Classical/operant conditioning and B.F. Skinner's quadrants
1/14
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
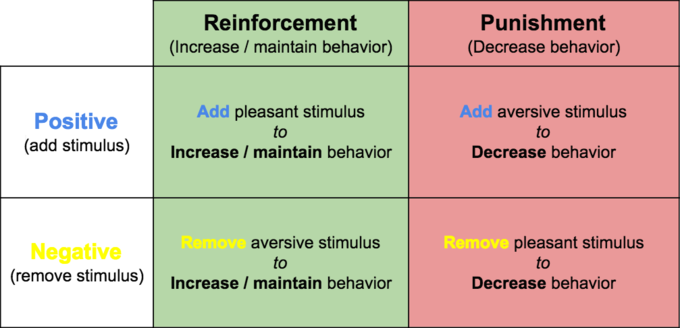
Describe B.F. Skinner’s quadrants.
Positive: addition of stimuli
Negative: removal of stimuli
Reinforcement: encourage/increase behaviour
Punishment: discourage/reduce behaviour
What is the definition of classical conditioning?
Learning through association/unconscious learning
How does classical conditioning work?
Neutral stimulus (NS): a stimulus that elicits no response (ie ringing bell)
Unconditioned stimulus (US): a stimulus that triggers a natural response; has not been taught (ie food)
Unconditioned response (UR): a natural response to a specific stimulus; has not been taught (ie salivating)
Conditioned stimulus (CS): a stimulus that triggers a conditioned response
Conditioned response (CR): a natural response conditioned to be triggered by a specific stimulus
US + NS = UR; US is now a CS, UR is now a CR
What kind of conditioning is Pavlov’s experiment an example of?
Classical conditioning
What is the definition of operant conditioning?
Learning from consequence; see B.F. Skinner’s quadrants
What is the difference between classical and operant conditioning?
Classical conditioning means responding to the environment; operant conditioning means affecting it through choice
How did Pavlov conduct his experiment?
Dogs were put in secure harnesses in a secluded environment and presented with food (US); the frequency of salivation was measured
The dogs were then presented with a metronome clicking (NS); they did not salivate
The metronome was played just before introducing the food; after several repeats, the metronome (CS) triggered salivation (CR)
What is a functional analysis?
A procedure to determine conditions a behaviour happens under
Give 3 reasons why an animal might perform a problem behaviour
Attention
Food/toys
Avoid or escape a situation
Sensory reinforcement (boredom)
Communicate needs (ie exercise)
What is an ABC functional analysis?
Antecedent > Behaviour > Consequences
Antecedent: what causes the behaviour?
Behaviour: what is the behaviour?
Consequence: what happens afterward?
What are behavioural diagnostics?
Where we look at the bigger picture to see why a problem behaviour might be occurring (ie individual history, unmet needs etc)
What makes a reinforcer effective?
Timing: should be given as the target behaviour is being performed
Performance: should be given only when the targeted behaviour occurs
Uniqueness: all animals (inc. individuals) have different effective reinforcers
What is the most common form of training in collections?
Positive reinforcement training (PRT)
What is the definition of learning?
A change in behaviour resulting from practice/experience
What is the definition of training?
A change in behaviour resulting from a practice/experience dictated by humans