MICR5831 L3: Genetic Machinery Translation 7/21/25
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
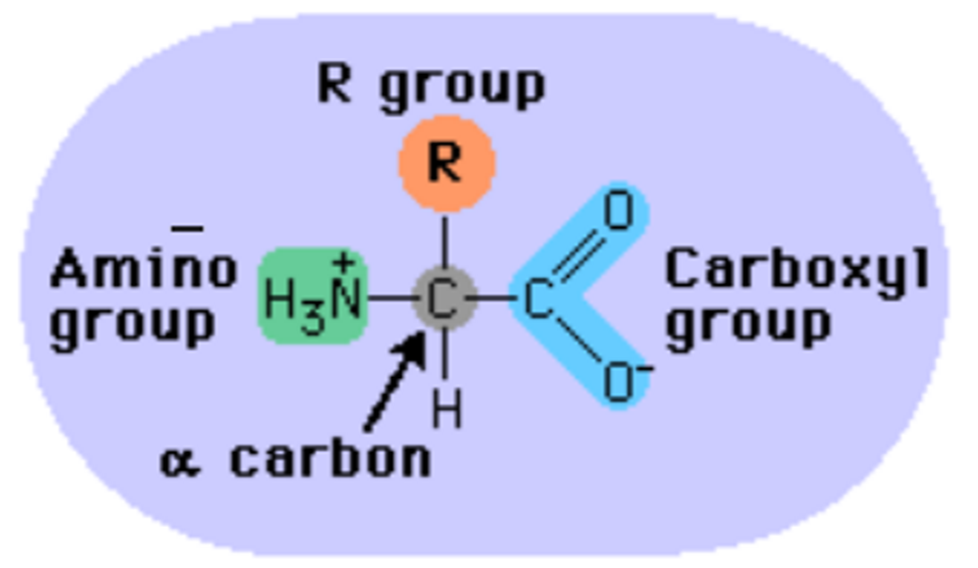
Draw and label a figure showing the major attributes of an amino acid. (slide 4)
1) Central alpha carbon
2) Amino group
3) Carboxyl group
4) R group
5) Hydrogen atom
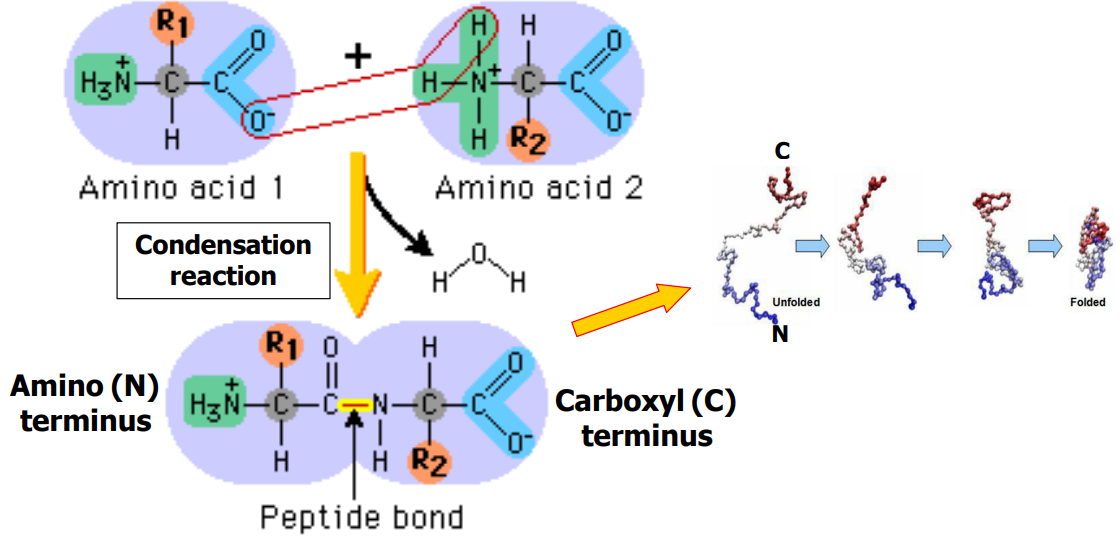
Explain the reaction that links two amino acids together. (slide 5)
-Condensation reaction
-Amino acid 1 (carboxyl) gives up oxygen
-Amino acid 2 (amino NH3 group) gives up 2 hydrogens
-C terminus (negative) + N terminus (positive) form new peptide bond
-H2O produced as byproduct
Explain the genetic code (slide 7)
-Three nucleotide bases (codon) encode an amino acid
-Genetic code is degenerate, 20 amino acids and 64 codons (3x STOP)
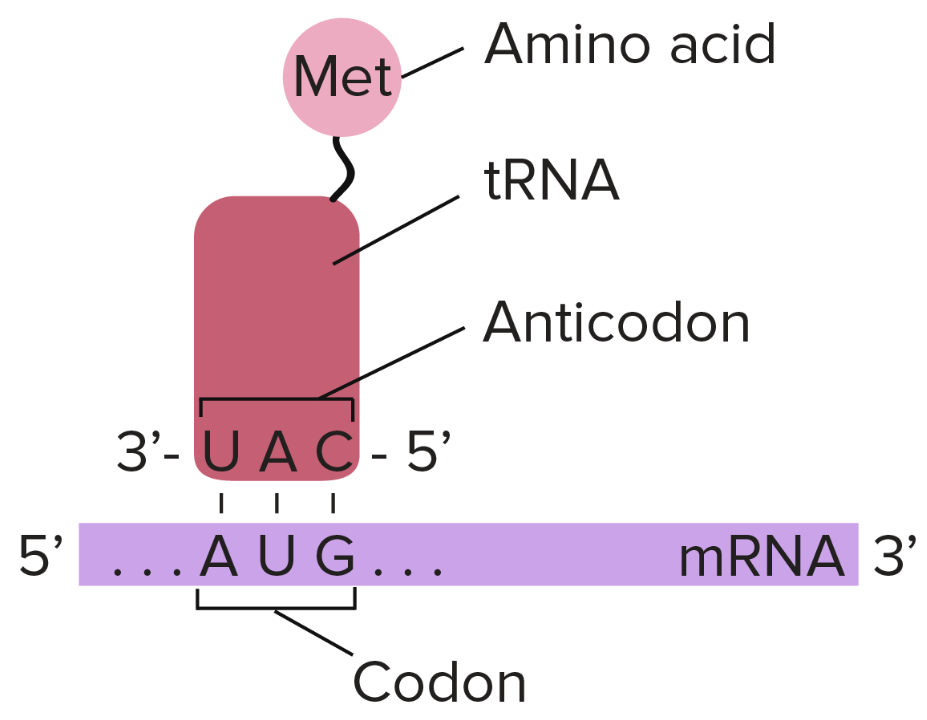
How does a tRNA recognize one codon? (slide 8)
-The first position of the codon is at the 5' end of the codon
-Binds to the third position (3' end) of the anticodon
How does a tRNA recognize multiple codons? (slide 9)
-Some tRNA's can bind at more than one codon
-Third nucleotide of the codon (on mRNA) and the first nucleotide of the anticodon (on tRNA) don't always follow strict rules
-Crick called this ability "wobble"
-Inosine (modified Adenosine) is in the first position in the anticodon of the tRNA
-Can bind to Uracil, Adenosine, or Cytosine in the third position of the codon
-This one tRNA recognizes three different codons
List the three binding sites found in ribosomes and give a brief description of what their function is. (slide 12)
E = exit : De-acylated tRNA exits ribosomal complex
P = peptidyl-tRNA : tRNA attached to the polypeptide chain
A = aminoacyl-tRNA : New tRNA enters ribosomal complex
How does a ribosome select a reading frame to translate? (slide 13)
-Binds to the Shine Dalgarno site
-Initiates translation from the start codon ATG
-Contains the binding sites for the tRNA molecules
Name the two components of a prokaryote ribosome and describe their function (slide 14)
Large Subunit (70S):
-Peptidyltransferase activity
-Catalyzes covalent bond between the amino acids
Small Subunit (30S):
-Binds to SD (Shine Dalgarno) site
-Initiates translation from the start codon ATG
-Contains binding sites for tRNA
Briefly describe the three steps in translation. (slide 17)
Initiation:
-Ribosome binds Shine Dalgarno sequence and facilitates tRNAMet alignment with Start codon (AUG)
Elongation:
-Ribosome moves along mRNA, new tRNAs align and peptide bonds formed between amino acids
Termination:
-Ribosome reaches Stop codon, releases new polypeptide and dissociates
Describe the first four steps in in the initiation of translation (slide 18)
1) 30S interacts with initiation factor (IF) and binds Shine Dalgarno sequence
2) Initiator tRNA binds (tRNAMet) aligns with start codon (AUG) in mRNA
3) 50S associates with 30S, releasing IF and forming 70S complex
4) tRNA occupies peptidyl (P) site of 50S subunit (aminoacyl (A) site is empty)
Describe the four steps in the elongation phase of translation (slide 19)
1) Second tRNA aligns with codon in A site
2) 50S mediates peptide bond formation
3) Ribosome moves to next codon, translocation of tRNAs
4) Proteins are synthesized N → C
What are the last three steps in translation termination? (slide 20)
1) Ribosome reaches STOP codon (UAA, UAG, UGA)
2) Release factors (RF) fill A site of 70S
3) Release of nascent (unfolded) protein polypeptide, disassociation of ribosome into 30S and 50S subunits
What is a cistron? What is a polycistron? How are they transcribed and translated (slide 22).
-Genes can be monocistronic (only one) or polycistronic (arranged end-on-end in operons)
-Polycistronic mRNA will contain multiple ORFs that will be translated separately to produce separate proteins
-After translation, proteins are spliced so inteins are removed and exteins are joined together
What is the one difference between the mRNA sequence and the coding strand of DNA?
T's are replaced by U's
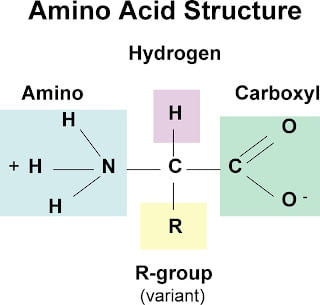
What are the components of an amino acid?
1) Central carbon
2) Carboxyl group
3) Amino group
4) R group (varies between amino acids)
5) Hydrogen group
What is the order for adding peptides together?
-N-terminus (positive) is added to C-terminus (negative)
-5' to 3' direction
What is necessary to create the peptide bond between the amino acids?
Condensation reaction
True or False: AUG is the only start codon
False, but the other start codons are likely only due to posttranscriptional modification
True or False: There are more codons than amino acids
True, 64 codons > 20 amino acids
Which codon has no wobble/degeneracy?
Tryp (Tryptophan)
What does it mean for the genetic code to be degenerate?
-Multiple codons respond to the same amino acid
-Last base is redundant (UGU and UGC are the same)
What makes it possible to fit 20 amino acids to 61 codons with only 31 kinds of tRNA?
Wobble base-pairings
True or False: tRNA only binds to one codon each
False
What is this?
-Wobble
-Some tRNAs can bind at more than one codon
-If inosine is in the first position at the anticodon, it can bind to U, A, or C at the 3rd position of the codon
-1 tRNA = 3 different codons
What is the relationship between each codon and anticodon?
-Antiparallel
-First position of codon at 5' end binds to 3' end of anticodon
If a genetic code is based on groups of 3 nucleotides, how many different reading frames will it have?
3 reading frames
Each ribosome has (blank) binding sites for mRNA and (blank) binding sites for tRNA
1 binding site for mRNA
3 binding sites for tRNA
Which tRNA binding site is this?
-New tRNA enters ribosomal complex
A (Aminoacyl tRNA)
Which tRNA binding site is this?
-tRNA is attached to the polypeptide chain
P (Peptidyl-tRNA)
Which tRNA binding site is this?
-De-acylated tRNA exits the ribosomal complex
E (Exit tRNA)
True or False: Methionine (AUG) can start anywhere in a protein
True
What is Methionine used for?
Translation initiation signal
What signs indicate that a Methionine (AUG) is the correct start signal for translation?
1) Ribosome binding site (RBS) motif in mRNA
2) Shine Dalgarno sequence located upstream
In addition to RBS motifs in the mRNA and a Shine Dalgarno sequence upstream of the AUG, what else can prokaryotes use to determine if this is the correct initiation signal?
Ribosome scanning ability
What does the 70S prokaryotic ribosome do?
-Facilitates tRNA interaction with mRNA
-Facilitates peptide bond formation between amino acids
What does the Large subunit of the 70S prokaryotic ribosome do during translation?
-Peptidyltransferase activity
-Catalyses the covalent bond between the amino acids
How does the large ribosomal subunit catalyze the covalent bond between amino acids during translation?
-Peptidyltransferase activity
-Catalyzes covalent bond
What does the Small subunit of the 70S prokaryotic ribosome do during translation?
-Binds to the Shine Dalgarno site
-Initiates translation from the start codon (ATG)
-Contains the binding sites for the tRNA molecules
What are the features of mRNA involved in translation?
-Shine Dalgarno sequence
-5' UTR, 3' UTR
-Start and stop codon
-Open Reading Frame
What happens during this step of translation?
-Initiation
-Ribosome binds Shine Dalgarno sequence
-tRNAMet aligns with Start Codon (AUG)
What happens during this step of translation?
-Elongation
-Ribosome moves along mRNA
-tRNAs align
-Peptide bonds form between amino acids
What happens during this step of translation?
-Termination
-Ribosome reaches Stop codon
-Releases new polypeptide and dissociates
Describe what happens during Initiation of translation (in full detail)
-30S interacts with initiation factor (IF) and binds Shine Dalgarno sequence
-Initiator tRNA binds (tRNAMet) aligns with start codon (AUG) in mRNA
-50S associates with 30S, releasing IF and forming 70S complex
-tRNA occupies peptidyl (P) site of 50S subunit (aminoacyl (A) site is empty)
During Initiation of translation, what does 30S Ribosome interact with in order to bind to the Shine Dalgarno sequence?
IF (Initiation Factor)
During initiation of translation, after 30S and IF bind to the Shine Dalgarno sequence:
What does the Initiator tRNA (tRNAMet) align with?
Start codon (AUG) in mRNA
During Initiation of translation, after the Initiator tRNA (tRNA) aligns with start codon (AUG) in mRNA:
What happens as a result of 50S and 30S associating together?
-IF (Initiation Factor) is released
-70S complex is formed
During Initiation of translation, after 50S and 30S associate together, releasing IF and forming 70S complex:
What site does the tRNA occupy?
-Peptidyl (P) site of the 50S unit
-Aminoacyl (A) site is empty
Describe what happens during Elongation of translation (in full detail)
-Second tRNA aligns with codon in A site
-50S mediates peptide bond formation
-Ribosome moves to next codon causing translocation of tRNAs
-Second tRNA occupies P site
-New tRNA occupies A site, new peptide bond formed and so on....
-Proteins are synthesized N → C
During Elongation of translation, in which site does the second tRNA align with the codon?
A site
During Elongation of translation, after the second tRNA aligns with the codon in A site:
What Ribosomal subunit mediates peptide formation?
50S Large Subunit
During Elongation of translation, after the 50S subunit mediates peptide bond formation:
What happens after the Ribosome moves to the next codon?
-tRNAs are translocated
-Second tRNA occupies P site
-New tRNA occupies A site
During Elongation of translation, after the ribosome moves onto the next codon and tRNAs are translocated:
How are the proteins synthesized?
Proteins are synthesized N -> C
Describe what happens during Termination of translation (in full detail)
-Ribosome reaches STOP codon
-Release factors fill A site of 70S mRNA
-Release of nascent, unfolded protein polypeptide
-Disassociation of ribosome into 30S and 50S subunits
During Termination of translation, what happens to the Ribosome first?
-Ribosome reaches STOP codon
-UAA, UGA, UAG
During Termination of translation, after the Ribosome reaches the STOP codon:
What 70S site do the Release Factors fill in?
A site
During Termination of translation, after the Release Factors (RF) fill the 70S A site:
What happens to the nascent/unfolded protein polypeptide?
What happens to the 70S Ribosome?
-Nascent protein polypeptide is released
-70S Ribosome dissociates into 30S and 50S subunits
What is a polycistron?
-Genes arranged end-on-end in operons
-Contains multiple ORFs
True or False: Polycistrons with multiple open reading frames will be translated separately to produce separate proteins
True
True or False: In bacteria, mRNA introns are removed/spliced out while exxons are joined together
False, bacterial mRNA is not spliced
True or False: In bacteria, protein inteins are removed/self-spliced while exteins are joined together
True
True or False: Bacterial proteins cannot be rearranged until after translation has occurred
True, splicing/rearrangement occurs post-translation but is very rare
What is this?
-Inteins
-Intervening sequences found in self-splicing proteins
-Flanked by exteins that join together post-splicing