Molecules to Metabolism | BIOLOGY HL
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Outline what molecular biology is and what it explains
explains living processes in terms of the molecules involved;
reductionist approach;
to work out the structure of organic molecules which make up living things;
e.g. DNA, RNA, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids;
understanding structure leads to understanding function;
how molecules interact with each other;
biochemical pathways to form new substances and break down others;
perhaps cannot yet explain emergent properties when all molecules are combined
Explain how the synthesis of urea falsifies vitalism
vitalism stated that living molecules cannot be made artificially;
urea discovered in 1720s;
in urine;
nitrogen containing compound;
waste product of protein breakdown;
however, was artificially synthesised in 1800s;
therefore, organic molecules from living things can be synthesised artificially
Explain how carbon can lead to diversity of compounds
carbon can form 4 covalent bonds;
therefore can become the backbone of molecules;
form chains;
ring structures;
link together;
form double bonds with itself;
can bond with just one atom like hydrogen, or multiple different ones;
giving a huge range of properties for organic molecules in living things
State the most frequently occurring chemical elements in living things
Most common in living organisms are Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen, then nitrogen.
Carbon C
Oxygen O
Hydrogen H
Nitrogen N
State that a variety of other elements are needed by living organisms (other than C,H,O,N,S)
Living organisms require CHONS plus calcium , phosphorus, iron and sodium and other elements
State one role for each of these S, Ca, Fe, Na, P in cells
Sulphur which is an important element in some amino acids.
Calcium which is found in bones / Teeth
Iron which is to be found in haemoglobin (animal)
Sodium which is needed for a nerve impulse
Phosphorus found in cell membrane structures- phospholipids
Describe the classifications of carbon compounds that life is based on
Carbohydrates - Compopsed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen;
ratio of 2 hydrogen to one oxygen atom;
henece the name carbohydrate;
Lipids - broad class of molecules that are insoluble in water;
including steroids, waxes, fatty acids, triglycerides;
mainly made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, though not a fixed ratio;
often in long chains; e.g. fatty acids
or ring shapes e.g. steroids
Proteins- made of one or more chains of amino acids;
contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur (only 2 of twenty);
Nucleic acids- subunit called a nucleotide;
contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorous;
two types, RNA (single stranded) and DNA (double stranded)
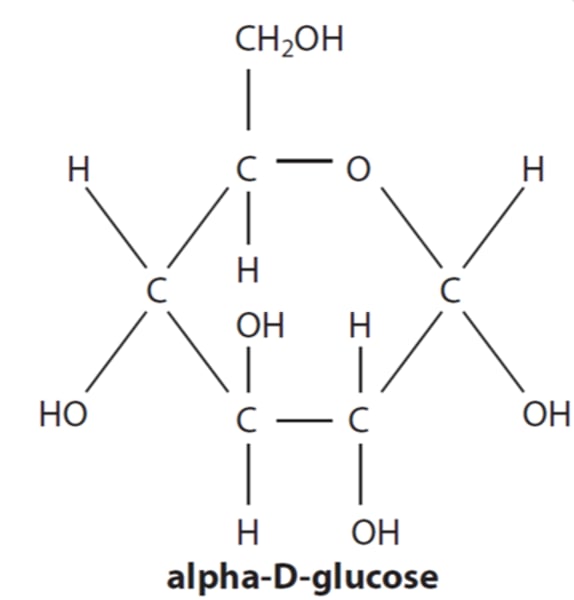
Draw a diagram of alpha D-glucose (or explain what it looks like verbally)
Ring structure;
but! 6th member of the ring is actually oxygen in top right;
carbon 3 has OH sticking up, all others are sticking down
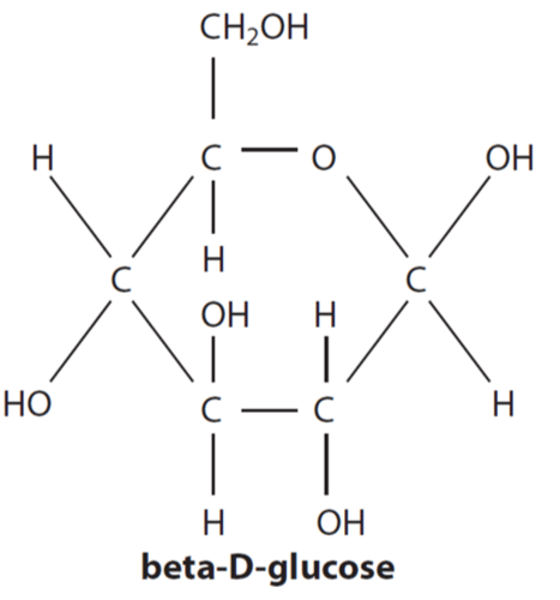
Draw a diagram of beta D-glucose (or explain what it looks like verbally)
Same as alpha BUT has 1st carbon OH group going down, as well as carbon 3
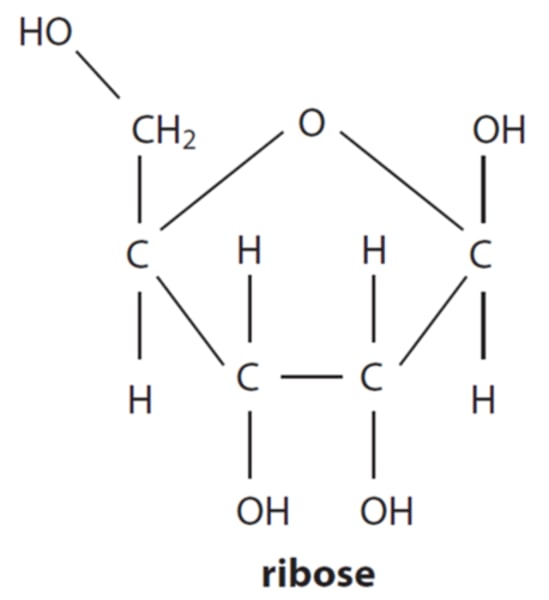
Draw a diagram of ribose (or explain what it looks like verbally)
5 carbon molecule;
pentagon shape;
oxygen is a top, not carbon;
formula is C5 H10 O5;
OHs for 1 and 5 point up, 2 and 3 point down
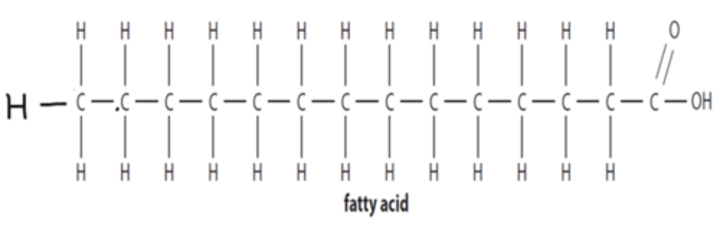
Draw a diagram of a saturated fatty acid (or explain what it looks like verbally)
Long chain of C and H, acid group at end with COOH structure;
no polar bonds;
therefore non-polar and hydrophobic;
e.g. phospholipid tails
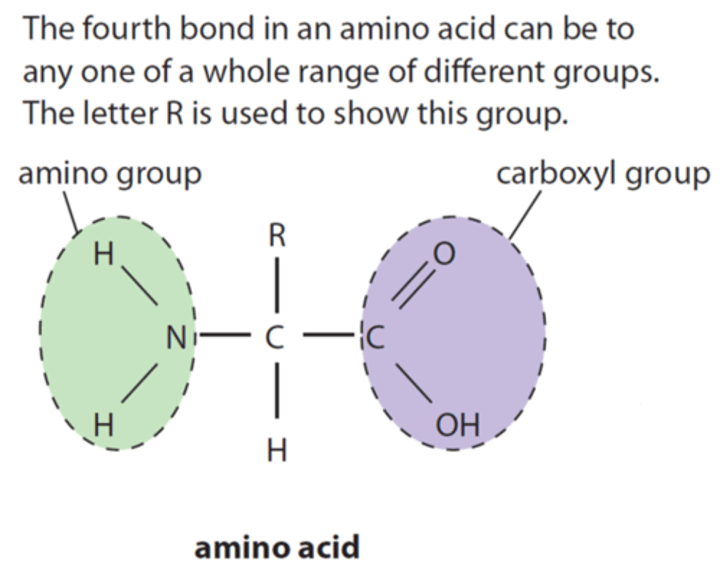
Draw a diagram of an amino acid (or explain what it looks like verbally)
NH2 group at one end, COOH group at other;
R group (which is actually usually C and other atoms) at top;
meaning variable group - Could be CH3, could be CH2CH3, depending on the amino acid
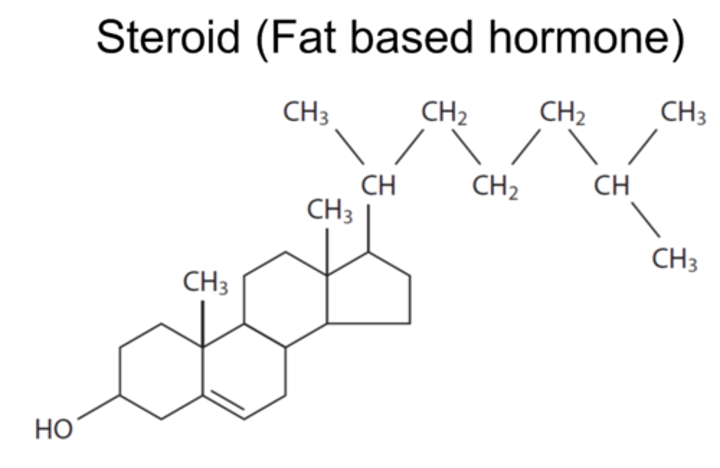
Identify molecules from diagrams (as above) plus steroid on this card
Ring shaped, with fat like stucture for parts (CH2 groups)
Outline metabolism
the web of enzyme catalysed reactions;
sum of all the reactions;
most take place in cytoplasm;
involve many steps;
eg. A-B-C-D, where each step is catalysed by a different enzyme;
Outline anabolism
synthesis of complex molecules;
from simpler ones;
e.g. protein synthesis from amino acids;
DNA from nucleotides;
photosynthesis of glucose from water and carbon dioxide;
starch from glucose
Outline catabolism
breakdown of large complex molecules into simpler ones;
release energy;
which can be captured in the form of ATP;
e.g. cell respiration where glucose is broken down;
digestion of starch into glucose molecules