Atoms, Molecules, and Ions in General Chemistry
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Atoms
Atoms are the smallest particles of an element that retain the chemical identity of that element.
Comparison to the macroworld
1022 atoms in 1 penny, equivalent to 1 grain of sand in a sandbox the size of Texas.
Silicon (Si) Atoms Size
Si atoms have sizes of ~ 0.2 nm or 2 Å.
Sir John Dalton
Proposed that atoms were indivisible and all atoms of a given element were identical.
J. J. Thomson
Discovered the electron using a cathode ray tube apparatus.
Cathode Ray Tube
An apparatus used by J. J. Thomson to discover the electron.
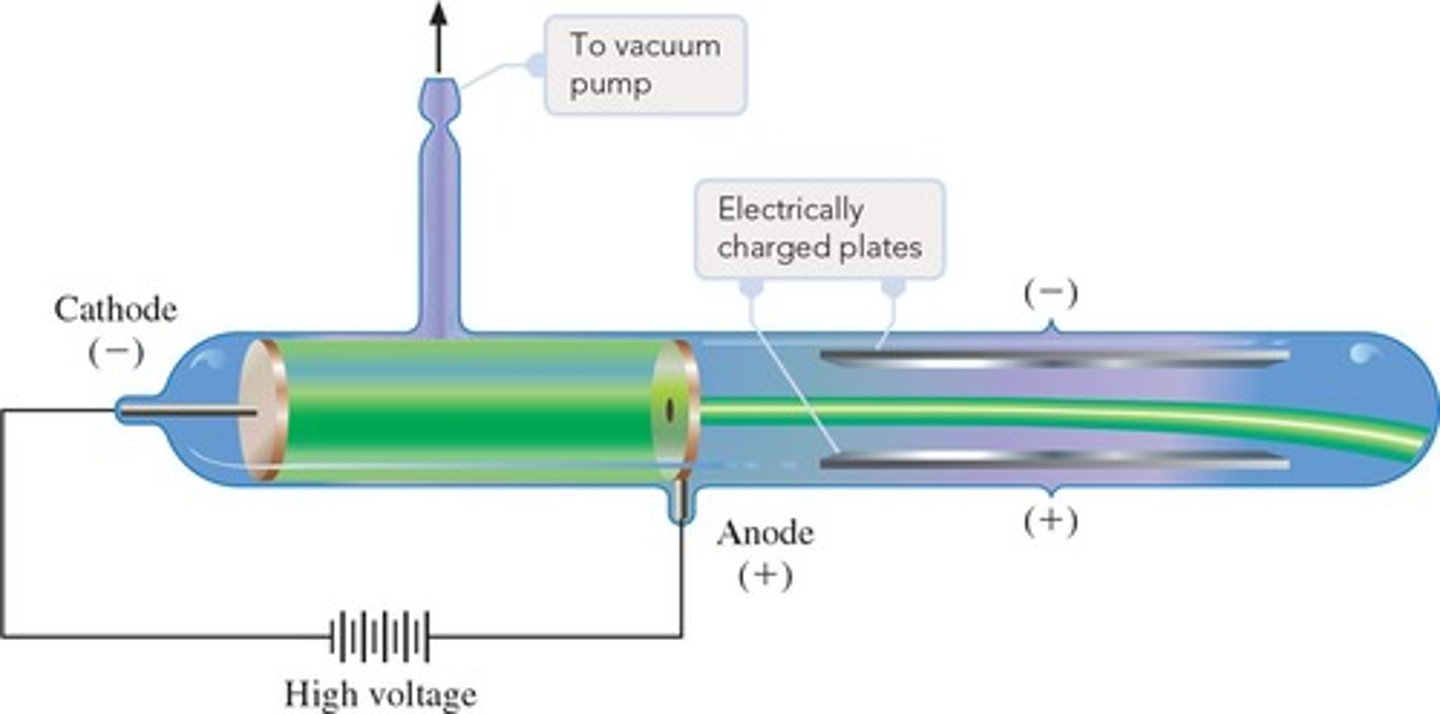
Cathode Rays
Cathode rays move toward the anode, indicating they must be negatively charged.
Mass-to-Charge Ratio of Electron
Thomson used his CRT experiment to determine the mass-to-charge (me/e) ratio of the electron.
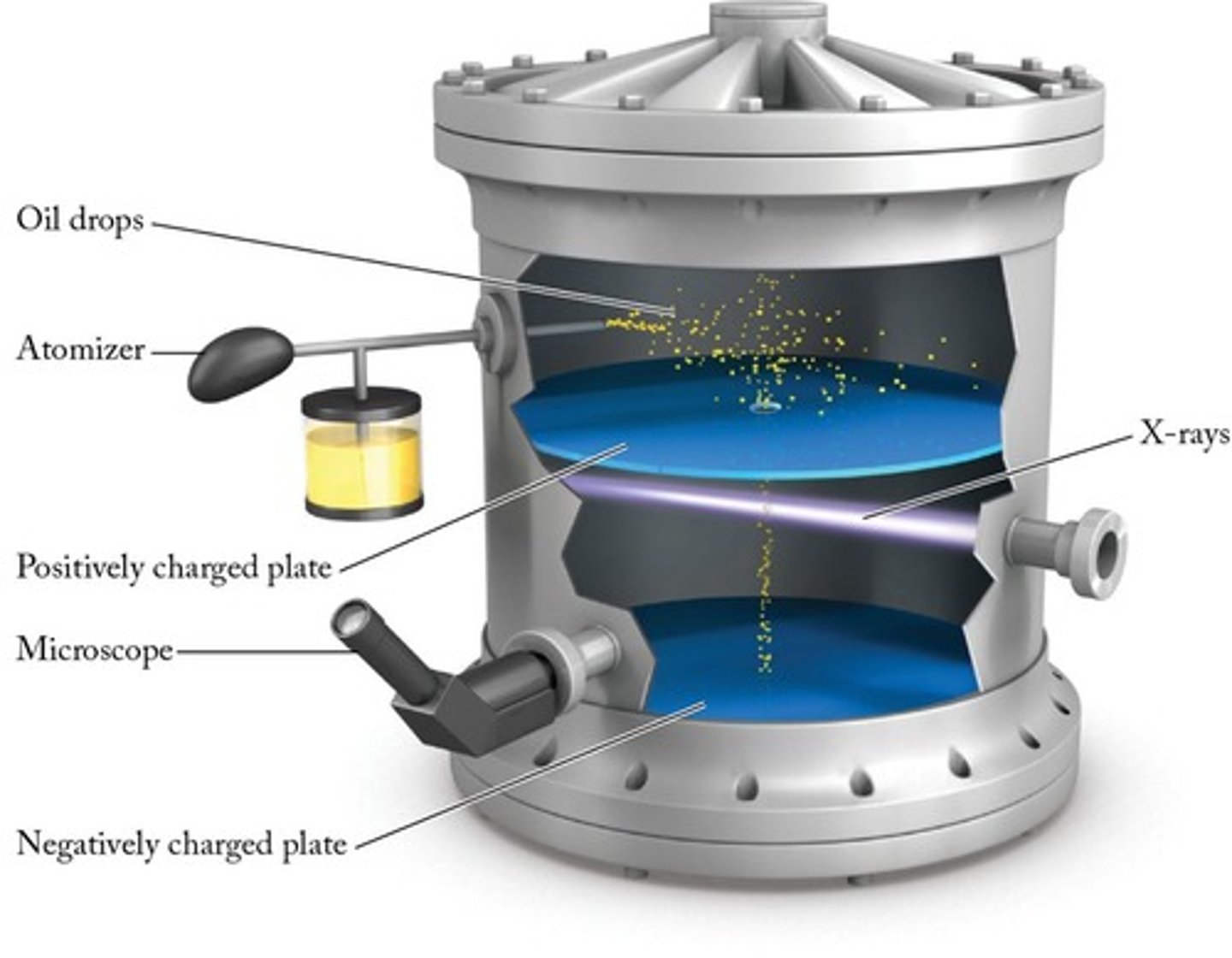
Robert Millikan
Conducted the oil-drop experiment to measure the charge of the electron.
Ernest Rutherford
Studied the nuclear structure of the atom and conducted the Gold-Foil Experiment.
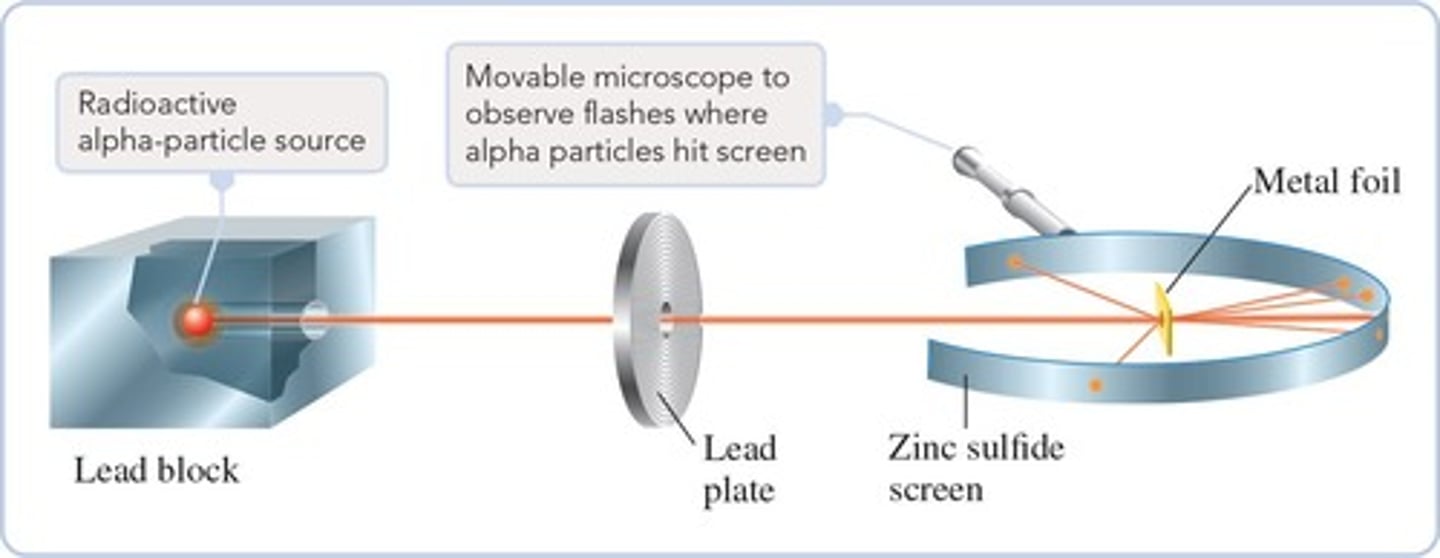
Gold-Foil Experiment
Demonstrated that most particles passed straight through gold foil, indicating most of an atom is empty space.
Nucleus
At the center of an atom is the nucleus, which must be positively charged and contains protons and neutrons.
Average Diameter of Nucleus
Average diameter of the nucleus is 10^-15 m (1 fm), which is 10^5 times smaller than the average diameter of an atom.
Proton (p+)
A positively charged subatomic particle that has an equal but opposite charge of the electron and mass 1800 times greater than that of an electron.
Neutron (n0)
A subatomic particle that is neutral in charge (charge of 0).
Three Subatomic Particles of the Atom
Proton (p+): Positively charged, Neutron (n0): Zero charge, Electron (e-): Negatively charged.
Periodic Table of Elements
Developed in 1869 by Dmitri Mendeleev, it consists of 18 Groups (vertical columns) and 7 Periods (horizontal rows).
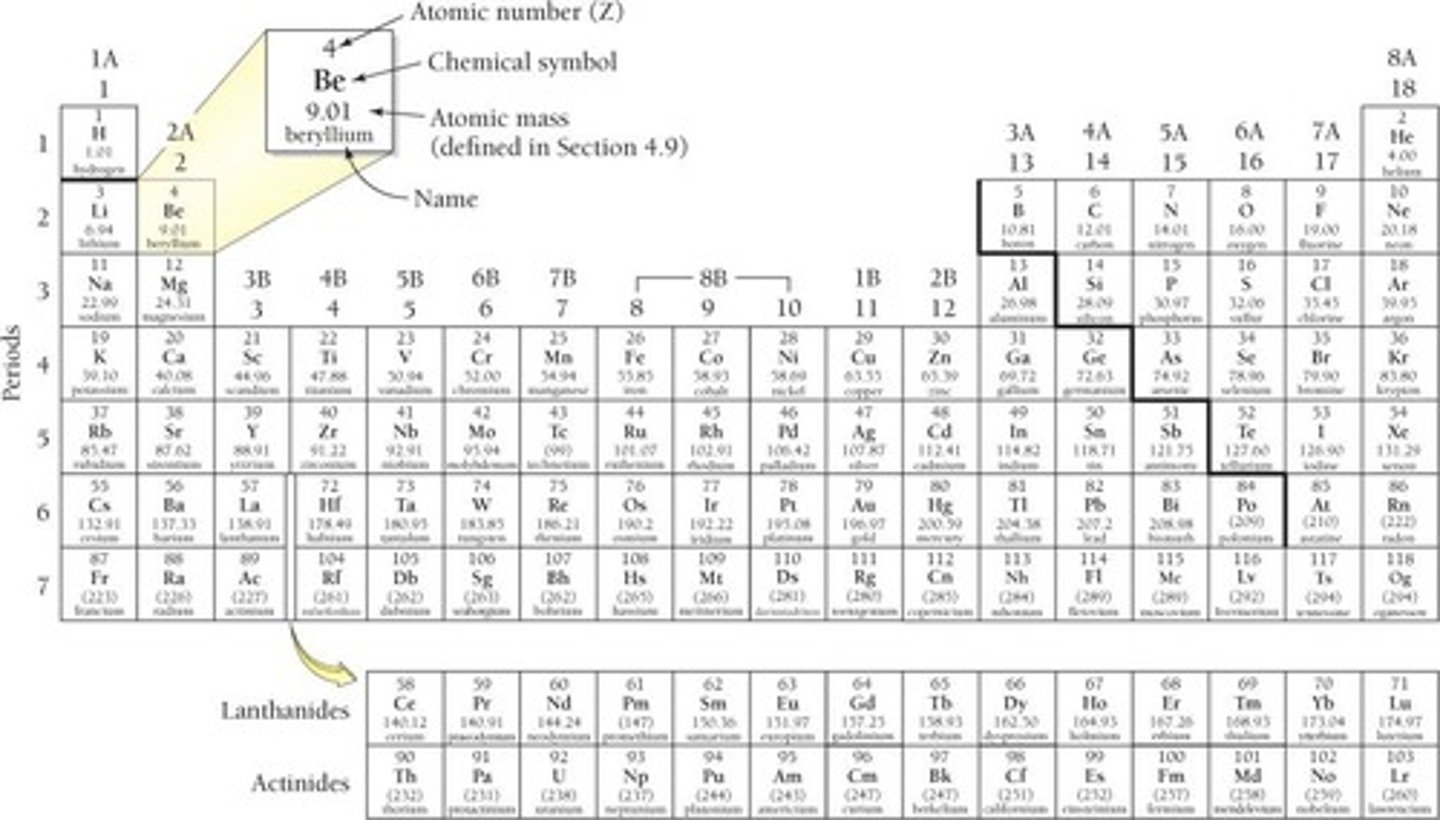
Groups (or Families)
Vertical columns in the Periodic Table where elements have similar properties, labeled by Arabic Numerals (1 - 18) or 1A, 2A,....8A; and 1B - 8B.
Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids
Elements in the Periodic Table can be classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids.
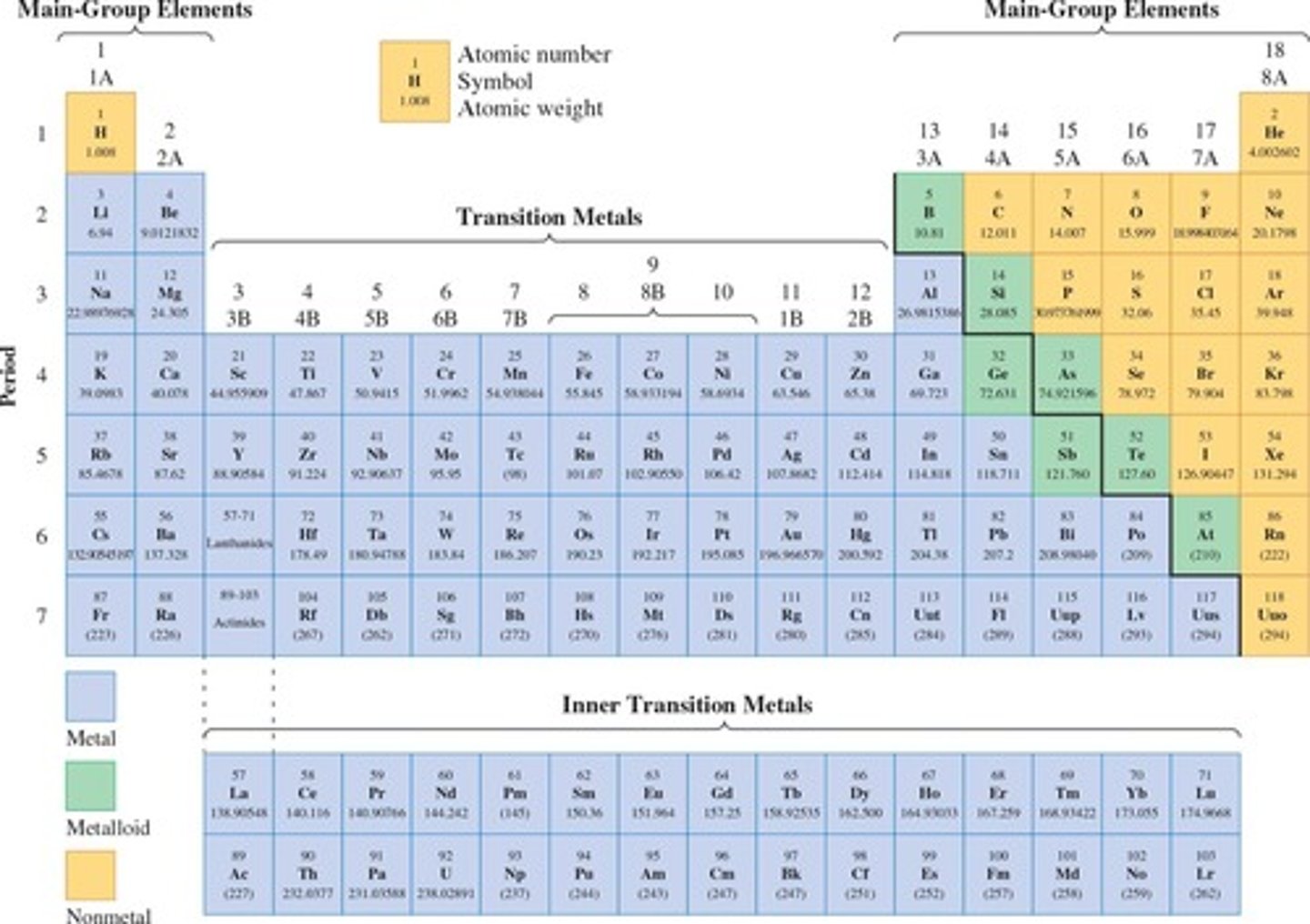
Atomic Number (Z)
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which defines the element.
Atomic Mass (A)
The sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
Bromine (Br)
Z = 35; A = 79.90 (round up to 80).
Iron (Fe)
Z = 26; A = 55.85 (round up to 56).
Atomic Mass Calculation
Atomic Mass (A) = p+ + n0. Therefore, n0 = A - p+ = A - Z.
Ions
Ions are defined as charged particles formed when atoms lose or gain one or more electrons.
Cations
Positively charged ions that are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons.
Anions
Negatively charged ions that are formed when an atom gains one or more electrons.
Charge of an Ion
The charge of an ion is indicated in the upper right corner of an element's symbol.
# e-
# e- = Z - charge of ion
Sodium ion (Na+)
Z = 11; A = 22.99 (round up to 23)
Aluminum ion (Al3+)
Z = 13; A = 26.98 (round up to 27)
Carbide ion (C4-)
Z = 6; A = 12.01 (round down to 12)
Chloride ion (Cl-)
Z = 17; A = 35.45 (round down to 35)
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same type of element that differ in mass number, or in their number of neutrons.
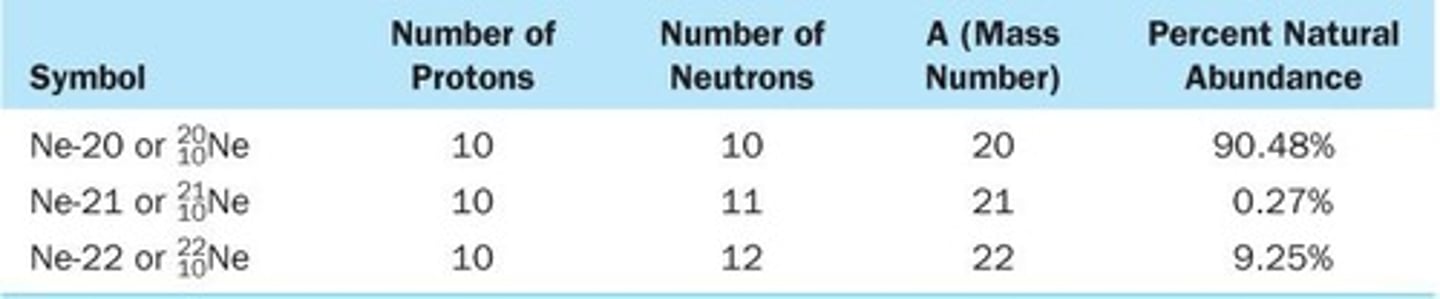
Symbolic Forms of Isotopes
A second common form for representing isotopes is the chemical symbol (or name) of the element followed by a hyphen and the mass number of the isotope.
Average Atomic Mass
The average atomic mass is calculated from the isotopes present.
Chemical Formulas
Representation of a chemical compound showing the elements present in the compound (written by their atomic symbols) and the number of atoms of each element in the compound (written as a subscript integer).
Water
Chemical formula: H2O
Iron(III) Oxide
Chemical formula: Fe2O3
Carbon Dioxide
Chemical formula: CO2
Calcium Nitrate
Chemical formula: Ca(NO3)2
Hydrogen Peroxide
Chemical formula: H2O2
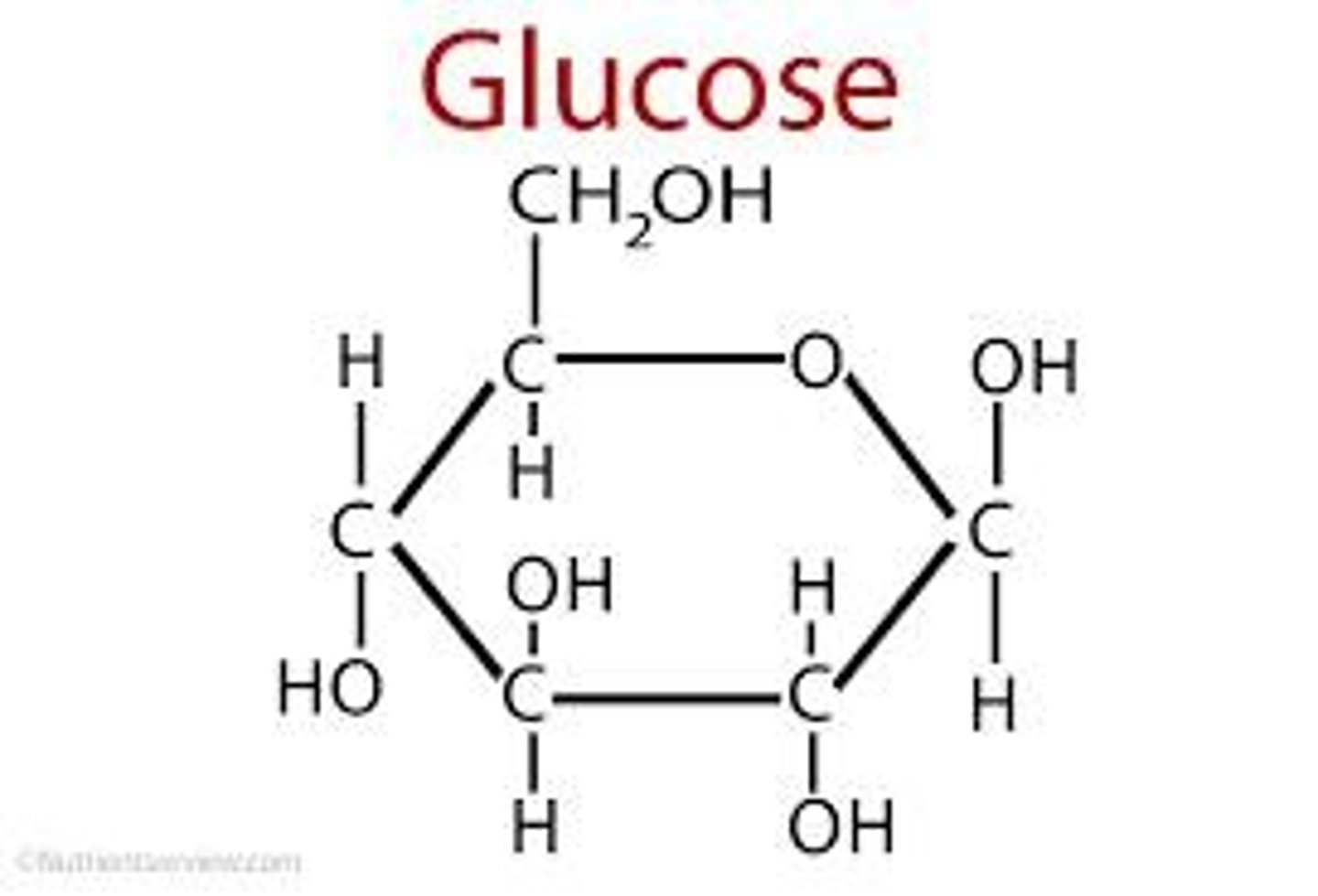
Glucose
Chemical formula: C6H12O6
Sodium Chloride
Chemical formula: NaCl
Caffeine
Chemical formula: C8H10N4O2
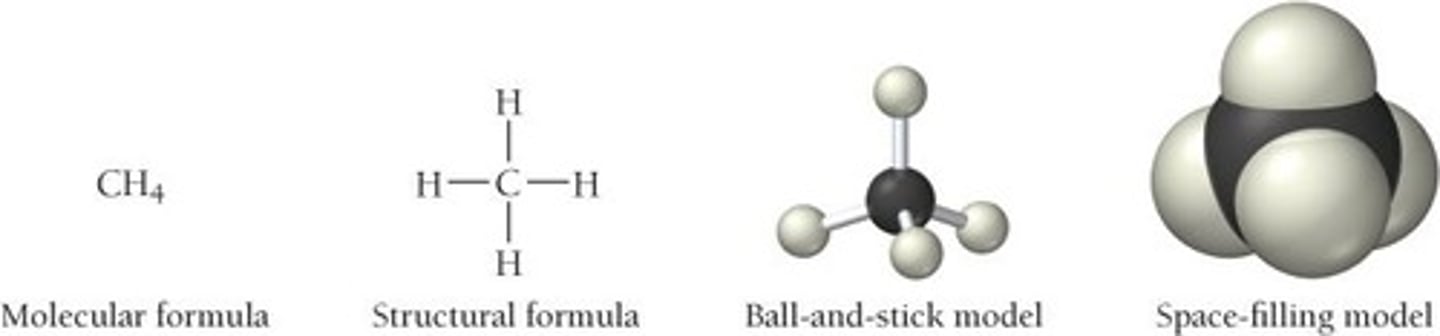
Molecular Formula
Shows the actual number of atoms of each type of element present in a compound. Also called the 'complete formula'.
Empirical Formula
Shows the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each type of element present in a compound. Also called the 'simplified formula'.
Structural Formula
Two-dimensional drawing of the chemical structure of a compound showing the chemical bonding of neighboring atoms in the compound represented by solid lines.
Binary
Two elements
Ionic compounds
Composed of metals that form only one type of ion (Type I) and more than one type of ion (Type II)
Binary Ionic Compounds
Composed of only one type of metal element & one type of nonmetal element.
Systematic Rule for Naming Binary Ionic Compounds
Base Name of Anion (Nonmetal) + '-ide' and Name of Metal Cation
Monatomic Anions
Base Name of Nonmetal Element + -ide + ion
Fluoride ion
F-
Oxide ion
O2-
Chloride ion
Cl-
Sulfide ion
S2-
Bromide ion
Br-
Nitride ion
N3-
Iodide ion
I-
Phosphide ion
P3-
Carbide ion
C4-
Monatomic Cations
Name of Element + ion
Sodium ion
Na+
Potassium ion
K+
Calcium ion
Ca2+
Type II Metals
Metals that form more than 1 type of ion
Roman Numeral (Stock) System
Name of metal with the charge of ion written by Roman numerals in parentheses following the metal name.
Old Latin Root System
Older Name of the metal ion, written in its Latin root stem, followed by the suffixes "-ous" or "-ic".
Criss-Cross Method
Look at the cation and anion components of the compound.
Oxoanion
Type of polyatomic anion that contains oxygen and another element.
Ammonium phosphate
NH4+ PO43-; Formula: (NH4)3PO4
Sodium hydroxide
Na+ OH-; Formula: NaOH
Potassium carbonate
K+ CO32-; Formula: K2CO3
Ferric chlorate
Fe3+ ClO3-; Formula: Fe(ClO3)3
Binary Molecular Compounds
Composed of two types of nonmetal elements.
Acid
An acid is a molecular compound that produces H+ ions when dissolved in water.
Binary Acids
Contain hydrogen and a nonmetal element.
Oxoacids
Contain hydrogen, oxygen, and another nonmetal element.
Hydrochloric acid
HCl
Hydrofluoric acid
HF
Hydrobromic acid
HBr
Hydroiodic acid
HI
Hydronitric acid
H3N
Hydrosulfuric acid
H2S (Base Name: 'sulfur')
Hydrophosphoric acid
H3P (Base Name: 'phosphor')
Chemical Equation
A representation of a chemical reaction that has the chemical formula(s) of the starting materials (REACTANTS) written on the left side and the chemical formula(s) of the end/finished materials (PRODUCTS) written on the right side.
General Setup of Chemical Equation
REACTANT(S) PRODUCT(S)
State Abbreviations
The physical state of a pure substance in a chemical equation is often specified by writing the correct abbreviation in parentheses after the chemical formula of the substance.
Balanced Chemical Equation
A balanced chemical equation is one in which the numbers of each type of atom on both sides of the equation are equal.
Integer Coefficients
Inserted in front of the formulas of the reactants and products when balancing chemical equations.
Combustion of methane
CH4(g) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g)
Balancing Order for Combustion Reactions
Balance Carbon, Balance Hydrogen, Balance Oxygen.
Example of Balancing Chemical Equations
C8H18(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g)
Polyatomic Unit
Treat the polyatomic unit as a single unit and balance it out as a whole.
Practice Examples
Ca + B2O3 B + CaO, NO2 + H2O HNO3 + NO, H2 + Mn2O3 Mn + H2O, C4H10 + O2 CO2 + H2O.