Microbiology Exam 2: Lesson 5-8
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
What is a proglottid?
A segment of a tapeworm containing reproductive organs.
What are tapeworms?
Flatworms (cestodes) with a thin, segmented body; parasitic in humans and animals.
What are roundworms?
Nematodes; unsegmented worms with a full digestive system; some parasitic in humans.
What is a saprobe?
A fungus or microorganism that feeds on dead or decaying organic matter.
What is an autotroph?
An organism that produces its own food (plants, algae, some protists).
What is a parasite?
An organism that lives in or on a host, deriving nutrients at the host’s expense.
What does monoecious mean?
A helminth with both male and female reproductive organs in one organism.
What does dioecious mean?
A helminth species where male and female are separate organisms.
What is the endosymbiotic theory?
Theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from free-living bacteria engulfed by early eukaryotic cells.
Mitochondria are descendants of purple non-sulfur bacteria.
Chloroplasts are descendants of cyanobacteria.
Nucleus function?
Control center; site of DNA replication, transcription (DNA to RNA), RNA processing.
traffic controlled by nuclear pores
Endoplasmic reticulum function?
Rough ER = protein synthesis; Smooth ER = lipid processing/storage.
Ribosome function?
Protein synthesis (80S ribosomes)
Golgi apparatus function?
Modifies and ships proteins.
Mitochondrion function?
Generates ATP (cell energy).
Chloroplast function?
Photosynthesis in plants/algae.
Cytoskeleton function?
Provides structure, anchors organelles, allows movement.
Plasma membrane function?
Selectively permeable barrier.
Flagella function?
Movement, thicker than prokaryotic flagella, 9+2 microtubule arrangement.
Cilia function?
Short, numerous; movement, feeding, filtering.
beat in oar-like strokes
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic cells nucleus?
Prokaryotes lack; eukaryotes have.
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic cells Organelles?
Prokaryotes = none; eukaryotes = many membrane-bound.
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic cells DNA?
Prokaryotes = single, circular chromosomes; eukaryotes = multiple, linear chromosomes
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic cells Ribosomes?
Prokaryotes = 70S; eukaryotes = 80S.
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic cells, cell wall?
Prokaryotes = peptidoglycan;
fungi = chitin;
protozoa/helminths = none.
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic cells flagella?
Eukaryotic
-Flagellum is thicker
-covered by extension of the cell membrane
-microtubules in a 9+2 arrangement
-microtubules slide past each other creating a whipping motion
Fungi
Saprophytic decomposers & pathogens
they are heterotrophic
Protists
Diverse single-celled organisms
most are harmless, free living inhabitant of water and soil
Helminths
Parasitic worms (studied microscopically) adults specimen are usually large enough to be seen with the naked eye
include tapeworms, flukes, and roundworms
What are the main forms of Fungi?
Macroscopic: mushrooms, puffballs, gill fungi
Microscopic growth forms: Yeasts (unicellular) vs. Molds (multicellular. filamentous)
Dimorphic: can switch between yeast and mold forms
Dimorphic
fungi can switch between yeast and mold forms.
-yeast form in body heat
-mold form at room temp.
Mold characteristics
Hyphae, Mycelium, and thallus
What is mycelium?
Tangled network of hyphae (body of mold).
What are hyphae?
Filamentous structures that make up molds (septate-divided in distinct cellular compartments or coenocytic- no separations).
What is a spore?
Reproductive structure of fungi. such as conidia
What is a yeast cell?
Round/oval unicellular fungus.
How do yeast cells replicate?
By asexual budding.
What are the two categories of fungi that cause human disease?
Primary pathogens – infect healthy individuals.
Opportunistic pathogens – infect immunocompromised individuals. (weakened immunity)
Mycoses
fungal infection
What is a trophozoite?
Active, motile, feeding stage of protozoa. it needs food and moisture
What is a cyst?
Dormant, resistant stage for survival when conditions in environment become unfavorable (encystment) and transmission.
what are the two life cycle and reproduction of protozoa?
Trophozoite and cyst
Which protozoan causes trichomoniasis?
Trichomonas vaginalis.
Which protozoan causes malaria?
Plasmodium spp.
Which protozoan causes brain infection (brain-eating amoeba)?
Naegleria fowleri.
What are the life stages of helminths?
Egg → Larva → Adult.
egg and larva are microscopic
How are pinworm infections diagnosed?
Scotch tape test.
What are flukes?
Non-segmented flatworms (trematodes).
What are tapeworms?
Segmented flatworms (cestodes), e.g., pork tapeworm (Taenia).
Example of a roundworm parasite?
Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm).
What is a virulent phage?
A bacteriophage that reproduces only by the lytic cycle
What is a temperate phage?
A phage that can reproduce by both the lytic and lysogenic cycles
What is host range?
The spectrum of host cells a virus can infect.
What is an obligate intracellular parasite?
A virus that can only reproduce inside a living host cell (cannot replicate independently).
How are viruses described?
as active or inactive rather than alive or dead
What are the main components of a virion?
Nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), capsid (made of capsomeres), envelope, and spikes
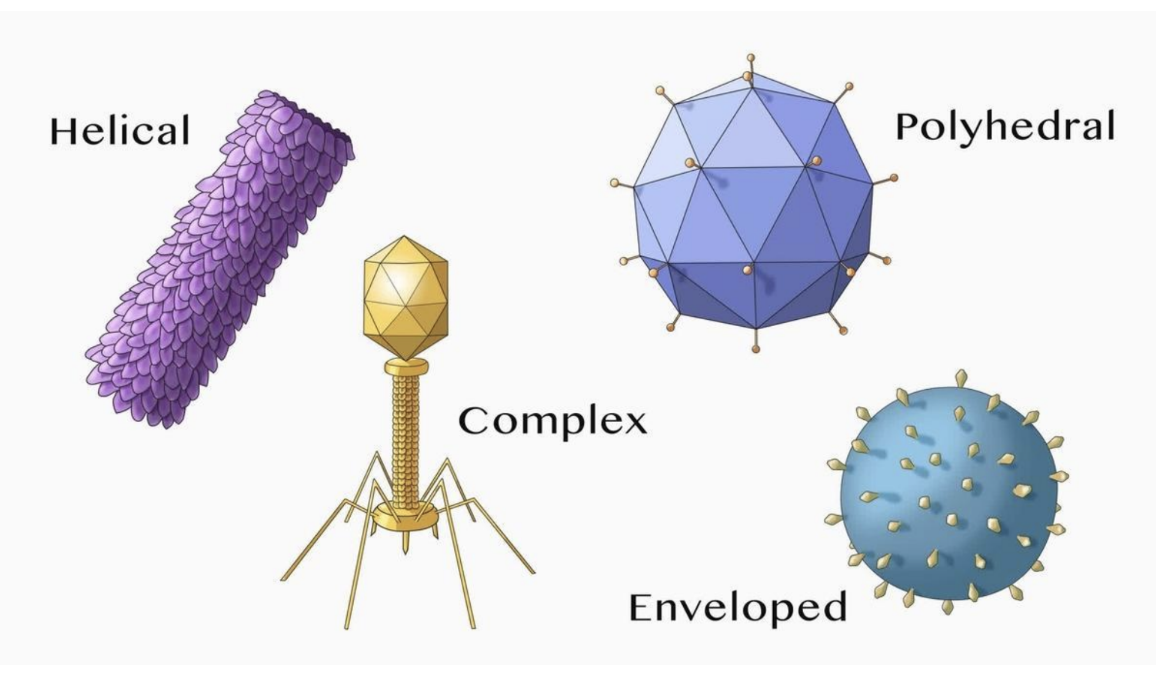
What are the four virion morphologies?
Helical, polyhedral, enveloped, complex
What are the two major virus classification systems?
ICTV(international committee on taxonomy of viruses)and Baltimore classification
How do we grow viruses?
Viruses must be grown in living cells:
Bacteriophages = plaques on bacterial lawns.
Animal viruses = animals, embryonated eggs, or cell cultures
How can we identify viruses?
Cytopathic effects (cell damage).
Serological tests – detect antibodies or viral proteins (neutralization, hemagglutination, Western blot).
Nucleic acid methods – PCR, qRT-PCR
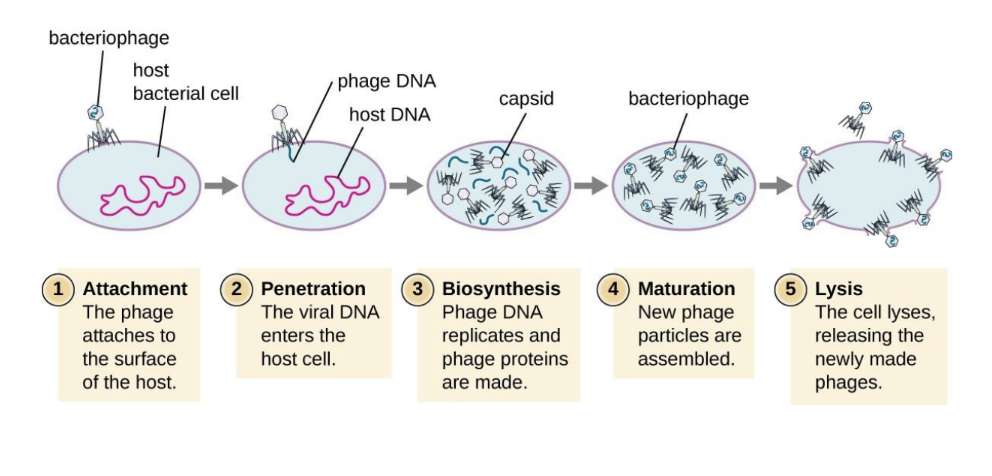
describe the lytic cycle of bacteriophage
phage causes lysis and death of host cell
1) Attachment- phage attaches by tail fibers to host cell
2) Penetration- lysozyme opens cell wall; tail sheath contracts to force DNA into cell
3) Biosynthesis- Production of phage DNA and proteins
4) Maturation- Assembly of phage particles
5) Release- Phage lysozyme breaks cell wall
6) Burst time- Amount of time it takes for the virion to mature from penetration to release
7) Burst size- how many virions are release
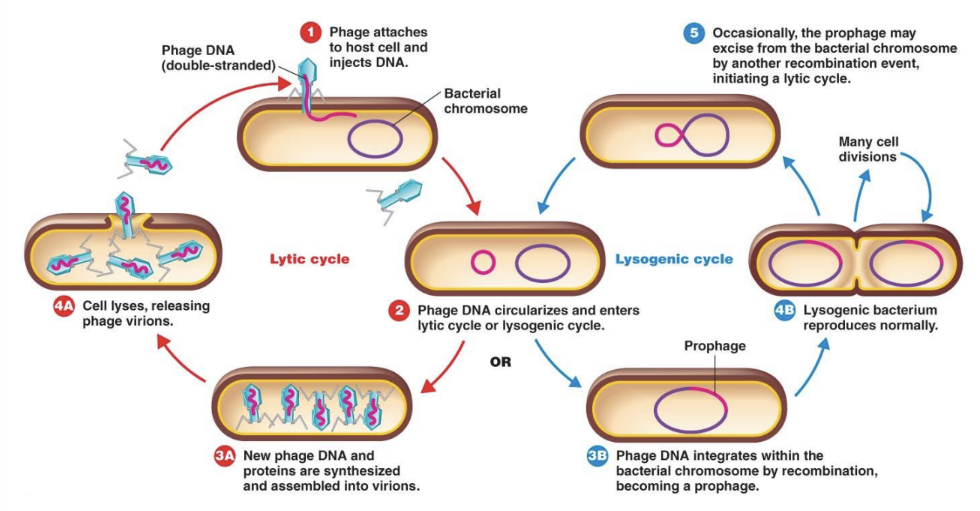
describe the lysogenic cycle of bacteriophage
Viral DNA integrates into the host genome (becoming a prophage) and replicates with the host cell without killing it immediately.
prophage DNA incorporated in host DNA
phage conversion- viral DNA can give bacteria new characteristics
Define lysogenic conversion
When a bacterium acquires new traits from a temperate phage’s DNA (e.g., toxin production in Corynebacterium diphtheriae or Vibrio cholerae)
Define latent infections
Virus remains dormant in host, reactivates later (e.g., herpes, shingles)
Know what prions are and specific names. How are they infectious and how acquired?
Prions: Infectious proteins (no nucleic acid)
Diseases: Scrapie (sheep), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome, fatal familial insomnia, mad cow disease
Infectious by: Misfolding host proteins; transmitted via inheritance, ingestion, transplants, surgical instruments
Know how plant viruses are transmitted and define viroids
Plant viruses: Enter through wounds or insect vectors
Viroids: Infectious naked RNA molecules that cause plant diseases (e.g., potato spindle tuber disease)
How can humans become susceptible to avian or swine flu?
Through zoonotic transmission – influenza viruses mutate or reassort in animals and then infect humans
What are the main ways viruses are transmitted?
Horizontal transmission (same generation):
Airborne/respiratory droplets
Direct contact
Indirect contact
Animal vectors (e.g., dengue, Zika)
Vertical transmission (mother → fetus):
Examples: HIV, Zika, Rubella
What are the two types of bacteriophage replication cycles?
Lytic cycle (destroys host) and lysogenic cycle (host survives with integrated viral DNA)
What is energy?
Energy is the capacity to do work, such as moving, growing, and reproducing.
What is metabolism?
Metabolism is all the chemical reactions in the cell.
What is the difference between anabolic and catabolic pathways?
Anabolic pathways build molecules and require energy; catabolic pathways break down molecules and release energy.
What is a metabolic pathway?
A sequence of chemical reactions, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme.
What is an enzyme and how do enzymes work?
Enzymes are biological catalysts (mostly proteins) that lower activation energy and speed up reactions. They bind substrates at the active site.
What is the enzyme-substrate complex and induced fit?
The enzyme-substrate complex forms when the enzyme binds the substrate. Induced fit is when the enzyme changes shape to better fit the substrate.
What determines substrate specificity in enzymes?
The unique shape of an enzyme's active site determines which substrates it can bind.
What factors influence enzyme activity?
Temperature and pH can denature proteins and affect enzyme activity.
What is competitive inhibition?
When a molecule similar to the substrate binds to the active site, blocking the substrate.
What is non-competitive (allosteric) inhibition?
When an inhibitor binds elsewhere (allosteric site), changing the enzyme's shape so the substrate can’t bind.
What is feedback inhibition?
The end product of a pathway inhibits an early enzyme, slowing or stopping the pathway if too much product is present.
What are the two main types of energy?
Kinetic energy (motion) and potential energy (stored energy).
What is an atom made of?
A nucleus (protons and neutrons) and electrons orbiting the nucleus.
How are chemical bonds formed?
By transferring or sharing electrons between atoms.
How is energy from nutrients made usable by cells?
By transferring energy from nutrients like glucose to ATP.
What is ATP and what is its role in coupling reactions?
ATP stores energy and couples exergonic and endergonic reactions in the cell.
What is cellular respiration?
A catabolic pathway that transfers energy from glucose to ATP through many steps.
What are the main stages of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain (ETC).
What happens during glycolysis?
In the cytoplasm, 1 glucose becomes 2 pyruvate (pyruvic acid) molecules, a total of 4 ATP molecules, and 2 molecules of NADH. No CO₂ is released and O₂ is not required.
What happens during pyruvate oxidation?
occurs in mitochondria
oxygen is required
Pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA
2 pyruvates —> 2 acetyl CoA , releasing CO₂ and electrons (NADH).
What happens in the Krebs cycle?
occurs in mitochondria
oxygen is required
2 Acetyl CoA enters, chemical bonds are rearranged, electrons and CO₂ are released, 2 ATP and NADH is produced
What is the electron transport chain (ETC) and its function?
Electrons from glycolysis and Krebs cycle are passed down the chain, powering proton pumps and ATP synthase. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor, making water.
In: NADH, FADH₂, O₂; Out: ~34 ATP, H₂O.
oxygen is vital
Where do the steps of carbohydrate catabolism occur in eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes?
Glycolysis: cytoplasm (both); Krebs/Intermediate: mitochondrial matrix (eukaryote), cytoplasm (prokaryote); ETC: mitochondrial membrane (eukaryote), plasma membrane (prokaryote).
What are alternatives to aerobic respiration?
Fermentation and anaerobic respiration (no oxygen required).
What is fermentation?
Continuation of glycolysis that restores NAD+; includes alcohol and lactic acid fermentation.
What is lactic acid fermentation?
Pyruvate is converted to lactate, no CO₂ is released, and NAD+ is regenerated.
What is alcohol fermentation?
Pyruvate becomes acetaldehyde (releasing CO₂), then acetaldehyde is turned to ethanol, regenerating NAD+.
What is anaerobic respiration?
Uses an electron transport chain with a final electron acceptor other than oxygen; yields less energy than aerobic respiration.
What is the difference between facultative and obligate anaerobes?
Facultative anaerobes can respire with oxygen or ferment without it; obligate anaerobes can’t survive in oxygen and only ferment or respire anaerobically.
Microbial growth
increase in number of cells (population/ colonies), not cell size
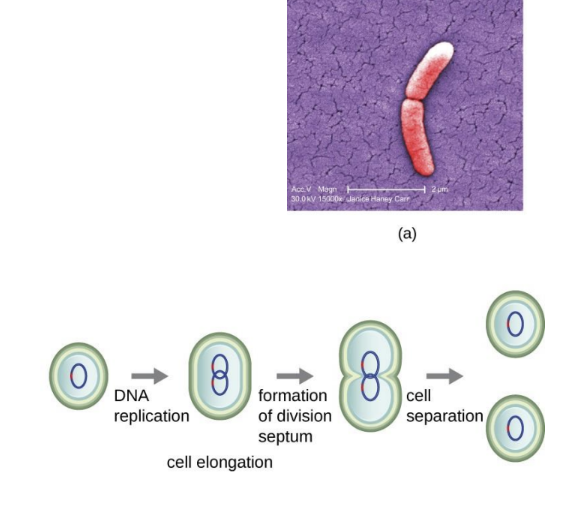
What is binary fission?
A process where one bacterial cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
What is generation time aka doubling time?
The time needed for one cell to divide into two (doubling time).
-Formula: Nf = N₀ × 2ⁿ.
Nf is the final number,
N0 is the initial number,
and n is the number of generations
-the average generation time is 30-60 min