Functions, Interfaces & Methods in Go
1/18
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is a function ? Examples
A set of instructions with a name (name being optional).
main() is invoked automatically when the program runs.
Other functions have to be manually invoked.
What do functions support ?
Reusability (Declare once, call a million times, good for repetitive tasks)
Abstraction (You only need to know what the function does. Hiding details that are not important is abstraction)

Examples of how functions enable Reusability.
A database program may have a
QueryDB()function.A music app may have
ChangeKey()function.An image processing app may have a
ThresholdImage()function.
Examples of how functions enable Abstraction.

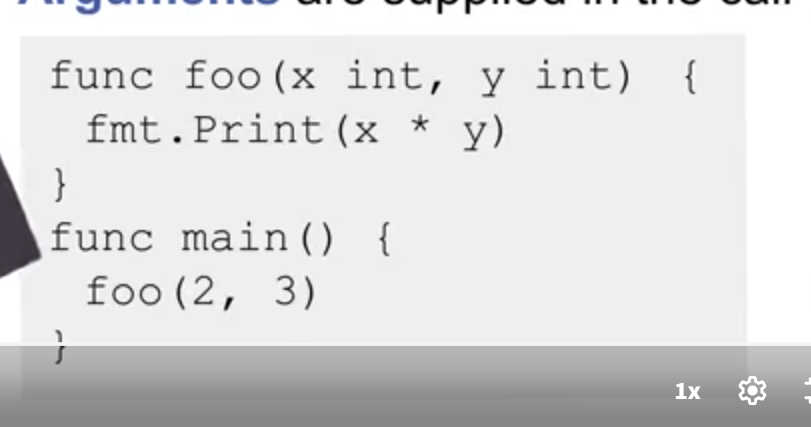
What are parameters and arguments ? Explain with the help of an example.
A function might need input data to perform compuation.
Parameters represent input data.
They must be mentioned inside the parentheses along with their types.
Arguments are passed and associated at the time of function call.
What are parameter options ?
If a function accepts no inputs, simply leave the parentheses empty.
If the function accepts consecutive inputs of the same type, just place the type at the end of the last parameter of that type.

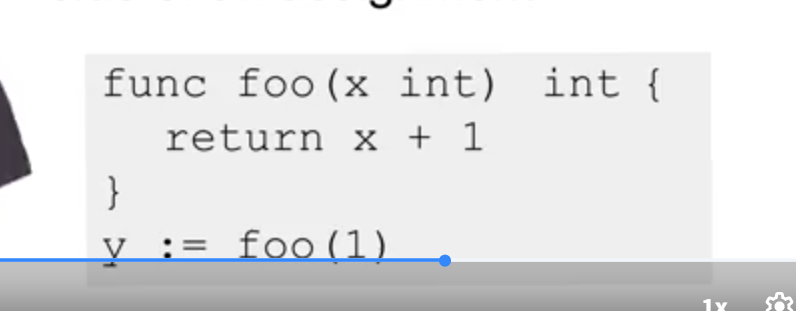
What are return values ?
Results of computation
Type must be mentioned in the declaration after the parentheses.
Call can be placed on the RHS of a shorthand variable assignment.
How to return multiple values ?
Comma separate the values returned.
In the function definition, comma separate the types of the return values in the same order as the return values themselves

Explain functions as first class values in Go
Functions can be treated like any other type in Golang (like string, int, float)
They can be assigned to variables.
They can be passed as arguments to functions (functions can have functions as parameters) and returned from functions.
They can be stored in data structures like slices.
They can be created dynamically.
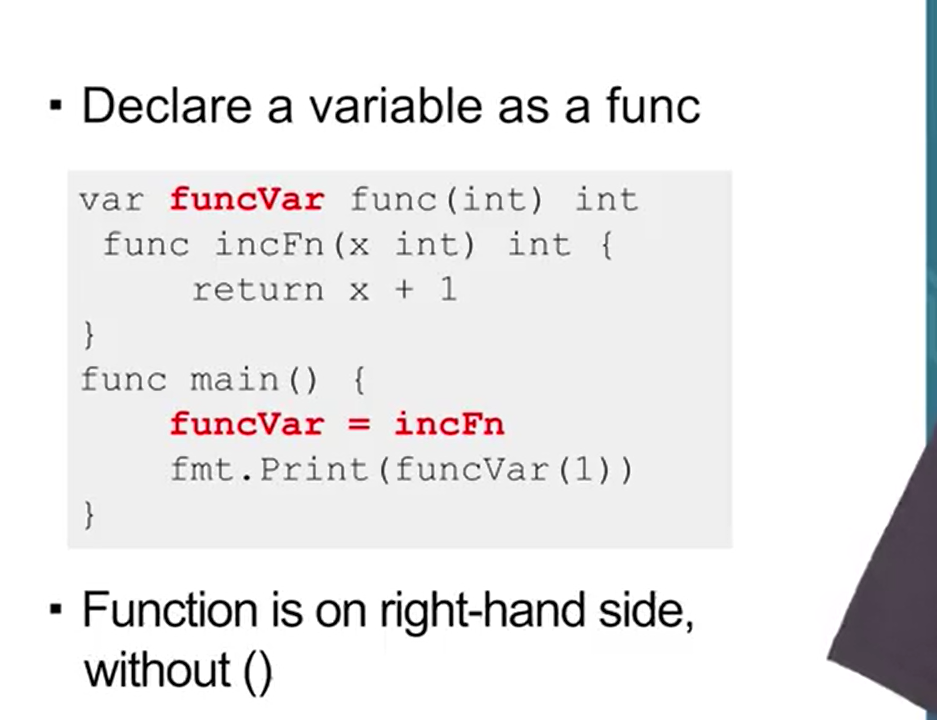
Give an example of how functions can be assigned to variables in Go
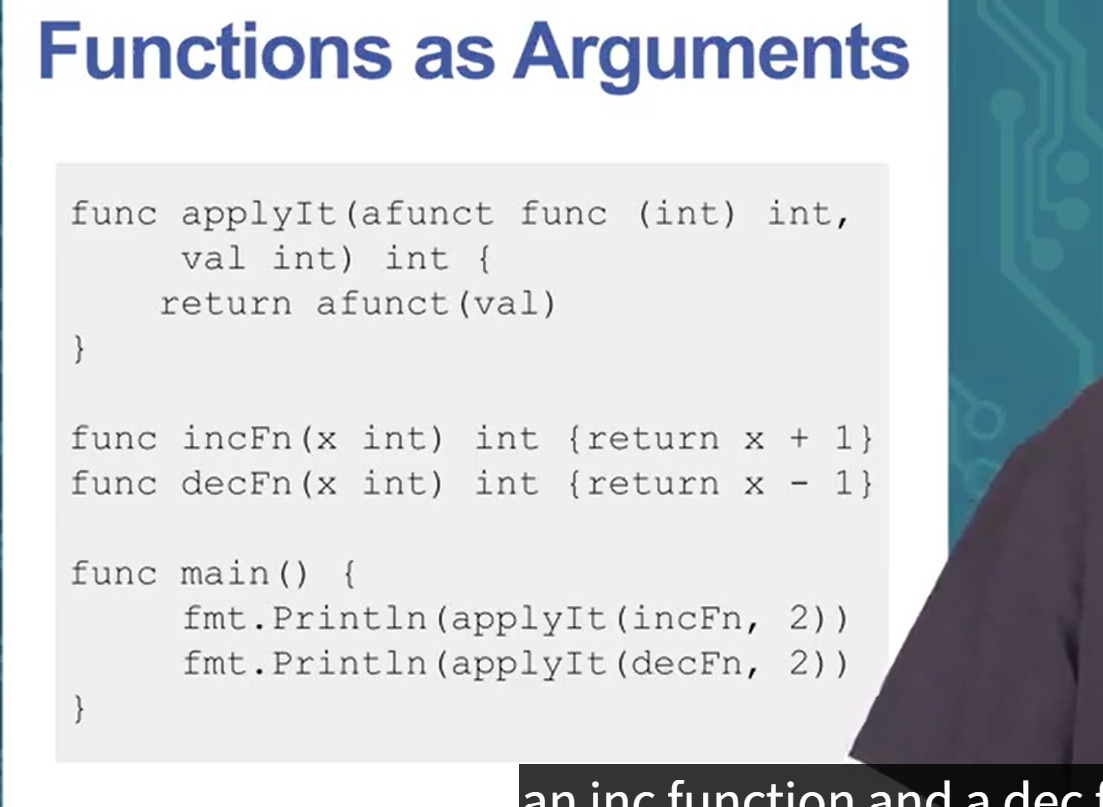
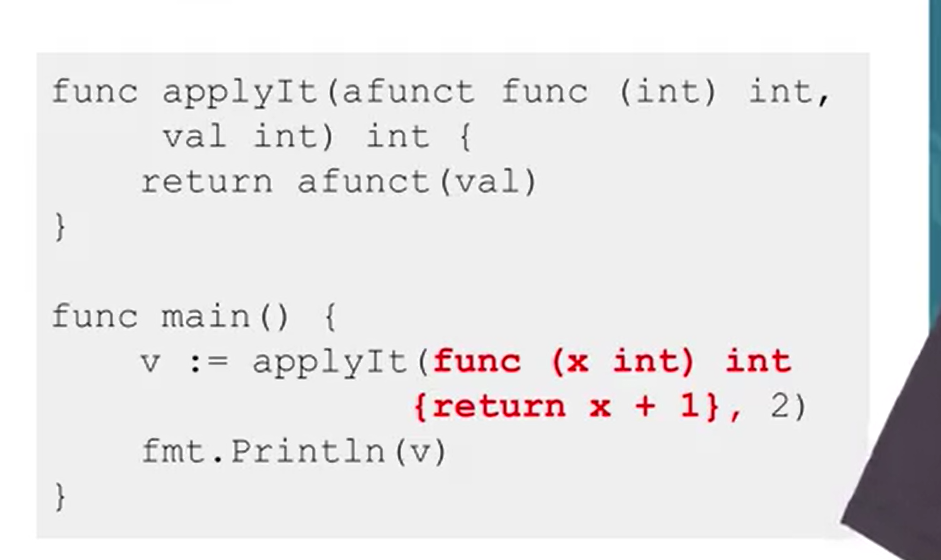
Give an example of how functions can passed to other functions
What are anonymous functions ? Explain with the help of an example
When functions are passed as arguments to other functions they need not have a name.
How are functions retuned from another functions ?
Possible due to closures
Used to create parameterized functions.
o_xando_yare in the closure of fn

What is an environment of a function ?
This concept is closely tied to lexical scoping in Go.
A set of all names (variable names for example) that can be accessed from a function.

What is a closure ?
Function + environment data is called closure.
When a function is passed as an argument or returned from another function, it has access to the environment where it was declared.
This basically means that when a function is called it has access (it remembers) the environment data and has access to it at runtime.
0,0 and 2,2 are remembered.

What is variadic in Golang ?
A function in golang can accept variable number of arguments.
Use the … to specify this in the function. The single argument then contains all the arguments available as a slice.

How to pass a slice to a function with variable number of arguments ?
Use the … operator after the slice.

What is defer ?
A deferred function is one that is executed after the wrapping function is executed.
Typically used for cleanup purposes.
Implemented using the defer keyword placed in front of the call.

How are arguments in the call deferred ?
The arguments are evaluated then and there. Only the call is deferred.
