1. Cardiovascular response to exercise
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Acute Adaptations
Increase blood flow to muscles, reduce blood flow to low activity tissues
Increase o2 delivery to working muscles
Reduce delivery to e.g. intestines
Chronically Adaptations
More effective o2 delivery during sub-maximal exercise + increased maximum o2 consumption (VO2 Max)
Delivers more o2 to active muscles mass
Cardiovascular factors that influence O2 Uptake + VO2 Max
Cardiac strucutre and function
Blood (plasma) vol - widen heart
Blood flow/distribution - in active muscles
o2 Extraction - arterio venous difference
Peripheral - what’s been taken up by the muscle
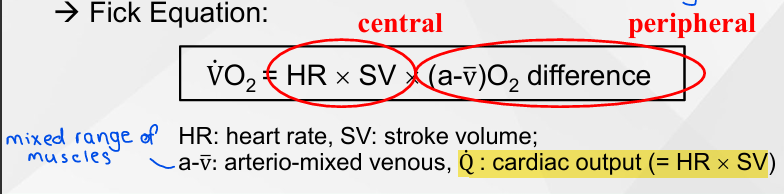
Cardiac Output
The volume of blood pumped out the heart per minute
Heart Rate x Stroke Volume
Stroke Volume
The volume of blood ejected out the left ventricle per beat
o2 Extraction: (a-v) o2 Difference
Training increases submaximal + maximal values in muscles
Active muscle - utilise o2 more efficiently
Increase oxidative capacity (higher oxidative enzyme content)
Physiological Cardiac Hypertrophy
enlarged heart (mass and size)
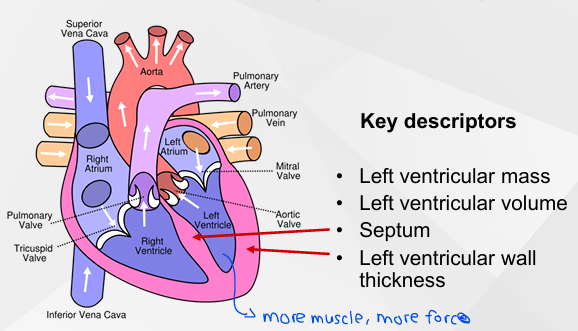
Heart Structure
Venous return
The volume of blood returning to the heart via the veins
Vascular resistance
the force that must overcome to push blood through the circulatory system
Preload
The amount of blood in the ventricle before contraction (end diastolic volume)
Determines cardiac muscle length before contraction
Determined by venous return
Increase CO + HR = Preload increase
Increase in moderate intensity
Afterload
The pressure against which the ventricle must contract (vascular resistance)
Higher the afterload, less blood ejected per heartbeat
Heart has limited force
Moderate intensity - can decrease, vessels open for o2
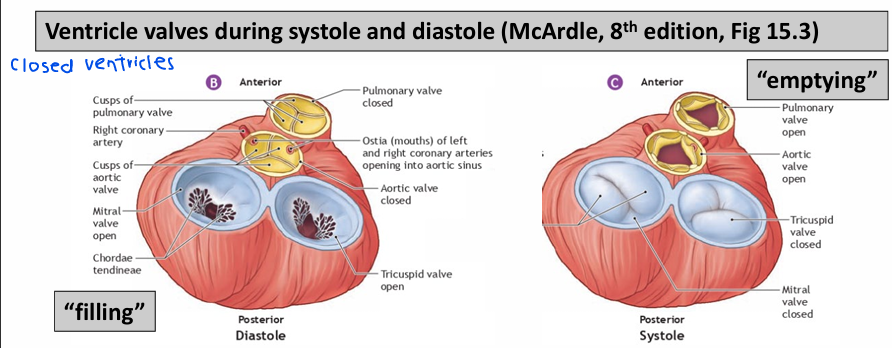
Ventricle valves during Systole and Diastole
Systole = contraction of heart (emptying)
Diastole = relaxation phase of heart (filling)
Contractility: The Frank-Starling Mechanism
Contractility = intrinsic ability of the heart muscle (myocardium) to generate force and to shorten during contraction, independent of how much it’s stretched (preload) or how much resistance it’s pumping against (afterload)
Principle based on length-tension relationship of ventricle
Greater stretch, greater contraction
Preload (end diastolic vol) increases, ventricular fiber length increases, increasing muscle tension

Athlete’s Heart: Potential Mechanisms
Left ventricular Mass - heavier in all athletes
Left ventricular Vol - larger in ENDURANCE athletes
Increased CO stretches out heart
Increased preload, Increases SV, Eccentric hypertrophy
Posterior wall/Septal thickness - larger in RESISTANCE
Beefier
Increased Afterload, Decreases SV, Concentric hypertrophy
Work against high resistance, decreases SV
Endurance training adaptations: Stroke Volume
Increased preload (ventricular filling) = Increase ventricular dimensions
Increased diastolic filling time due to bradycardia
Bradycardia = slow HR
Increased contractility
Increased maximal SV

Endurance Training Adaptations: Heart Rate
Increased SV = Decreased HR for the same CO (sub-maximal exercise)
Max HR unchanged
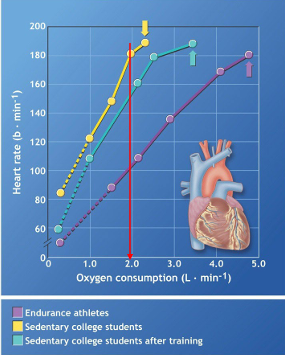
Endurance Training Adaptations: Cardiac Output (Q)
Product of SV x HR
Most significant adaptation - major determinant of VO2 Max
Sub-Max Exercise = lower CO (increased o2 extraction)
Better muscle oxidative capacity - higher a-vO2 diff (more enzymes)

Acute Blood Redistribution
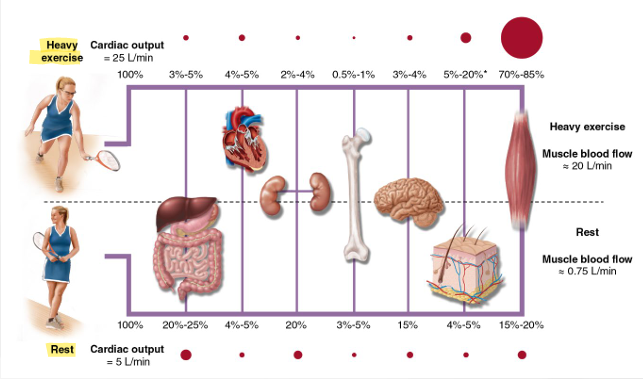
Acute Blood Flow Regulation
Muscle activity, pH go up
Muscle metabolites + Temp
Dilator substances produced by endothelium e.g. NO (open BV’s)
Pressure changes within vessels - myogenic
Symp Acticvity - reduce blood flow to low activity tissues (adrenalin receptors)
Training the heart through increases in blood vol?
Primary Mechanisms for Blood Vol Increase:
Increase in plasma proteins - Albumin (Osmotic effect)
Increase in total body water - alterations in kidney function (Reduced urine output, Increased water retention)

Effects of Various Training Modalities on Blood Volume
Increased Haemoglobin = Increased VO2 Max
Strong relationship
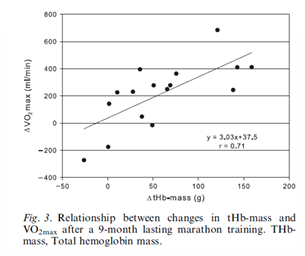
Blood Volume Changes

March 2019, Nordic skiing: Blood doping scandal rocks sport as five athletes arrested
EPO = induces production of RBC
Blood Transfusions - blood doping
Autologous - own blood
Homologous - another person’s blood
Aerobic training adaptations overview: increasing oxygen delivery to muscle
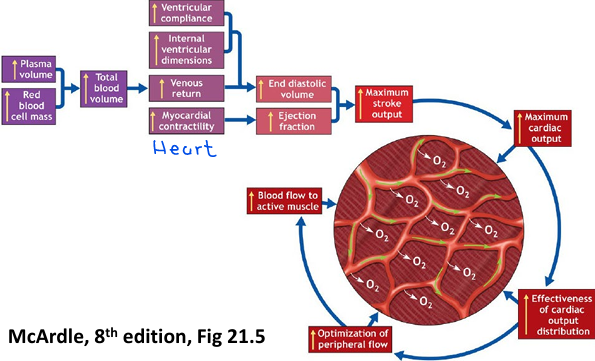
Summary
