Histology Final Exam
1/546
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
547 Terms
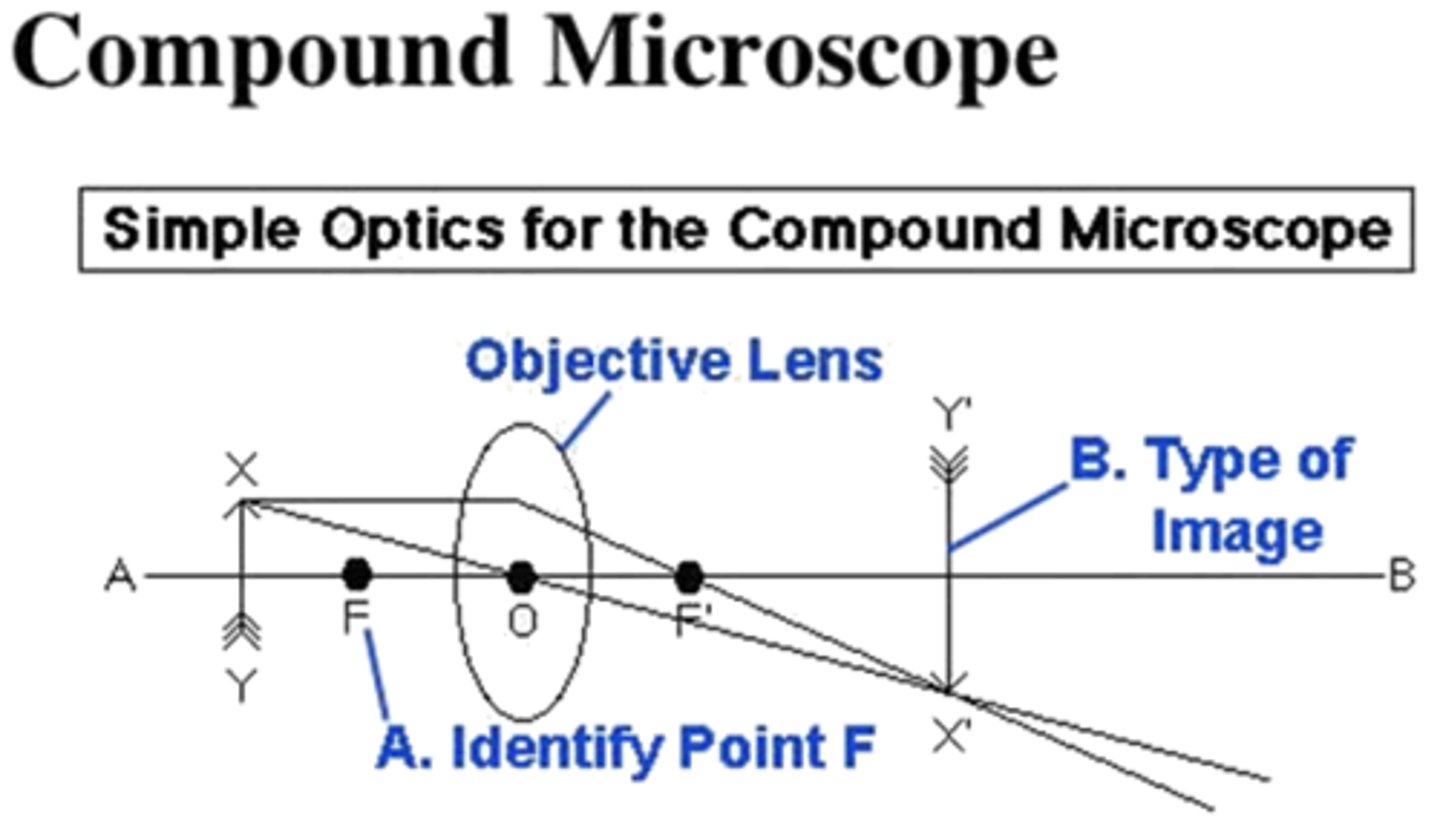
answer only question c in the image below
1. real image
2. imaginary image
3. principle axis
4. optical center
5. object
6. focal point
imaginary line
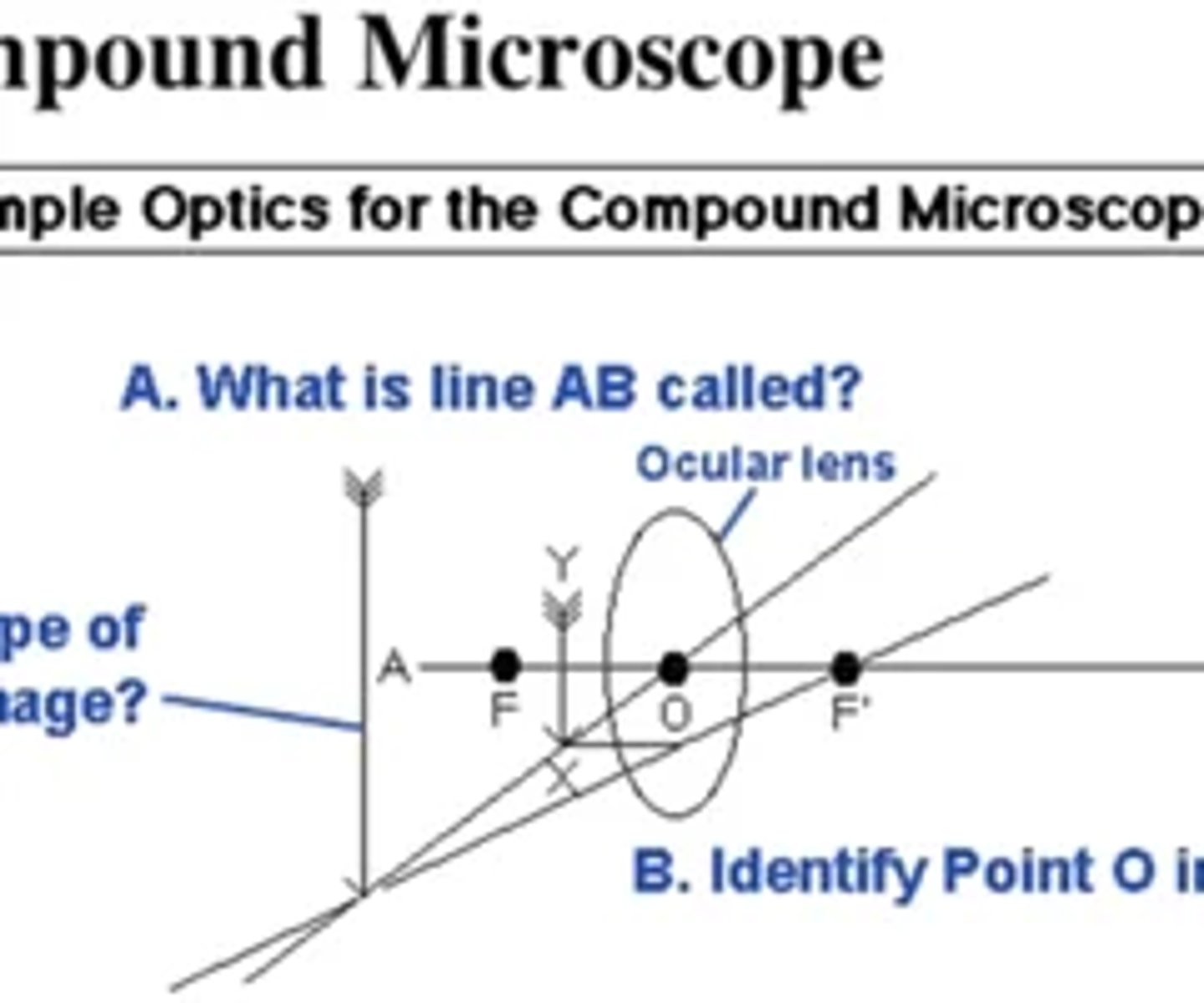
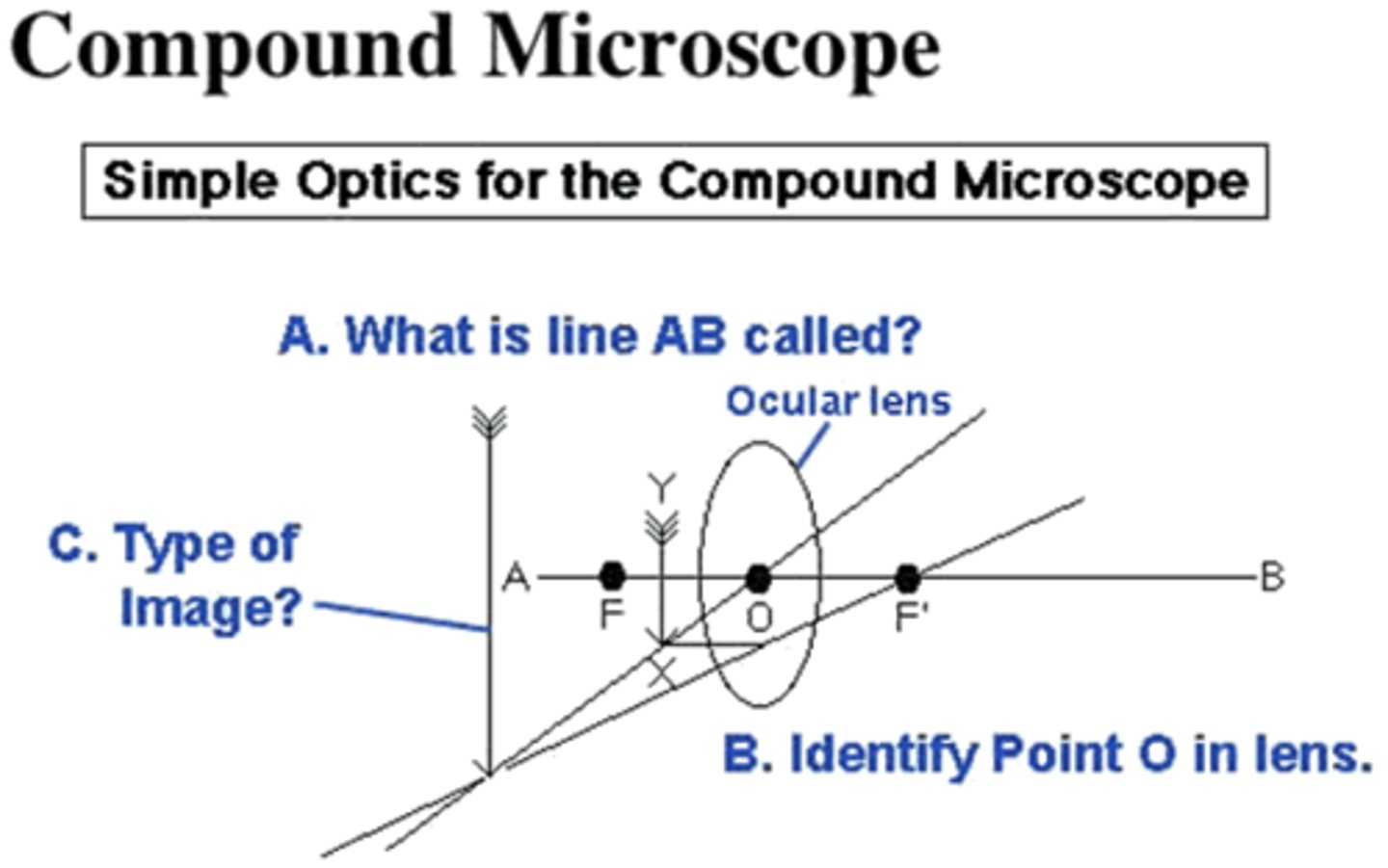
What is line AB called in the image below?
1. imaginary image
2. object
3. principle axis
4. optical center
5. focal point
6. real image
principal axis
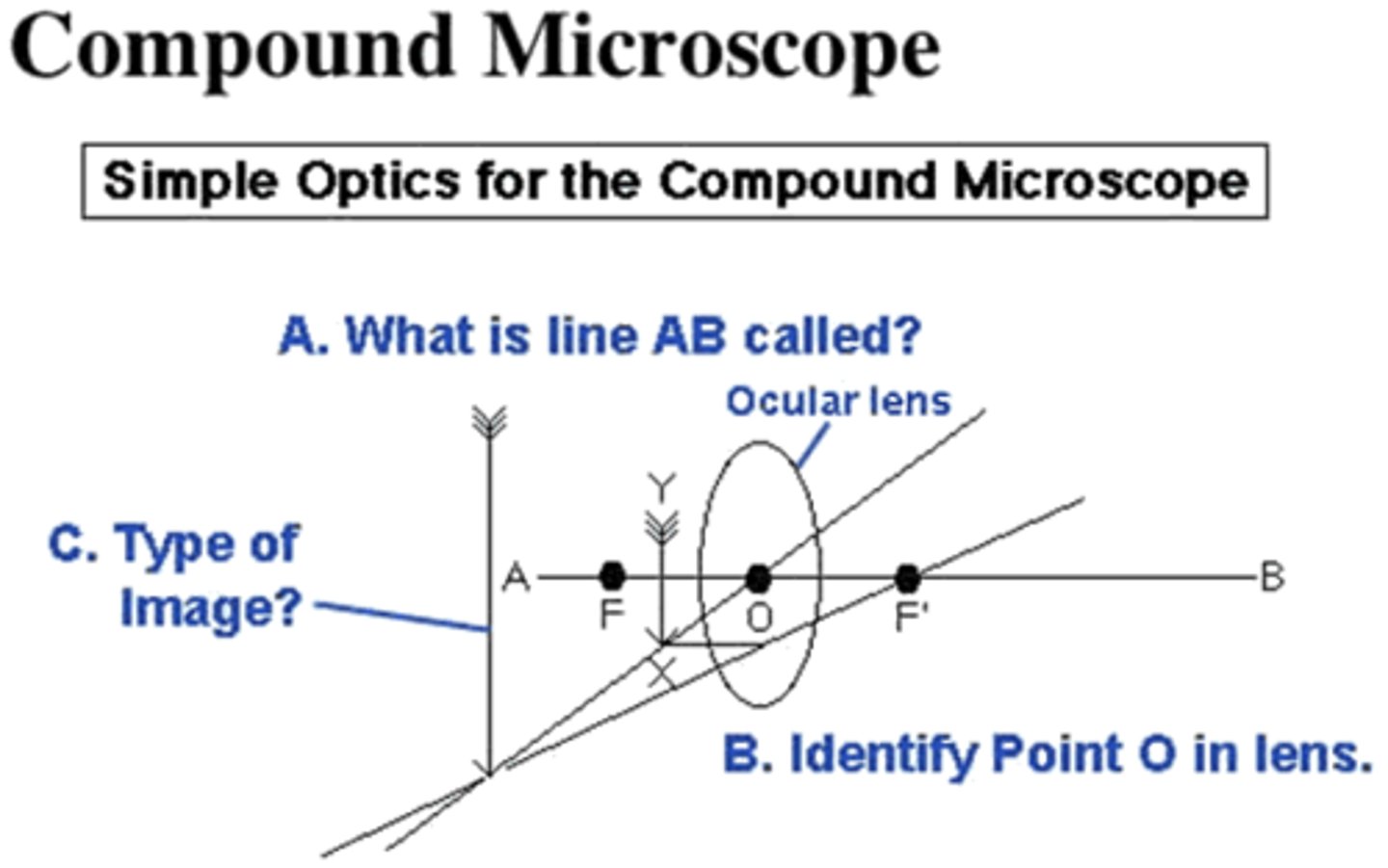
Answer only Question A on the image below:
1. real image
2. focal point
3. object
4. imaginary image
5. optical center
6. principle axis
focal point
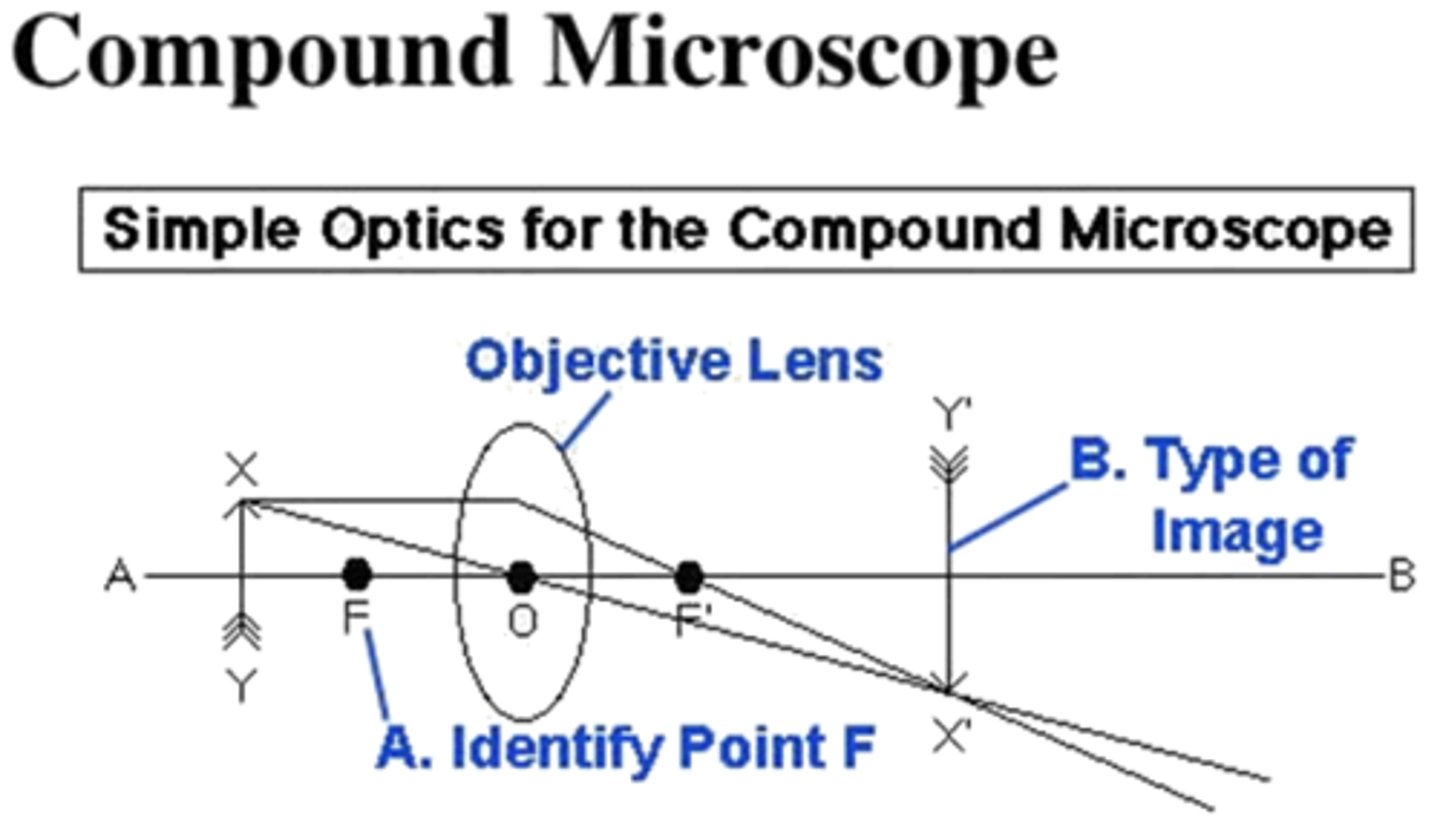
answer question b on the image below
1. real image
2. imaginary image
3. principle axis
4. optical center
5. object
6. focal point
optical center
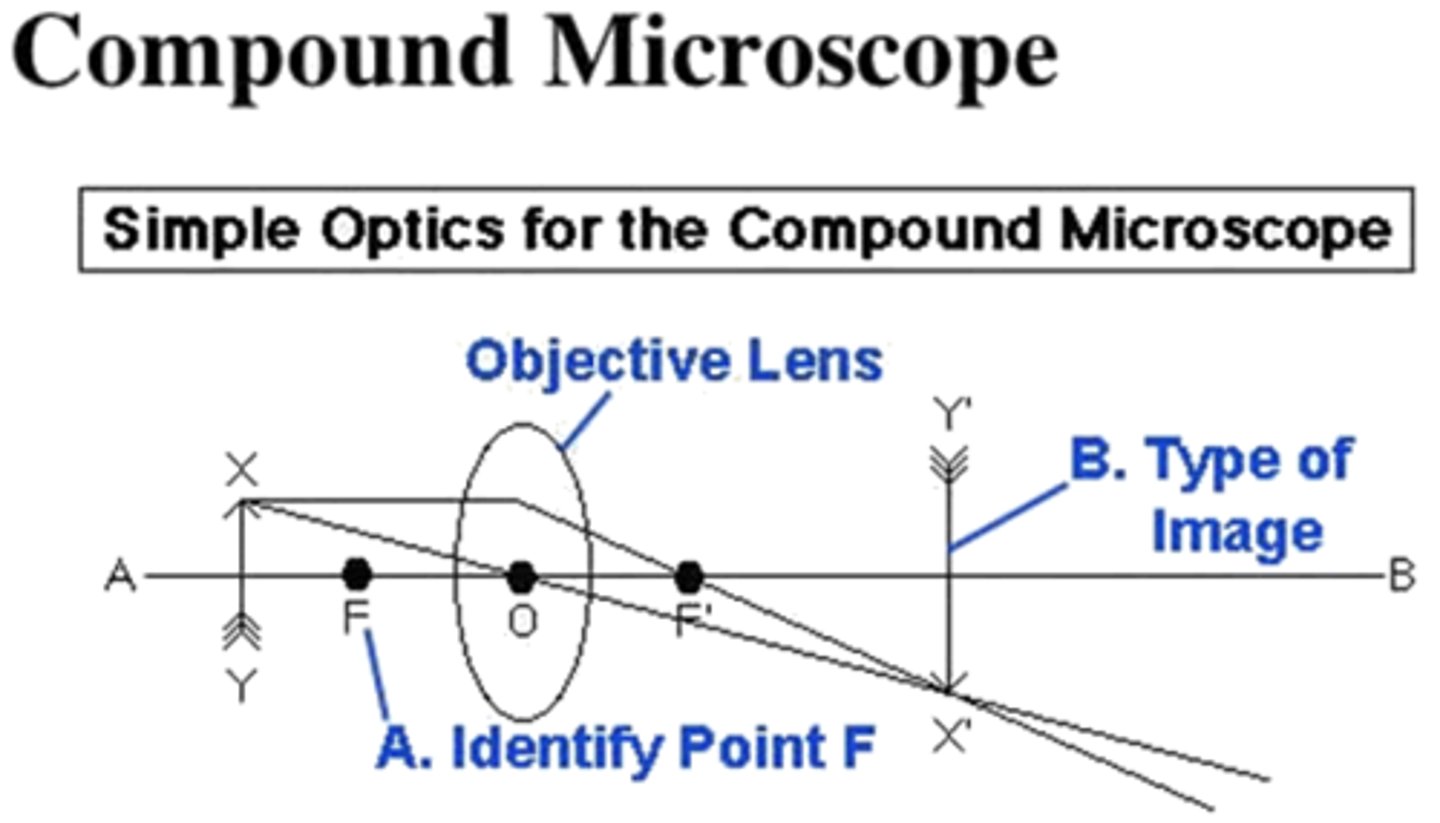
Answer Question B on the image below:
1. real image
2. imaginary image
3. principle axis
4. optical center
5. object
6. focal point
real image
Answer Question B.
1. principle axis
2. focal point
3. object
4. optical center
5. imaginary image
6. real image
optical center
Fusion of a secretory vesicle with the plasma membrane is termed:
exocytosis
T/F: An amphipathic molecule possesses a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic portion.
true
T/F: A phospholipid is not an amphipathic molecule
false
Which function listed below is not one associated with the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
exocytosis
T/F: Phospholipids in the cell membrane are arranged so that their non-polar ends face outward away from the middle and their polar regions face inward toward the middle of the membrane.
false
where in the oviduct regions would you expect to find lining epithelium with the most cilia?
fimbrae and ampulla
choose from the options below the correct order of oviduct regions that an ovulated egg must pass through from the ovary to the uterus?
infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus, pars distalis
what is similar about the kidney nephron and the lymphatic system?
both filtrate substances
in looking at the lining of the kidney nephron, which part below shows tubules lined with cuboidal cells having many microvilli?
proximal convuluted tubule
which of the following is associated with spermiogenesis?
the formation of functional sperm by the stripping away of extra cytoplasm
people who undergo severe injury such as crushing of the limbs can suffer shock which results in what symptoms?
spasm or contraction of kidney blood vessels
which function below takes place in the primary covulated tubule of the kidney nephron under healthy conditions?
Na+ reabsorption
which organ or gland does not have both exocrine and endocrine secretions?
not kidney, liver, nor pancreas
T/F: once the secretory vesicle or granule delivers its contents to the plasma membrane for exocytosis, the membrane of the secretory vesicle or granule becomes part of the plasma membrane
true
the proacrosmal granules formed in the golgi region of the maturing sperm stains with PAS (periodic acid schiff) stain which is indicative of a substance rich in what?
polysaccharides
T/F: Primary spermatocytes undergo mitosis to produce secondary spermatocytes.
false
Each ovary is covered by a germinal epithelium which is what type of epithelium?
1. stratified squamous
2. pseudostratified squamous
3. simple squamous
4. simple cuboidal
simple cuboidal
The Graafian Follicle is also called a:
1. Primary Follicle
2. Tertiary Follicle
3. Primordial Follicle
4. Secondary Follicle
Secondary Follicle
T/F: The next layer beneath the germinal epithelium in the ovary is where the follicles are found.
false
T/F: If no fertilization takes place, the corpus luteum degenerates permitting the ovary to begin secretion of follicle stimulating hormone which starts the menstrual cycle again.
false
T/F: Primordial Follicles can be found in the medulla and consists of a large oocyte surrounded by a single layer of flattened epithelium.
false
When a primary oocyte enters the long prophase of meiosis I, its 46 chromosomes become microscopically discernable as long, slender threads and is described as ____________.
1. zygotene
2. dictyotene
3. pachytene
4. diplotene
5. leptotene
leptotene
______________ from the anterior pituitary stimulates the interstitial cells in the testis to produce testosterone.
1. Follicle stimulating hormone
2. Androgen-binding protein
3. Inhibin hormone
4. Luteinizing hormone
Luteinizing hormone
If fertilization of an ovulated egg occurs, what hormone action below is true.
1. Follicle Stimulating Hormone stimulates oocyte maturation
2. Estrogen stimulates Follicle Stimulating Hormone
3. Progesterone stimulates production of Luteinizing Hormone
4. Progesterone inhibits production of Luteinizing Hormone
Progesterone inhibits production of Luteinizing Hormone
The syncitiotrophoblast found in the late blastocyst is unusual because it ___________________.
1. arises from the inner cell mass of the late blastocyst
2. forms Nabothian cysts
3. consists of layers of pale staining cells
4. is formed of cells that have fused together to form a multinucleated mass with no cell boundaries
is formed of cells that have fused together to form a multinucleated mass with no cell boundaries
T/F: Spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis describe the same process of sperm maturation.
false
T/F: Primary oocytes form during prenatal life just like sperm.
false
T/F: During gestation, there is a placental barrier which separates the blood of the mother from the fetus.
true
T/F: The exocrine portion of the testis produces testosterone.
false
The prostate is composed of many _________ glands
1. simple alveolar
2. compound tubular
3. simple tubular
4. compound tubuloalveolar
compound tubuloalveolar
If marked breast enlargement occurs in males at puberty, it is referred to as _________________.
1. corpus albicans
2. atresia
3. gynecomastia
4. colustrum
gynecomastia
T/F: When the Graafian Follicle matures, its size spans the width of the ovary cortex.
true
T/F: Spermatids form into spermatozoa without undergoing cell division.
true
The portion of the penis which is trimmed during circumcision is called the ____________.
1. corpus spongiosum
2. prepuce
3. tunica albuginea
4. corpora cavernosa
prepuce
The unusual feature of the second maturation division for a maturing oocyte is that _____________________.
1. no DNA synthesis occurs
2. no polar body is produced
3. chiasma are easily seen
4. two polar bodies are produced
no DNA synthesis occurs
T/F: One of the roles of the Sertoli cells is to phagocytose residual cytoplasm extruded by devloping sperm
true
T/F: As the Primordial Follicle matures, the adjacent connective tissue forms a capsular sheath around follicle cells called the theca folliculi.
true
______________ cells are present between seminiferous tubules and produce increased levels of testosterone during puberty to promote spermatogenesis.
1. Stem
2. Sertoli
3. Interstitial (Leydig)
4. Myoid
Interstitial (Leydig)
T/F: The formation of the corpus luteum following ovulation is important because the corpus luteum then begins to secrete estrogens.
false
T/F: In the adult, the Sertoli cells are fixed to the basal lamina of the seminiferous epithelium.
true
The chief initial placental source of human chorionic gonadotrophin is the ________________.
1. syncytiotrophoblast
2. Nabothian cysts
3. cytotrophoblast
4. corpus albicans
cytotrophoblast
Which function below does not belong to the oviduct.
1. transports egg to uterus
2. provides environment for fertilization
3. endometrium undergoes thickening
4. receives ovum
endometrium undergoes thickening
T/F: Male primordial germ cells arise from the yolk sac mesoderm.
false
In a cross section of a sperm at the midpiece, the axoneme is surrounded by _____________.
1. the mitochondrion and the coarse fibers
2. the coarse fibers
3. the mitochondrion
4. the dorsal and ventral columns of coarse fibers
the mitochondrion and the coarse fibers
Which is the correct sequence below to describe the process of spermiogenesis.
1. cap phase to Golgi phase to acrosomal phase
2. Golgi phase to cap phase to acrosomal phase
3. Golgi phase to acrosomal phase to cap phase
4. acrosomal phase to Golgi phase to cap phase
Golgi phase to cap phase to acrosomal phase
Prenatal development of the primary oocyte is completed by its entering a protracted resting stage knowns as _____________.
1. leptotene
2. pachytene
3. zygotene
4. dictyotene
5. diplotene
dictyotene
T/F: The space inside the seminiferous tubules is really a space that is continuous with the space outside your body mass.
true
_____________ cells are tall simple columnar cells found in the seminiferous tubules which provide a nourishing environment for sperm development.
1. Myoid
2. Interstitial (Leydig)
3. Sertoli
4. Stem
Sertoli
The funnel shaped opening of the oviduct that opens into peritoneal cavity and is situated near the ovary is called the:
1. pars interstitialis
2. isthmus
3. infundibulum
4. ampulla
infundibulum
The spermatogonia which produce primary spermatocytes are called:
1. Dark type A spermatogonia
2. Type B spermatogonia
3. Secondary spermatocytes
4. Pale type A spermatogonia
Type B spermatogonia
Which of the listed components is not part of the uterine mucosa or endometrium?
1. simple columnar epithelium
2. simple tubular endometrial glands
3. endometrial stroma
4. myometrium
myometrium
A hormone called _________ is produced by the corpus luteum towards the end of pregnancy which functions to soften the dense connective tissue of the cervix.
1. progesterone
2. estrogen
3. relaxin
4. inhibin
relaxin
T/F: At the time of ovulation, the muscles of the oviduct contract rhythymically in the direction of the uterus helping to move the egg toward uterus.
true
The maternal portion of the placenta is derived from the region of the endometrium that underlies the implantation site called the ________________.
1. amnion
2. chorion
3. decidua basilis
decidua basilis
T/F: In the ovary, the atretic follicles are those that are next in line to ovulate.
false
Fertilization of the human egg normally occurs in the ____________ region of the oviduct.
1. isthmus
2. infundibulum
3. pars interstitialis
4. ampulla
ampulla
T/F: Pre-cancerous lesions and carcinomas of the cervix are most likely to develop at the junction where the stratified squamous nonkeratinizing epithelium of the cervical canal meets the simple columnar epithelium of the vagina,
false
If fertilization of the ovulated egg does not occur, the corpus luteum involutes to form a small white fibrous scar called the corpus _________.
1. radiata
2. inhibin
3. lutein
4. albicans
albicans
The region of the oviduct which passes into the uterus is called the:
1. ampulla
2. isthmus
3. pars interstitialis
4. infundibulum
pars interstitialis
T/F: Between the developing oocyte and the follicular cells is formed the zona pellucida.
true
T/F: The Theca interna is composed primarily of connective tissue supporting blood vessels which form a capillary bed in the theca externa.
false
T/F: The viscosity of cervical mucus is of a relatively thin consistency prior to ovulation making it easier for spermatozoa to negotiate.
true
Renewing stem cells which produce mature sperm are called:
1. Pale type A spermatogonia
2. Dark type A spermatogonia
3. Secondary spermatocytes
4. Type B spermatogonia
Pale type A spermatogonia
The fetal portion of the placenta is derived from the _____________
1. chorion
2. amnion
3. decidua basilis
chorion
The outer edge of the oviduct infundibulum forms a fringe-like area called:
1. stigma
2. villi
3. fimbrae
4. cumulus oophorus
fimbrae
T/F: The presence of intercellular bridges providing cytoplasmic continuity between developing spermatogonia of the same cell lineage explains why these cells develop in synchrony.
true
T/F: In the seminiferous tubules, spermatogenic cells are located throughout the network of Sertoli cells with the earliest germ cells located closest to the basal lamina of the seminiferous tubule.
true
The outermost mesothelial covering of the testis is derived from the membranous lining of a serous sac evaginated from the _________________.
1. prostate
2. peritoneum
3. seminiferous tubules
4. seminal vesicles
peritoneum
Name the type of epithelium lining the oviducts
1. stratified squamous
2. pseudostratified squamous
3. simple squamous
4. simple columnar
simple columnar
The testis is surrounded by a thick fibrous capsule called the:
1. tunica albuginea
2. germinal epithelium
3. fibrous epithelium
4. theca externa
tunica albuginea
As the Graafian Follicle matures, fluid is secreted to form a crescent-shaped cavity called the:
1. cumulus oophorus
2. corpus luteum
3. zona pellucida
4. antrum
antrum
The 2/3 portion of the oviduct closest to the uterus is called the:
1. pars interstitialis
2. infundibulum
3. isthmus
4. ampulla
isthmus
The outermost mesothelial covering of the testis is termed the _________________.
1. ductili efferentes
2. rete tesis
3. tunica albuginea
4. tunica vaginalis testis
tunica vaginalis testis
Reserve stem cells which produce mature sperm are called:
1. Type B spermatogonia
2. Pale type A spermatogonia
3. Dark type A spermatogonia
4. Secondary spermatocytes
Dark type A spermatogonia
0.001mm is equivalent to
1. 1 angstrom
2. 1 micron
3. 0.1nanometer
4. 1 nanometer
1 micron
T/F: A cryostat is a special type of microtome used in surgical analysis to produce frozen tissue sections.
true
T/F: A compound light microscope normally found in student labs consists of a convex lens known as the objective lens and a concave lens called the ocular lens.
false
T/F: An imaginary image is one that can only be viewed by looking through the lens such as in a magnifying glass.
true
T/F: An imaginary image is produced when the object to be viewed is placed inside the focal point of the convex lens.
true
T/F: A transmission electron microscope employs an electron beam which passes through a tissue section and is captured on a photographic plate for a permanent record
true
T/F: A scanning electron microscope is used when the electron beam passes through the thin tissue section in a fast scanning motion
false
A special microtome able to produce very thin sections must be used for tissue samples to be used with the electron microscope for the following reason:
1. to see the finer structure of tissue cells at higher magnification
2. to more easily permit light to be transmitted through the tissue section
3. to inhibit heat build-up while observing tissues with the electron microscope
4. to permit the passage of electrons through the tissue section
to permit the passage of electrons through the tissue section
Choose the best answer which fits how a phase contrast microscope works
1. utilizes the components of a light optical microscope with a scanning system which can produce images of biological specimens in three dimensions
2. utilizes a polarizing filter with light microscope to study the difference in the angles of rotation when molecules or structures are present in a highly ordered fashion in cells and tissues
3. utilizes light projected onto the specimen from an angle so that only scattered light reaches the objective lens
4. utilizes small differences in the refractive index to visualize different cell parts
Utilizes small differences in the refractive index to visualize different cell parts
Light microscope sections must be thin for the following reason:
1. to make it easier to remove water from the section
2. to inhibit cell breakdown due to enzymatic action
3. to permit fast and reliable staining
4. to more easily permit light to pass through the section
to more easily permit light to pass through the section
T/F: Histology is primarily the study of the structure of cells, tissues, and organs and the relationship of microscopic structure and function.
true
T/F: In simple optics of a convex lens, an imaginary image is one that can be projected onto a screen and viewed with our own eyes.
false
T/F: In a compound microscope, the objective lens produces an image that falls outside the focal point of the ocular lens.
false
T/F: In an electron microscope, the glass lens must be of a special construction to permit the electrons to pass through.
false
If the object size is 1 microns, calculate the magnification produced using a 50x objective lens and 10x ocular lens
1. 1000 microns
2. 2500 microns
3. 500 microns
4. 3500 microns
500 microns
In the paraffin technique for producing sections for microscopic study, which statement describes the process of dehydration, clearing and embedding.
1. the fixed tissue is first placed in xylene and then paraffin
2. the fixed tissue is placed in successively stronger ethyl alcohol concentrations, xylene and then paraffin
3. the fixed tissue is heated and placed directly in paraffin
4. the fixed tissue is placed in successively stronger ethyl alcohol concentrations and then in paraffin
the fixed tissue is placed in successively stronger ethyl alcohol concentrations and then in paraffin
If you would like to produce a three dimensional image of a biological specimen, which type of microscope listed would you use?
1. phase contrast microscope
2. confocal scanning microscope
3. polarizing microscope
4. fluorescence microscope
confocal scanning microscope
T/F: Staining of a tissue section is necessary to provide contrast to cellular components to make them visible in the light microscope.
true
T/F: Tissues are composed solely of particular types of cells
false
T/F: Our brains invert the image on our retina so that we can see the world right-side up
true