UA renal diseases
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Most glomerular disorders result from
immunological disorders that include the kidney
Lab finding of blood, protein, and casts indicate
glomerulonephritis
RBC casts, Dysmorphic RBCs, hyaline and granular casts, WBCs in the urine after a strep infection indicate
Post streptococcal glomerulonenephritis
Increased IgA serum levels remain after some macroscopic hematouria indicating
IGA nephropathy
marked protenuria (>3.5 G/day), fat droplets, oval fat bodies, fatty casts, Hypoalbuminemia in the blood, indicate
Nephrotic syndrome
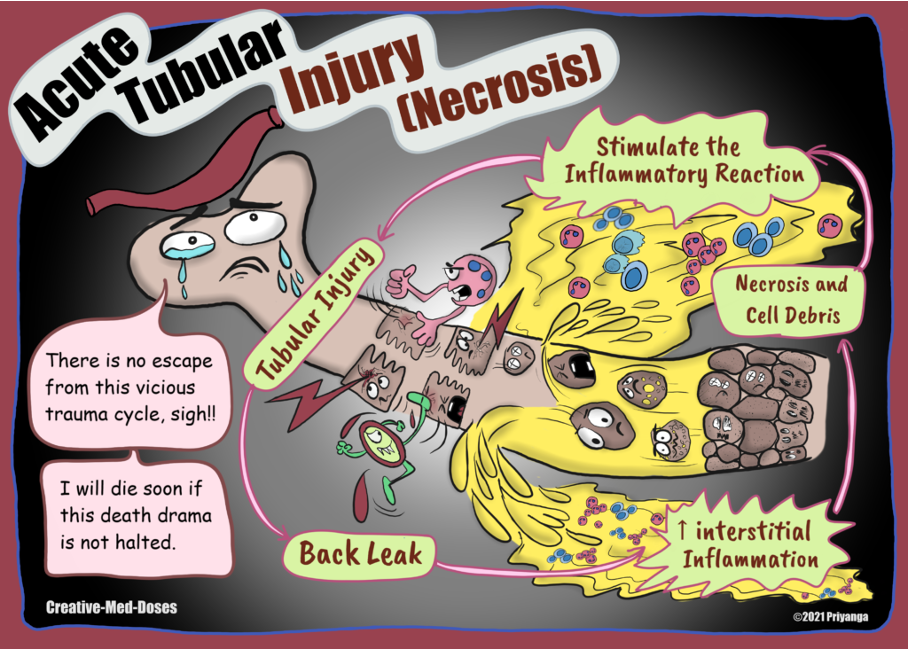
What can cause acute tubular necrosis
Shock, trauma, surgical procedures, and expire antibiotics
acute tubular necrosis
damage to the renal tubular epithelial cells
Diabetes insipidus
tubules are unable to respond to ADH or lack of ADH is occurring causing excessive amounts of urine to be excreeted
Low specific gravity, pale yellow urine, polyuria, polydipsia, decreased production or function of ADH
Diabetes insipidus
What type of diabetes is not a tubular disorder
Diabetes mellitus
highrt specific gravity, pale yellow urine, polyuria, polydipsia, and small amounts for albumin
early neuropathy in diabetes mellitus patient
failure to reabsorb in the PCT
Fanconi syndrome
inability for renal tubules to absorb cystine
cystinuria
Affects the kidneys ability to secrete hydrogen ions or reabsorb bicarb
renal tubular acidosis
Infection of the baladder
cystitis
infection of anything above the bladder
Pyelonephritis
WBC, WBC clumps, bacteri, nitrate + (sometimes) indicate
UTI
WBC casts, granular casts, waxy casts, broad casts, polyuria, burning with urination, lower back pain, indicate
Pyelonephritis
Rash, increased eosinophils, causing kidney issues and lower back pain that is treated with steroids
acute interstitial nephritis
decrease glomerular filtration less than 25ml/min, rise in BUN and creatine, high electrolytes in the blood indicate
renal failure
Lithotripsy
High energy shock waves are used to break up stones
75% of calculi are made from
calcium oxalate
What affects the formation of kidney stones
Ph
chemical concentration
urinary stasis
PKD is a disease that is associated with
formation of cysts in kidneys
GFR decline rate in PKD
4-5 mL/min/year
How is the progression of IgA neuropathy monitored
Protein
What is a sign or symptom of nephrolithiasis
Back ache
dizziness
unbearable pain
What is the main cause of acute interstitial nephritis
Drugs such as NSaids, PPi’s, and antibiotics
What bacteria is the most common cause of both cystitis and pyelonephritis
E.coli
What is the main difference between cystitis and pyelonephritis
Cystitis affects the bladder, while pyelonephritis affects kidneys
CKD causes what
toxic build up of substances in the body
What is the most common cause of CKD
Diabetes mellitus
What is the most immediate life threatening concern of ESRD
High Potassium
ESRD is
the final stage of CKD with eGFR<15mL/min
What are some symptoms of fanconis
-Increased thirst
-Dehydration
-Muscle weakness
-Fatigue
-Growth failure
What is the microscopic finding in urine that confirms ATN
muddy brown cast
A positive chemical test for blood with no red blood cells found in the sediment:
Indicates the presence of hemoglobin or myoglobin
An inherited disorder producing a generalized defect in tubular reabsorption is:
Fanconi syndrome
The highest level of proteinuria are seen with
nephrotic syndrome
The presence of fatty casts is associated with all of the following except:
focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
nephrotic syndrome
minimal change disease
diabetes insipidus
diabetes insipidus
Minimal change disease causes
an autoimmune response to the glomeruli that causes massive amounts of protein in the urine
When observing RTE casts, the cells are primarily
embedded in a clear matrix
The presence of fatty casts is associated with
diabetes
crush injuries
nephrotic syndrome
Increased transitional cells are indicative of
catheritization
malignancy
A finding of dysmorphic RBCs is indicative of
glomerular bleeding
Transitional epithelial cells are sloughed from the
bladder
Most glomerular disorders are caused by
immunological disorders
Spherical, concentric circles with radial striations
Leucine
Sheaths of fine needles
tyrosine
Maltese cross
free fat cholesterol
Notched corners
cholesterol
Hexagonal plates
Cysteine
“coffin-lid”
TPO4
“thorny-apple”
Ammonium biurate
“envelope”
CaOx dihydrate
“dumbbell”
CaOx and CaH2CO3
The matrix of casts consists of this substance which is constantly produced by RTEs:
Tamm-Horsfall protein
Damage to the glomerular membrane can be suspected when the sediment contains:
Red blood cells casts
An increase in urinary white blood cells is called:
Pyuria
Ghost RBCs are seen in:
dilute alkaline urine
Where do the immune complexes get deposited in the kidney in Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis?
Glomerulus
How much protein is being spilled each day in nephrotic syndrome?
>3g/24 hours
What describes cystinuria and what it can lead to
The kidneys fail and to reabsorb cystine leading to high levels in the urine and kidney stone formation
What does minimal change disease look like under a microscope
Normal under a regular microscope, but under an electron microscope there are damaged podocytes