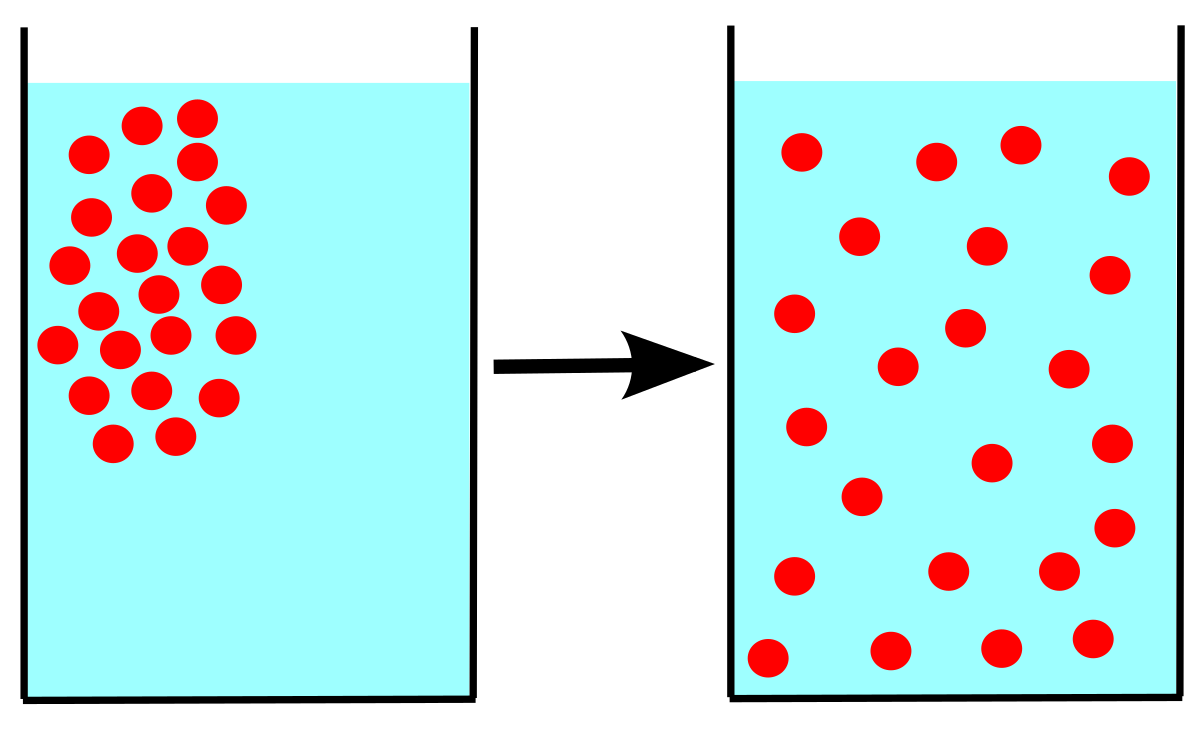
Concentration Gradient
Moving from high concentration to low concentration = moving to a place with LESS molecules or LESS crowded.
Diffusion
Natural flow of movement without help does not need ATP (energy).
Passive Transport
Goes with the concentration gradient (high to low) .
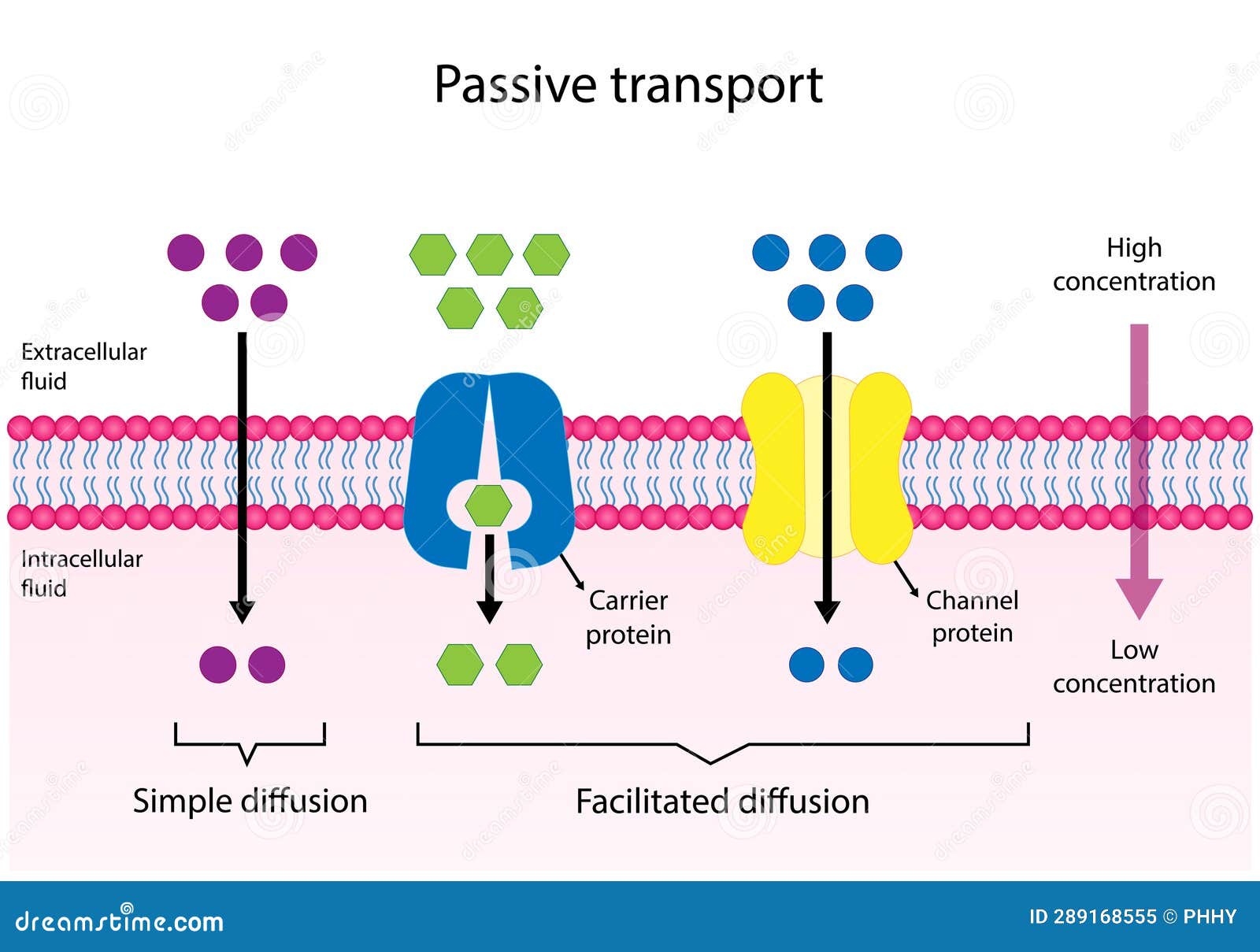
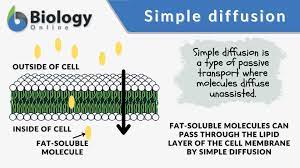
Simple Diffusion
Small molecules that can pass through the membrane easily.
Facilitated Diffusion
Molecules are too big or hydrophillic and need proteins' help to pass.
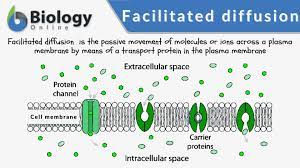
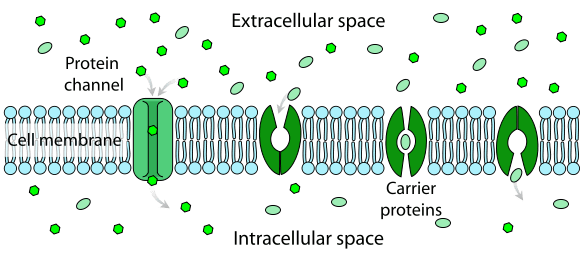
Channel Proteins
Like a tunnel for molecules to move through. (ex./ Aquaporin)
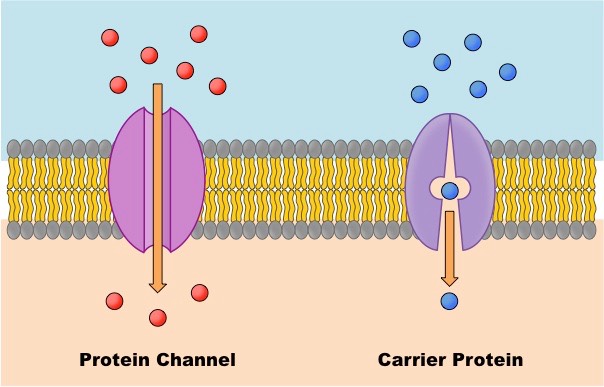
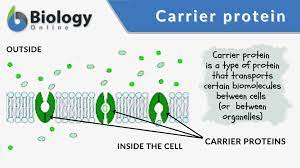
Carrier Proteins
"Carry" molecules through. (ex./ Sodium-Potassium pump (Na/K pump)
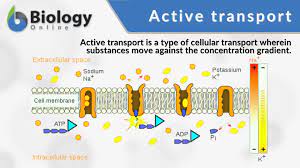
Active Transport
From low concentration to high concentration (to more crowded) = Against concentration gradient; requires energy to move molecules across membrane.
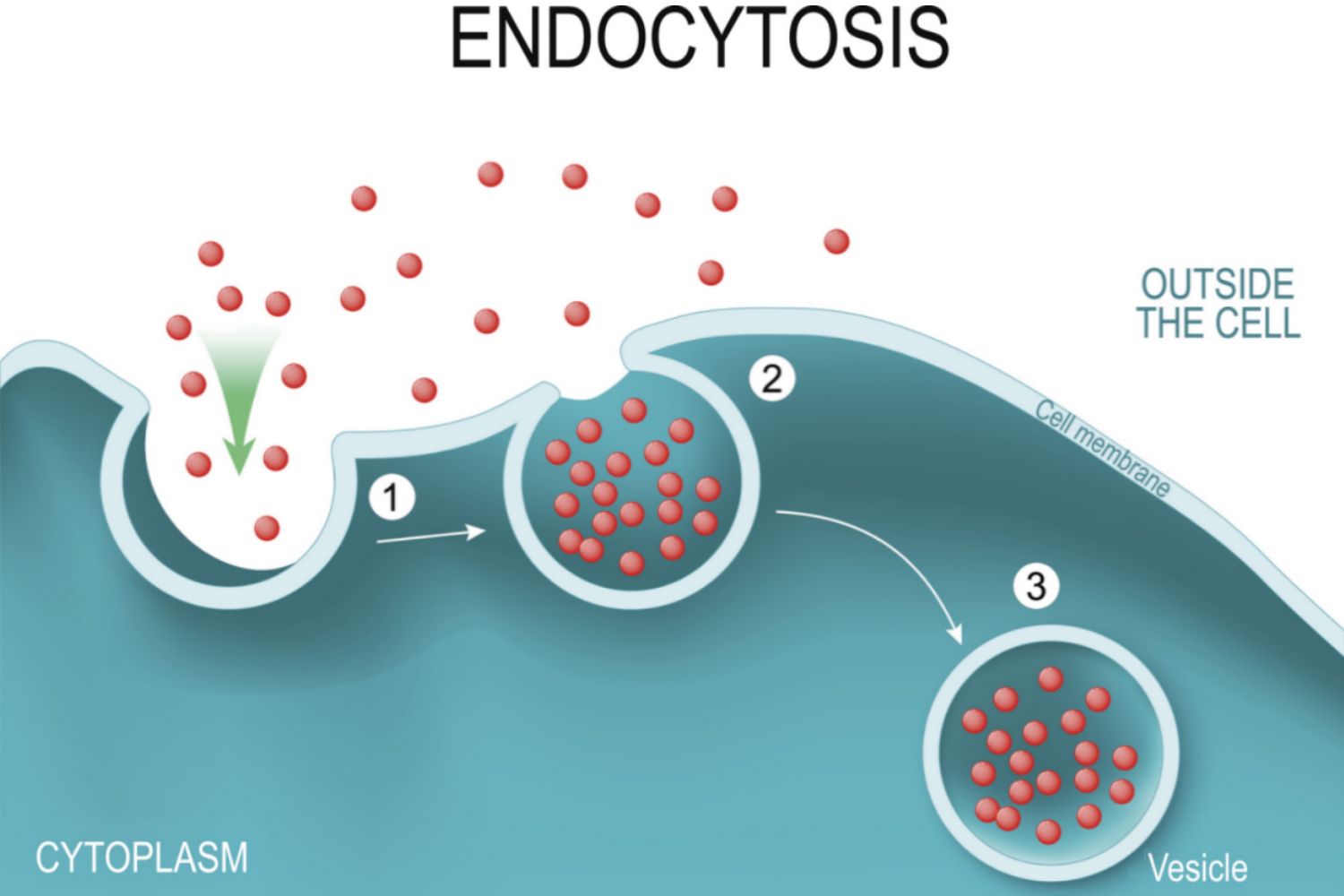
Endocytosis
Import of macromolecules travel through vesicles that are from the plasma membrane.
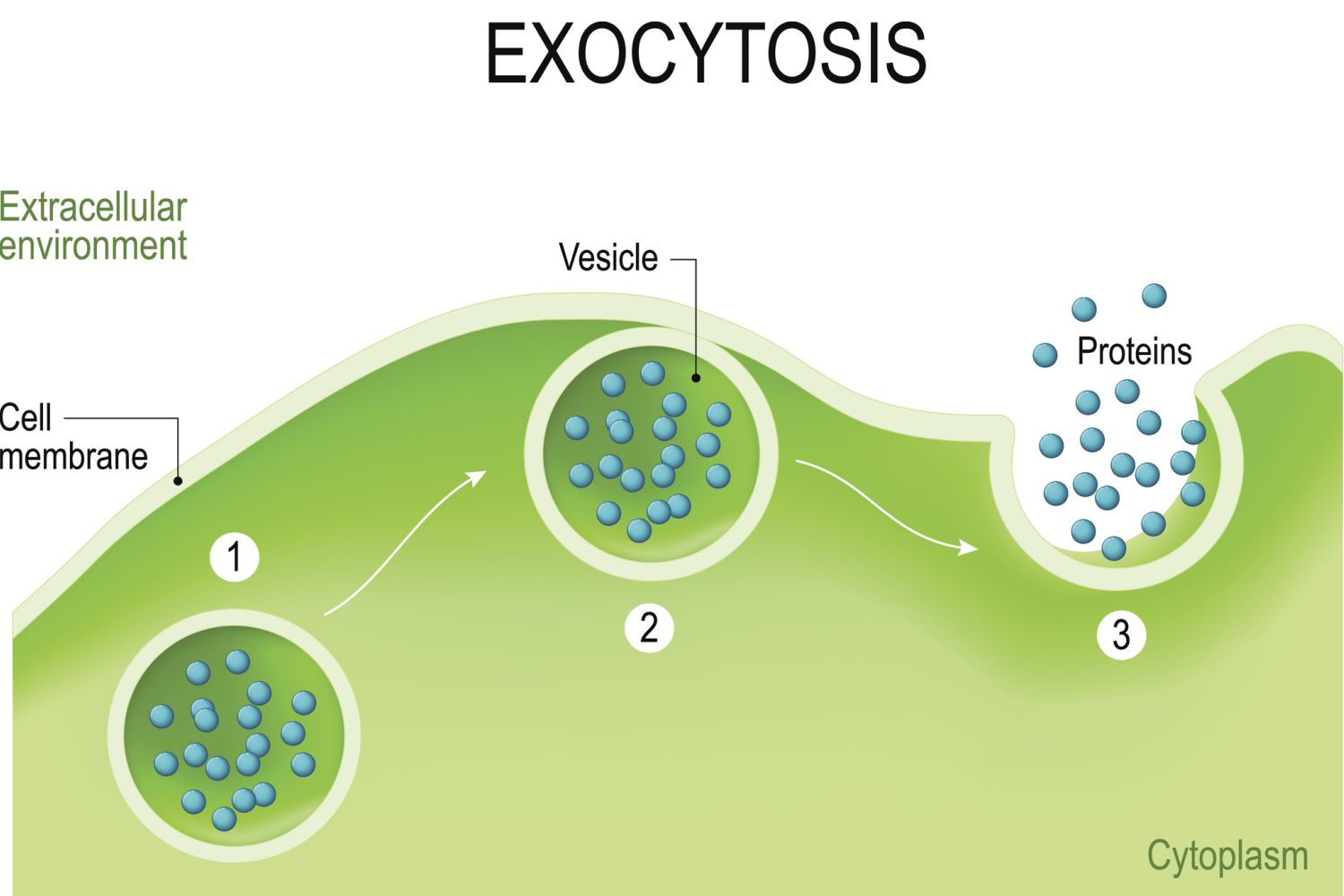
Exocytosis
Internal vesicles fuse w/ membrane to export macromolecules.