module 2 tuts p7
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Pharmacognosy
Study drugs from natural sources: plants, animals, microbes
Crude drugs
drugs of plant, animal and microbial origin that contain natural substances that have undergone only the processes of collection and drying
Quality
Intrinsic value of a drug
Purity
Absence of adulterants
EVALUATION OF CRUDE DRUGS
Organoleptic Evaluation
Physical Evaluation
Microscopic Evaluation
Pharmacologic Evaluation (Bioassay)
Chemical Evaluation
Organoleptic Evaluation
Use of sense organs – the macroscopic appearance of the drug, its odor and taste, the sound or “snap” of the fracture, and the feel of the drug to the touch.
Physical Evaluation
Applies physical constants (e.g., optical rotation, solubility, melting point) to the active constituents of drugs.
Ex. Cinnamomum camphora - bark
Natural camphor - +41 to +43 Dextrorotatory
Synthetic camphor - 0; a Racemic Mixture
Microscopic Evaluation
Employed for powdered drug samples.
Use of microscope.
Pharmacologic Evaluation (Bioassay)
Employs animals or excised organs to evaluate the physiological activity/effect of drugs
Ex. Rabbits for head drop assay (tubocurarine), pyrogen test, assay of insulin
Cats for mydriatic effects of atropine; and for assay of glucagon
Chemical Evaluation
Use of reagents or chemical
Preferred method of determining official potency.
Ex. Titration (% purity)
C. Organoleptic method (MACROSCOPIC)
This method of evaluating crude drugs involves the use of the organs of senses. The analyst evaluates the macroscopic appearance of the drug, its odor and taste, the sound or “snap” of the fracture, and the feel of the drug to the touch.
A. Microscopic method
B. Biological method
C. Organoleptic method
D. Chemical method
A. Physical method
This method of evaluating crude drugs makes use of physical constants, such as optical rotation, to the active constituents of drugs.
A. Physical method
B. Chemical method
C. Biological method
D. Organoleptic method
anticancer
Taxol (Paclitaxel) is an ___ agent.
Taxus
Taxanes were originally identified from plants of the genus __
Paclitaxel (taxol)
Prototype of taxane
From bark of Taxus brevifolia / Pacific Yew
inhibit
Taxanes ____ the depolymerization of microtubules
True
The taxanes, paclitaxel and docetaxel, and cabazitaxel inhibit the depolymerization of microtubules
Rationale: This stabilizing effect prevents cell division.
True
Paclitaxel, docetaxel, cabazitaxel are TAXANES
Sinigrin is an Isothiocyanate Glycoside
Prunasin is a Cyanogenic Glycoside
True
Taxanes are diterpenes
PRUNASIN
A cyanogenic glycoside that occurs in the bark of Prunus serotina
CYANIDE FORMING GLYCOSIDES = TOXIC
Used as anticancer agent = laetrile or vit. B17
Aglycone is MANDELONITRILE.
Yields hydrogen cyanide on hydrolysis
Hydrocyanic acid (HCN)
Cyanogenic Glycosides when hydrolyzed yield cyanide also known as ___
Prunasin, amygdalin
Cyanogenic Glycosides
Aglycone: MANDELONITRILE
Prunasin
Amygdalin
Laetrile (Vitamin B17) = obsolete anticancer agent
Cyanogenic Glycosides
Sources:
Kernels of Apricot (Prunus armeniaca)
Kernels of Bitter Almond (Prunus amygdalus var. amara)
Stems and barks of Wild Cherry (Prunus serotina)
GLYCOSIDES
They are acetals in which the hydroxyl of the sugar (glycone) is condensed with the hydroxyl group of the non-sugar component (aglycone)
GLYCOSIDES
Both alpha- and beta-glycosides exist, but ONLY the beta form occurs in nature
Natural enzymes like emulsin hydrolyze only the beta forms
Emulsin
Collective term for Amygdalase and Prunase
AMYGDALASE catalyzes the hydrolysis of AMYGDALIN → PRUNASIN
PRUNASE catalyzes the hydrolysis of PRUNASIN → MANDELONITRILE → HYDROCYANIC ACID
They are beta glucosidases
True
The non-sugar component of glycosides is aglycone or genin, and the sugar component is glycone.
Naringin
Flavonol Glycoside
Aglycone: Flavonoid
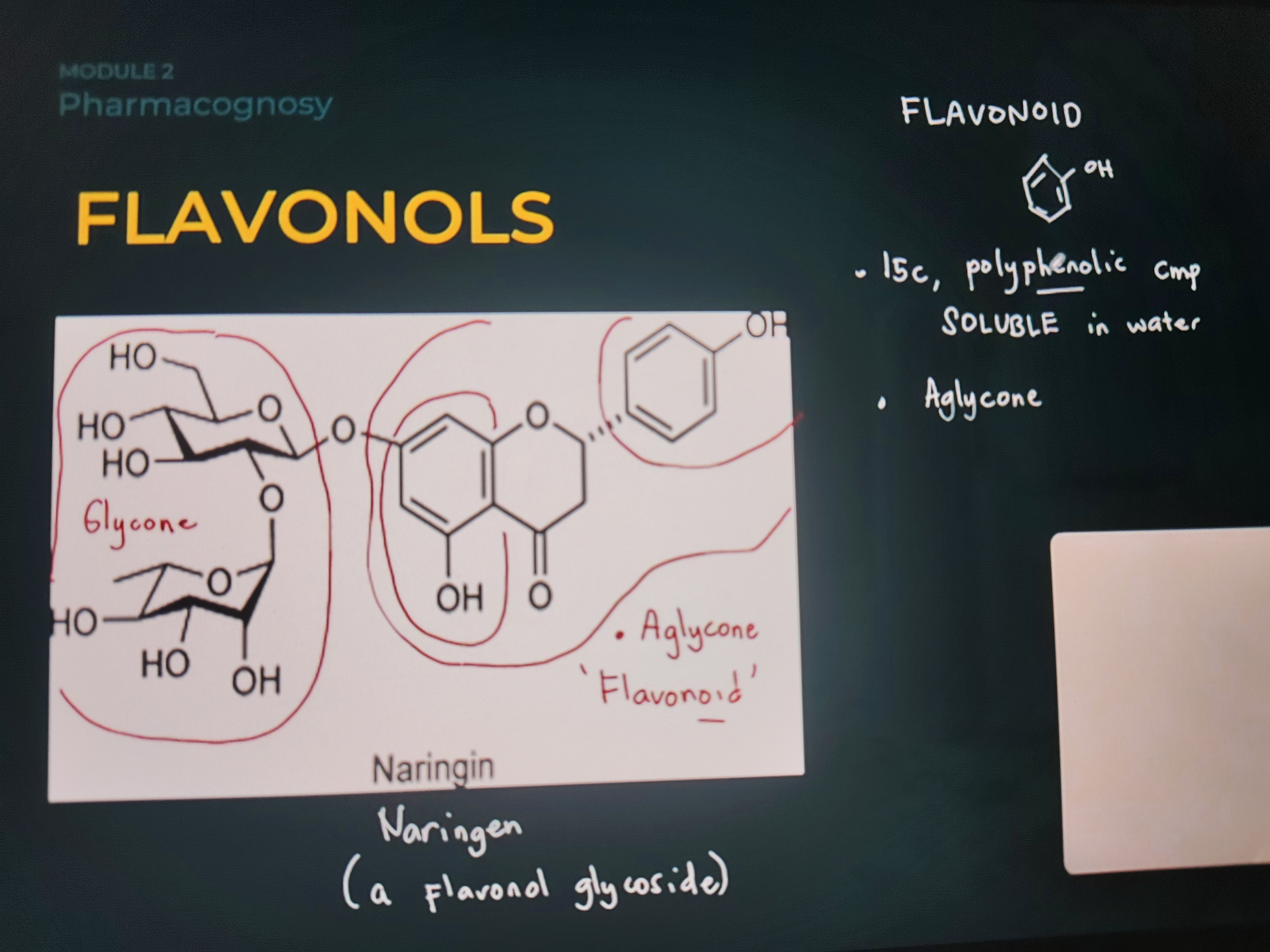
FLAVONOIDS
POLYPHENOLIC molecules containing 15 CARBON atoms and are SOLUBLE in water.
Examples are naringin, rutin, quercitrin, and hesperidin
Vitamin P (Permeability Factors)
Rutin & Hesperidin are ____ (Permeability Factors); they are Flavonol Glycosides
Treatment of capillary fragility
Treat symptoms of common colds
phenolic
Arbutin is a ___ Glycoside
Vitamin P (Permeability Factors)
Rutin and hesperidin are called
are used in the treatment of conditions characterized by capillary bleeding and increased fragility
FLAVONOIDS
These are aglycones of flavonol glycosides
Hydrolyzable Tannins
Hydrolysis: + HCl
Converted to PHENOLIC ACIDS and SUGARS
Gallic acid & Ellagic acid (Gallotannins)
Ferric Chloride Test
Bluish black ppt
Bromine Water Test
No precipitate
Less resistant to microbial degradation
Leather: BLOOM LEATHER
Non-hydrolyzable Tannins (Condensed Tannins)
Hydrolysis: + HCl
Not hydrolyzed
Polymerize forming red insoluble compounds called as PHLOBAPHENES
Product of condensation of Flavan-3-ols or Flavan-3,4-diols
Ferric Chloride Test
Greenish black test
Bromine Water Test
Has precipitate
More resistant to microbial degradation compared to hydrolyzable tannins
Leather: TANNER'S RED LEATHER
Hydrolyzable Tannins
Gallotannin is a ____
Gallic Acid
Hydrolyzable Tannins consist of ___ or related polyhydric compounds esterified with glucose
PHENOLIC ACIDS & SUGARS
Hydrolyzable Tannins readily hydrolyze to form ____ and ____
Non-hydrolyzable Tannins (Condensed Tannins)
result from the CONDENSATION of 2 or more flavan-3-ols such as catechin or flavan-3,4-diols such as leucocyanidin
PHLOBAPHENES
Non-hydrolyzable Tannins (Condensed Tannins)
When treated with hydrolytic agents, they tend to polymerize, yielding insoluble, red-colored products called ____
Non-hydrolyzable Tannins (Condensed Tannins)
are SOLUBLE in water, alcohols, and acetone and can coagulate proteins
Non-hydrolyzable Tannins (Condensed Tannins)
are more resistant to microbial attack than hydrolysable tannins
RESINATE
The metallic salts of resins are called
True
Metallic salts of resin acids are called RESINATES
Balsams
Are resinous mixtures that contain cinnamic acid, benzoic acid, or both, or esters of these acids
True
Resins are INSOLUBLE IN WATER; Resins are SOLUBLE in ALCOHOL + ORGANIC SOLVENTS
RESINS
Chemically, ___ are complex mixtures of resin acids, resin alcohols, resinotannols, esters, and resenes
Cinchona Alkaloids
Used as antimalarial agents
QUINIDINE - antimalarial and antiarrhythmic agent
CHEMICALLY, they are QUINOLINE ALKALOIDS
Parent alkaloid is CINCHONINE
CINCHONINE is the DEXTRO ISOMER of CINCHONIDINE
QUINIDINE is the DEXTRO ISOMER of QUININE
Cinchona Alkaloids
Source
Bark of Cinchona succirubra (Red)
Bark of Cinchona calisaya (Yellow)
Cinchonine
the parent alkaloid of the quinine series
6-methoxycinchonine
Quinine and Quinidine chemically _____
QUINOLINE ALKALOIDS
Cinchonine, Cinchonidine, Quinine, and Quinidine are
True
CINCHONINE is the DEXTRO ISOMER of CINCHONIDINE
QUINIDINE is the DEXTRO ISOMER of QUININE
ANTIMALARIAL
Cinchona alkaloids are ___ agents
GUMS AND MUCILAGES
POLYSACCHARIDES
HETEROGLYCAN
Upon hydrolysis, they yield different types of sugar units
Ex. Carrageenan (marine gum) → Glucose, Arabinose, Galactose, Fructose
Shrub or Plant Exudates
Aki & Travis Stayed in India
Aki - Acacia
Travis - Tragacanth
Stayed - Sterculia (Karaya gum)
India - Indian Gum (Ghatti)
Alcohol, USP
Acacia gum is incompatible with ___ (turbid soln)
Tragacanth
MOST RESISTANT TO ACID HYDROLYSIS
Sterculia (Karaya Gum)
MOST FETID GUM (amoy tae)
Ghatti
Substitute for acacia
Marine Gums
Dan and Al went to Japan to buy a Car
Dan - Danish Agar
Al - Algin
Japan - Japanese Isinglas (Agar)
Car - Carrageenan
Algin
Isolated from brown seaweeds (Macrocystis pyrifera)
Seed Gums
The Queen & St. John must be Guarded from Psychotics
The Queen - Quince or Cydonium
St. John - St. John’s Bread (Locust Bean Gum)
Guarded - Guar gum
Psychotics - Psyllium
Microbial Gums
Xanthan - Xanthomonas campestris
Dextran
Cellulose Derivatives Gum
Carboxymethylcellulose
Alternative to gums n mucilages
Pectin
Plant Extract; Extracted from the inner rind of citrus fruits and apple pomace
True
Locust Bean Gum → Seed Gums
Pectin → Plant Extract
Xanthan → Microbial Gum
Carboxymethylcellulose → Cellulose Derivatives
Tragacanth → Shrub or Tree Exudate
VOLATILE OILS
also known as essential oils, are aromatic oily liquids found in many plants. They are highly volatile and evaporate easily at room temperature.
VOLATILE OILS
Isoprenoids or Terpenoids (via mevalonic acid pathway)
Phenylpropanoids (via shikimic acid pathway)
METHODS OF EXTRACTING VOLATILE OILS
Water Distillation
Direct Steam Distillation
Water and Steam Distillation
Destructive Distillation
Expression
Ecuelle
Enfleurage
Enzymatic Action
Water Distillation
Dried parts
Example: Turpentine oil - from dried parts of Pinus palustris
Direct Steam Distillation
Fresh parts
Example: Spearmint oil from Mentha spicata; Peppermint oil from Mentha piperita
Water and Steam Distillation
Dried or Fresh
Example: Clove oil; Cinnamon oil
Destructive Distillation
Aka pyrolysis (subjected to high temperature without the presence of air)
Empyreumatic oils
Example: Tar oil from Pinus palustris
True
Distillation is the most common but it employs heat so it cannot be used in heat sensitive volatile oils
For heat labile volatile oils, expression is used (ecuelle & enfleurage & sponge method)
Ecuelle
Citrus volatile oils
Example: Lemon oil from Citrus limon
Enfleurage
Flower petals
Example: Rose oil
Enzymatic Action
Glycosidic volatile oils
Example: Mustard oils
Black mustard - Sinigrin → Allyl Isothiocyanate
White mustard - Sinalbin → Acrinyl Isothiocyanate
They are converted by MYROSIN to Allyl and Acrinyl Isothiocyanate = glycosidic volatile oils
True
Volatile oils contain
Terpenoids - H, C, and another element (isoprenoids) via MVA
Terpenes - H, C (isoprene) via MVA
Phenylpropanoids - aromatic via shikimic acid pathway
TERPENES
Made up of isoprene units
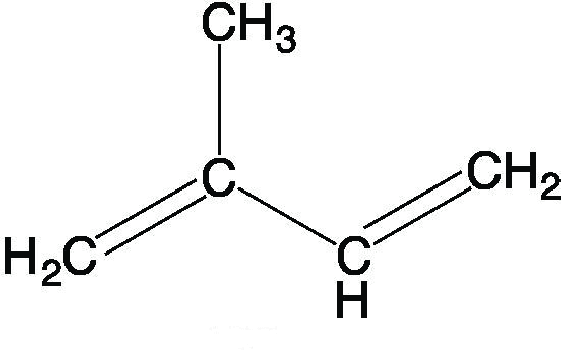
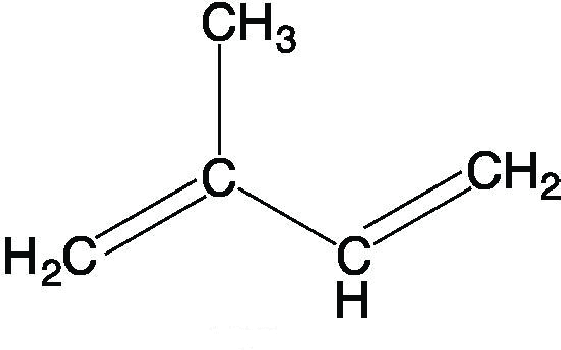
ISOPRENE
5-carbon compound: CH₂=C(CH₃)-CH=CH₂
Iso = branch/substituent on the 2nd carbon
Ene = double bonds
C5H8
Monoterpenes
2 isoprene units - C₁₀H₁₆
Examples:
Carvone (Caraway oil) - ketone
Linalyl acetate (Lavender oil) - ester
Diosphenol (Buchu oil) - ketone
Methylsalicylate (Wintergreen oil) - ester
Sesquiterpenes
3 isoprene units - C₁₅H₂₄
Examples:
Artemisinin ⭐
Bisabolol
Farnesol
Eudesmol
Artemisinin
Novel antimalarial agent (new); isolated from a plant Sweet Wormwood (Artemisia annua
Ester derivative:
Artesunate - prone to hydrolysis
Ether derivative
Artemether - most potent
Combined with Lumefantrine
For chloroquine resistant malaria
Metabolite of Artesunate, Artemether, Artemisinin
Dihydroartemisinin
Artesunate
Ester derivative of artemisinin; prone to hydrolysis
Artemether
Ether derivative of artemisinin - most potent
Combined with Lumefantrine for chloroquine resistant malaria
Dihydroartemisinin
Metabolite of Artesunate, Artemether, Artemisinin - not a prodrug
Least stable form
Diterpenes
4 isoprene units - C₂₀H₃₂
Examples:
Phytol
Retinal/Retinol/Vitamin A
Paclitaxel
Gingkolides
Bilobalides
Triterpenes
6 isoprene units - C₃₀H₄₈
Examples:
Lanosterol
Squalene
Tetraterpene
8 isoprene units - C₄₀H₆₄
Examples:
Beta carotene (precursor of retinol)
Lycopene
Lutein
True
Volatile oils act as insect attractants and insect repellants
Glandular Hairs
Sa labia maraming hair
Lamiaceae / Labiatae (MINT family)
Mentha piperita - peppermint
Mentha spicata - spearmint
Thymus vulgaris - thyme
Lavandula angustifolia - lavender
Origanum vulgare - oregano
Modified Parenchymal Cells
Si pare na mahilig sa pipe
Piperaceae
Piper nigrum - black pepper
Peperomia pellucida - pansit pansitan or ulasimang bato for gout
Vittae (oil tubes)
Sa belli may tae
Apiaceae / Umbelliferae (carrot family)
Foeniculum vulgare - fennel
Coriandrum sativum - coriander
Carum carvi - caraway
Conium maculatum - poison hemlock
Schizogenous and Lysigenous Passages
Pinaceae (pine) & Rutaceae (citrus)
Pinus palustris
Pinus strobus
Citrus spp
Artemisia absinthium
D. Steam Distillation
Peppermint oil is isolated from the fresh leaves of Mentha piperita. Determine the best method to isolate the oil.
A. Enfleurage
B. Extraction with a volatile solvent
C. Expression
D. Steam Distillation
B. Diterpenes
What type of terpenes are retinol and phytol?
A. Monoterpenes
B. Diterpenes
C. Triterpenes
D. Sesquiterpenes
B. Diterpenes
This group of terpenes are composed of 20 carbon atoms.
A. Sesquiterpenes - C15
B. Diterpenes
C. Triterpenes - C30
D. Tetraterpenes - C40
B. Schizogenous intercellular spaces
What special secretory structures are found in Pinus palustris?
A. Modified parenchyma cells
B. Schizogenous intercellular spaces
C. Vittae
D. Glandular hairs
CH2=C(CH3)-CH=CH2
Isoprene is a
A. 5-carbon compound with the formula: CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2CH3
B. 3-carbon compound with the formula: CH2=C=CH2
C. 4-carbon compound with the formula: CH2=CH-CH=CH2
D. 5-carbon compound with the formula: CH2=C(CH3)-CH=CH2