hmi104 - hip, gluteal region and thigh
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
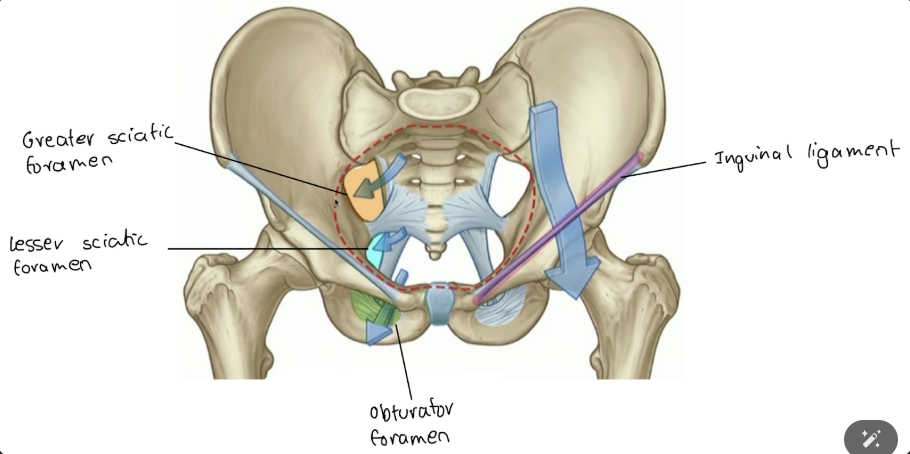
What does the greater sciatic foramen go to?
To the gluteal region and posterior thigh (i.e. sciatic nerve, piriform muscle, pudendal nerve)
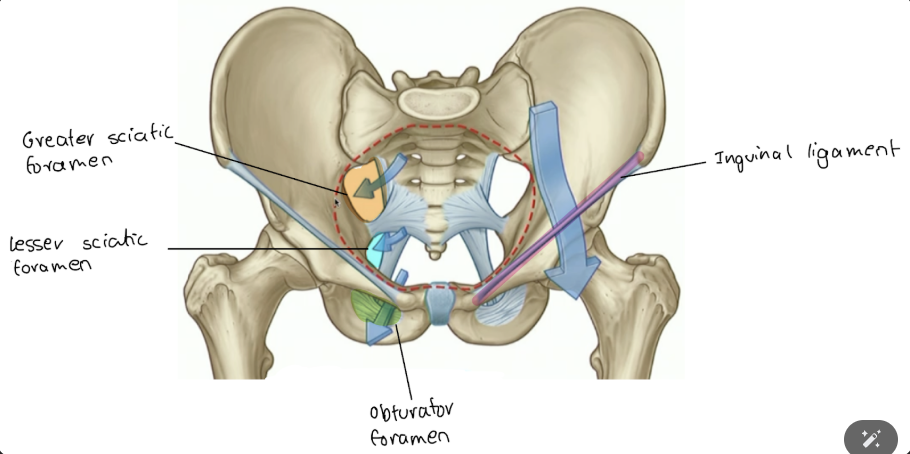
things go through the lesser sciatic foramen to where?
to perineum and gluteal region (i.e. pudendal nerve)
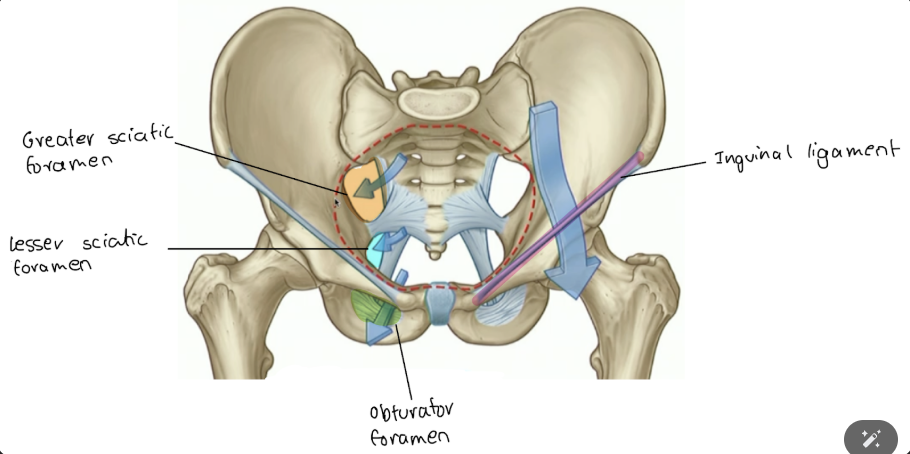
things go through the obturator foramen to where?
to medial thigh (i.e. obturator nerve, vessels)
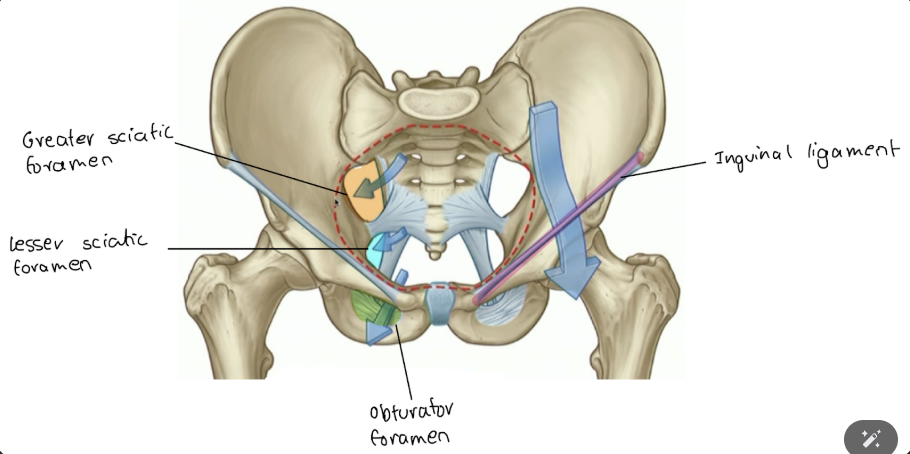
things go below the inguinal ligament to where?
to anterior thigh (i.e. femoral artery, nerve and vein)
What are the functions of the hip?
Both hip and knee joints are extended in standing position due to joint structure and ligaments, requiring minimal muscle effort and conserving energy.
Hip adduction minimizes lateral shift in the centre of gravity (helps maintain balance without side-to-side movement)
Rotation allows for greater steps
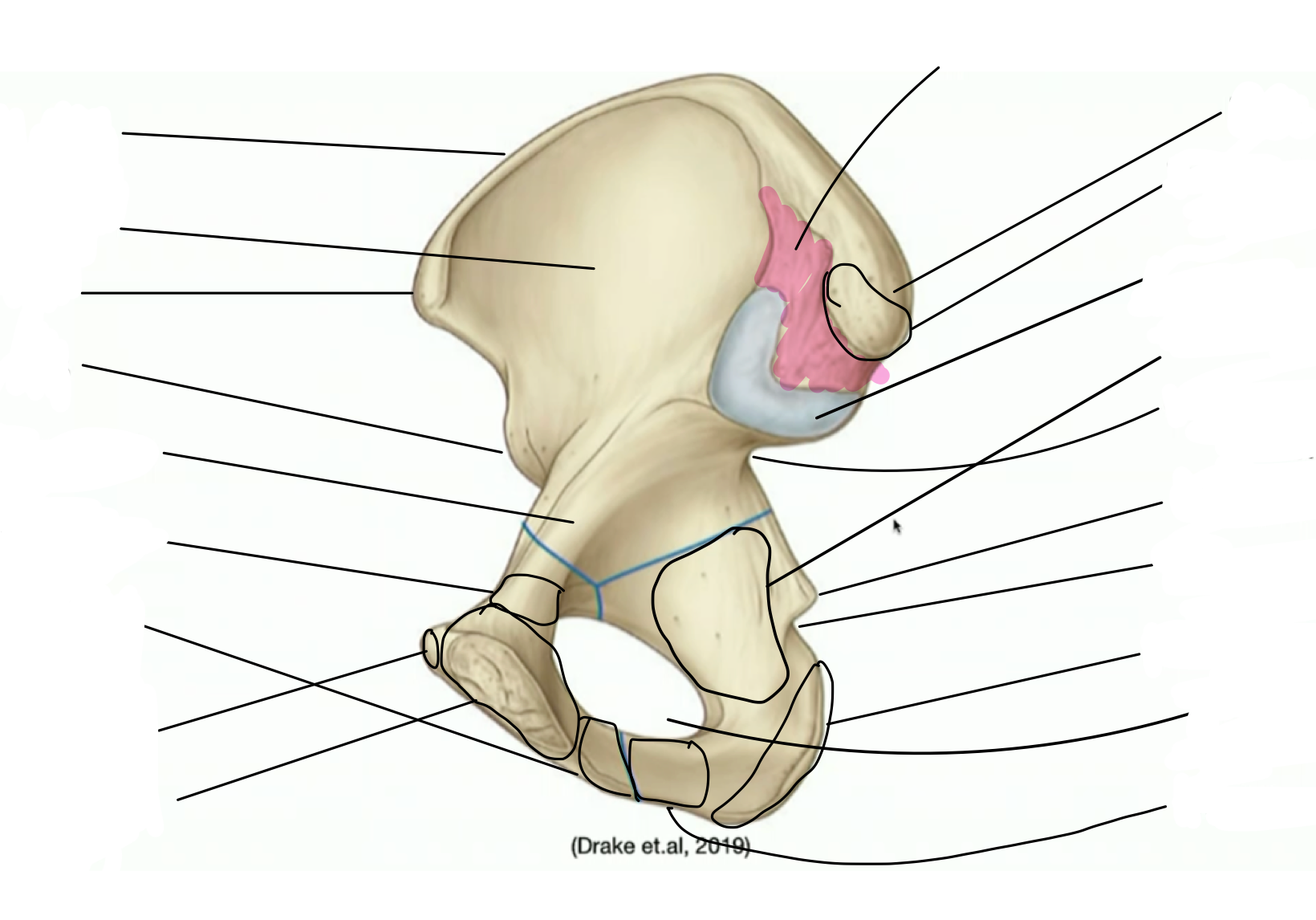
Label the pelvis
the blue part is the auricular surface of the illium

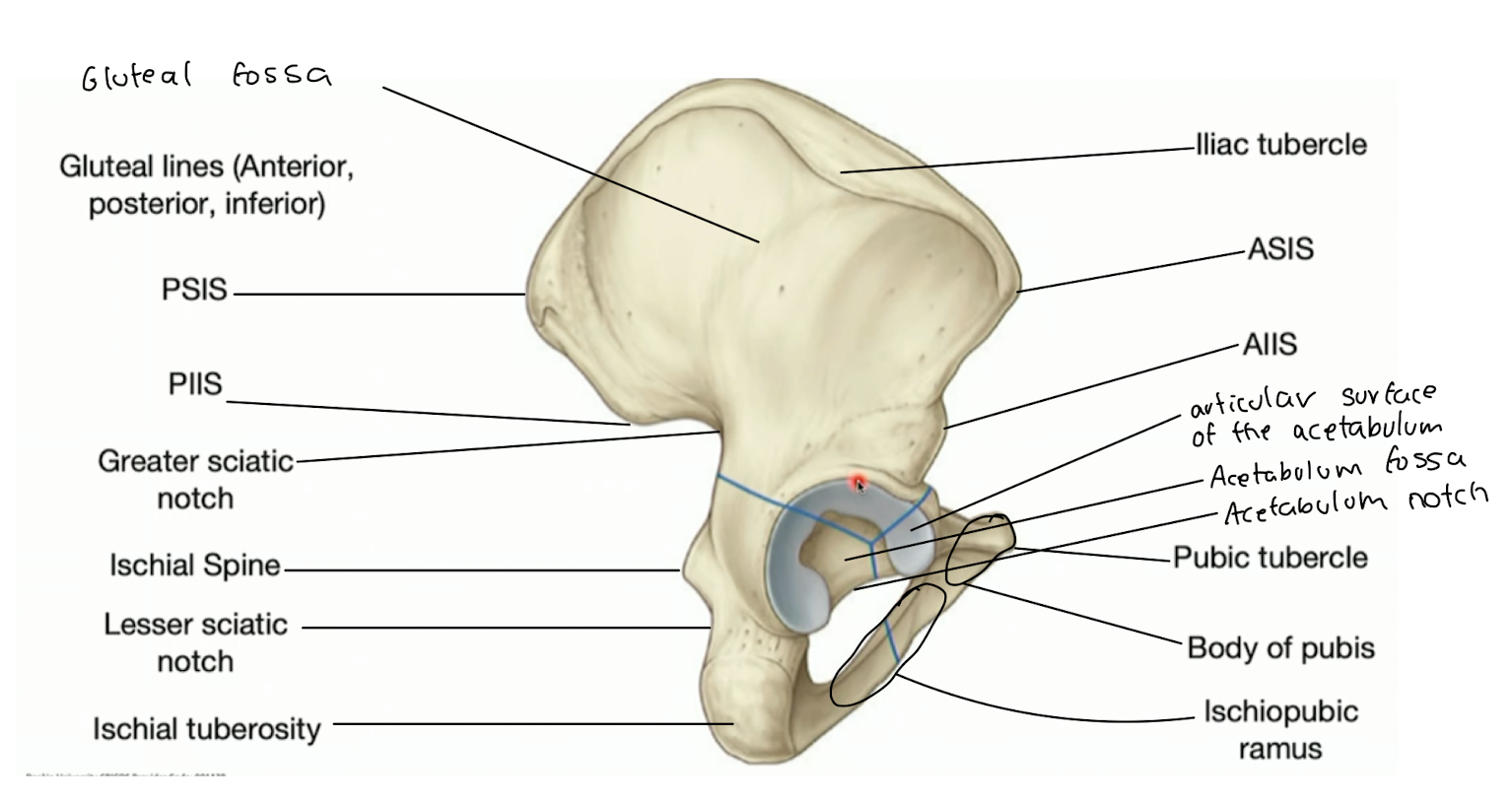
label the pelvis; additionally label the gluteal fossa, acetabulum notch and fossa.

Label the proximal femur
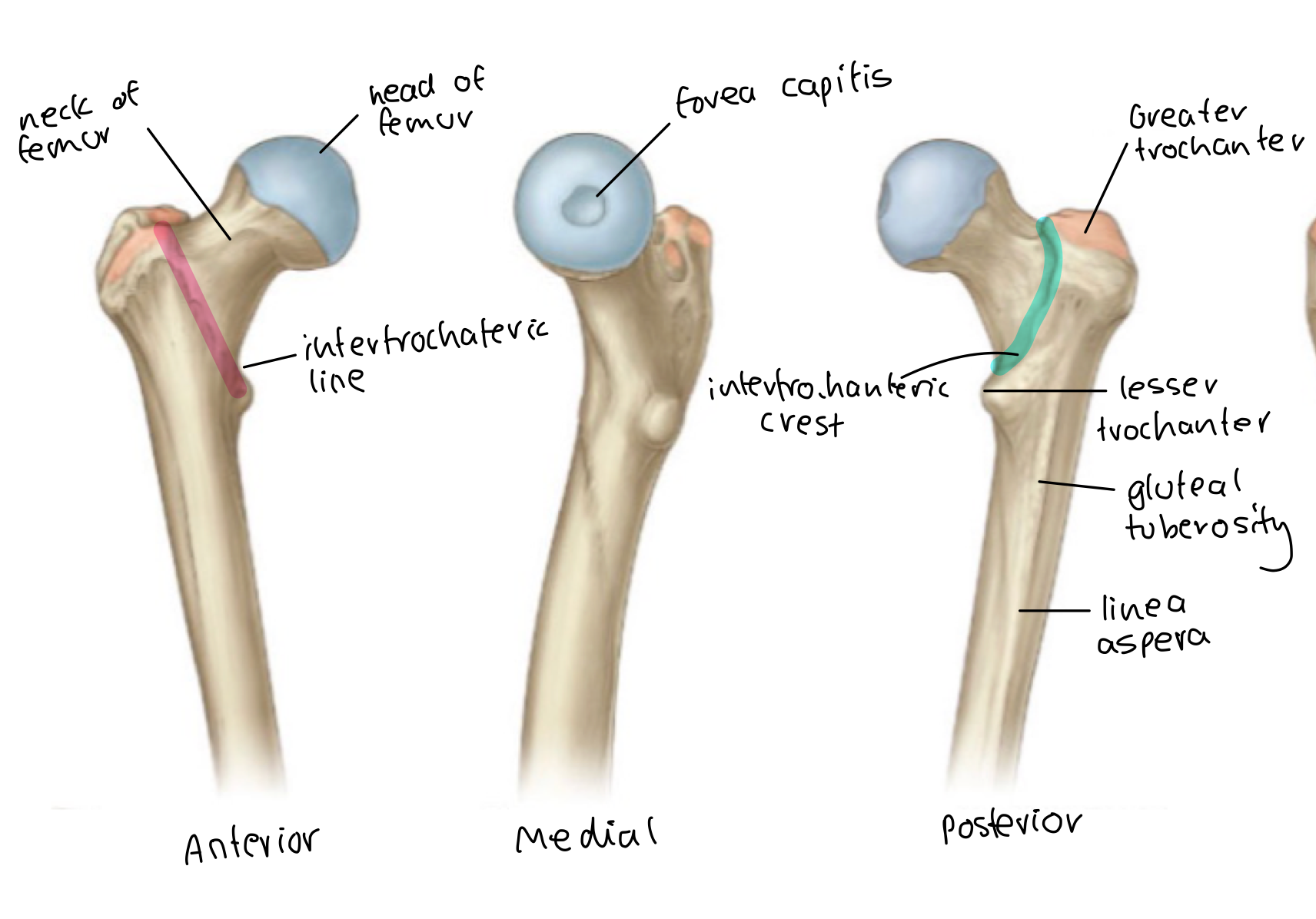
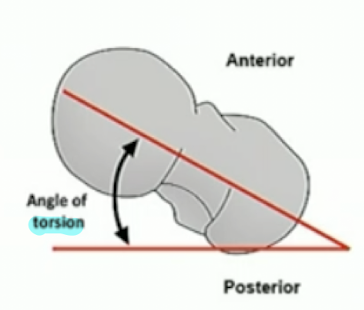
Normal inclination and torsion angle of the femur
inclination: 120 degrees
torsion:15-20 degrees

why do we internally rotate the leg when we take a picture of the pelvis?
due to the torsion angle, it helps to get the femoral neck in frame.
importance of femoral neck inclination
increases ROM and makes sure the greater trochanter doesn't get too close to the acetabulum when abducting and adducting.
does the greater trochanter sit posterior or anterior to the femoral head?
posterior
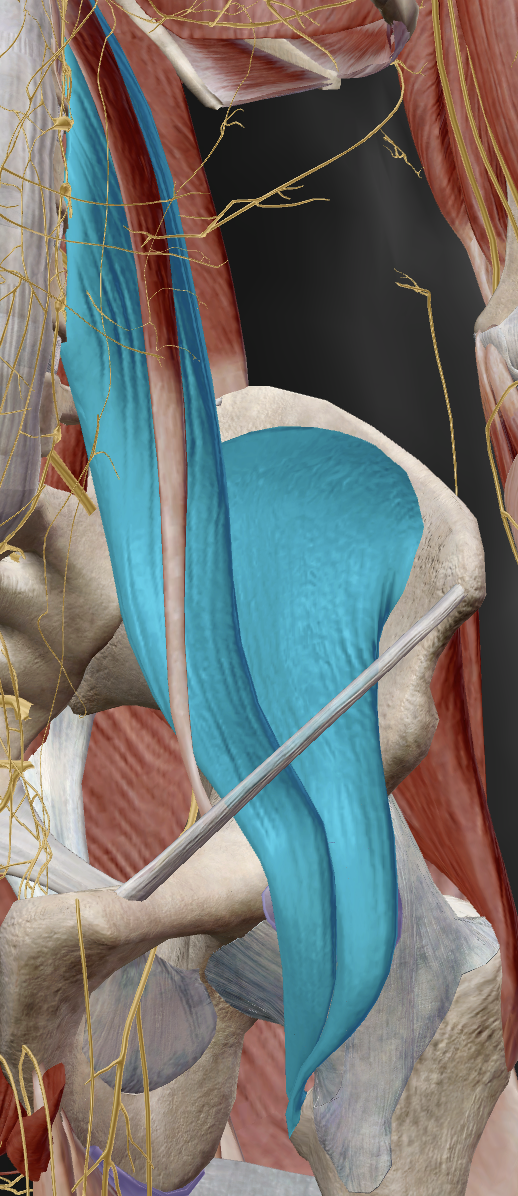
what muscles attach to the lesser trochanter?
illacus and psoas
where does the acetabulum labrum sit and what is it’s importance?
coats the upper surface of the lunate surface
More coverage of femoral head and improve congruency
overview of how the ligament and artery of head of femur gets to femoral head.
Ligament to the head of the femur gives passage to the artery of ligament of head which branches from the obturator artery through the acetabular notch (foramen).
pathway to artery of ligament of head starting from internal illiac.
Internal illiac artery → obturator artery → acetabular branch of obturator artery → artery of ligament of head
what is the blue anatomy?
fibrous capsule - inside this capsule is intracapsular, outside is extracapsular
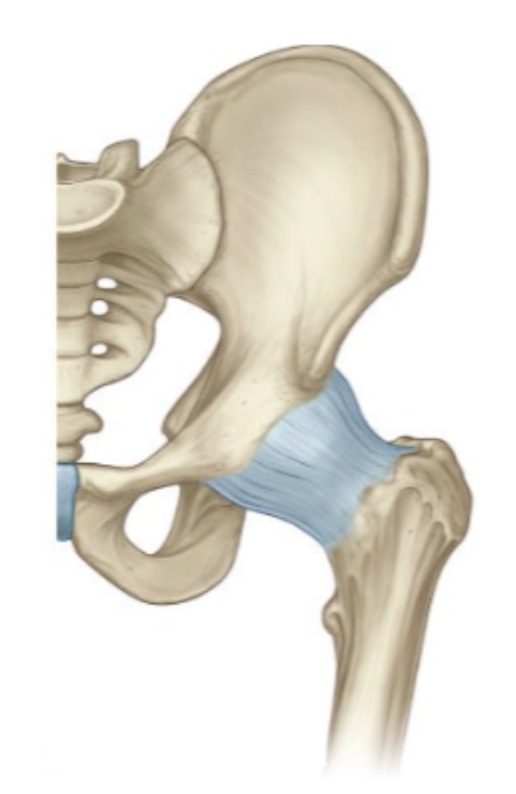
Ligaments in the hip joint and what they do
restrict extension
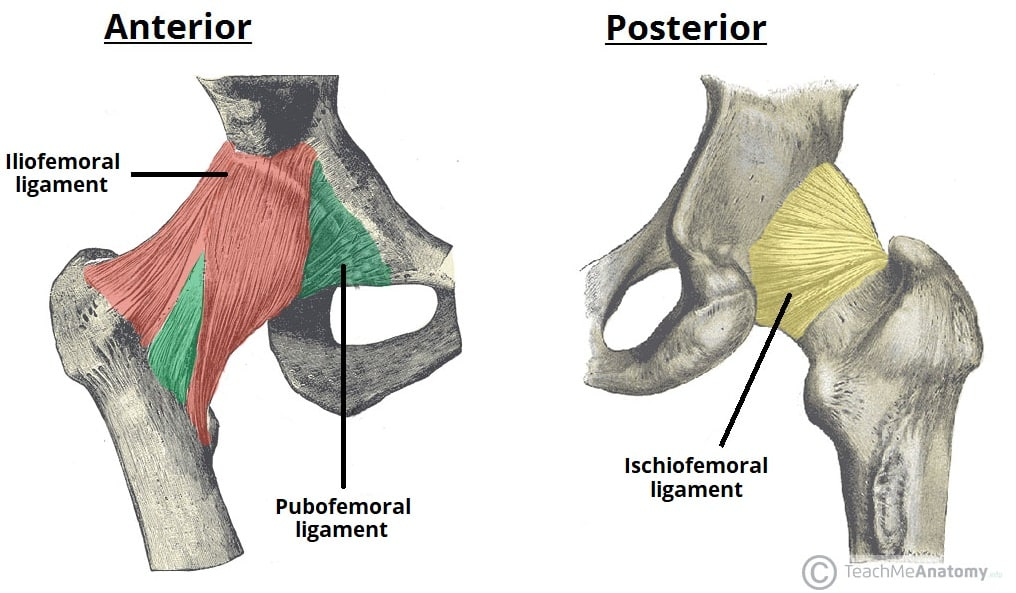
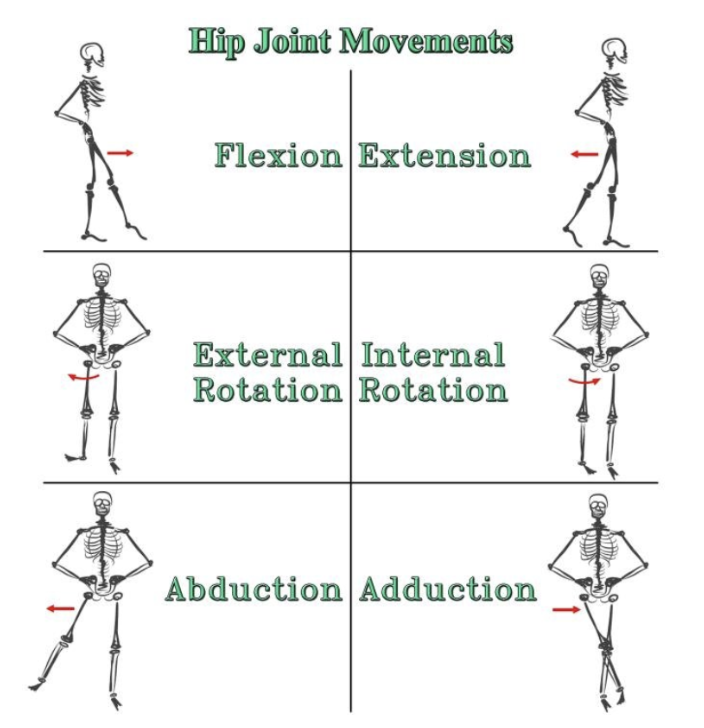
ROM at hip joint
Flexion, extension (sagittal plane)
Adduction, abduction (coronal plane)
Rotation (transverse plane)
Circumduction - combination all the movements
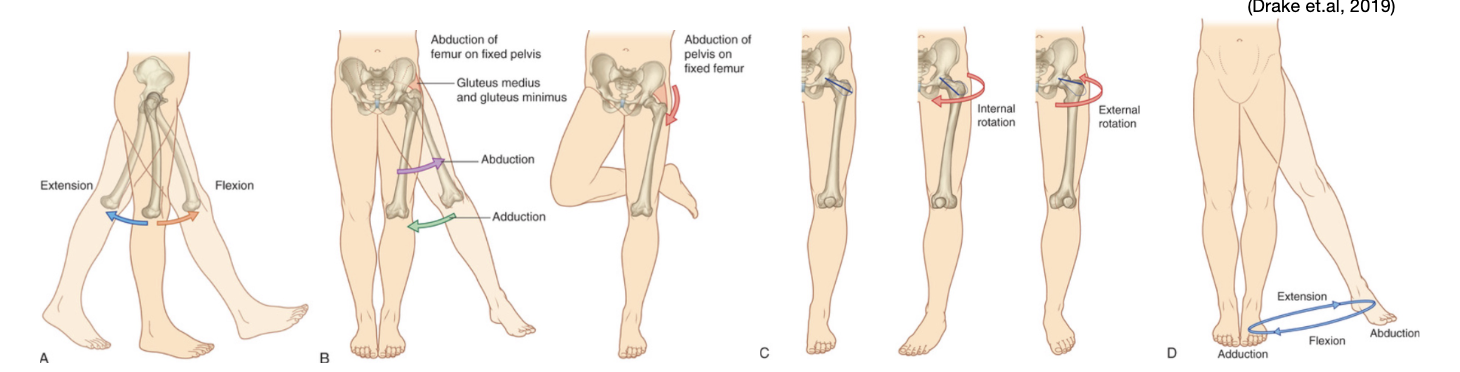
what goes through the greater sciatic foramen?
Pudendal nerve
Piriformis muscle
Sciatic nerve
what goes through the lesser sciatic foramen?
access to the perineum
Pudendal nerve
obturator internus
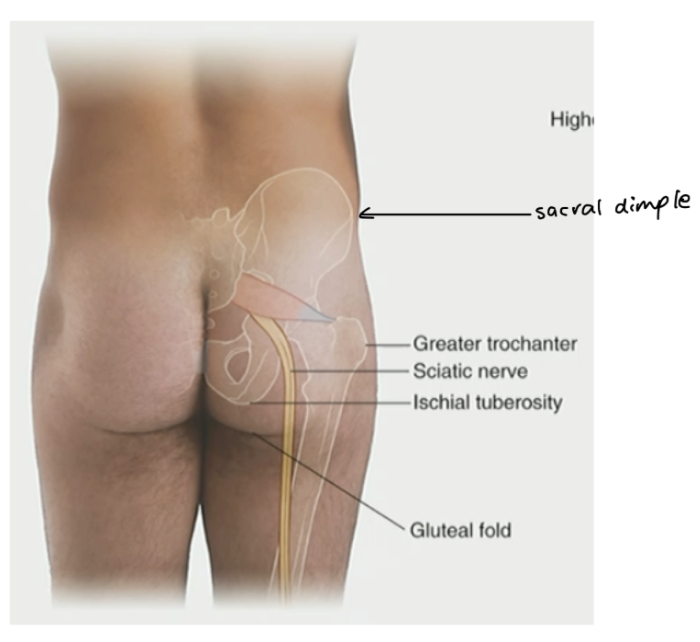
Sacral dimple (hip dip) is at the same level of what?
PSIS
Which muscles are responsible for lateral rotation of the hip?
Deep hip muscles:
Piriformis
Superior/inferior gamelli
Obturator internus
Qaudratus femoris
what are the 3 regions of the thigh?
anterior, medial and posterior compartments
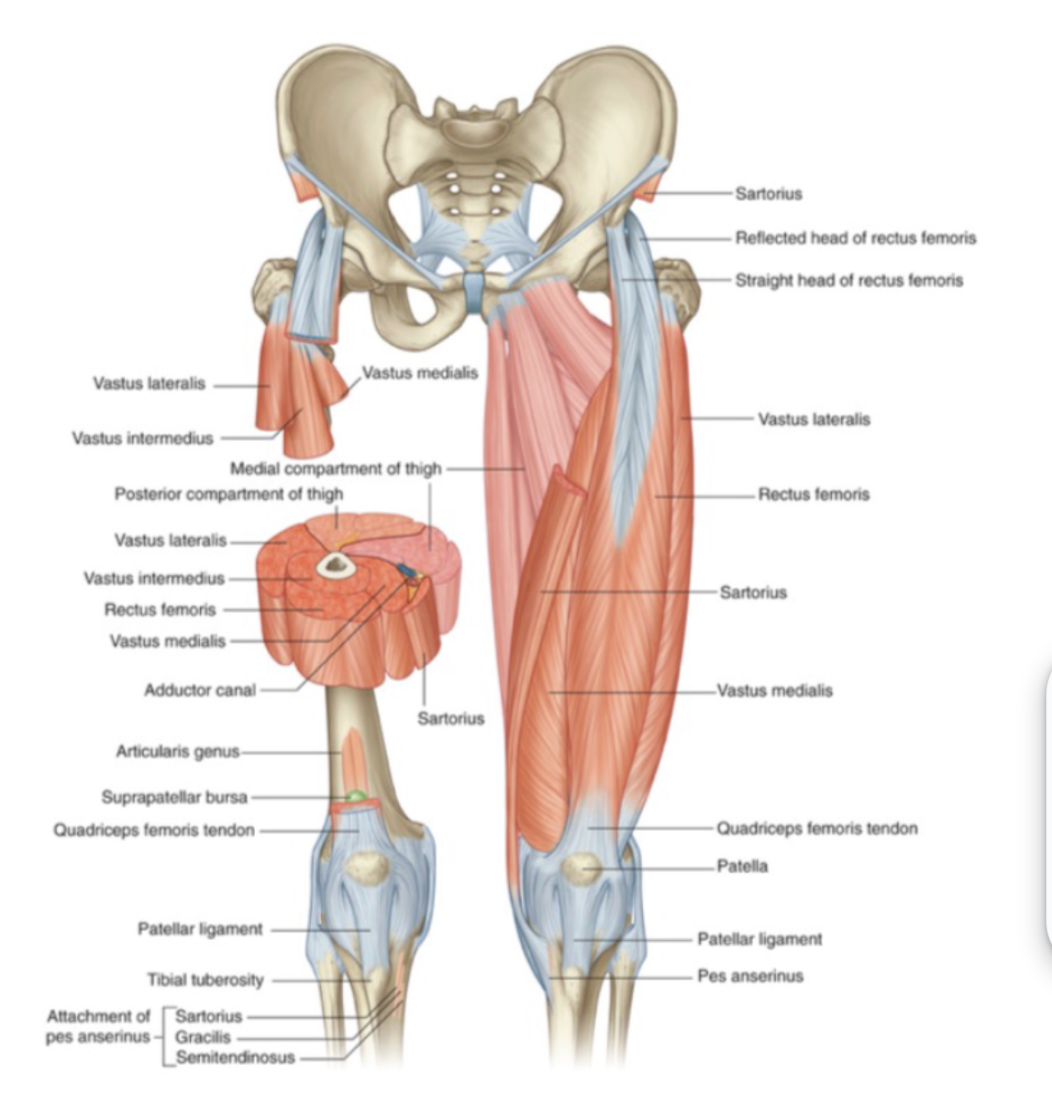
muscles and supply of nerve as well as attachment points of the anterior thigh
illiacus and psoas
attach to lesser trochanter - avulsion
Quadricep muscles
rectus femoris
attaches to the AIIS - avulsion
vastus medialis
vastus intermedius
vastus lateralis
Sartorius
attaches to ASIS - avulsion
Protects femoral artery
Supplied by the femoral nerve
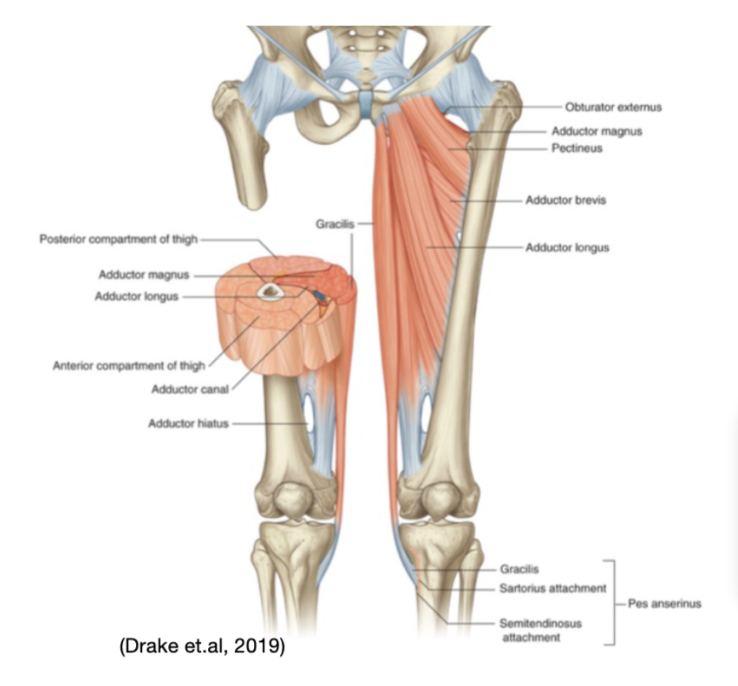
muscles and supply of nerve as well as attachment points of the medial thigh
Obturator externus
Adductor group
Adductor longus
Adductor brevis
Adductor magnus
Gracilis
Pectineus
All attach relatively to the pubis
Innervates by the obturator nerve
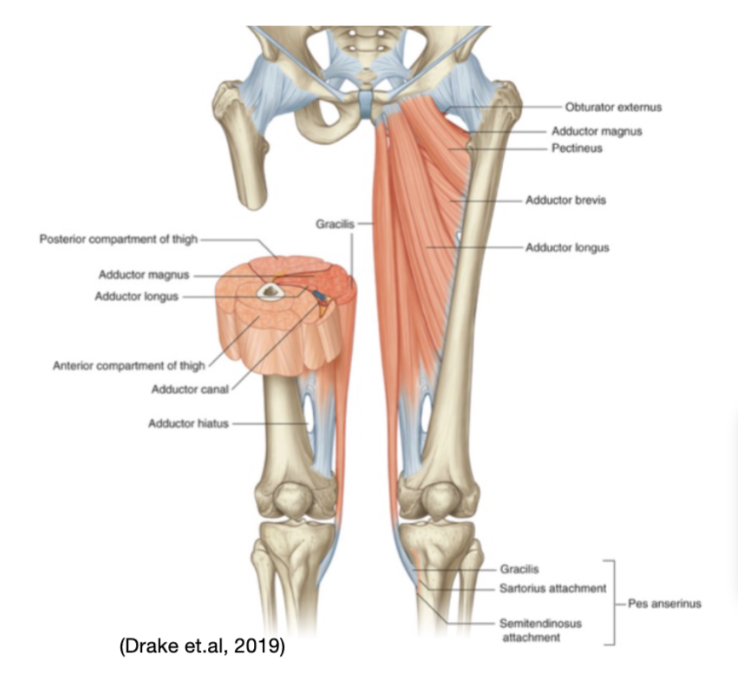
what landmark causes the femoral artery to become popliteal artery?
Superficial femoral artery changes to popliteal fossa after it goes into the adductor hiatus posteriorly and turns into popliteal artery. This hiatus is found on the adductor magnus.
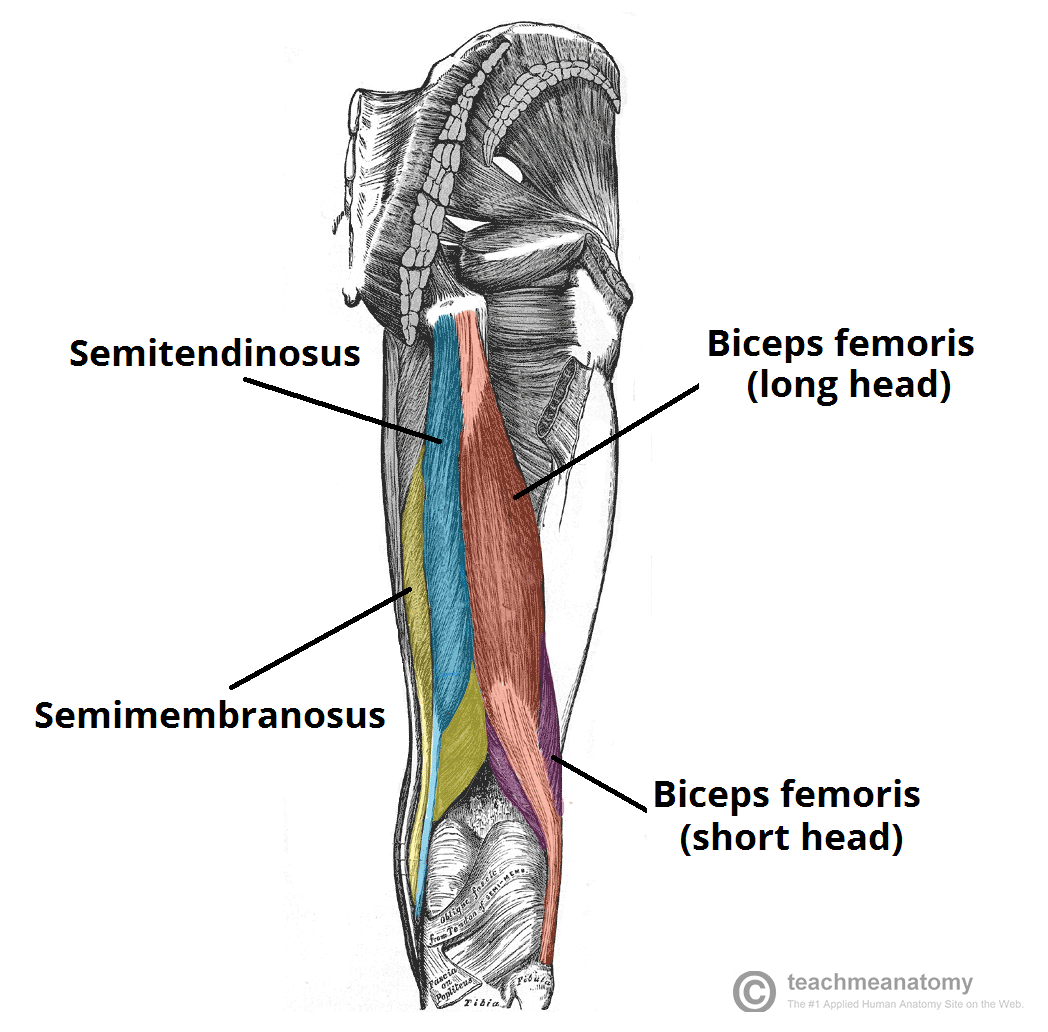
muscles of the posterior thigh and their attachment points
Three large hamstring
Bicep femoris
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
All attach to the ischial tuberosity - avulsion
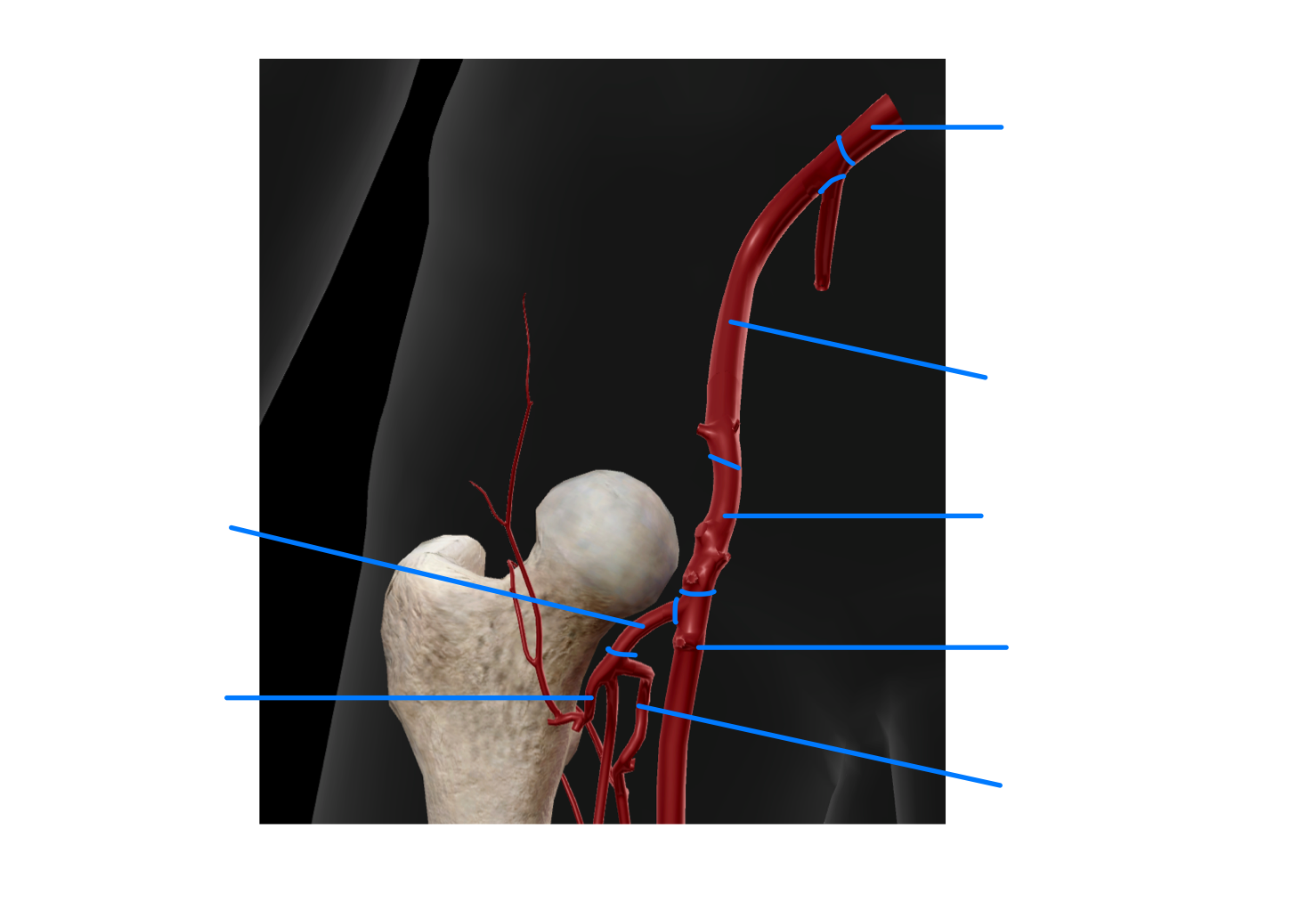
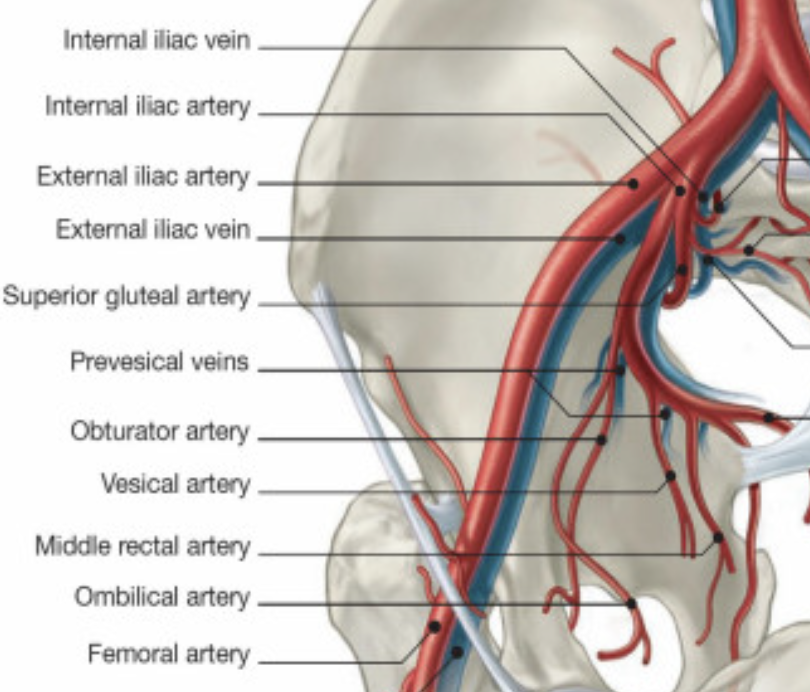
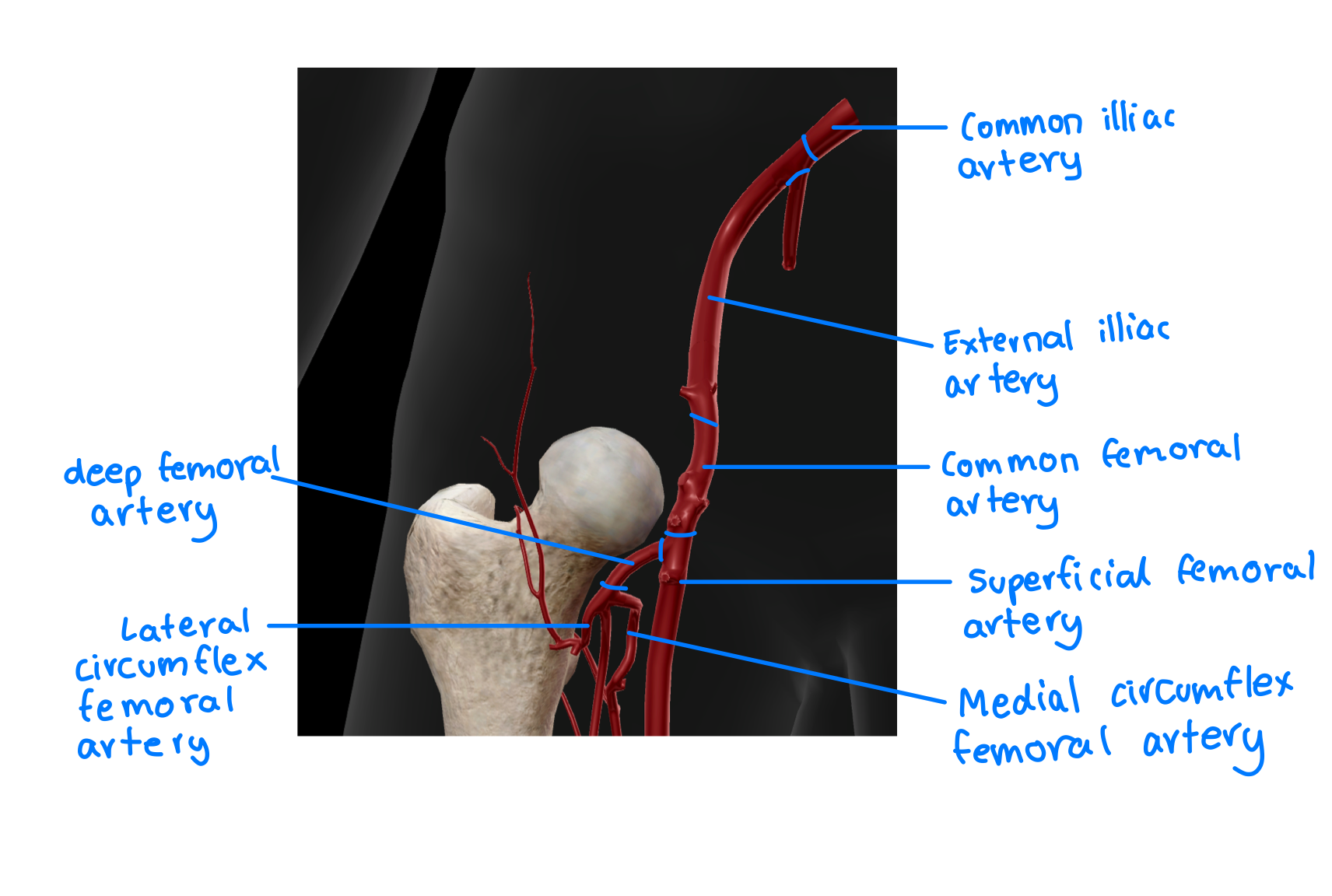
Main blood supply to femoral head and neck pathway starting from common illiac artery
Common iliac artery - external iliac artery - common femoral artery - deep femoral artery - lateral/medial circumflex artery - reticular arteries supplies to the neck and head of the femur
What location of the neck of femur fracture is more prone to AVN?
Neck of femur fracture more proximal increases AVN

Borders of the femoral triangle
Superior - inguinal ligament
Lateral - sartorius
Medial - Adductor longus
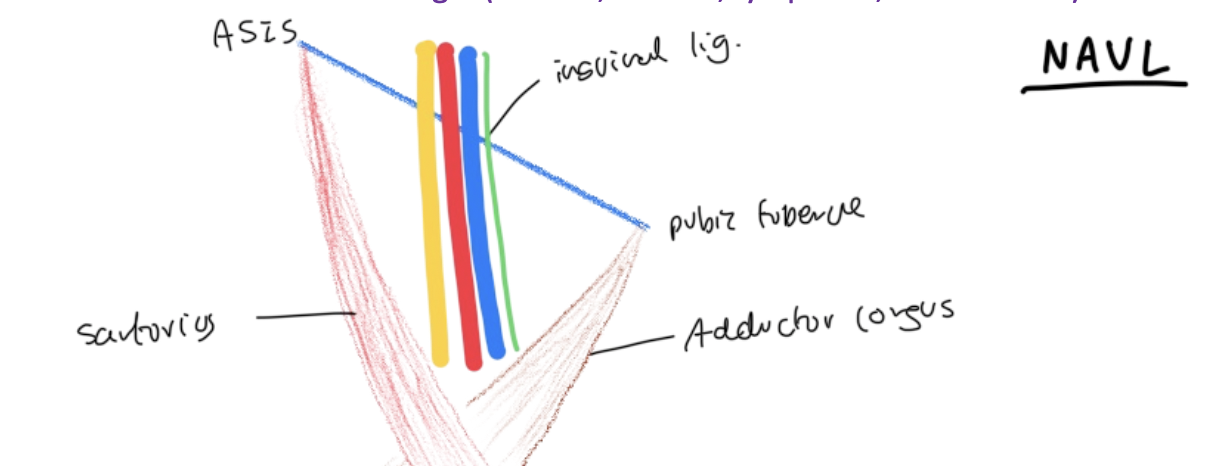
Contents of the femoral triangle going from lateral → medial
Nerve, Artery, Vein, Lymphatics
what is meant by the term avulsion fracture?
a bone fracture caused by tendon/ligament pulling a piece of bone away from the main body
why are pelvic avulsion fractures more common in young patients?
due to the presence of apophysis in the pelvis which are weaker than surrounding bone, meaning they can be pulled off more easily by ligaments and tendons
What is apophysis?
bony outgrowth that serves as attachment points for ligaments and tendons
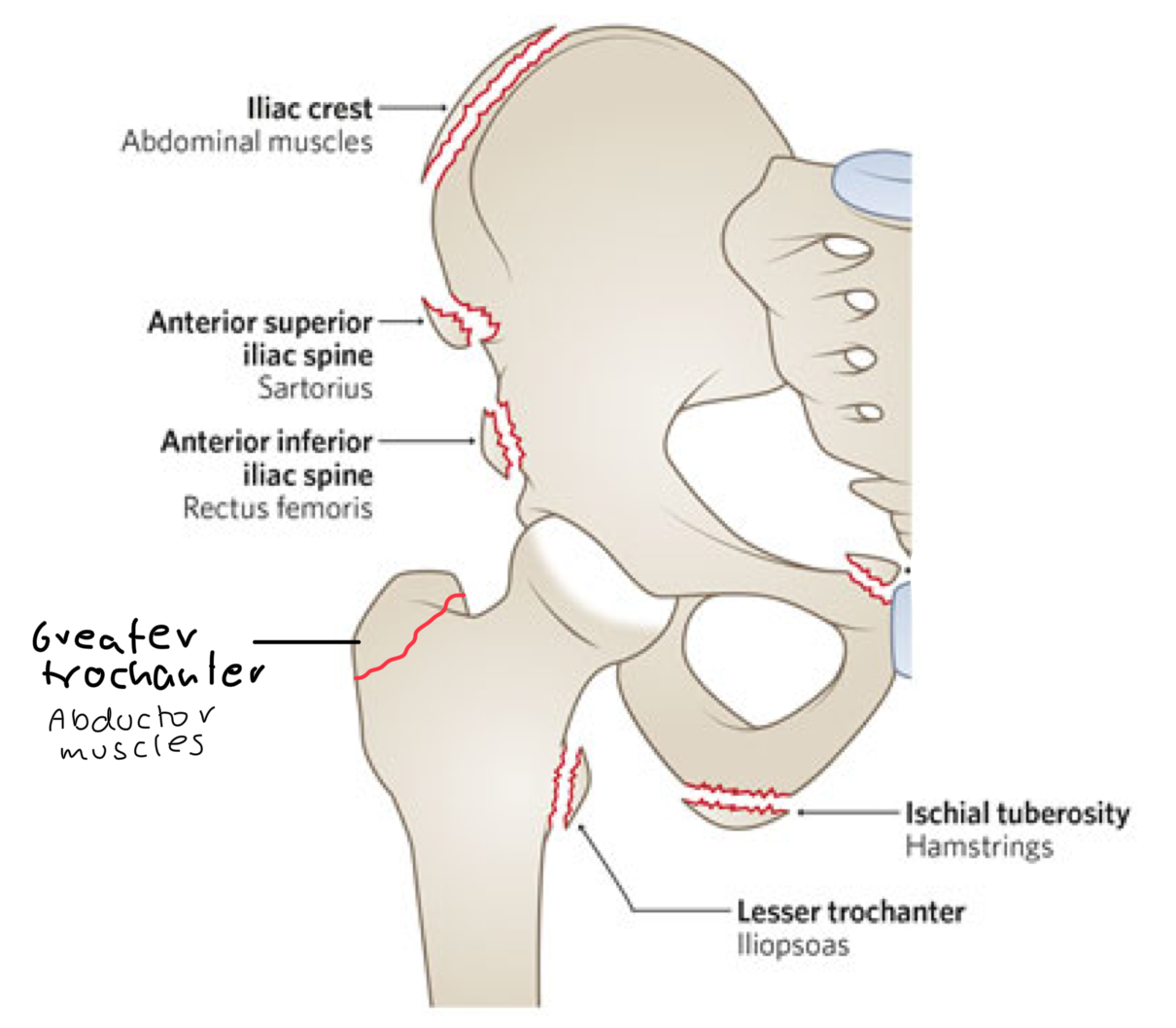
what muscles attach to the greater trochanter?
Gluteus medius
gluteus minimus
piriformis
obturator internus
superior/inferior gemellus
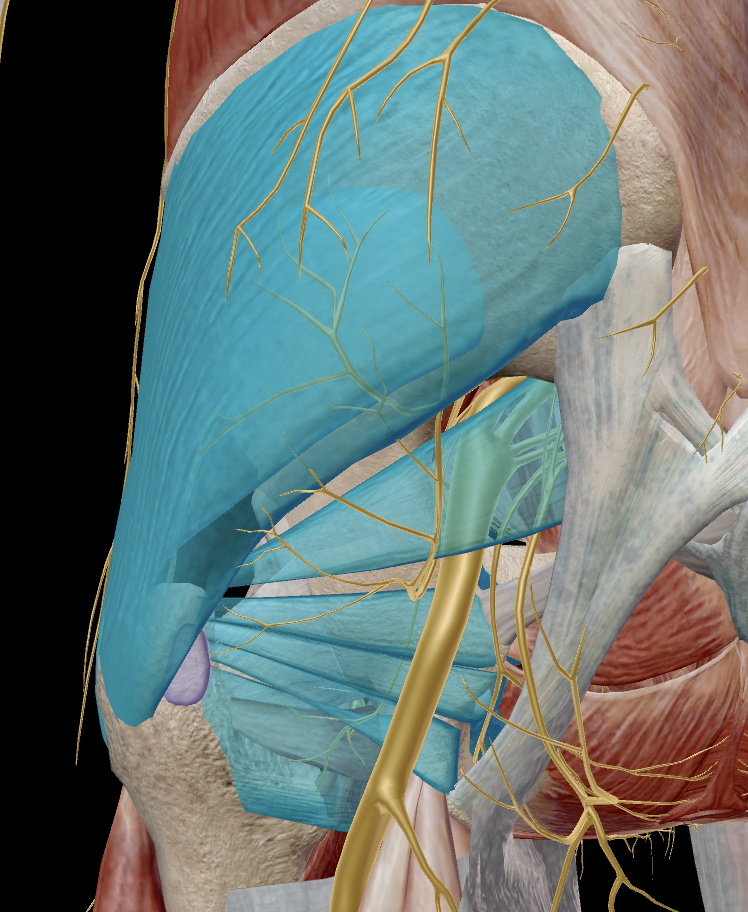
What muscles are responsible for abduction at the hip?
gluteus medius
gluteus minimus
tensor fascia latae
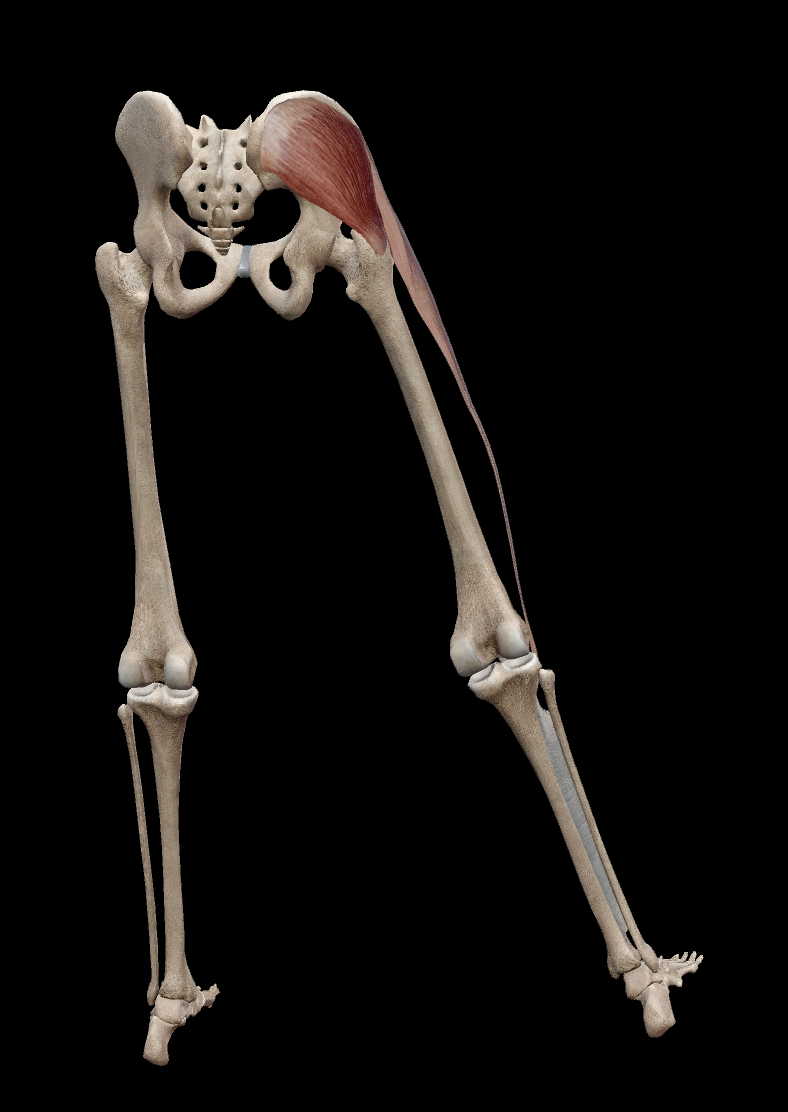
what muscles are responsible for extension at the hip?
gluteus maximus
hamstring muscles
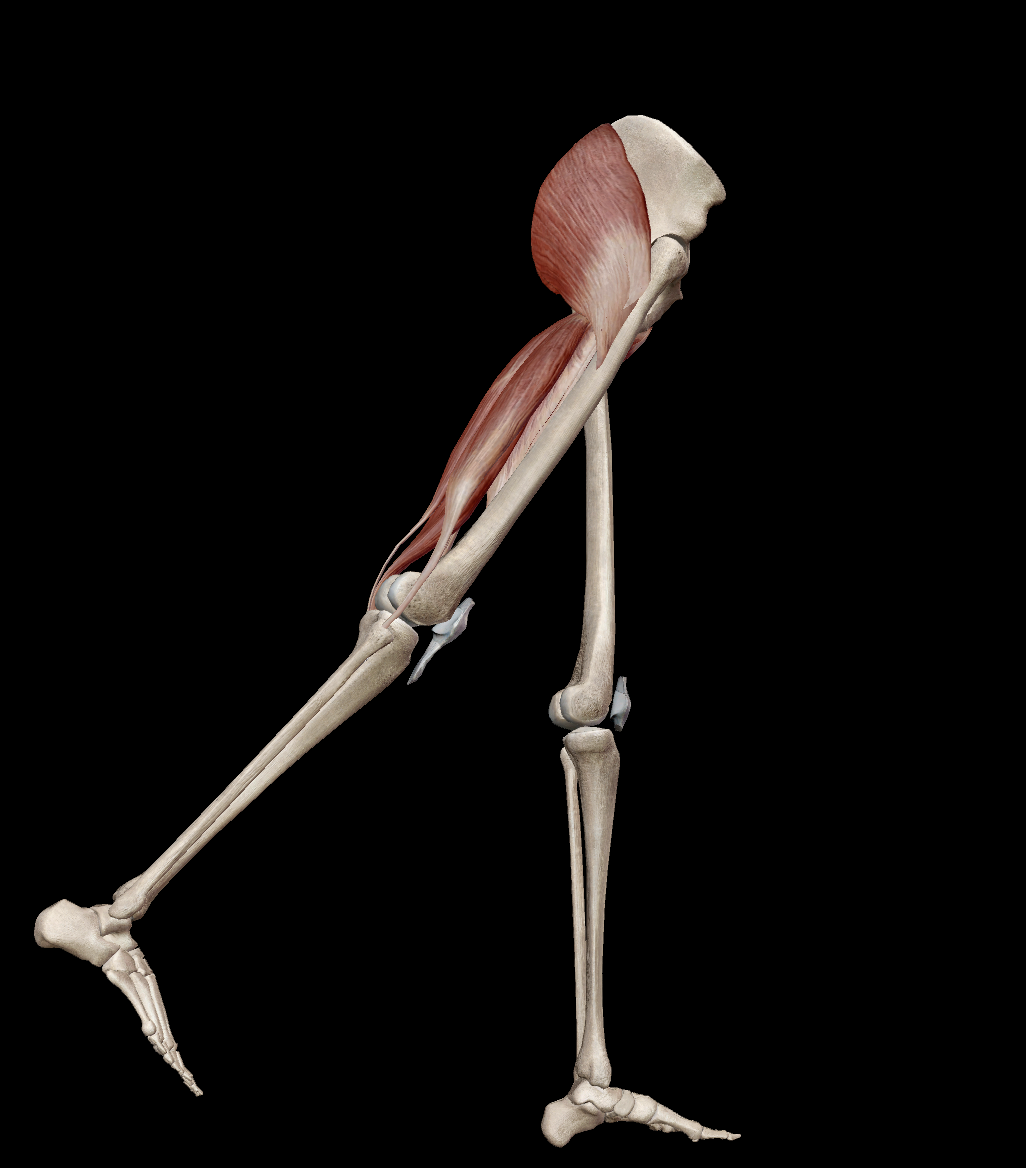
what muscles are responsible for adduction at the hip?
pectineus
adductor longus
adductor brevis
adductor magnus
gracilis

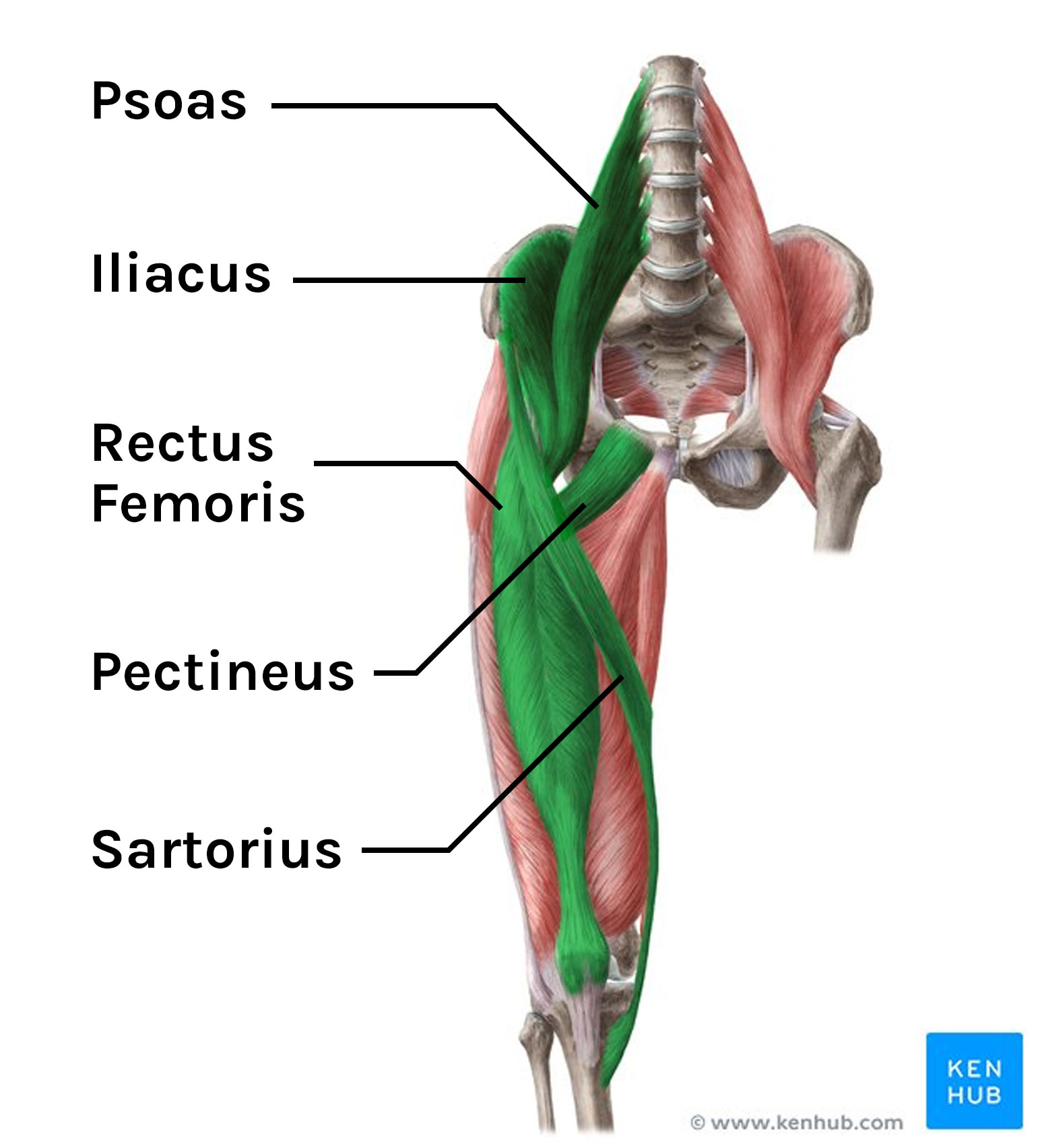
what muscles are responsible for flexion at the hip?
hip flexors (iliacus, psoas)
rectus femoris
sartorius
What are the attachment points of the inguinal ligament?
ASIS and pubic tubercle
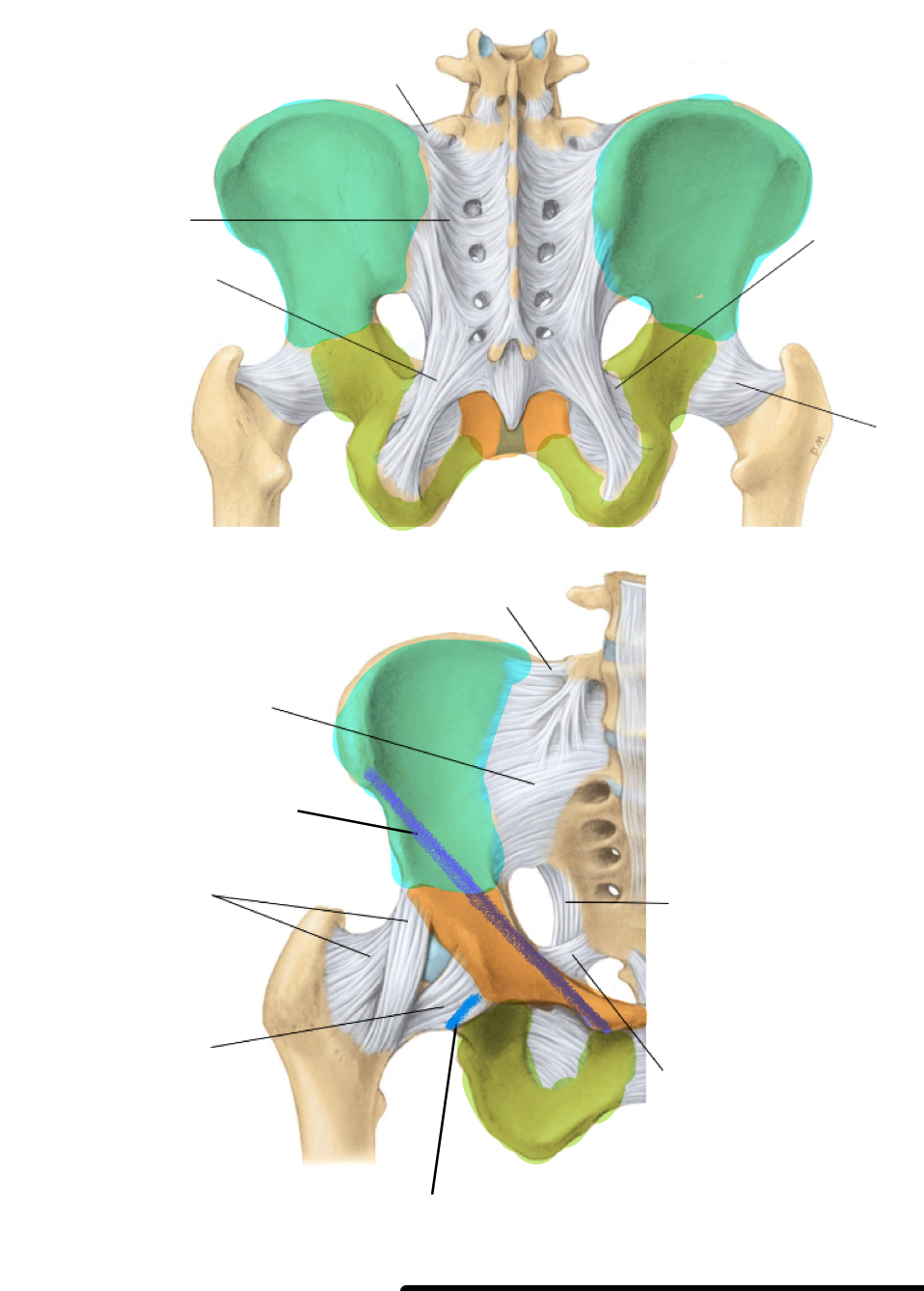
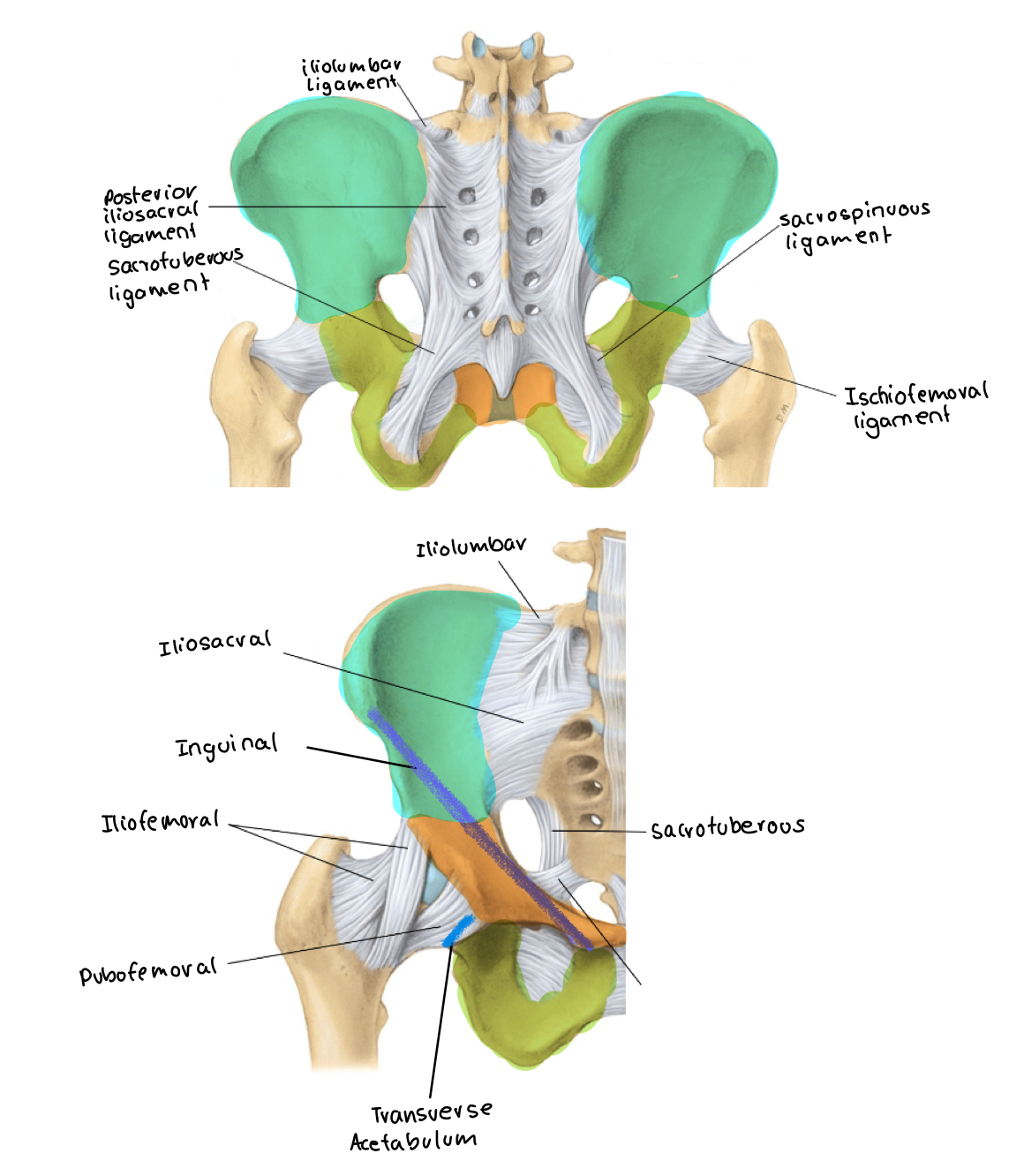
label the ligaments in the pelvis
the missing one is sacrospinous
what causes the ASIS to appear lower than expected?
Due to the anterior pelvic tilt
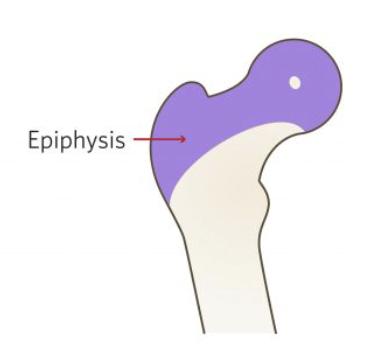
Femoral head starts ossifying at ____
baby (4 months)
Greater trochanter starts ossifying at ___
preschooler (4 years)
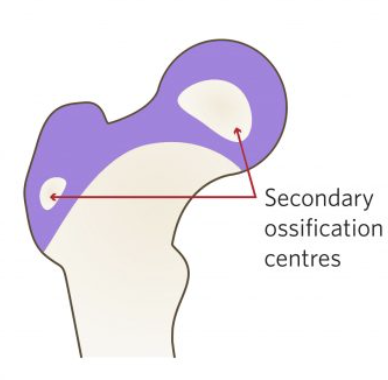
Lesser trochanter starts ossifying at ___
teenager (14 years)
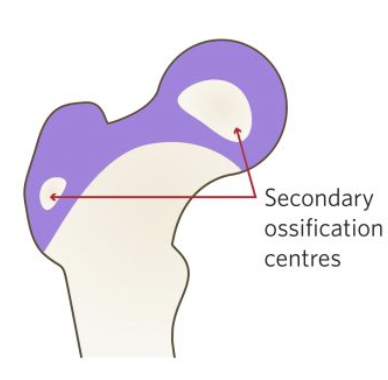
The greater troch, lesser troch and femoral head fuses with the shaft at….
young adult (16-18)
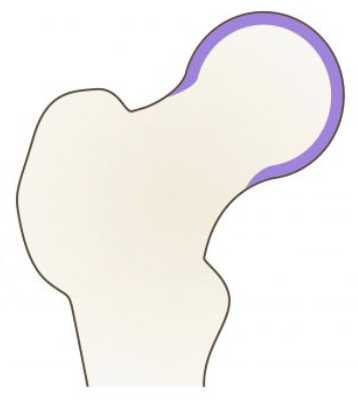
What nerve would be most affected if there was a posterior and superior dislocation of the hip and why?
the scaitic nerve sits right behind the hip joint
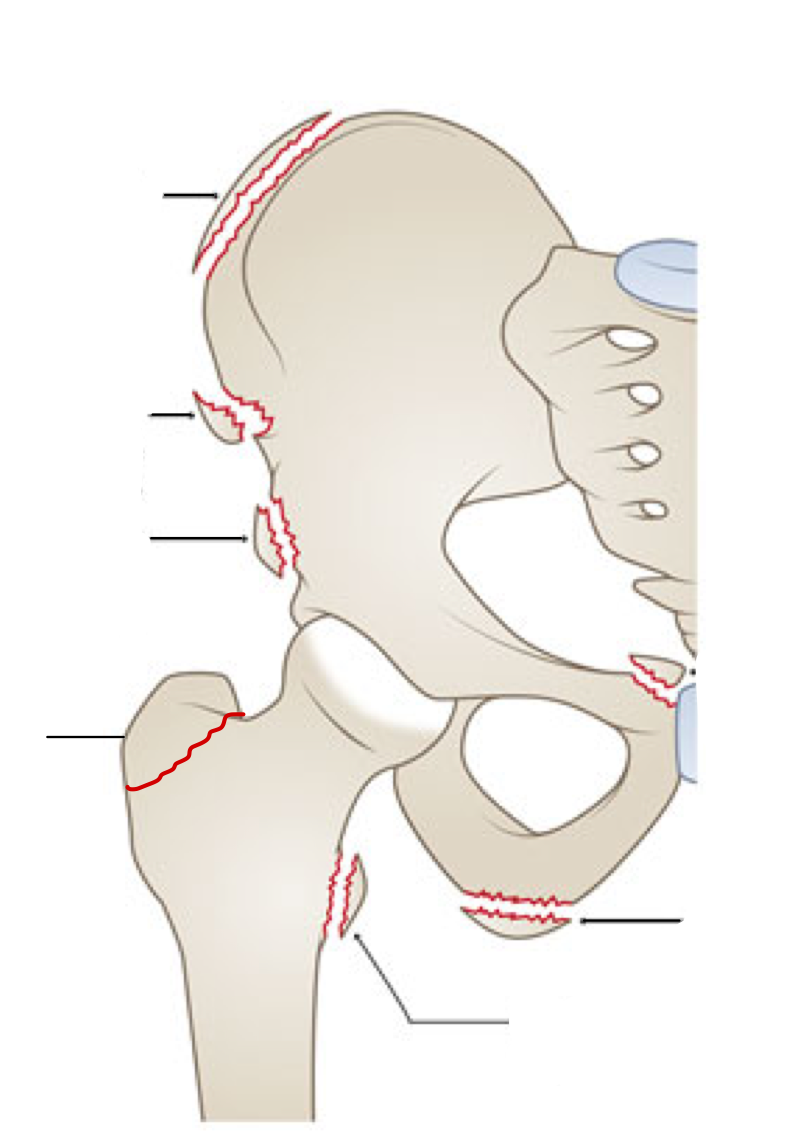
label the landmark and what muscles attach here.
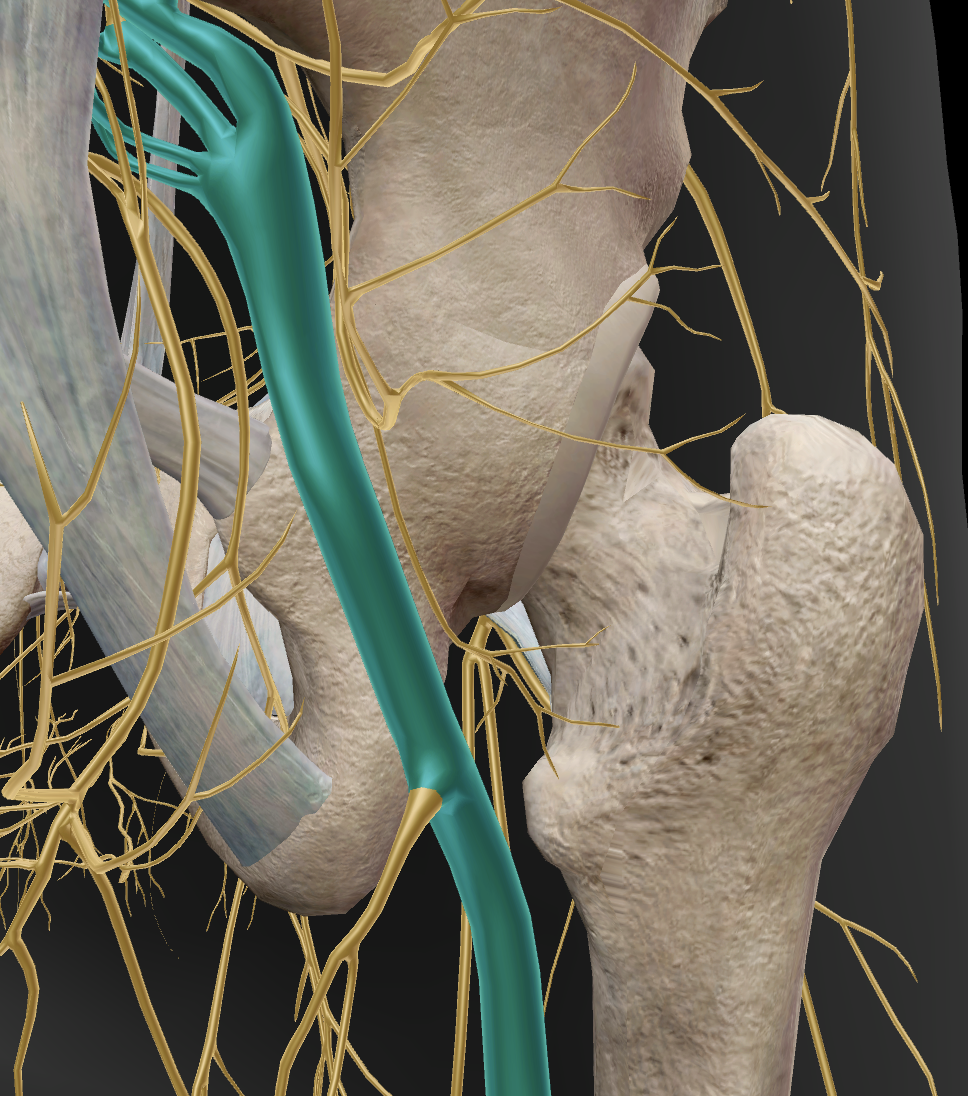
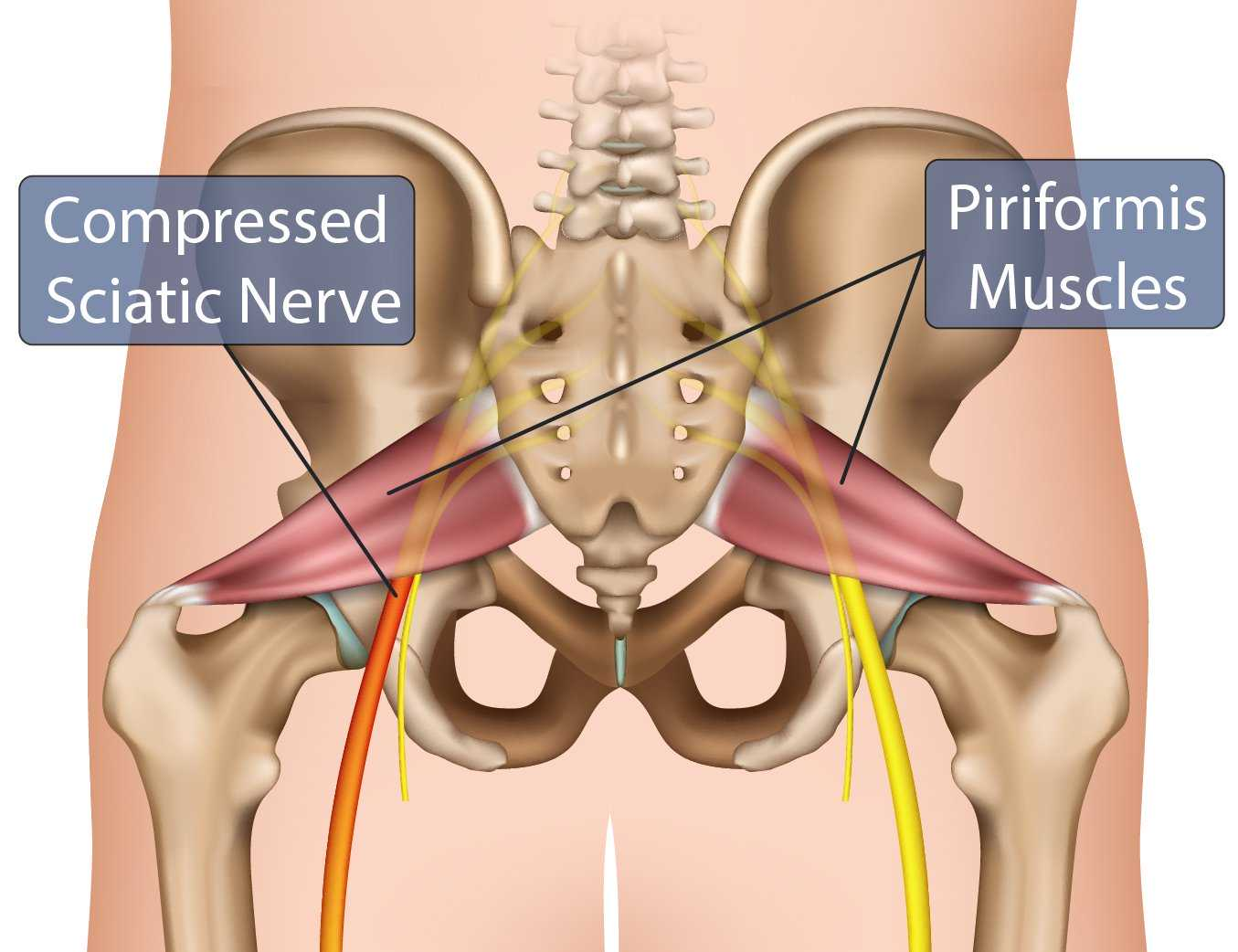
What muscle does the sciatic nerve travel under?
The piriformis
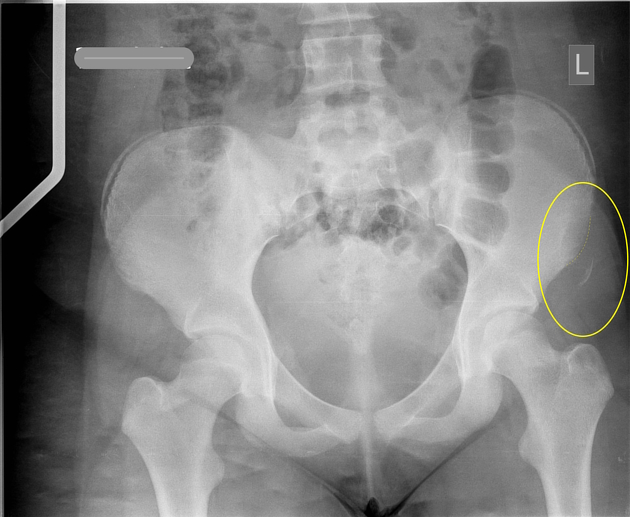
What could have caused this fracture?
ASIS avulsion fracture caused by the sartorius muscle from forceful flexion, lateral rotation or abduction of the hip
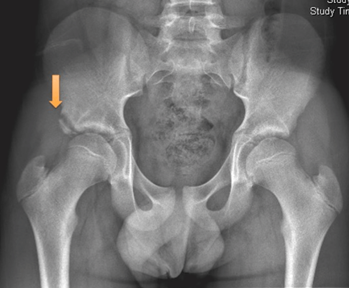
What could have caused this fracture?
AIIS avulsion fracture caused by the rectus femoris from forceful hip flexion
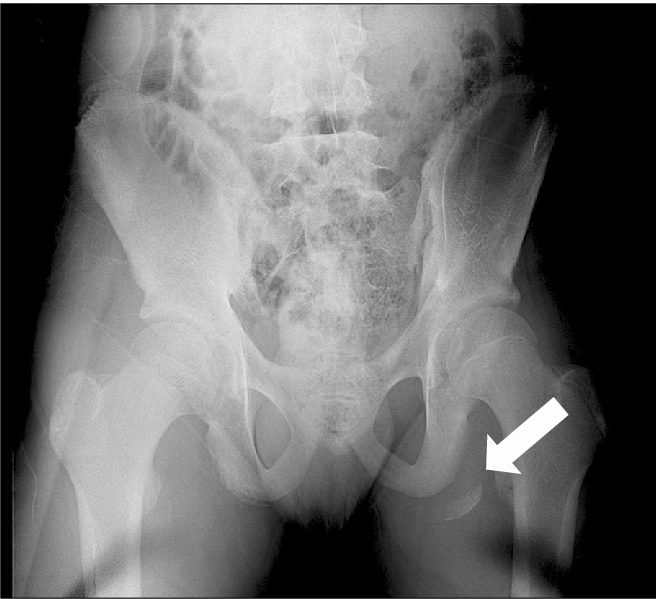
What could have caused this fracture?
Ischial tuberosity avulsion fracture caused by the hamstring muscles from forceful hip extension
what muscles does the sciatic nerve innervate? What foramen does it exit out of?
exits through the greater sciatic foramen and supplies the posterior thigh
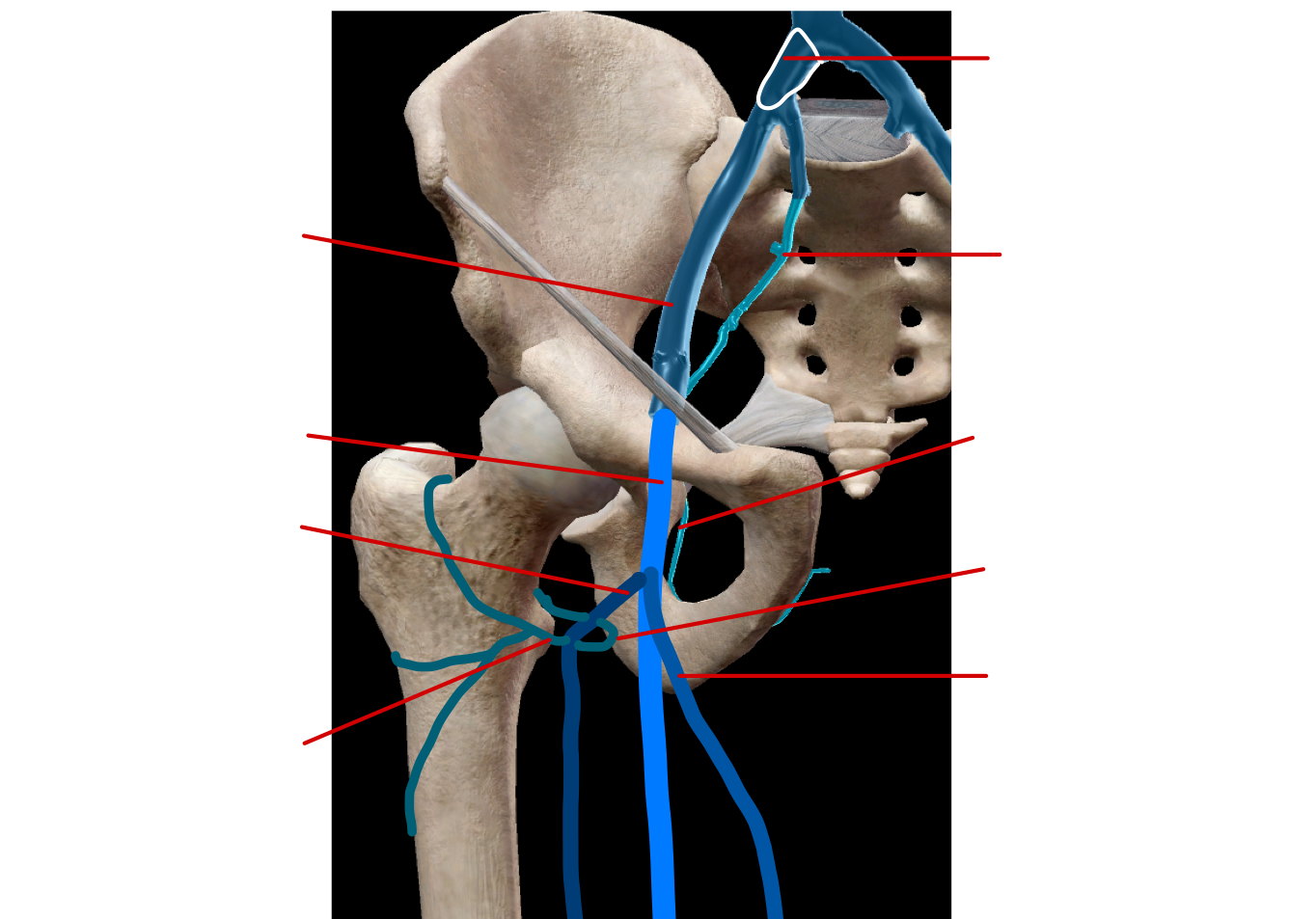
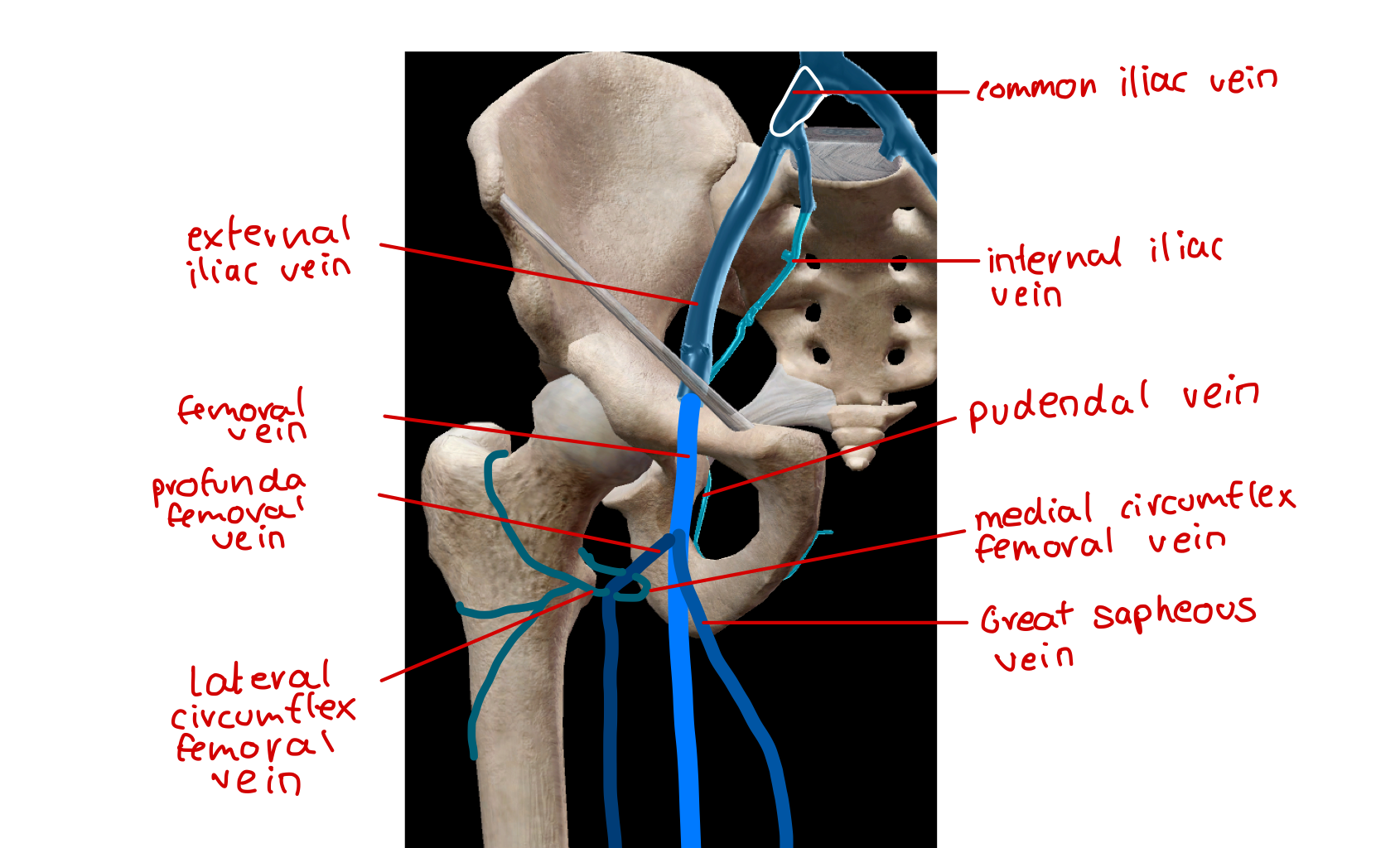
label the veins in the hip region
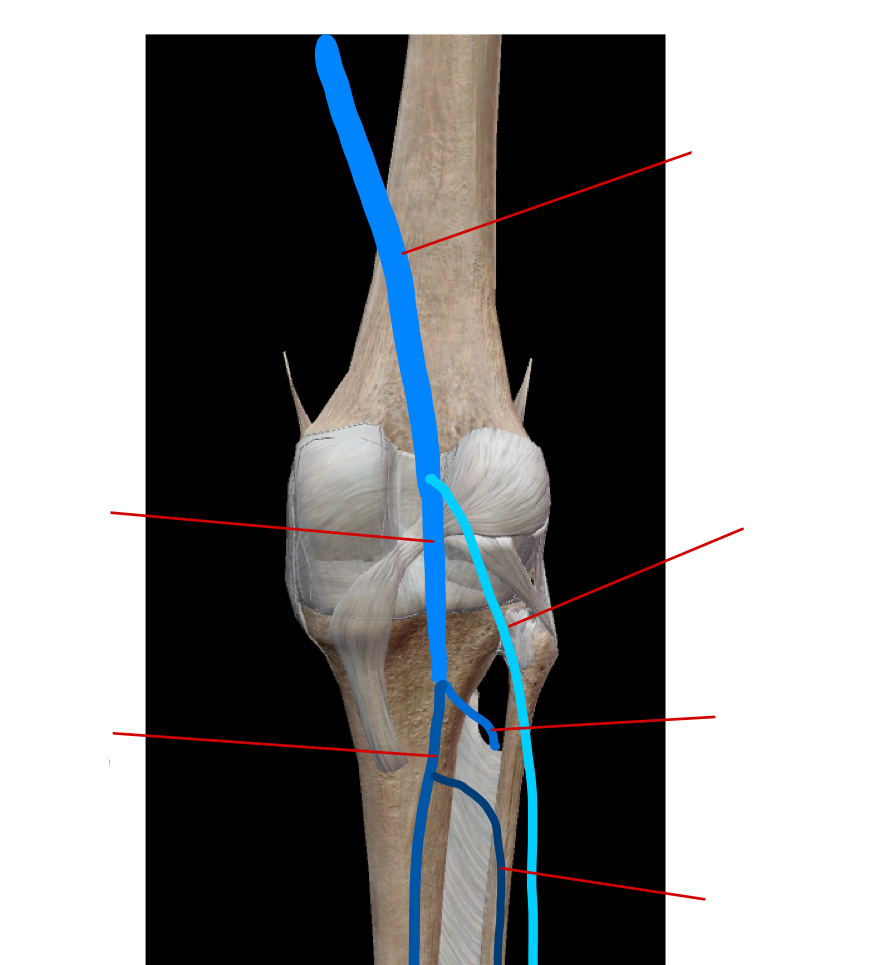
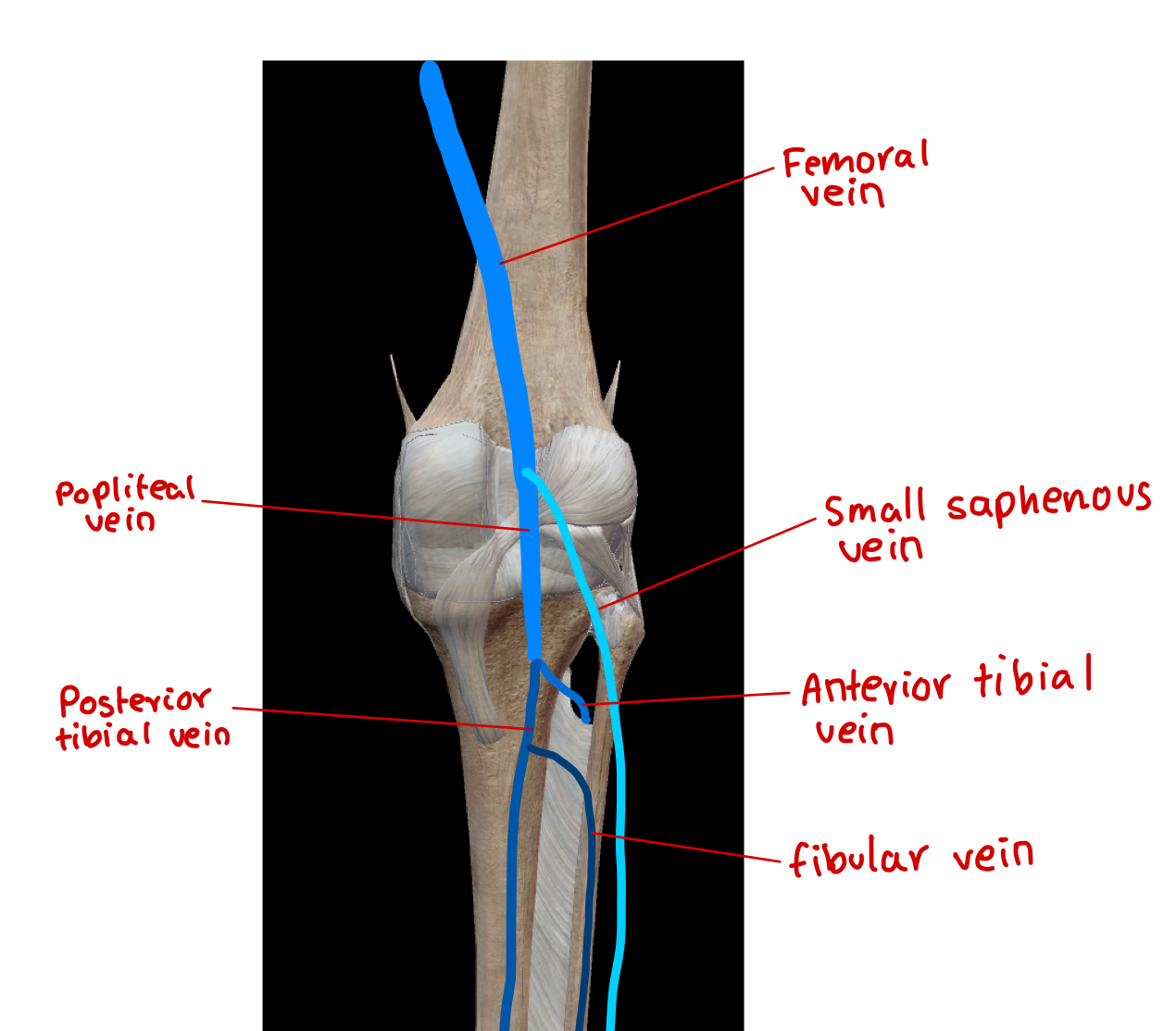
label the vein in the lower limb
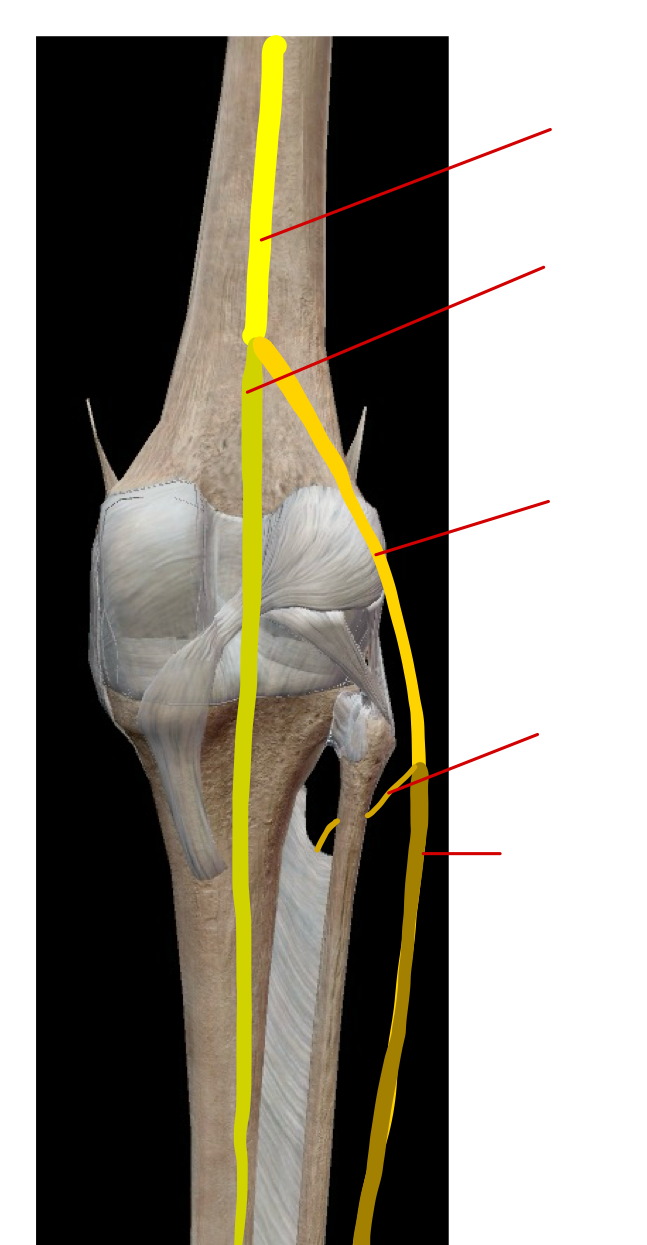
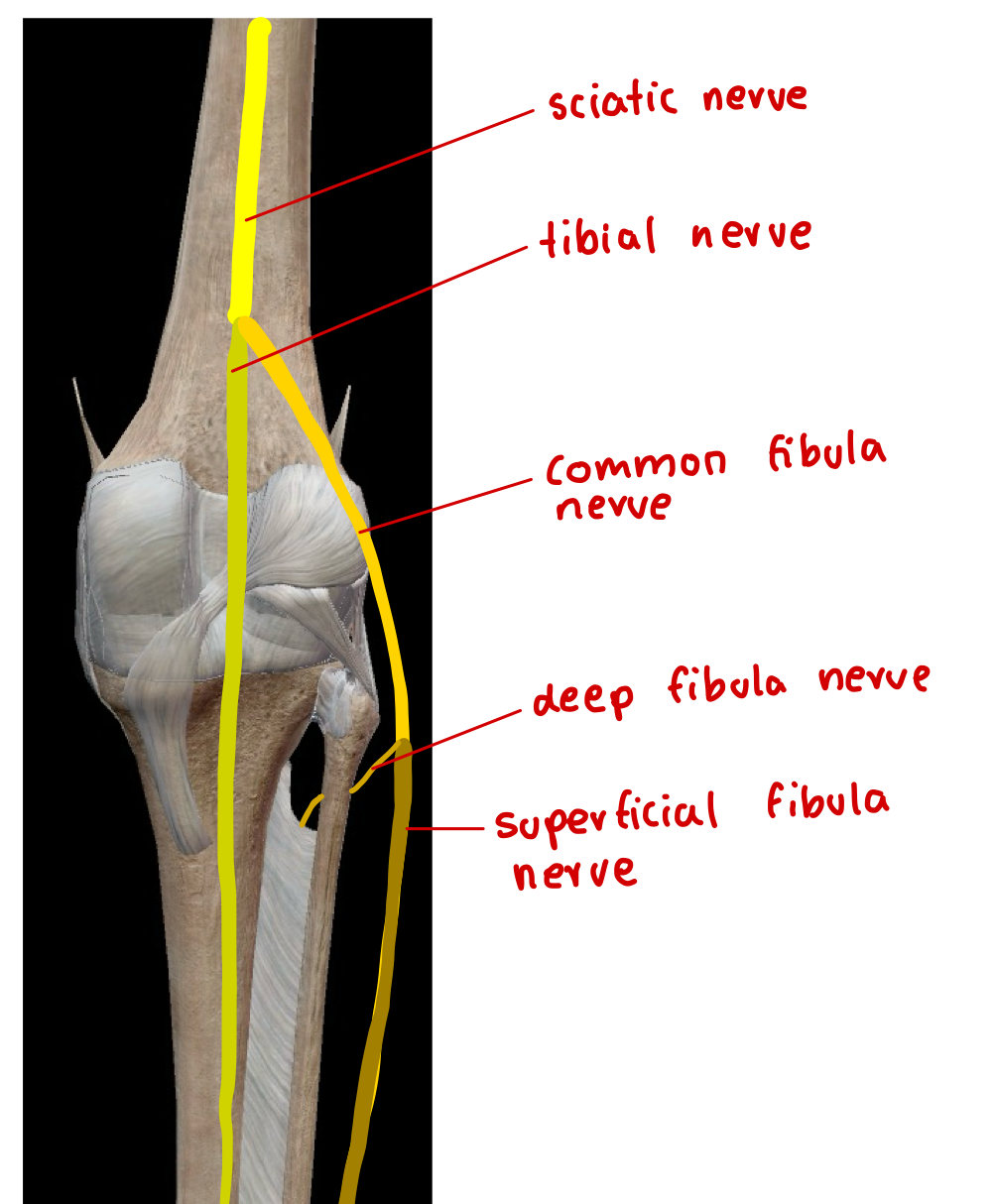
label the nerves in the lower limb
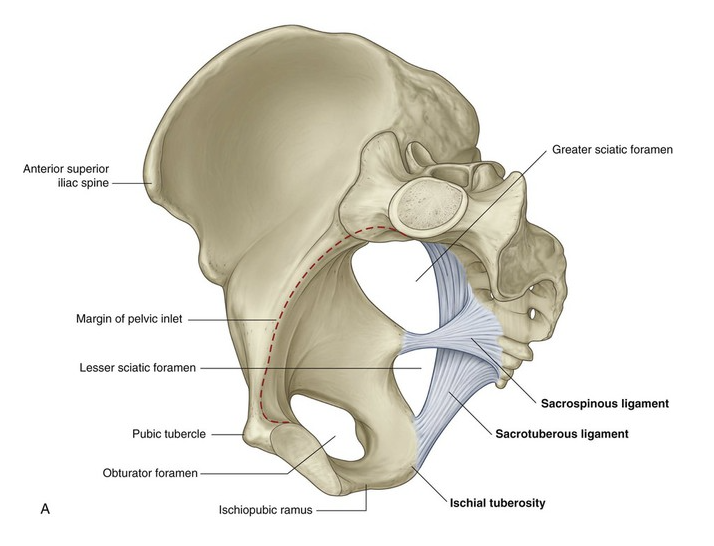
What two ligaments help to convert the greater and lesser sciatic notch into foramina?
sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments
When does the ishium, pubis and the ilium fuse?
At 16-18 years of age
What does the Sartorius muscle protect?
The femoral artery
Are intertrochanteric fractures extra or intra-capsular?
extracapsular