The Female Reproductive System
1/28
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
ovaries
woman’s gonads that creates eggs and has a bumpy surface
oocyte
immature egg cell
ovum
mature egg cell
what structure of the ovaries make the surface bumpy?
follicles, structures that contain one oocyte each that are developing and have cells around the oocyte to nourish it as well as protect it
what hormones do the cells in the follicle produce?
estrogen, a sex hormone
how many eggs are in each follicle?
1
females are born with all the eggs they will have around millions. around how many are released within the reproductive years? why?
while females are born with millions of follicles with oocytes, only few hundreds release ovums during her reproductive years since many of the others die off as the woman ages.
ovulation
an event that happens around every 28 days in which the follicle is mature and releases an egg that is immature as it isn’t fully mature yet. the half mature egg is called the secondary oocyte which hasn’t completely finished meiosis.
the secondary oocyte becomes an ovum only during fertilization.
menopause
the end of reproductive years in a woman typically around 50 years old
corpus luteum
the remaining follicle that has released the immature egg and grows to become endocrine tissue that secretes estrogen as well as progesterone (hormone that helps maintain the uterine lining)
what happens if the released egg is never fertilized?
after a certain number of days, if the egg is still not fertilized, the corpus luteum degenerates and a new follicle begins to mature once again (marking the beginning of a new ovarian cycle)
oviduct (aka. fallopian tube)
the pathway through which the egg travels through after it is released by the follicle.
the entrance of this pathway has finger-like projections that don’t touch the ovaries. there is a tiny space between the opening of the oviduct and the ovary.
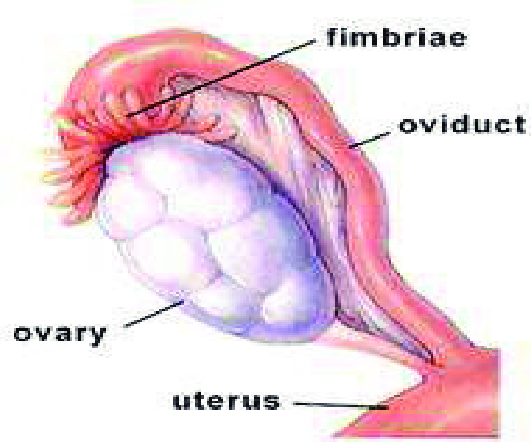
what happens after an egg is released from the follicle?
the finger-like projections at the beginning of the oviduct pass over the surface of the ovary to guide the egg to the oviduct. cilia in the oviduct move the egg toward the uterus. when the egg is moving through the oviduct, it is waiting to be fertilized by the sperm.
at the end of the fallopian tube, if it’s not fertilized, it is broken down by the body and it’s cell parts are recycled.
the egg can be fertilized anywhere in the oviduct, but it’s generally in the upper portion. the zygote will begin to divide and become an embryo as it moves along the fallopian tube. it then implants in the endometrium.
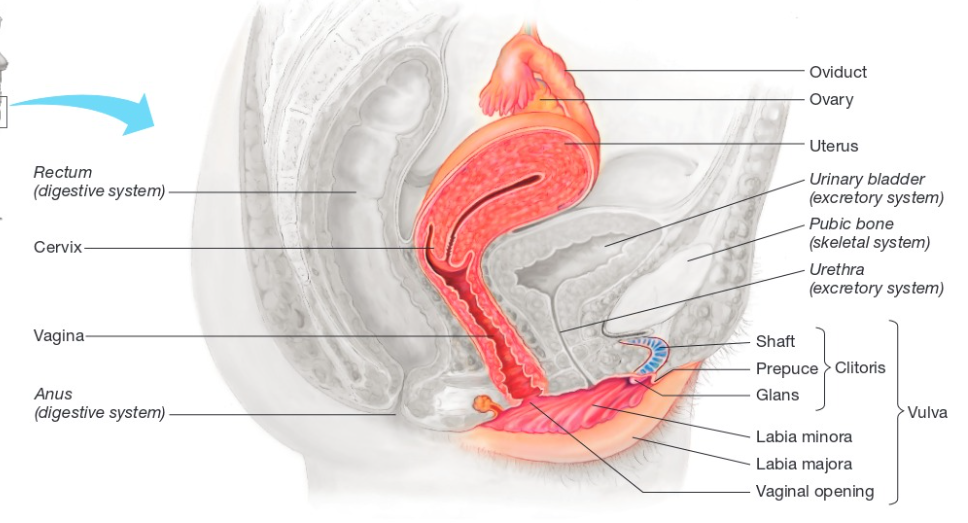
uterus
the womb; the place where the pregnancy takes place with a thick, muscular wall and an endometrium that lines the wall
endometrium
the lining of the uterus that is highly supported by blood vessels
embryo
(week 1-8) a stage including the first division of a zygote (unicellular) until its body structures start to appear
fetus
(week 8- birth) a human that is growing and developing the body structures
ectopic pregnancy
an abnormal pregnancy in which the embryo implants in an area other than the uterus, making the pregnancy unviable and dangerous if ruptured. the mother can bleed to death.
surgery is needed.
tubal pregnancy
a type of ectopic pregnancy in which the embryo implants in the oviduct
cervix
narrow neck at the base of the uterus
“it’s the cervix that dilates during pregnancy not the vagina!”
pap test
swabbing cells from the cervix to detect for cervical cancer
vagina
a channel that is muscular but has thin tissues and acts as the birth canal
where the penis is inserted as a result is also where the sperm travels through
there are glands within the vagina that secrete mucus regularly as well as during sexual arousal, reducing abrasion during intercourse and keeping the vagina moist overall
vulva
collection of the external female genital parts
labia minora
pair of thin folds that border the vagina and urethra
labia majora
pair of thick folds that protect the vagina
hymen
thin tissue that partially covers the vaginal opening
what are the structures involved in sexual arousal (due to their sensitivities and their filling with blood and enlarging during sexual intercourse) ?
vagina, labia minora, clitoris
clitoris
small erectile organ
shaft inside the body supporting the glans with lots of nerves making it sensitive to touch outside the body with a prepuce a tiny bit of skin that covers the glans.
female reproductive system (summed)