HSC Biology Module 6
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
How do mutations occur?
1. spontaneous mutations: e.g. naturally occurring electromagnetic radiation from sun causes cancer
2. induced mutations: e.g. artificially electromagnetic radiation
where do mutations occur?
1. germine mutation
2. somatic mutation
what are the types of mutations?
1. chromosome mutation
2. chromosome abnormalities
3. point mutation
4. substitutions
5. frame shift
What is a Mutagen?
A chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and causes a mutation.
Carcinogenic mutagens
causing mutations that result in cancer
What are the DNA repair mechanisms?
1. base excision repair
2. nucleotide excision repair
3. mismatch repair
4. double stranded break repair
what are the three mutagens?
1. physical e.g. electromagnetic radiation
2. chemical e.g. x rays
3. naturally occurring e.g. virus in host cells
electromagnetic radiation
transmitted through waves e..g UV radiation acts as mutagen casing 2 adjacent base pairs to form covalent bonds causing dimer structure
5 ways mutations classified
1. DNA affected (gene or chromosome)
2. arise (spontaneous or induced)
3. change DNA structure (point, frameshift, deletions, insertions, translocations)
4. DNA functioning and proteins (nonsense, missence, neutral, silent)
point mutation
gene mutation in which a single base pair in DNA has been changed
1. substitution
2. frameshift
Subsitution mutation
1 base is change for a different base e.g. sickle cella Anaemia
1. missense: change in amino acid
2. non sense: stop codon
3. silent/neutral: sam amino acid
frameshift mutation
mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide
1. insertion
2. deletion
gene mutation
a change in the base sequence of a gene
chromosomal mutation
A change in the chromosome structure, resulting in new gene combinations
chromosomal deletion
A mutation involving the loss of a section of a chromosome
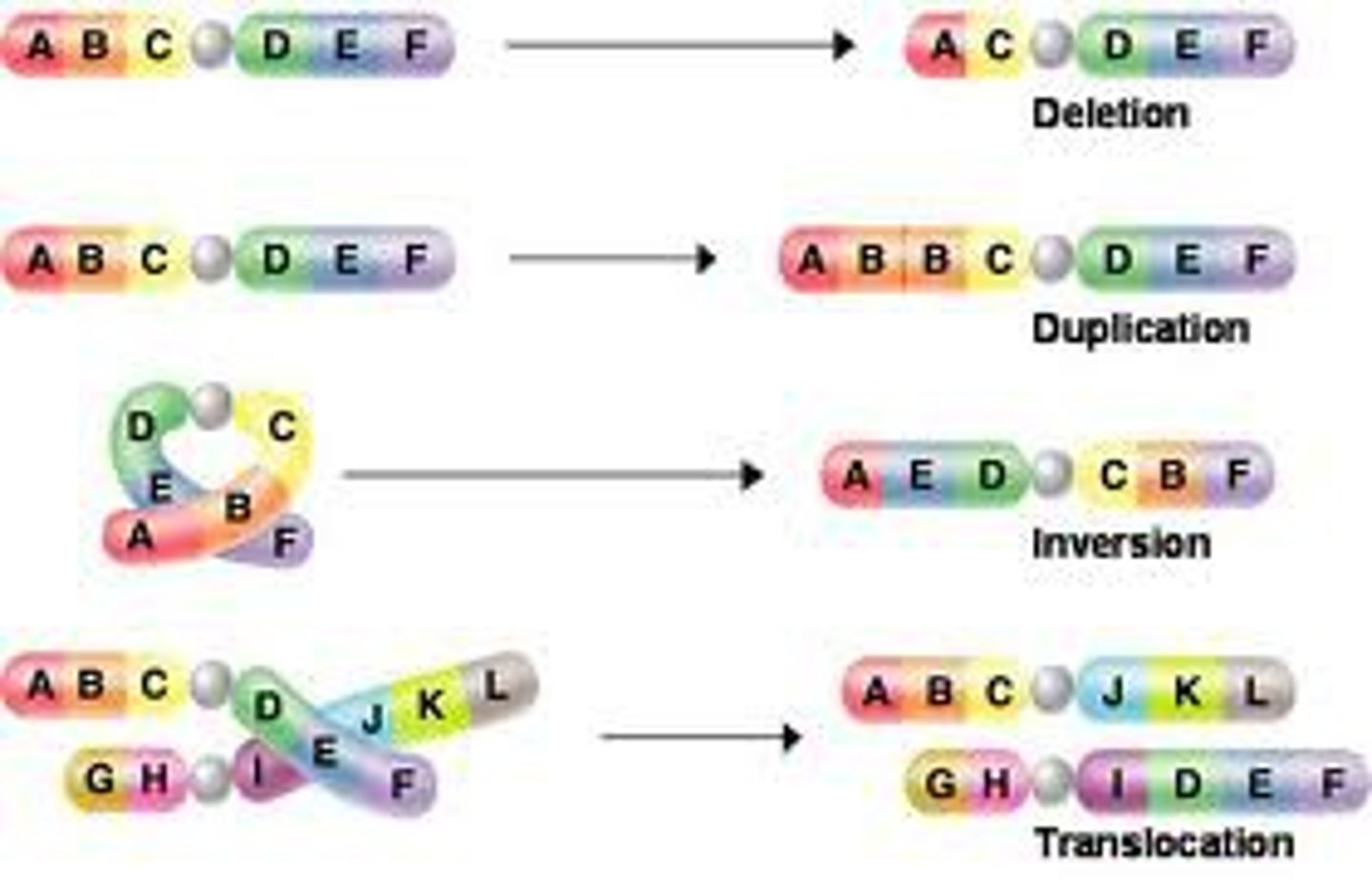
chromosomal duplication
A mutation involving the duplication of a section of a chromosome
chromosomal inversion
When part of the chromosome becomes oriented in the reverse of its usual direction
chromosomal insertion
section breaks off and attaches to different chromosome which lowers genetic variation
chromosomal translocation
When part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another non homologous, chromosome.
Aneuploidy
Abnormal number of chromosomes.
example of aneuploidy
Down syndrome (trisomy 21) extra copy of chromosome 21
karyotype chromosomal diagnosis
describes abnormality and if there is a disability
somatic and germline mutations
1. somatic: most mutations not inherited
2. germline: in gonads producing gametes and mutation inherited
effect of somatic mutation
1. no effect
2. cell dies
3. becomes cancerous
effect of germline mutation
1. no gamete involved means no effect
2. gametes involved new inheritance mutation
what are examples of non coding DNA (introns)
telomeres: protect chromosome deterioration
chromosomal errors
crossing over fails and chromosomal aberrations may be introduced
e.g. inverted
what are changes in chromosomal numbers (non-disjunction)?
when sister chromatids do not separate correctly e.g. Down syndrome
difference in mutation, variation, variability
mutation: unusual error
variation: difference in characteristics
variability: different forms of gene in population
selective pressure
when the environment pushes an individual or population to adapt or evolve
sexual selection
when individuals select mates based on heritable traits
mutation
formation of new alleles
genetic drift
A change in the allele frequency of a population as a result of chance events rather than natural selection.
founder effect
change in allele frequencies as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population e.g. colonisation
bottle neck effect
A change in allele frequency following a dramatic reduction in the size of a population
gene flow (migration)
movement of alleles from one population to another e.g. immigration
Biotechnology
A form of technology that uses living organisms, usually genes, to modify products, to make or modify plants and animals, or to develop other microorganisms for specific purposes.
ancient biotechnology
1. farming and selective breeding
2. crossbreeding
3. food production (cheese and bread)
4. fermentation (alcohol )
5. medicine (plants and herbs)
Modern Biotechnology
1. DNA splicing (restriction enzymes splice bases)
2. DNA amplification (polymerise chain reaction tor replicate)
3. recombine DNA (DNA ligase joins fragments)
social and ethical implications
agriculture(GM): GM organisms, habitat destruction
industrial (anthrax): bioterrorism, increased defence
medical (insulin): labelling, animal welfare
biological control
the intentional release of a natural enemy to attack a pest population
Bioterrorism
the deliberate spread of pathogenic organisms into a community to cause widespread illness
BIOTECHNOLOGY monoclonal antibodies
a collection of identical antibodies that interact with a single antigen site
examples of gene technology
1. gene silencing
2. marker assisted breeding (desirable traits)
3. CRISPR-Cas9 (restriction nuclease to regulate genes)
why is biotechnology limited?
1. financial positions
2. lifestyle
3. social profile
example of biotechnology for greater good
1. recombinant DNA for BT Cotton
2. genetically modified organisms for golden rice
what is golden rice
GM rice crop enhanced with Vitamin A
POSITIVE: more nutritional value and vitamins kore accessible
NEGATIVE: increased retail price, adding new genes to gene pool
difference between traditional and bio fortification
fortification: nutrients added while processing
bio fortification: breeding crops with added nutritional value e.g. golden rice
social implications of biotechnology
1. privacy (DNA profiling stores information)
2. health (GM have different ingredients)
3. societies views (damage environment)
4. social equality, access, cost (golden rice)
ethical implications of biotechnology
1. legal implications (who should know of genetic disorders)
2. medical intervention and consent (pregnant woman of disorder that can't be treated)
3. philosophical, cultural and religion (acting as God)
4. animal welfare (transgenic pigs impact joints)
loss of biodiversity
overtime reduced increase in biotechnology
conservation biology
short term new gene means more variation
uses of biotechnology
1. agriculture (Bt Cotton)
2. industrial (bacteria to decrease toxic waste)
3. medical (knockout mice to model diseases like cancer)
Bioremediation
The use of living organisms to detoxify and restore polluted and degraded ecosystems
Biosensors
Microbes that can locate biologically active pollutants
Biopharming
Use of genetically engineered animals to act as biofactories for producing drugs, vaccines, antibodies, hormones, industrial chemicals such as plastics and detergents, and human body organs.
Xenotransplantation
A transplantation of an organ, tissue, or cells between two different species.
future use of biotechnology
e.g. coral reefs
reduce devastation on coral reeds by global warming, increase water temp and bleaching
'super coral' though selectively breeding coral, investigating genomes and insert genes from heat resistant corals through CRISPR-Cas9
reproductive technologies
1. selective breeding
2. artificial insemination
3. artificial pollination
4. cloning
5. IVF
6. transgenic species
7. whole organism breeding
8. recombinant DNA
artificial insemination
a process of fertilisation in which a man's sperm is placed directly into a woman's vagina e.g. sport horses
POSITIVE: cost effective, transport, reduce mating
NEGATIVE: one father
artificial pollination
process of cross pollination in which pollen collected from one plant is manually transferred to the stigma of a second plant
POSITIVE: breeder control
NEGATIVE: not exact in determining genes
IVF (in vitro fertilisation)
creating an embryo (joining a sperm and an ovum/ova) outside of a human body in Petri dish
POSITIVE: treat fertility issues
NEGATIVE: religious issues (acting as God)
whole organism cloning
Creating a whole new organism using the DNA of an already existing individual
gene cloning
the production of multiple copies of a single gene
therapeutic cloning
the use of SCNT to produce human embryos for research purposes
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
A technique for amplifying DNA in vitro by incubating with special primers, DNA polymerase molecules, and nucleotides.
1. denaturing
2. annealing
3. extension
Recombinant DNA technology
technology that combines genes from different sources into a single DNA molecule
e.g. transgenic organism
Transgenic Organism (GMO)
genetically modified organism; any organism that contains genes from other organisms
three examples of transgenic species
1. knockout mice (stem cells)
2. hepatitis B vaccine (recombinant DNA)
3. pig organs (xenotransplantation)
Process of Recombinant DNA
1. gene isolated
2. DNA fragments joined by ligase
3. plasmid inserted back into cell copies produced
4. gene inserted into another species
Recombinant DNA
insulin
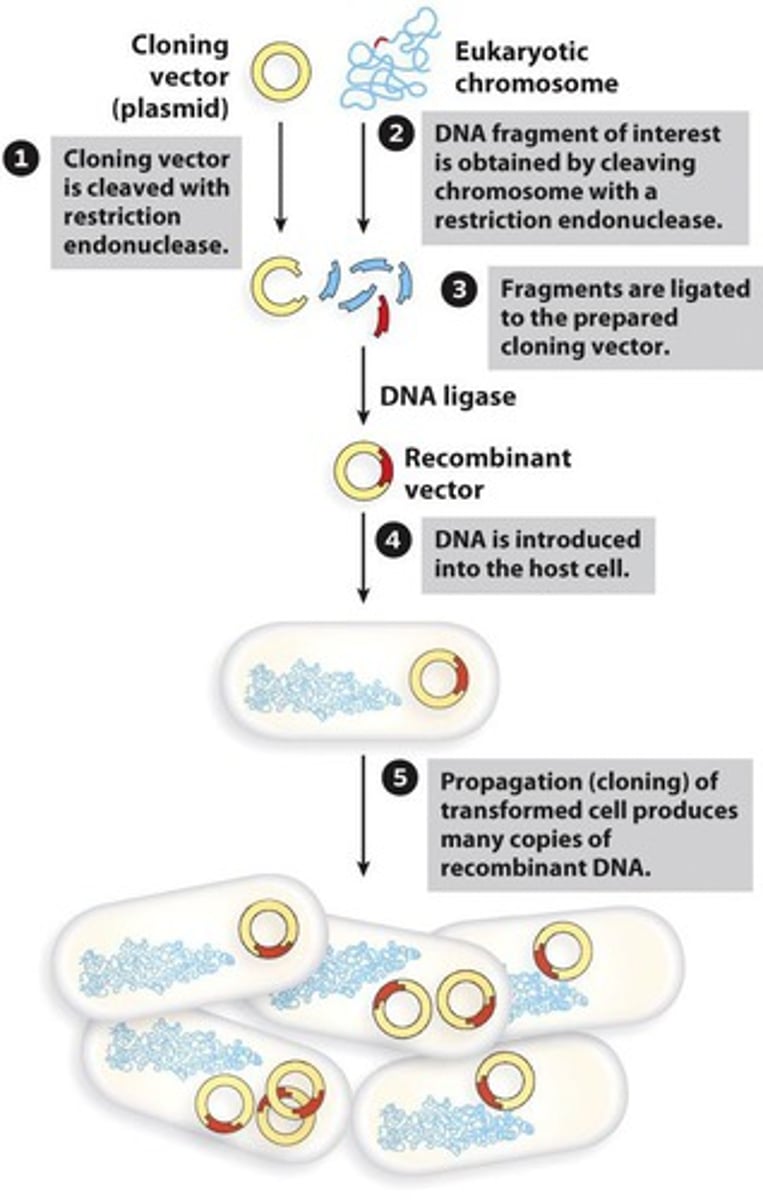
restriction enzymes
Enzyme that cuts DNA at a specific sequence of nucleotides
Vector
same self replicating DNA fragment e.g. E coli
gene delivery techniques
inserting desired gene into genome of a species
1. microinjection
2. biolisitcs
3. electroporation
4. transaction by viral vector
Bt cotton
contains a gene that enables the plant to produce its own pest-killing toxin e.g. caterpillar
knockout mice
-gene is intentionally deleted (knocked out)
- used to study human diseases
hepititis B vaccine
Recombinant DNA
how does xenotransplantation work?
organs from transgenic swine have complementary surface markers that inhibit activation of organ
gene therapy
The insertion of working copies of a gene into the cells of a person with a genetic disorder in an attempt to correct the disorder
Charles Darwin, Origin of Species
Presented the theory of evolution, which proposed that creation was an ongoing process in which mutation and natural selection constantly give rise to new species. Sparked a long-running religious debate over the issue of creation.
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism)
a single base-pair site where variation is found in at least 1% of the population