Neurons and Glial cells
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
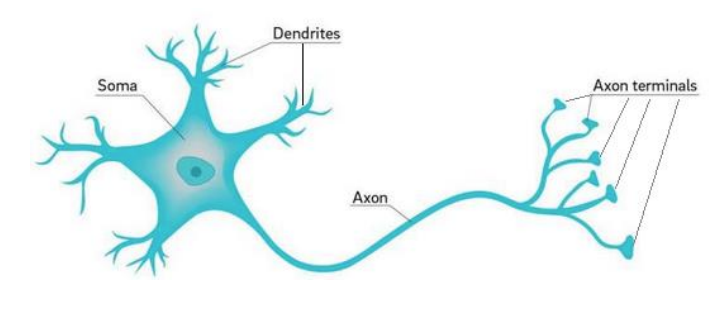
Each neuron contains
cell body (soma)
dendrites
1 axon with axon terminals
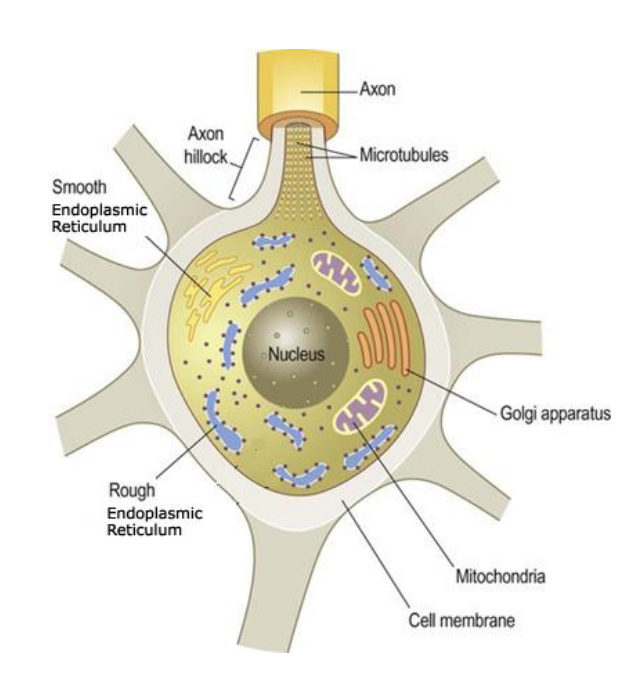
Cell body
Carries out the living processes of neurons, contains important organelles that help do this:
nucleus - contain DNA
Mitochondria - powerhouse of the cell
ER & GA - produce & release neurotransmitters
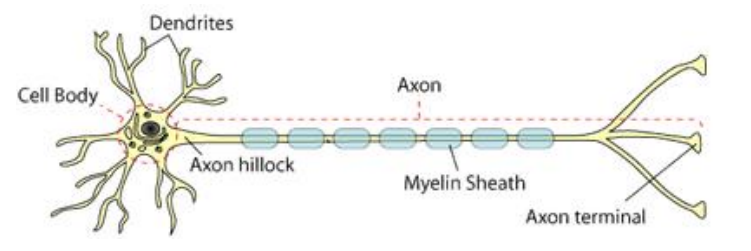
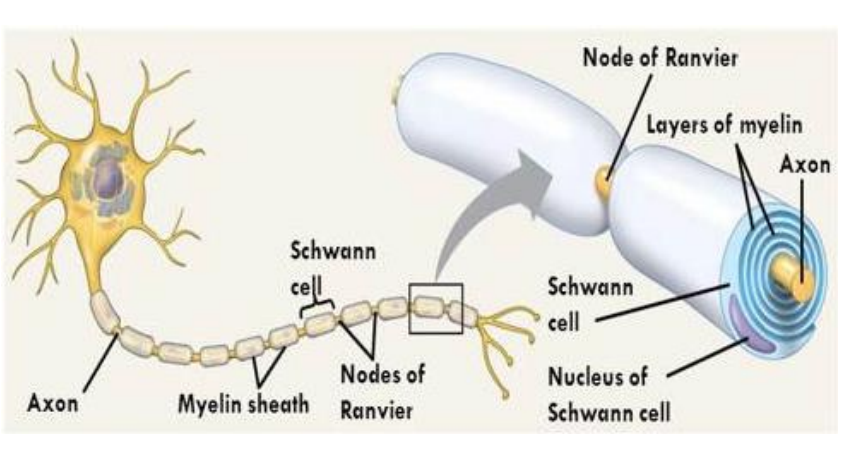
Axon
contains axon hillock - where nerve impulse is generated, not covered in myelin
can be covered in myelin - insulates and protects fibres, speeds up rate transmission of nerve impulses
can branch and have own processes
axon terminal - region where transmitter are stored and released, forms synaptic contacts with other cells
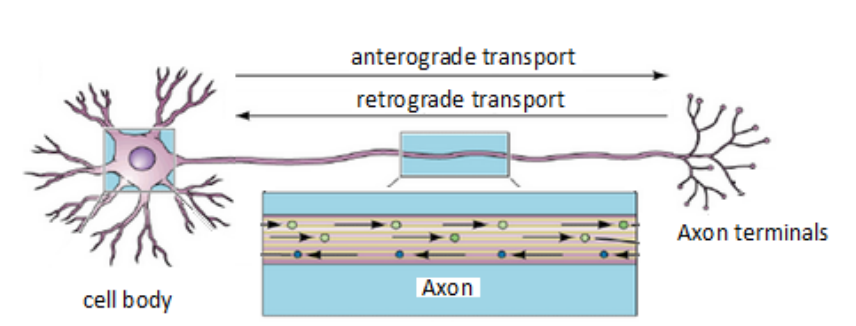
Axon transport
carries important material between cell body & axon terminals -
Axon contains microtubules:
allows transport of substances in both directions:
anterograde transport = cell body to terminals, e.g. transmitter
retrograde transport = terminals to cell body, e.g. worn-out mitochondria, membrane components
Dendrites
function: receive signals and bring info to the cell body
are covered by thousands of tiny dendritic spines - each creating a synapse with axon terminals of other neurons
play an important role in learning
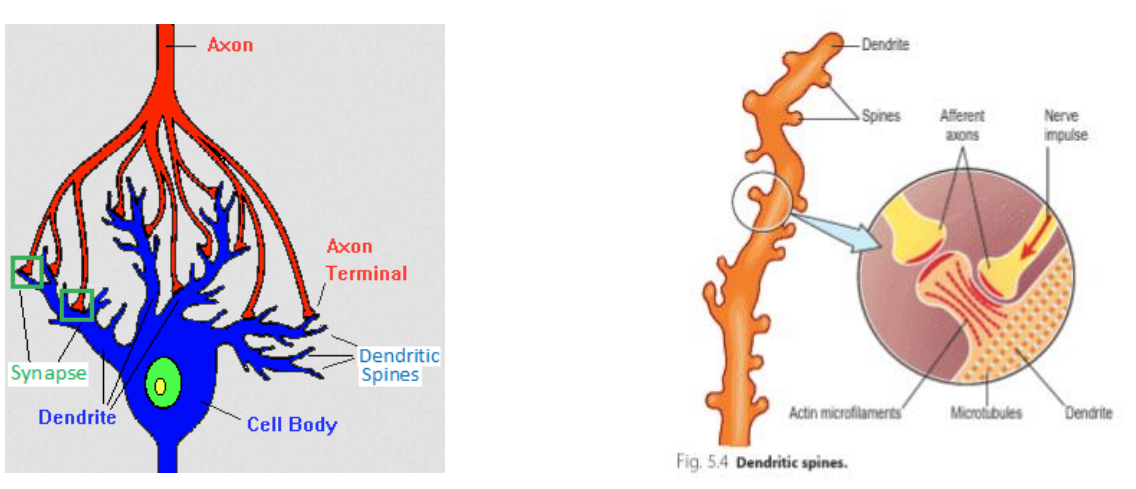
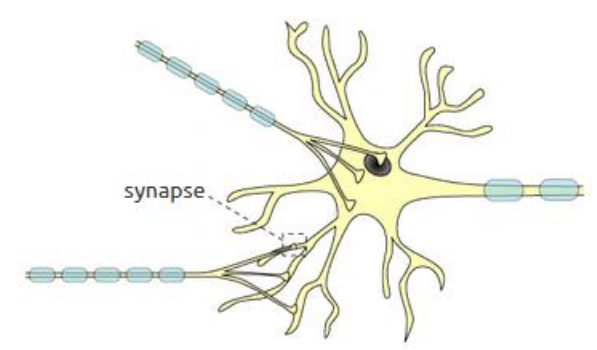
Synapse
= connections between neurons
typical neuron of the cortex creates thousands of synapses with other neurons
Dendrites & cell body are covered with synapses
Axons usually have synapses only at the axon terminal
New connections between neurons = structural foundation for learning
Cortical neurons
Pyramidal cells
Purkinje cells
Granule cells
Pyramidal cells
long axon
found in neocortex
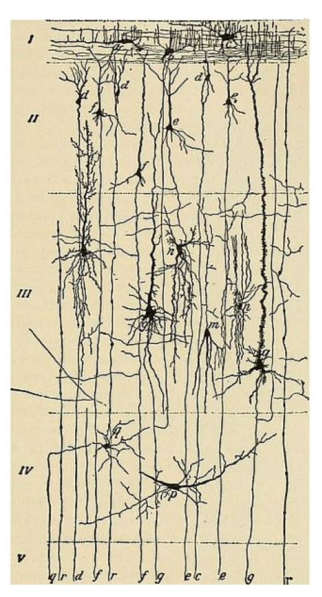
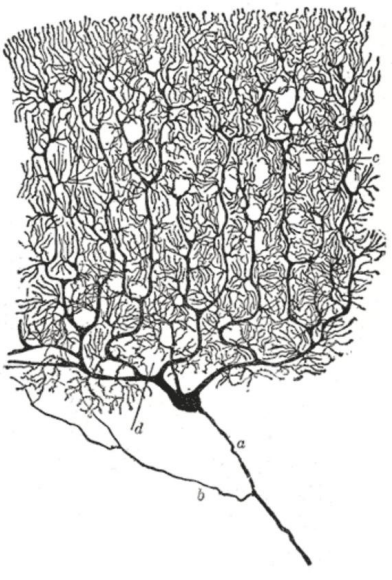
Purkinje cells
similar to pyramidal in shape, but many more dendritic spines
found in cerebellar cortex
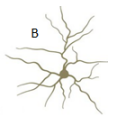
Granule cells
star-shaped, short axons = make local contacts with other cells
in sensory cortices
Neuroglia Functions
create structural support for the brain
serve to support & protect neurons
DO NOT carry nerve impulses
Main Types of Glial cells
astrocytes
microglia
oligodendrocytes & Schwann cells
ependymal cells
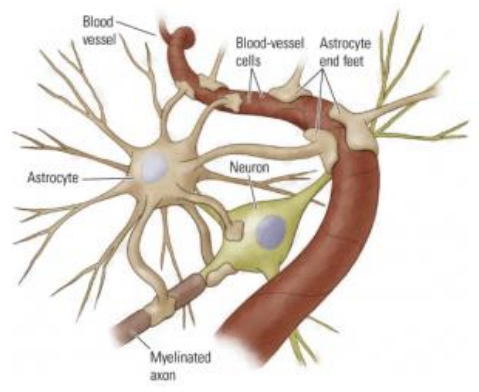
Astrocytes
have their ‘end-feet’ on neurons & blood capillaries
‘end-feet’ wrap around capillaries, creating a protective cover = Blood-Brain barrier
transport nutrients to neurons
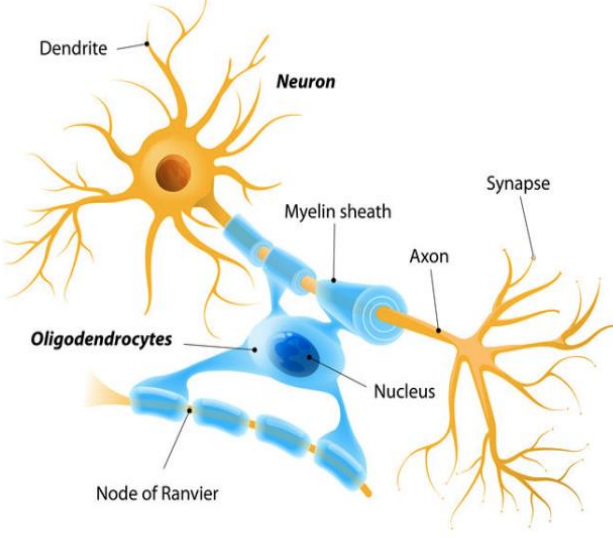
Oligodendrocytes
provide the myelin to neurons in the CNS
wrap tightly around axons to from the myelin sheath
speed up the signal/nerve impulse (AP) that travels down the axon
Schwann cells
cover the axons in the PNS & form the myelin sheath
make contact with only one axon & provide only a single segment of myelin
Microglia
Phagocytes; clean up the CNS
can detect damaged/injured or unhealthy neurons and waste products/dead material
travel towards these and digest them
eat foreign invaders (bacteria & viruses)
immune cells of the brain
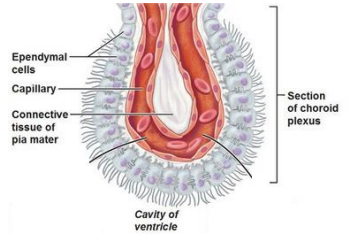
Ependymal cells
cover the ventricles in our brain & the central canal of the spinal cord
protective barrier between brain & cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
cover the choroid plexus of each ventricle
Choroid plexus acts as a blood–CSF barrier