NAPLEX: Travelers
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Sources for medication for Travling
1. CDC: Yellow Book
2. International Society of Travel Medicine (ISTM) Guidelines
What should traveler's have when they leave the U.S?
1. A list of medical conditions and medications (Rx + OTC)
2. Travel vaccines documented on the International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP) "Yellow Card"
3. Rx medications stored in original containers.
4. All medication and medical supply should be in carry-on luggage.
Live Travel Vaccines
Cholera PO
Typhoid PO
Yellow Fever SC
Common Food and Water diseases while traveling
*Travelers Can't Poop in Their Home*
-Traveler's Diarrhea
-Cholera
-Polio
-Typhoid Fever
-Hepatitis A
Traveler's Diarrhea
cause
onset
duration
- 80-90% bacterial (E. coli)
- Onset 6-72h
- Can last 3-7 days
Traceler's diarrhea prevention
non med and med
"boil it, cook it, peel it, or forget it"
hand hygiene
meds:
bismuth subsalicylate (pepto bismol) if no CI
abx if high risk
Traveler's Diarrhea Prophylaxis
- Pepto-Bismol (Any patient)*
- Rifaxamin (High risk patients)
When should Pepto-Bismol be avoided?
In patients with ASA allergy, pregnancy, renal insufficiency, gout or if taking anticoagulants.
>16 years old to avoid Reye's syndrome
Traveler's Diarrhea Treatment
Treatment:
Mild: Loperamide PRN
Moderate: Loperamide ± antibiotics
Severe: Antibiotics ± loperamide
**Azithromycin 1,000mg x1 dose**
What antibiotics are used to treat Traveler's Diarrhea
Azithromycin (Preferred)
Quinolones
Rifaxamin
Loperamide dosing for TD
4mg after first loose stool, then 2 mg after each subsequent loose stool.
Max: 8mg/day OTC or 16mg/day Rx
When is Loperamide contraindicated?
Children under 2 and if diarrhea is bloody
Typhoid Fever
cause
sx
where commonly occurs
-Caused by Salmonella typhi
-Presents has headache, malaise, anorexia, spleen/liver enlargement, rash
-Africa, Southeast Asia, Caribbean, Central/South America
Typhoid Fever Vaccines
1. Typhim VI
-IM injection ≥2 weeks before travel
-2 years old+
-Revaccinate every 2 years
2. Vivotif
-Live
-Oral Capsule ≥1 week before travel
-6 years old+
-Revaccinate every 5 years
-Store in refrigerator
Cholera
Caused by vibrio cholerae
-"Rice-water stools"
-Africa, Southeast Asia, Haiti
Cholera Vaccine
Vaxchora
-Oral liquid, Live
-Given ≥10 days before travel
-Patients aged 18-64 years
Polio
-Usually vaccinated in childhood
-Single, lifetime booster dose
-Proof of vaccination may be required
-Found in Afghanistan, Myanmar, Guinea, Laos, Nigeria, Madagascar, Pakistan and Ukrain
Polio Vaccine
IPOL
-IM injection
-Given ≥4 weeks before travel
-Single booster dose for previously vaccinated adults
Hepatitis A
cause
causes what
-Caused by Hepatitis A Virus
-Can cause jaundice, nausea, asymptomatic
-Acute, self-limiting
Hepatitis A Vaccines
Vaccines: all inactivated
Havrix (IM)
VAQTA (IM)
Twinrix (IM) - Hep A & B
Diseases from blood and bodily fluid
Hepatitis B
Meningococcal meningitis
hep b causes what if chronic?
cirrhosis, liver failure, liver cancer
who is hep b rec'd for?
if plan to
-receive medical care
-provide medical work
-have unprotected sex
-get piercings/tattoos
Hepatitis B Vaccines
which and how given?
Vaccines:
Engerix-B (IM)
Recombivax HB (IM)
Twinrix (IM) - Hepatitis A & B
-3 dose series over 6 months
Meningococcal meningitis
cause
where
transmission
required for which countries
when can you get it?
-Neisseria meningitidis
- Seasonal in African endemic zone (Dec-June)
-Transmitted through oral/nasal (coughing, kissing)
-Required for Saudi Arabian Hajj and Umrah pilgrimage
-Must be given <3 years ago & >10 days before for pilgramge
Meningococcal Meningitis Vaccine
Vaccines
Menquadfi (IM)
Menveo (IM)
Both Quadrivalent
-Serotypes ACWY
Meningococcal meningitis Classic Triad
Nuchal rigidity (stiff neck)
Headache
Fever
Diseases from Insect Bites (Travel)
*insects Make You Destroy Japanese Zoos*
Malaria
Yellow Fever
Dengue
Japanese Encephalitis
Zika Virus
Prophylactic Measures against bug bites
-20%-50% DEET
-SPF first, then DEET
-Permethrin-treated clothing, gear, bed nets - do not let touch skin
-Minimized exposed skin
Dengue Fever
transmissions
sx
vaccine?
treatment?
-Transmitted by mosquitoes
-75% asymptomatic
-5% Severe bleeding/organ failure, shock
-No vaccine so prevent bites
supportive care
Malaria
transmission
sx
4 species
-parasite transmitted by Anopheles mosquito
-High fever, shaking, chills, flu-like
- Four species:
1. Plasmodium falciparum (most deadly)
2. Plasmodium malariae
3. Plasmodium ovale
4. Plasmodium vivax (50% of cases in India and becoming more resistant)
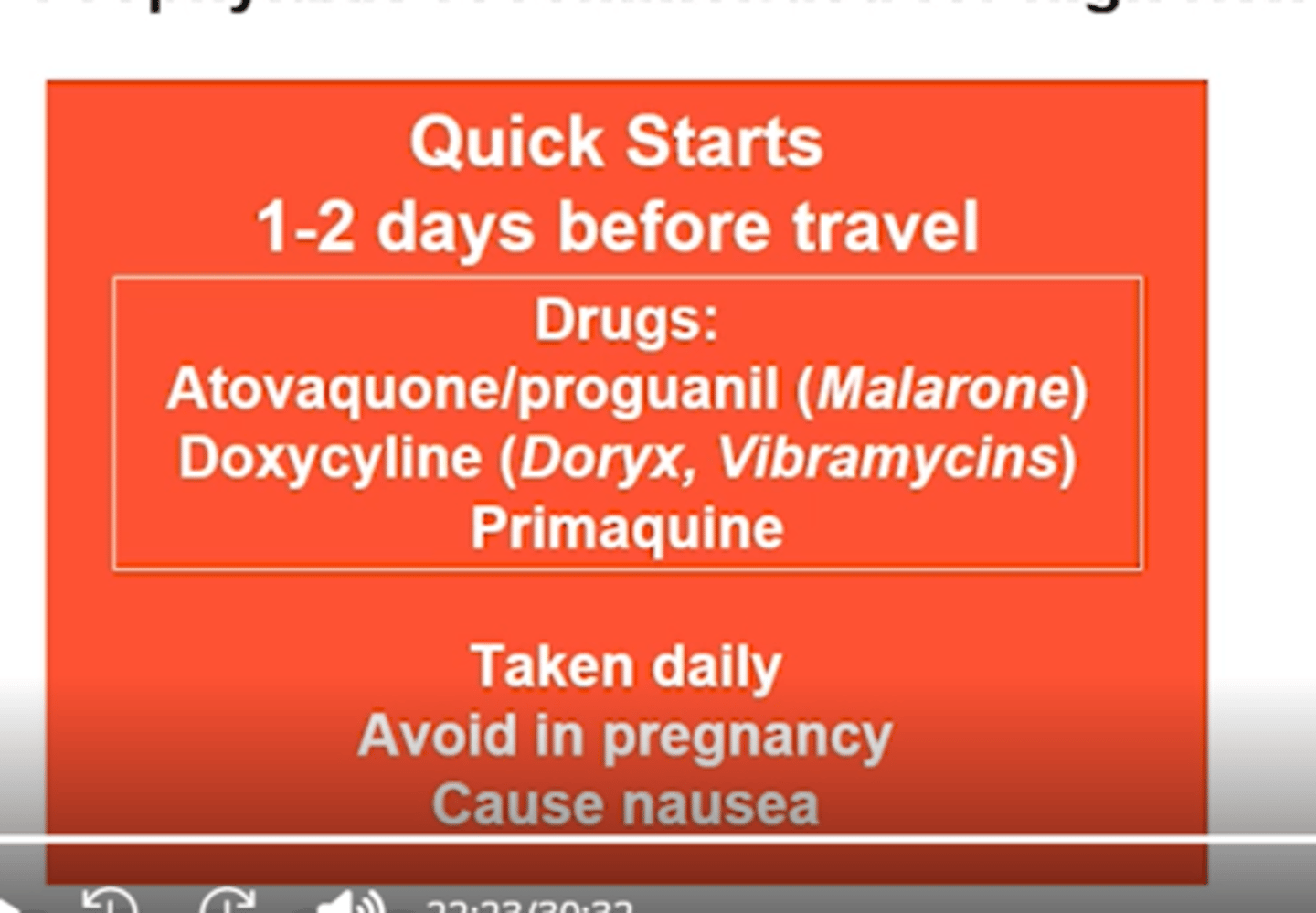
Malaria Prophylaxis Quick Start
when initiated?
drug treatment plans (start/stop)
how taken?
avoid in?
side effect
1-2 days prior to travel
Atovaquone/proguanil (Malarone):
-Stop 1 week after travel
Doxycycline (Doryx, Vibramycin):
-Stop 4 weeks after travel
-Causes photosensitivity
Avoid in children <8
Primaquine:
-Most effective against P. vivax
-Stop 1 week after travel
-Avoid in G6PD deficiency
All:
-Taken daily
-Avoid in pregnancy
Malaria Prophylaxis Advanced Start
when start
treatment plans (start/stop)
side effects
avoid in who
how taken?
1-2 weeks prior to travel
Chloroquine:
-Start: 1-2 weeks before
-Stop: 4 weeks after
-Renal toxicity/Visual changes
Mefloquine (Lariam):
-Start: ≥2 weeks before
-Stop: 4 weeks after
-Avoid in patients with psych, seizures or arrhythmias
Both:
-Taken Weekly
-Safe in pregnancy, children

Japanese Encephalitis
sx
where is highest risk?
who should get vaccine?
-Usually asymptomatic, can lead to encephalitis
-Highest risk in rural areas of agriculture or
-Higher risk with those who are planning on extended outdoor stays (hiking, etc)
Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine
Ixiaro (IM, inactivated)
- patients aged > 2 months
- extended exposure to outdoors or >/= 1 month in area
Yellow Fever
where found? do they require?
symptoms are similar to?
ci in?
avoid use with (drug interaction)
-Found more in tropical areas
-Similar symptoms to influenza
-High risk areas require "Yellow Card", valid 10 days after vaccine
-CI with egg allergy, severely immunocompromised
-Risk of serious adverse effects
-Avoid concurrent use of NSAIDs due to increased risk of bleeding
Yellow Fever Vaccine
YF-Vax (SC, Live)
-Given ≥10 days before travel
-1 dose, but some countries require booster q10 years
Zika Virus
transmitted by
what causes?
-Transmitted mainly by Aedes mosquito
-Sexual and blood transfusion-associated transmission as well as mosquito
-Infant microcephaly (small head)
is there a vaccine for zika? other prevention?
no vaccine yet
avoid unprotected sex and mosquito bites
Treatment for altitude sickness
when start?
ci?
side effects?
Diamox (acetazolamide)
-Start day prior to travel
-CI with sulfa allergy
-Polyuria and photosensitivity