McGraw Hill Marketing Chapter 1-5
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Marketing
An organizational function and a set of processes for creating, capturing, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization
Marketing plan
A written document composed of an analysis of the current marketing situation, opportunities and threats for the firm, marketing objectives and strategy specified in terms of the four Ps, action programs, and projected or pro forma income (and other financial) statements
Exchange
The trade of things of value between the buyer and the seller so that each is better off as a resul
Marketing Mix (Four Ps)
Product, price, place and promotion - the controllable set of activities that a firm
Goods
Items that can be physically touched
Services
Any intangible offering that involves a deed, performance, or effort that cannot be physically possessed; intangible customer benefits that are produced by people or machines and cannot be separated from the producer
Ideas
Intellectual concepts - thoughts, opinions, and philosophies
B2C (Business-to-Consumer)
The process of selling merchandise or services from one business to another
C2C (Consumer-to-consumer)
The process in which consumers sell to other consumers
Value
Reflects the relationship of benefits to costs, or what the consumer gets for what he or she gives
Value Cocreation
Customers act as collaborators with a manufacturer or retailer to create the product or service
Relational Orientation
A method of building a relationship with customers based on the philosophy that buyers and sellers should develop a long-term relationship
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
A business philosophy and set of strategies, programs and systems that focus on identifying and building loyalty among the firm's most valued customers
Supply Chain
The group of firms that make and deliver a given set of goods and services
Marketing Channel
The set of institutions that transfer the ownership of and move goods from the point of production to the point of consumption; consists of all institutions and marketing activities in the marketing process
Entrepreneurs
A person who organizes, operates, and assumes the risk of a new business venture
core aspects of marketing
(1)Satisfying customer needs and wants
(2)About an exchange
(3)Product, price, and promotion decisions
(4)Can be performed by both individuals and organizations
(5)Affects various stakeholders
(6)Helps create value
price
everything the buyer gives up - money, time, & energy- in exchange for the product
promotion
communication by a marketer that informs, persuades, and reminds potential buyers about a product or service to influence their opinions and elicit a response
place
represents all the activities necessary to get the product to the right customer when that customer wants it
product
goods, services, or ideas that satisfy customer needs
Marketing Environment Analysis Framework
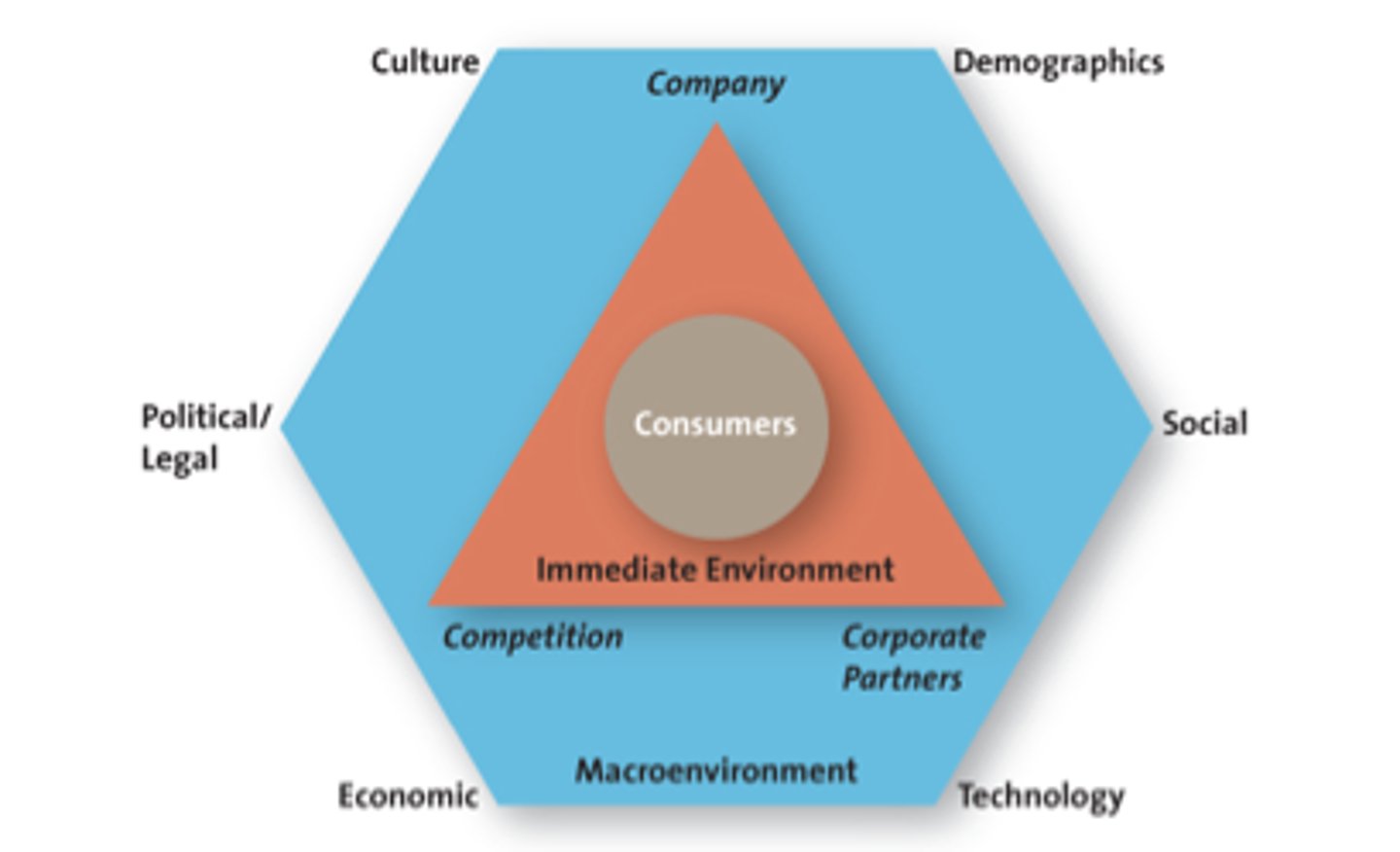
The Immediate Environment
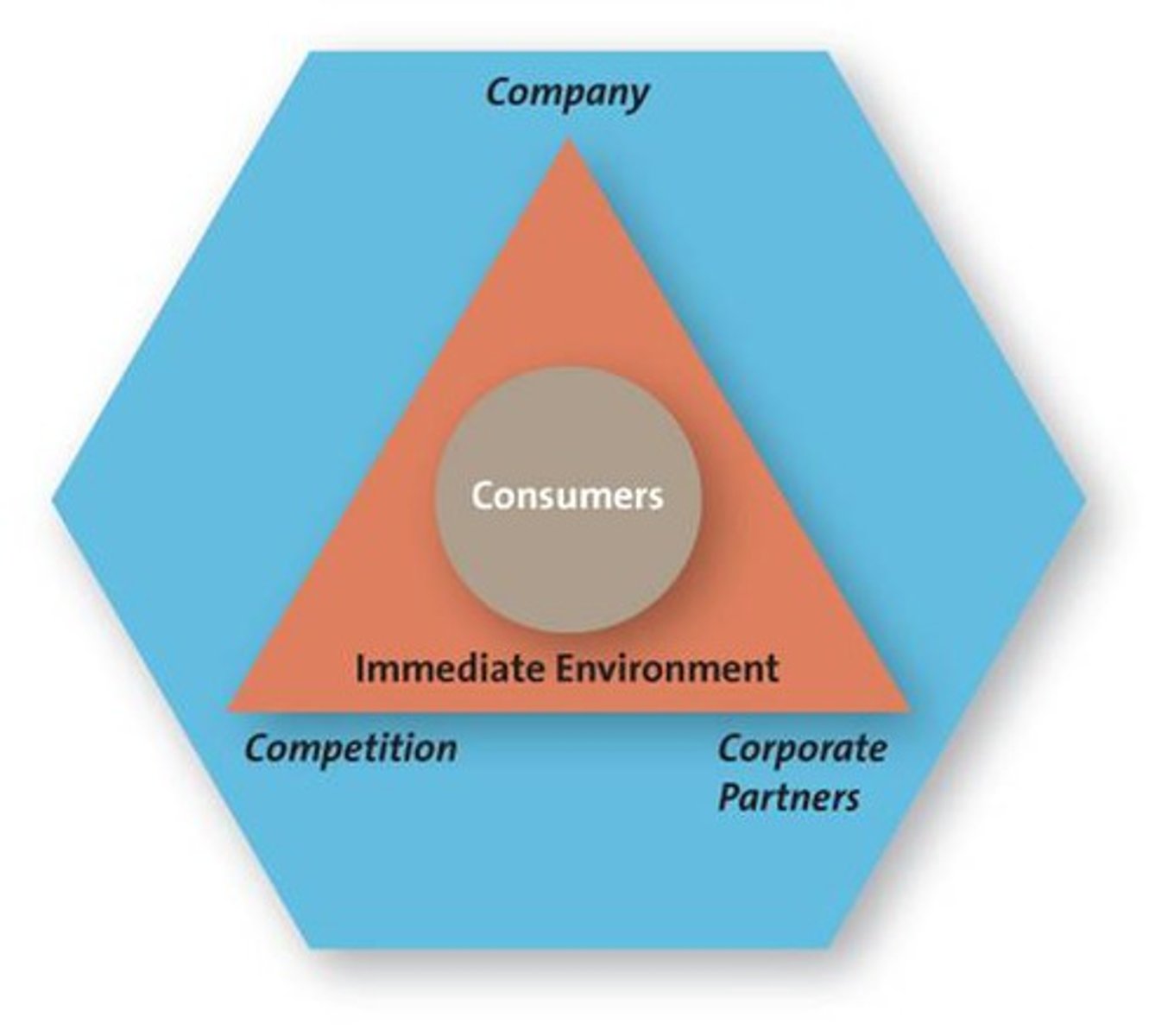
Company
Core competency>Existing knowledge, facilities, patents, etc.>New markets, new products, etc.
Competitors
-Know strengths & weaknesses
-Proactive rather than reactive strategy
-Always be prepared for reaction of competitors
Corporate Partners
-Firms are part of alliances
-Align with competitors, suppliers, etc.
-Just in Time Delivery Systems (JIT)
-Ability to deliver goods and services to customers when and where they want them.
Macroenvironmental Factors
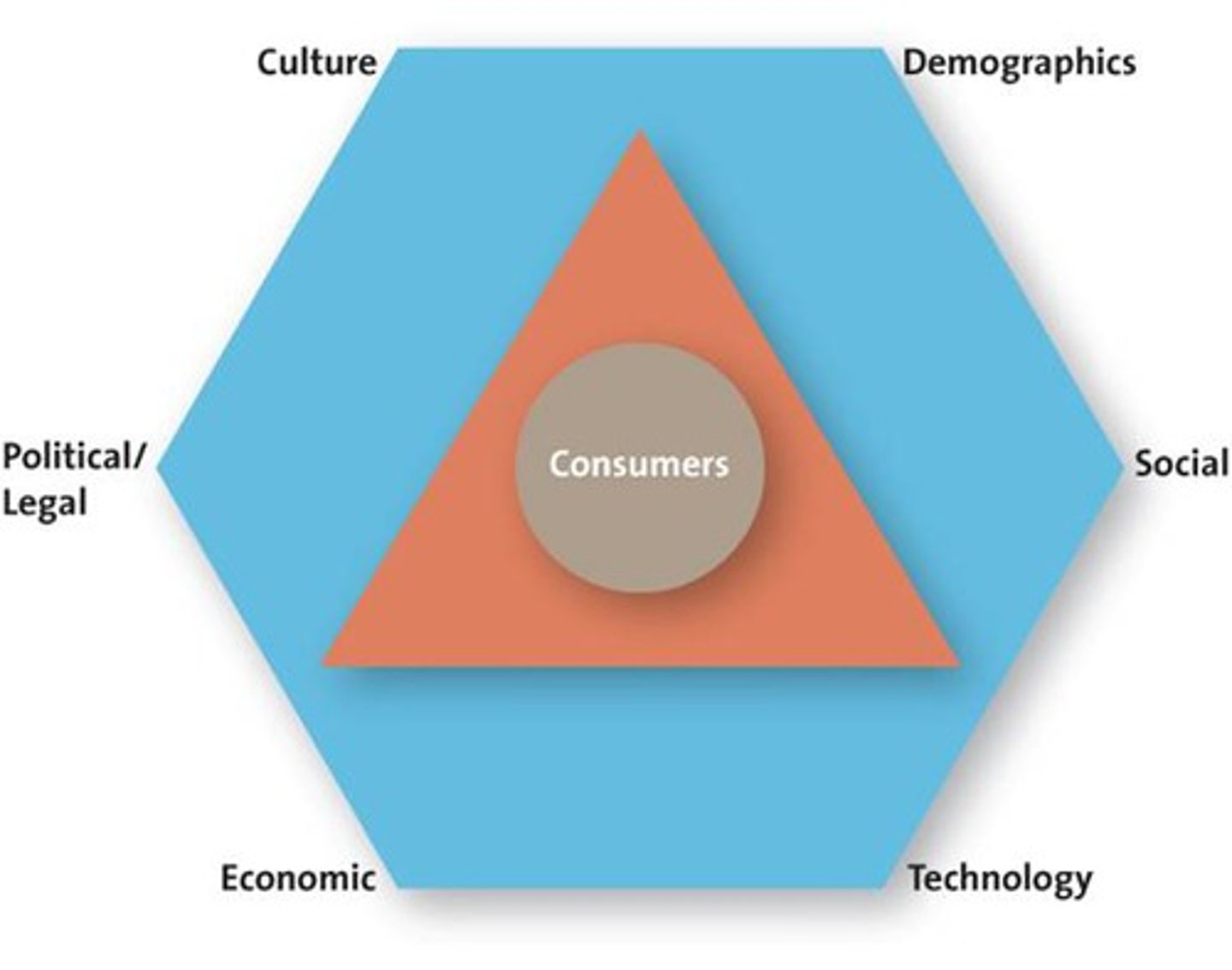
Culture
Country Culture vs. Regional Culture
Demographics
-Provides an easily understood snapshot of the typical consumer in a specific target market
-Ex: age, gender, income, education
-Demographic segmentation is probably the most common because the information is so widely available.
Income
-Purchasing power is tied to income
-Younger people have more purchasing power because they have no bills yet adults have more income
Education
Education is related to income,
which determines spending power
Gender
•Male/female roles have been shifting
Ethnicity
By 2050, minorities will represent 50% of the population.
Social Trends
-Health and Wellness Concerns
-Greener Consumers
-Privacy Concerns
Health and Wellness Concerns
-Worldwide Pandemics or Epidemics
-Child-Teenage Obesity
Greener Consumers
Customers who appreciate firms efforts to supply them with environmentally friendly merchandise. (ex: electric cars)
Privacy Concerns
-Loss of privacy, identity theft, do not call, do not email
-In recent years, firms have had to inform consumers of the steps they take to protect their privacy
Technological Advances
Technology has impacted every aspect of marketing
-New products
-New forms of communication
-New retail channels
Economic Situation
Inflation and interest rates affect firms' ability to market goods and services
Political/Regulatory Environment
•1890: Sherman Antitrust Act •1914: Clayton Act
•1914: Federal Trade Commission •1936: Robinson-Putman Act
business ethics
Refers to a branch of ethical study that examines ethical rules and principles within a commercial context, the various moral or ethical problems that might arise in a business setting, and any special duties or obligations that apply to persons engaged in commerce.
marketing ethics
Refers to those ethical problems that are specific to the domain of marketing.
Deceptive advertising
A representation, omission, act, or practice in an advertisement that is likely to mislead consumers acting reasonably under the circumstances.
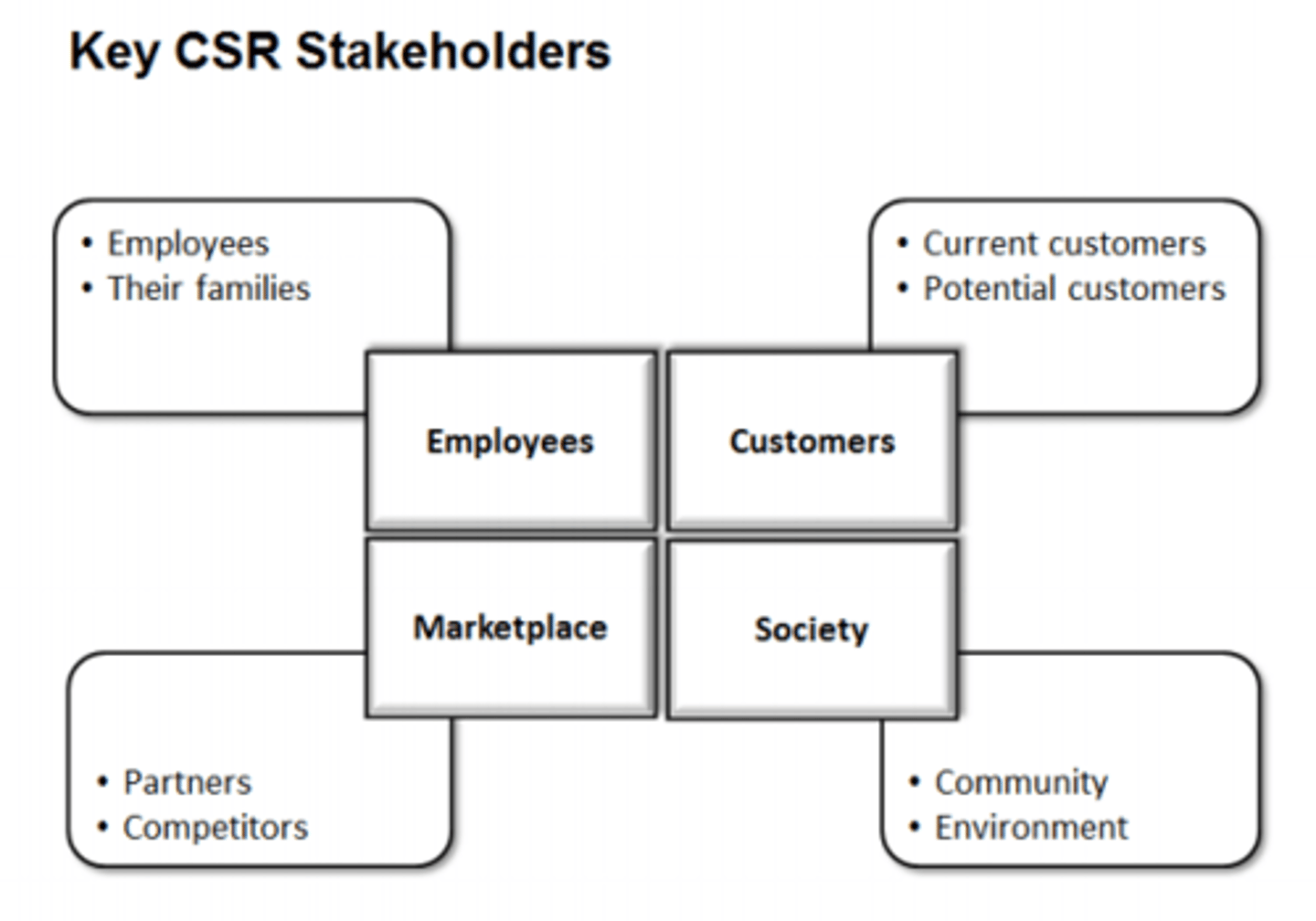
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Refers to the voluntary actions taken by a company to address the ethical, social, and environmental impacts of its business operations and the concerns of its stakeholders.
CSR Stakeholders Chart
Sustainability
Everything we need for our survival is dependent on the environment
Social Media
is media content used for social interactions such as Youtube, Facebook, and Twitter.
Creators
those hip, cool contributors, sit at the cutting edge and plan to stay there.
Bonders
are social media top enhance and expand their relationships, which they consider all important in their lives.
Professionals
who are constantly on the go and busy, want to appear efficient, with everything together, so they use social media to demonstrate just how smart they are.
Sharers
really want to help others, and the best way to do so is by being constantly well informed so that they can provide genuine insights to others.
Blog
a Web page that contains periodic posts.
Corporate Blogs
a website created by a company and often used to educate customers.
Professional Blogs
websites written by people who review and give recommendations on products.
Personal Blogs
websites written by people that receive no products or remuneration for their efforts.
Microblog
differs from a traditional blog in size. Consists of short sentences, short videos, or individual images. twitter is an example.
Gamification
is the process of process of building customer loyalty through the offering of free apps.
Corporate social responsibility
describes the voluntary actions taken by a company to address the ethical, social, and environmental impacts of its business operations and the concerns of its stakeholders.
sentiment analysis
allows marketers to analyze data from these sources to collect consumer comments about companies and their products.
hits
total requests for page
page views
the number of times any pages gets viewed by any visitor
bounce rate
the percentage of times a visitor leaves the site almost immediately.
click paths
how users proceed through the information.
conversion rates
what percentage of visitor as the marketer hopes.
keyword analysis
what keywords people use to search on the internet for their products and services.
social media strategist
creates social media marketing campaigns and measures the results.
community manager
handles corporate forums and blogs.
blogger
posts articles on relevant websites
social media marketing specialist
distributes promotional channels using a wide range of social media channels.
search engine marketing associate
focuses on search engines to increase the organic search ranking for a website.
online customer service representative
responds to customer feedback.
campaign strategy
Marketing strategy
Identifies a firm's target market, a related marketing mix (its 4 P's) anf the baes on which the firms plans to build a sustainable competitive advantage
sustainable competitive advantage
is an advantage over the competition that is not easily copied and can be maintained over a long period of time
customer excellence
focuses on retaining loyal customers and excellent customer service
operational excellence
achieved through efficient operations and excellent supply chain and human resource management
product excellence
having products with high perceived value and effective branding and positioning
locational excellence
having a good physical location and internet presence
planning phase
The first step of marketing plan, in which markerting executives in conjunction with other top managers define the mission and/ or vision of the business
control phase
the part of the strategic marketing planning process when managers evaluate the performance of the marketing strategy and take any necessary corrective actions
diversification strategy
a growth strategy whereby a firm introduces a new product or service to a market segment that it does not currently serve
implementation phase
the part of the strategic marketing planning process when marketing managers (1) identify and evaluate different opportunities by engaging in segmentation, targeting, and positioning and (2) implement the marketing mix using the four Ps
Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC)
represents the promotion dimension of the 4 Ps; encompasses a variety of communication disciplines- general advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, public relations, direct marketing, and electronic media- in combination to provide clarity, consistency, and maximum communicative impact
market development strategy
a growth strategy that employs the existing marketing offering to reach new market segments, whether domestic or international
market growth rate
the annual rate of growth of the specific market in which the product competes
market penetration strategy
market positioning
The process of defining the marketing mix variables so that target customers have a clear, distinctive, desirable understanding of what the product does or represents in comparison with competing products.
market segment
a group of consumers who respond similarly to a firm's marketing efforts
Market Segmentation
the process of dividing a market into groups of cutomers with different needs, wants or characteristics. Who therefore might different appreciate products or services geared especially for them
Market share
percentage of a market accounted for by a specific entity
Marketing plan
A written document composed of an analysis of the current marketing situation, opportunities and threats for the firm, marketing objectives and strategy specified in terms of the four Ps, action programs, and projected or pro forma income (and other financial) statements.
Metric
a measuring system that quantifies a trend, dynamic, or characteristic
Mission Statement
A broad description of a firm's objectives and the scope of activities it plans to undertake; attempts to answer two main questions: What type of business is it? What does it need to do to accomplish its goals and objectives?
product development strategy
a growth strategy that offers a new product or service to a firm's current target market
product lines
groups of associated items, such as those that consumers use together or think of as part of a group of similar products
related diversification
a growth strategy whereby the current target market and/or marketing mix shares something in common with the new opportunity
relative market share
a measure of the product's strength in a particular market, defined as the sales of the focal product divided by the sales achieved by the largest firm in the industry
segmentation, targeting, and positioning (STP)
firms use these processes to identify and evaluate opportunities for increasing sales and profits
situation analysis
Second step in a marketing plan; uses a SWOT analysis that assesses both the internal environment with regard to its Strengths and Weaknesses and the external environment in terms of its Opportunities and Threats.
Strategic Business Unit (SBU)
a division of the firm itself that can be managed and operated somewhat independently from other divisions and may have a different mission or objectives