Dental Materials Exam 1 (1/2)
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
What is Dental Science?
The study of teeth, gums, and the mouth, and how to keep them healthy.
What is Patient Education?
Teaching patients how to care for their teeth and gums to prevent problems.
Who is Pierre Fauchard?
Known as the “Father of Modern Dentistry,” he wrote the first complete book on dental care in the 1700s.
Who is G. V. Black?
Called the “Father of Operative Dentistry,” he created modern ways to fill cavities and restore teeth.
Why do we study dental materials?
To understand the behavior of materials used
To handle materials properly
To assess and treat individual patient and their individual needs
To educate the patient
What are Standards (in dental materials)?
Rules or guidelines that describe how a dental material should perform.
What are Specifications (in dental materials)?
Detailed requirements that a dental material must meet to be considered acceptable.
What is the ADA?
The American Dental Association, which tests and approves dental products for safety and effectiveness.

What is this?
The Seal of Acceptance of the ADA

What does the ADA Seal of Acceptance represent?
The material has been proven safe and effective through testing, but it may not have exact physical standards for certification.
The ___ regulates dental materials and devices for safety and efficacy…
FDA

What is “ISO”
The International Organization for Standardization — it sets worldwide standards for dental materials.
What is “CE”
A European mark (“Conformité Européenne”) that shows a dental product meets safety and health standards in Europe.
How do we discuss dental materials?
A: By looking at:
The four classes of materials
Their use
Where they are made (location of fabrication)
How long they last (longevity of use)
What are the four classes of Materials?
Metals (Gold, Amalgam, Titanium)
Ceramics
Polymers
Composites
What are ceramics (in dental materials)?
Compounds made from metallic and non-metallic elements. They are inert and have excellent biocompatibility.
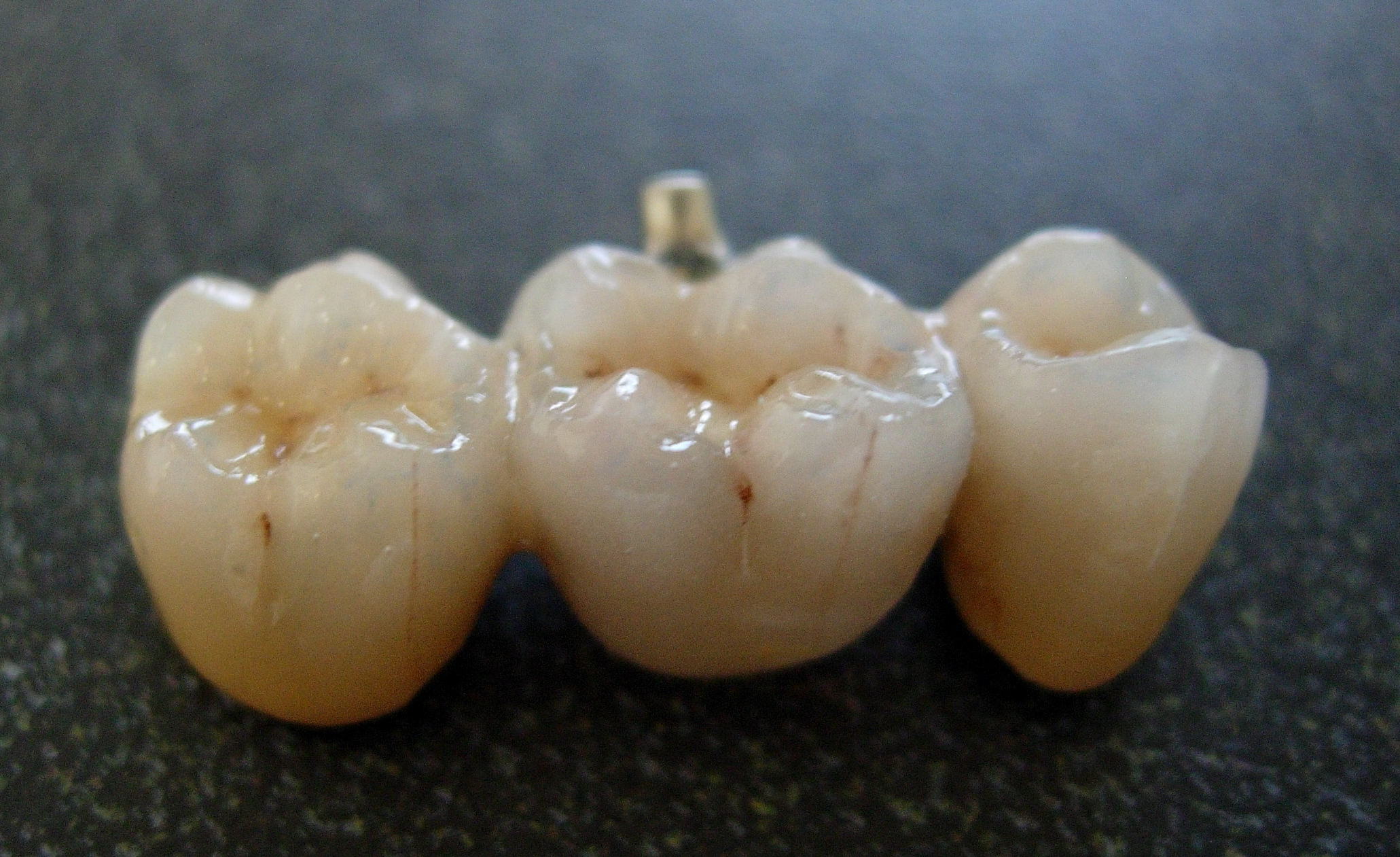
When are ceramics used?
Inlays, onlays, and full crowns
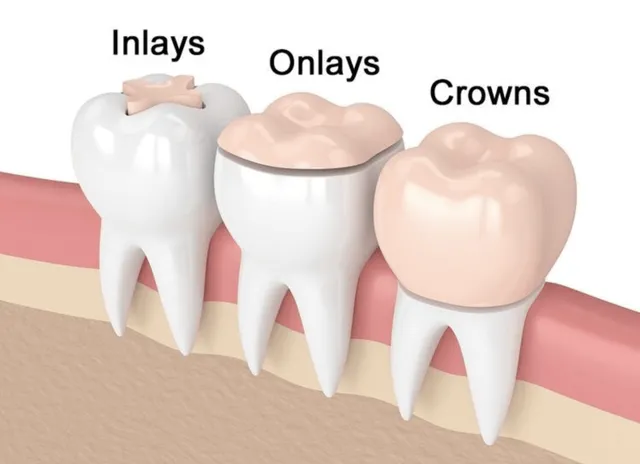
What is an inlay?
A custom filling that fits inside the grooves of a tooth but does not cover the cusps.
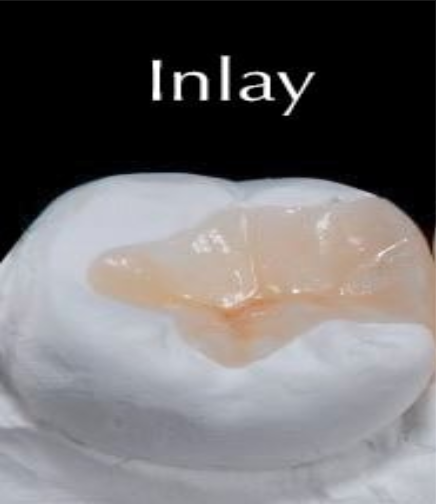

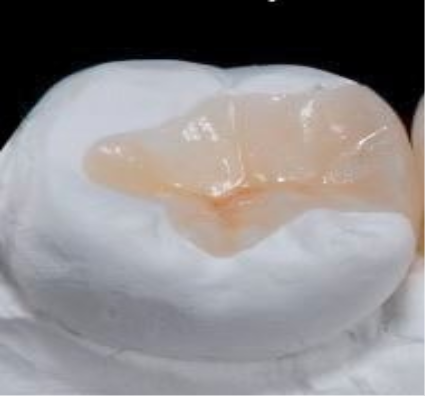
What is this?
Inlay
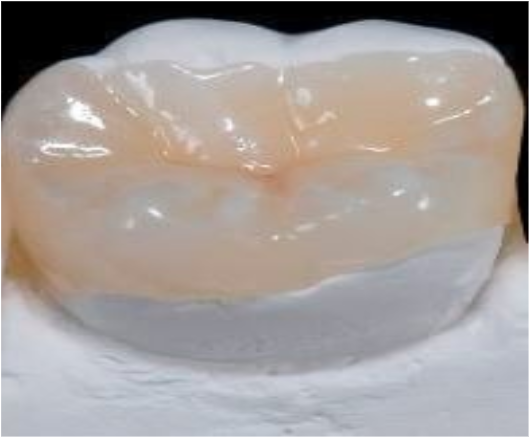
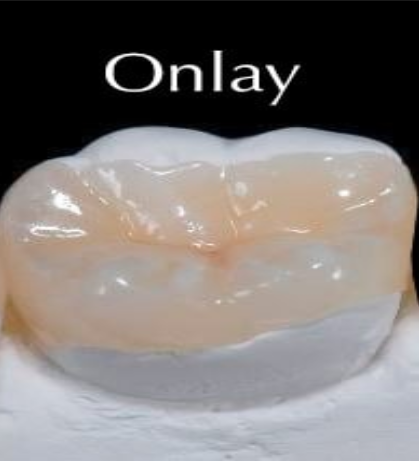
What is this?
Onlay
What are cusps (in teeth)?
The pointed or raised parts on the chewing surface of a tooth.
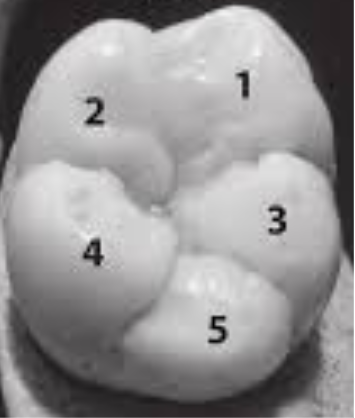
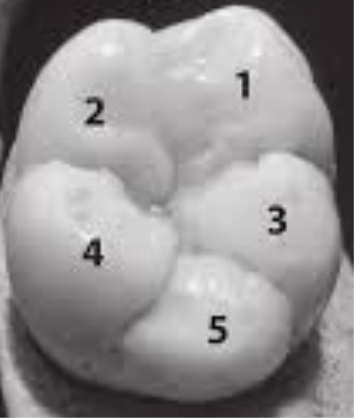
What is this and example of?
Cusps
What is an onlay?
A custom restoration that covers one or more cusps of a tooth, but not the whole tooth.
What is a crown?
A full-coverage restoration that completely caps or replaces the visible part of a tooth.
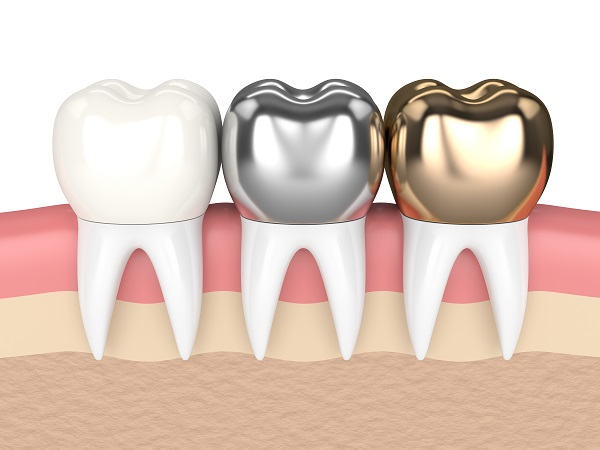
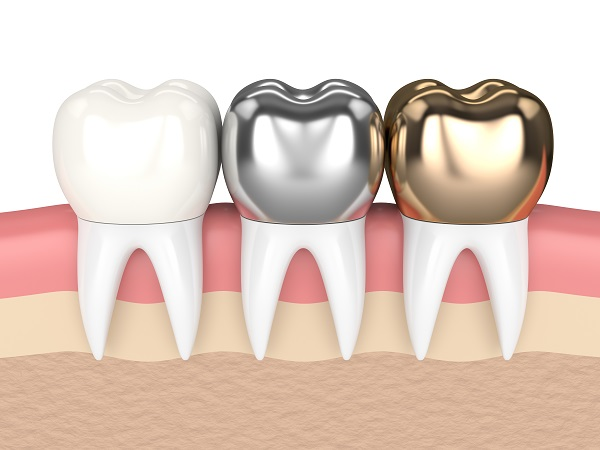
What is this?
A crown
When are metals used?
For restorations, prosthetics implants, instruments
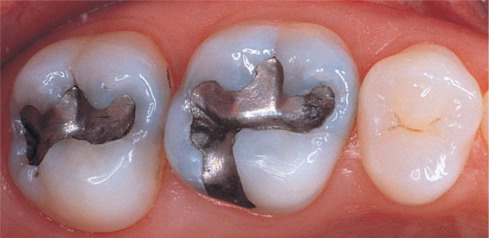
What is this?
Amalgam
What is a Restoration?
A dental treatment that repairs or replaces part of a tooth to bring back its shape and function.
What is this?
Prosthetic implant
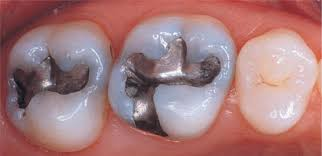
What is this?
Amalgam
What are Polymers (in dental materials)?
Large, chain-like molecules (plastics/resins) used in things like dentures and fillings.
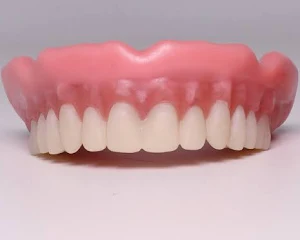
When are polymers used?
Dentures and fillings
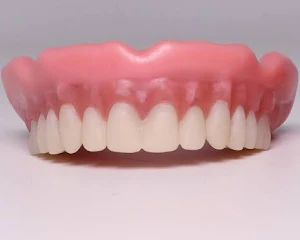
What is this?
Dentures
What are Composites (in dental materials)?
Materials made by combining two or more different substances (like resin + filler) to improve strength and appearance.
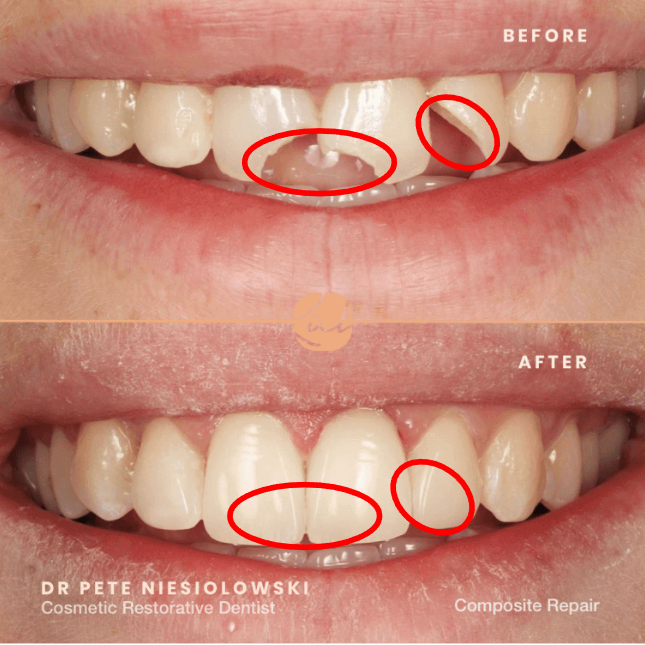
What are Metals (in dental materials)?
Strong, durable materials (like gold, amalgam, or alloys) used for crowns, fillings, and instruments.
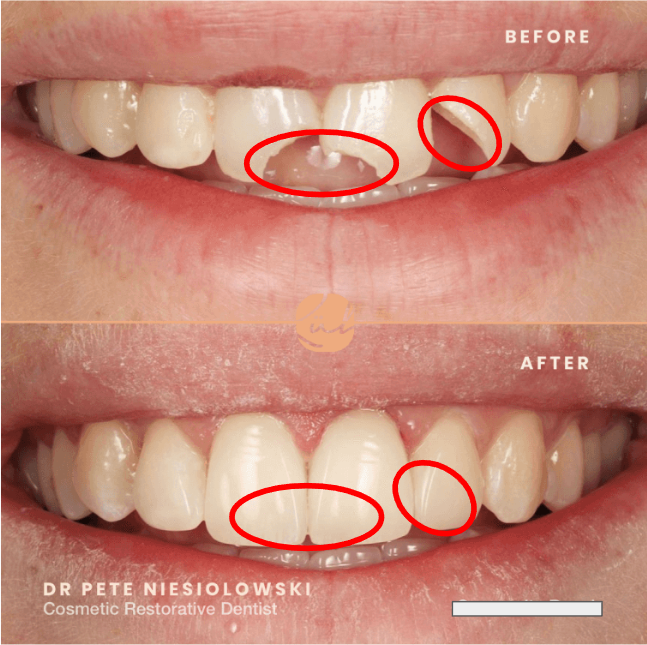
What is this an example of?
Composite restoration
When are composites used?
Restorations
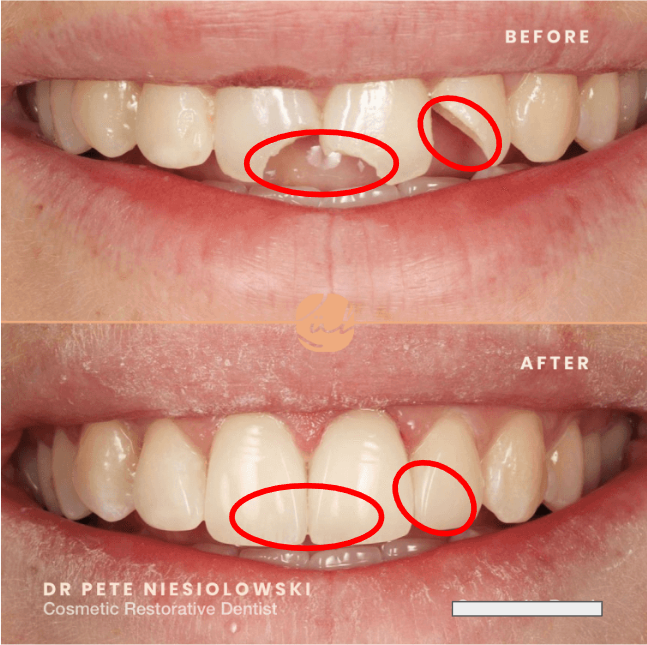
How are dental materials classified by use?
Restorations
Impressions & Models
Cements
Temporary Materials
Preventive Materials
Polishing Materials
Implants
Specialty Materials
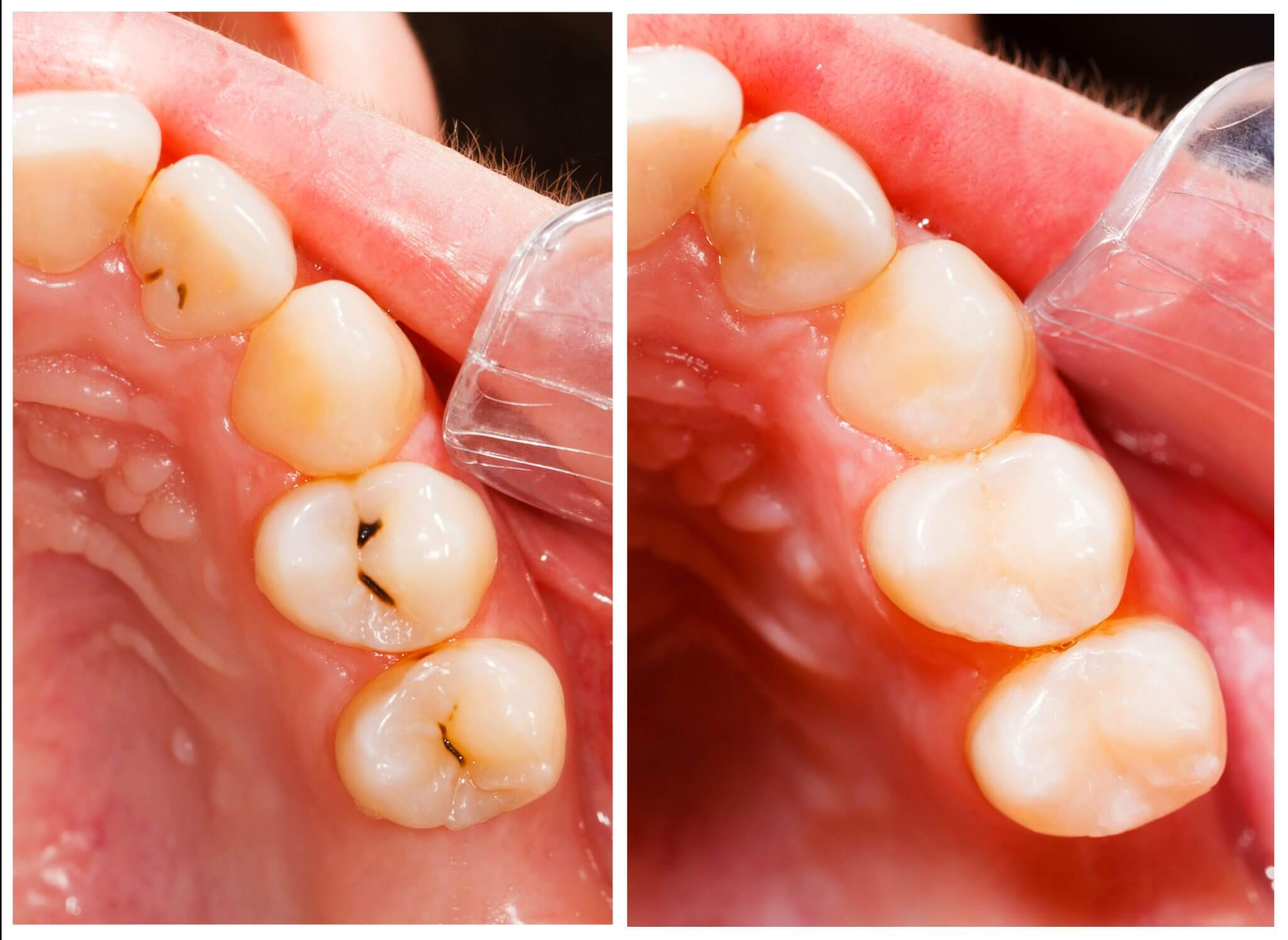
What are Fillings?
Restorations that repair holes or damage in teeth, usually after decay is removed.
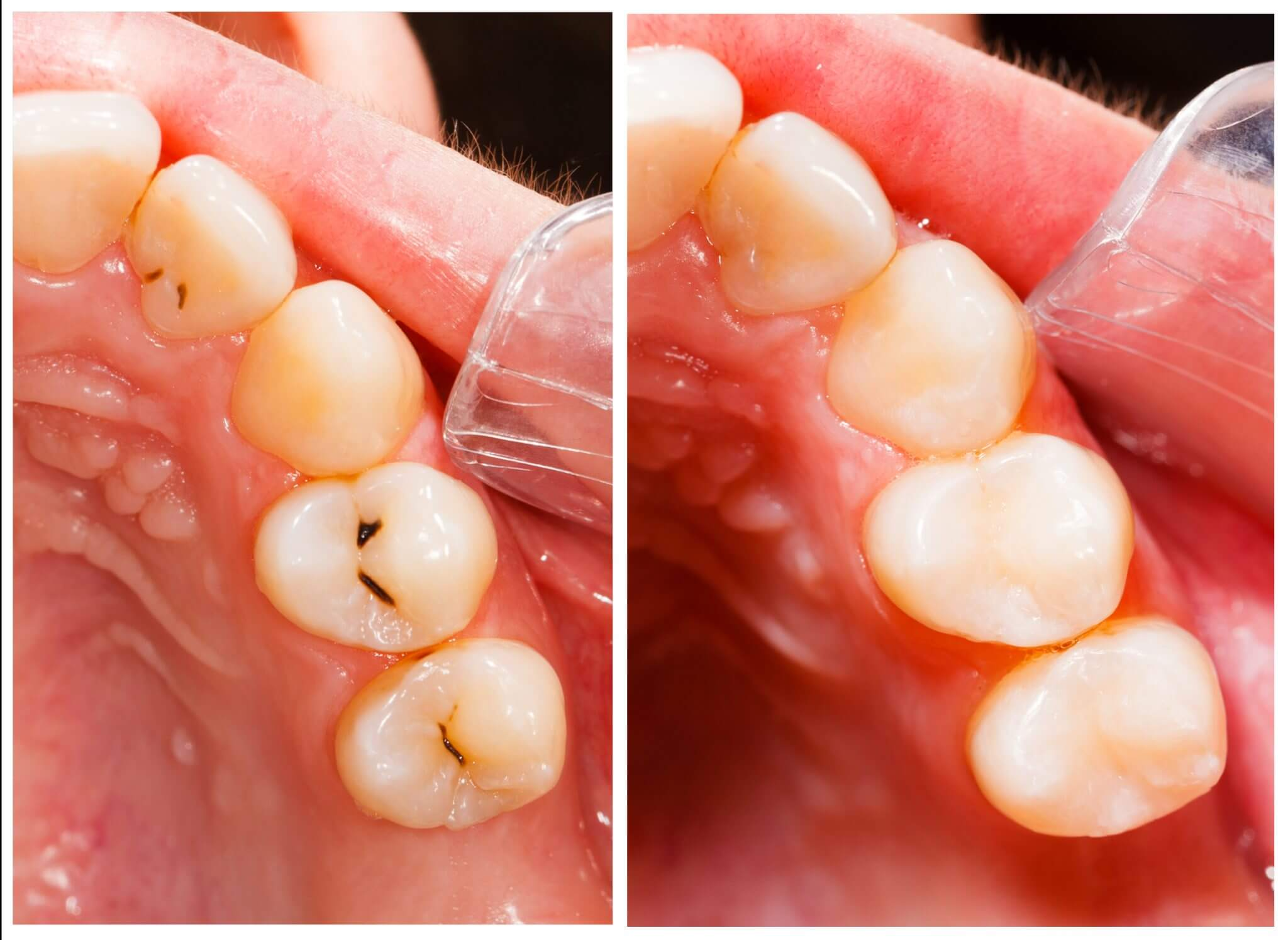
What is this?
Filling
What is Direct Restoration?
A filling made directly in the mouth in one visit (e.g., composite/amaglams).
What are some examples of Direct Restorations?
Composites and amalgams
What is Indirect Restoration?
A restoration made outside the mouth (like in a lab) and then placed in the tooth (e.g., Crowns, bridges, onlays, inlays, dentures veneers).
What are some examples of Indirect Restorations?
Crowns, bridges, onlays, inlays, dentures, veneers
What is Amalgam made of?
A mixture of metals, mainly silver, tin, copper, and mercury.
What is Composite made of?
A mix of polymer resin and glass filler.
What is a Bridge?
A fixed restoration that replaces one or more missing teeth, anchored to nearby teeth or implants.
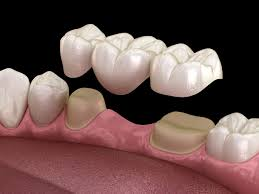
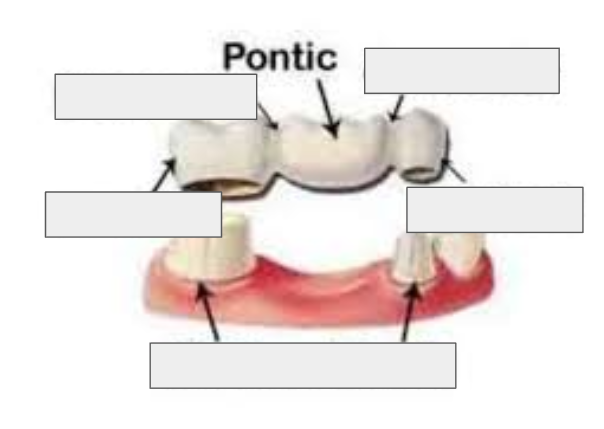
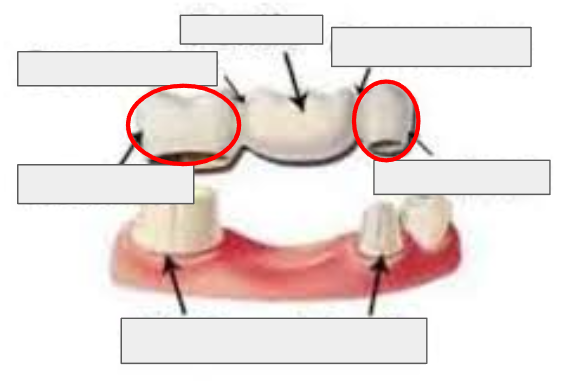
What is a Pontic?
The false tooth that replaces the missing tooth in a bridge.
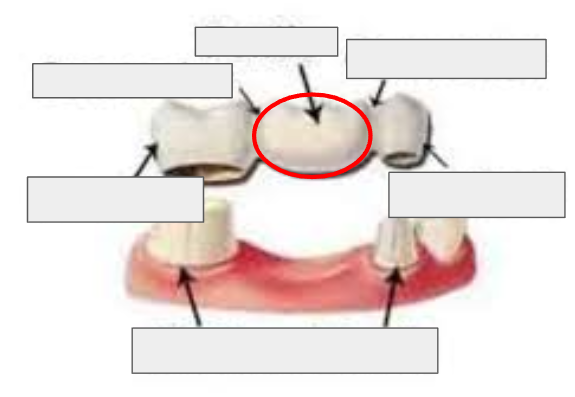
What is this?
Pontic of a bridge
What is a Connector (in a bridge)?
The part that joins the pontic to the abutment retainer.
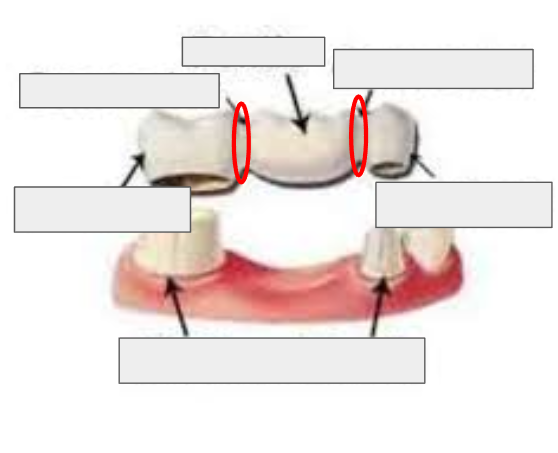
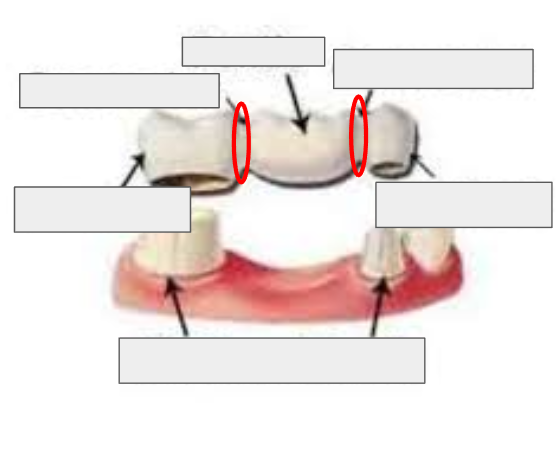
What is this?
Connecter of a bridge
What are Abutment Teeth?
The natural teeth that support a bridge; they are usually shaped or ground down to fit retainers.
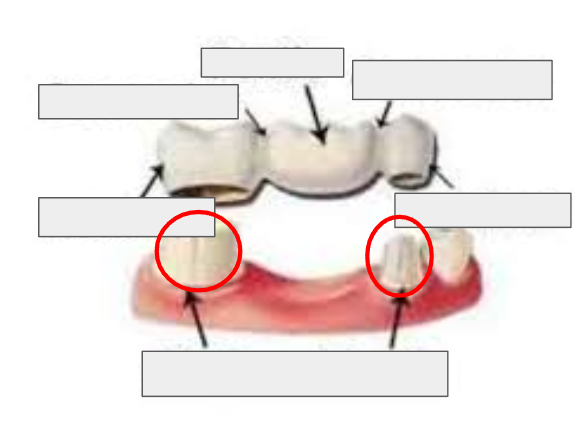
What is this?
Abutment Teeth
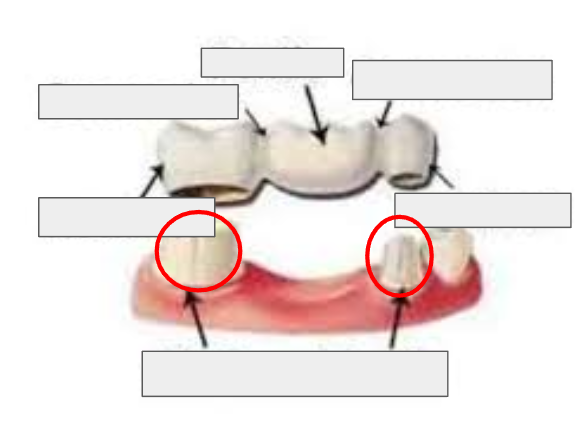
What is a Retainer
The part of the bridge that fits over an abutment tooth and holds the bridge in place.
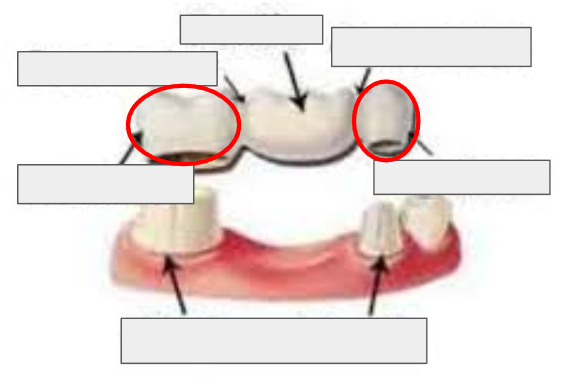
What is this?
Retainer
What are Dentures?
Removable appliances that replace missing teeth and surrounding tissues.
What is the function of Dentures?
To restore chewing, speech, and appearance when teeth are missing.
What is a Full Denture?
A removable appliance that replaces all the teeth in an arch (upper or lower).
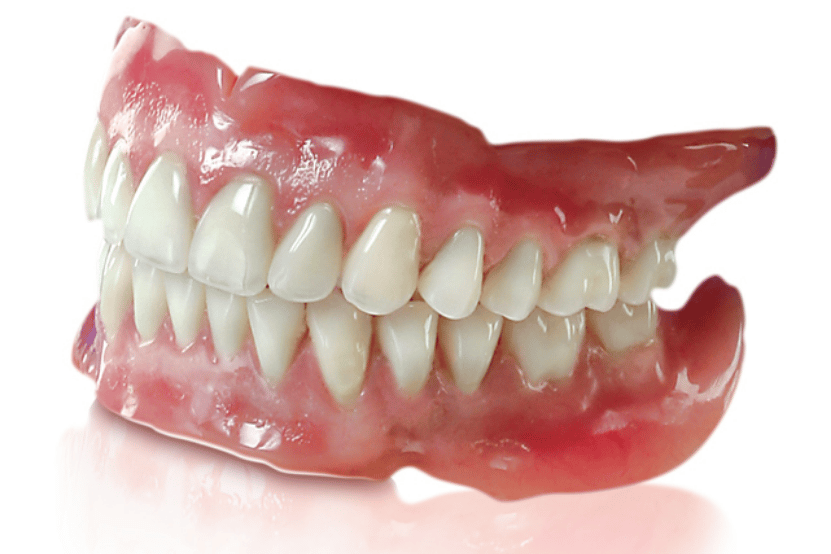
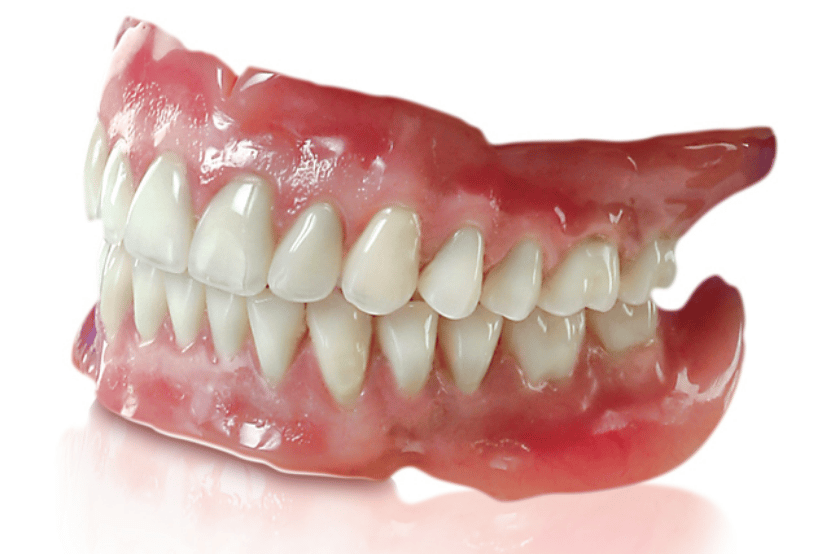
What is this?
A full denture
What is an Overdenture?
A denture that fits over remaining natural teeth or implants for extra support.
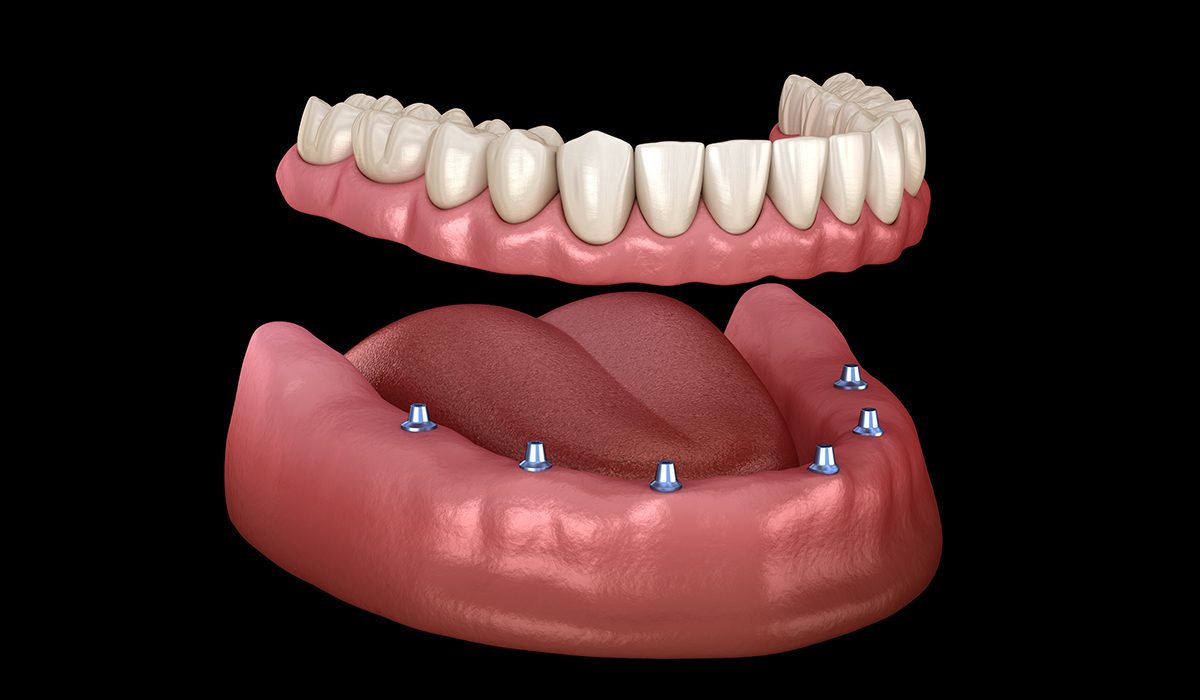
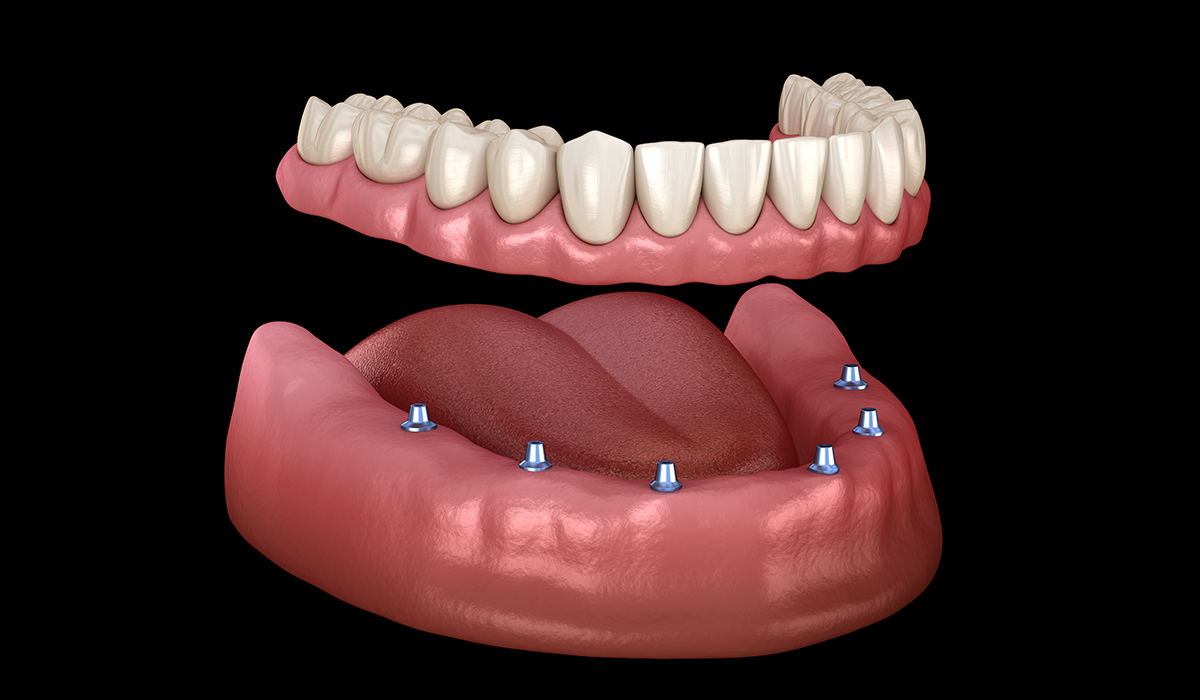
What is this?
Overdenture
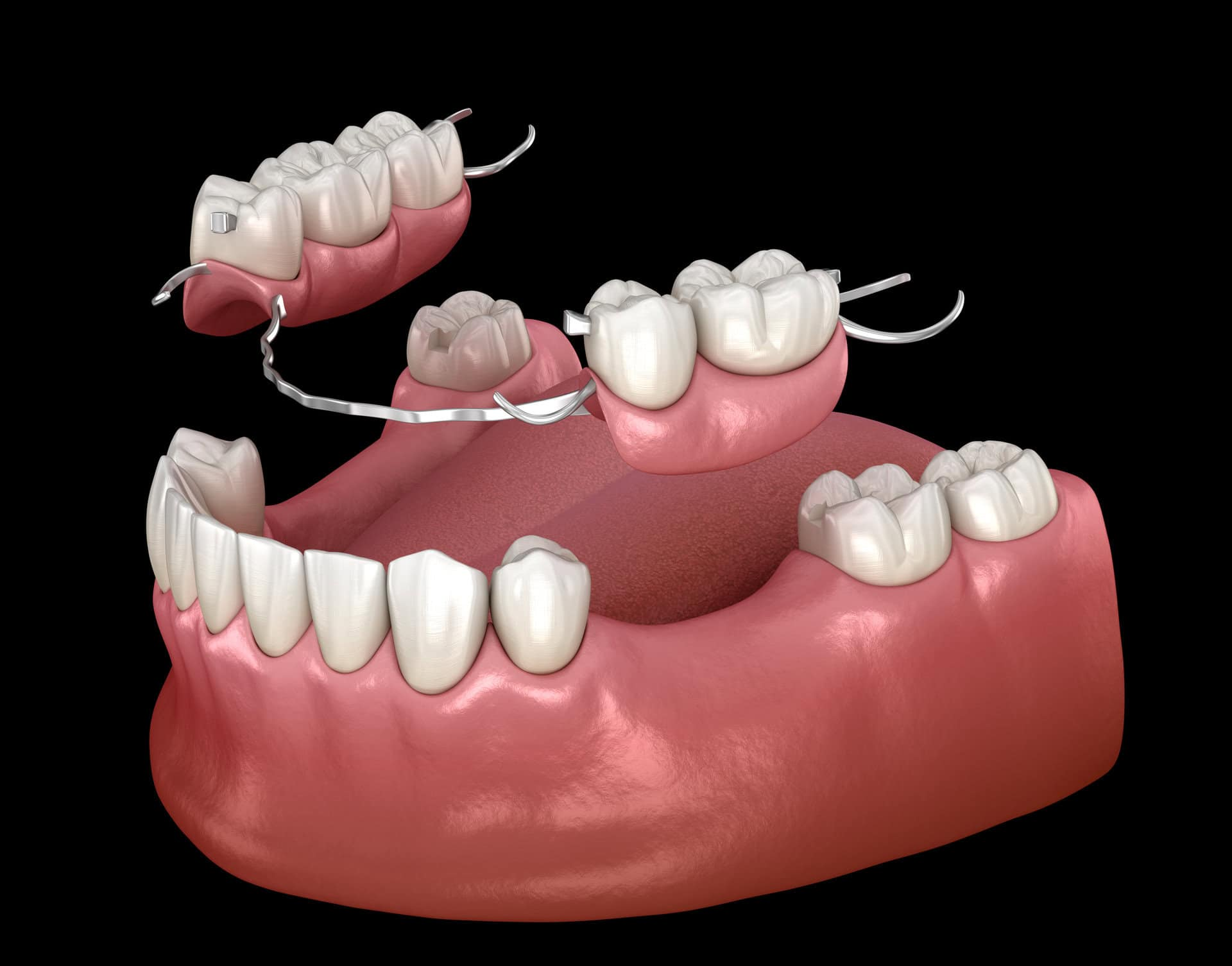
What is a Partial Denture?
A removable appliance that replaces some missing teeth, attaching to the natural teeth that remain.
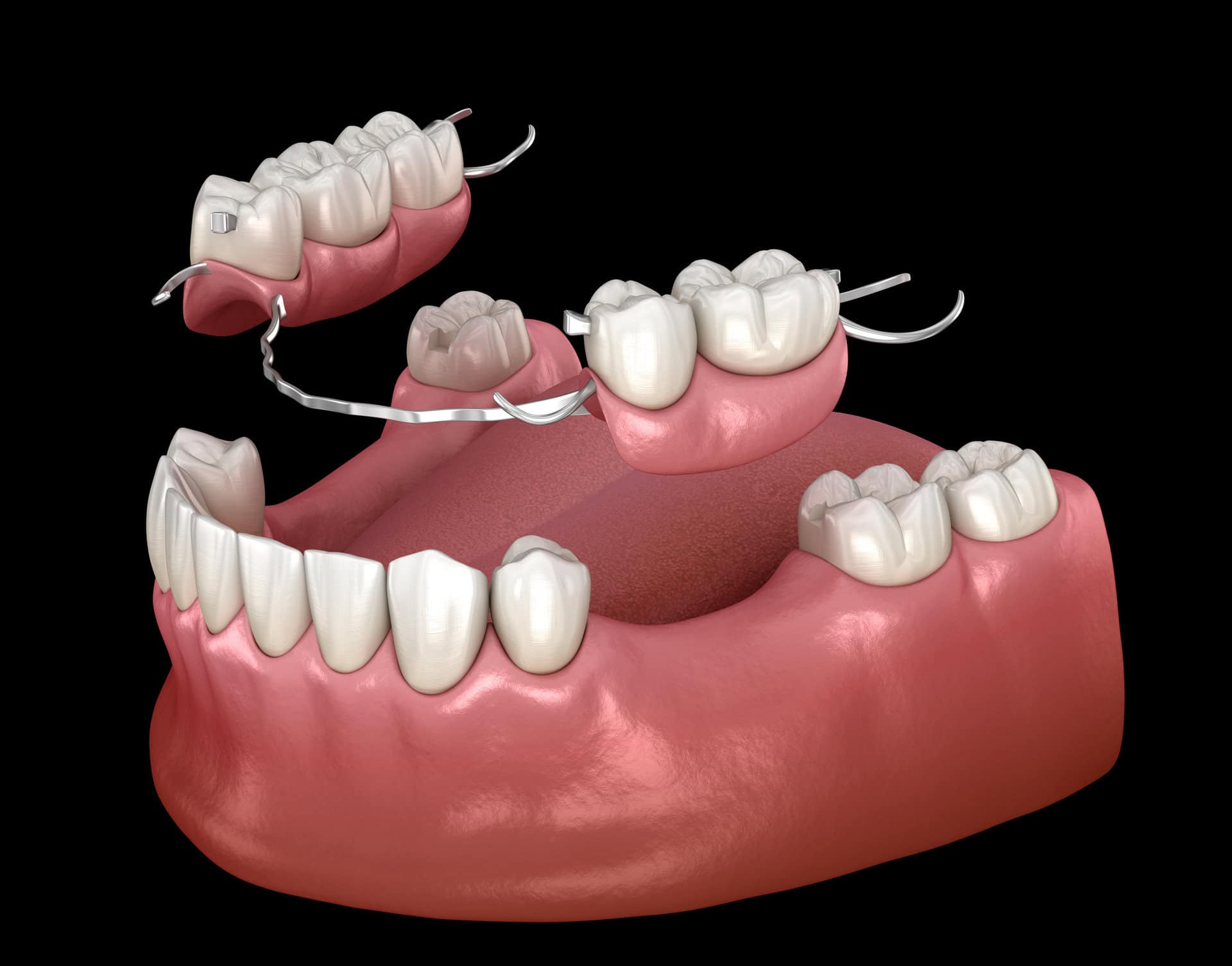
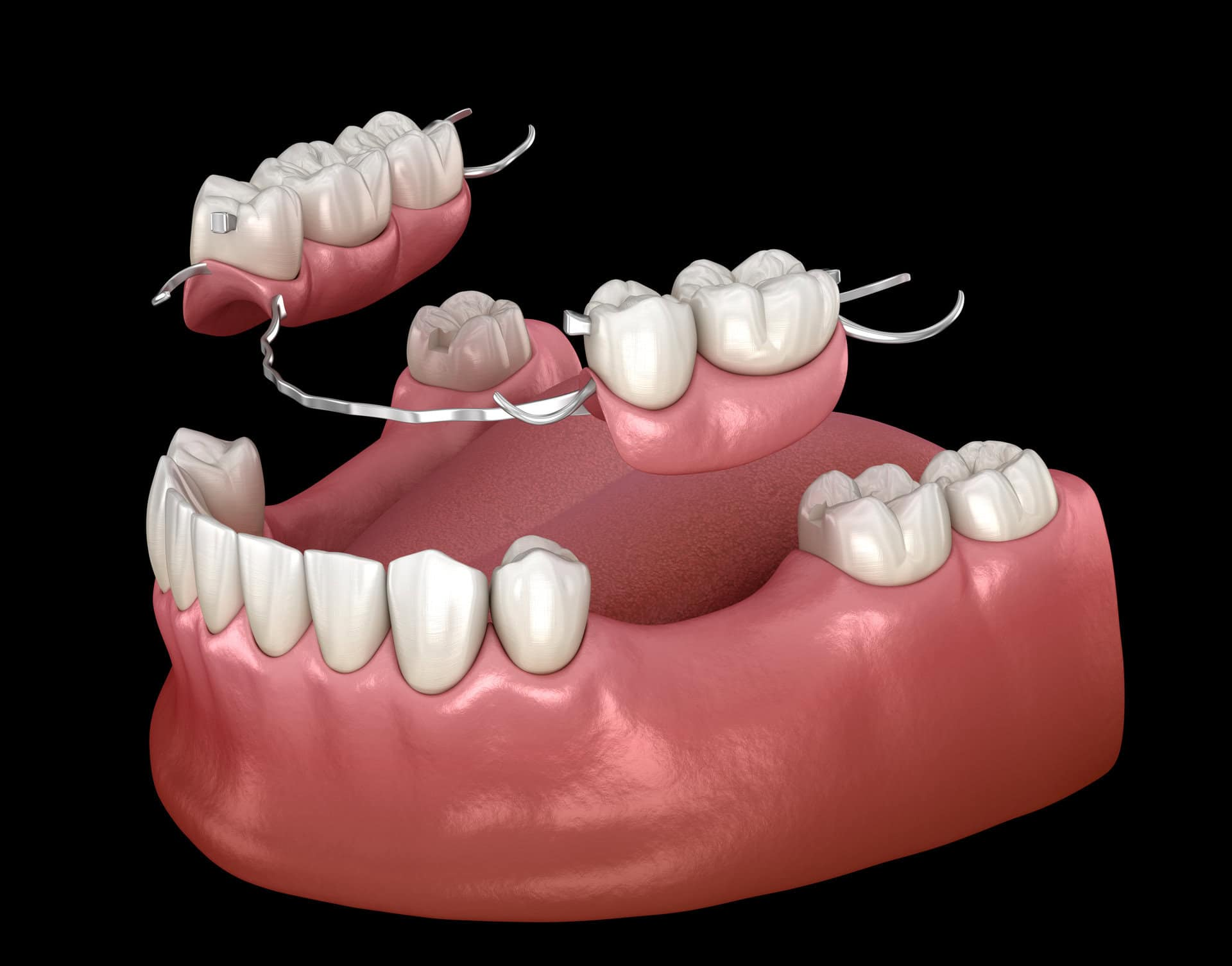
What is this?
Partial Denture
What are Impressions?
Negative molds of the mouth that capture the shape of teeth and tissues.
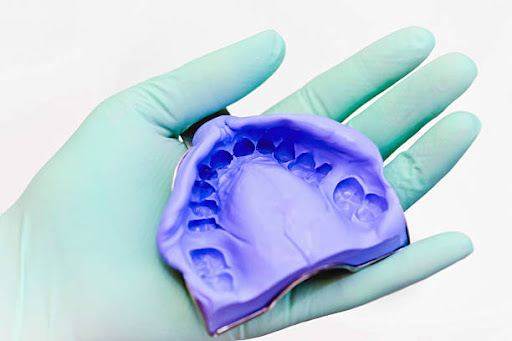
What is this?
An impression
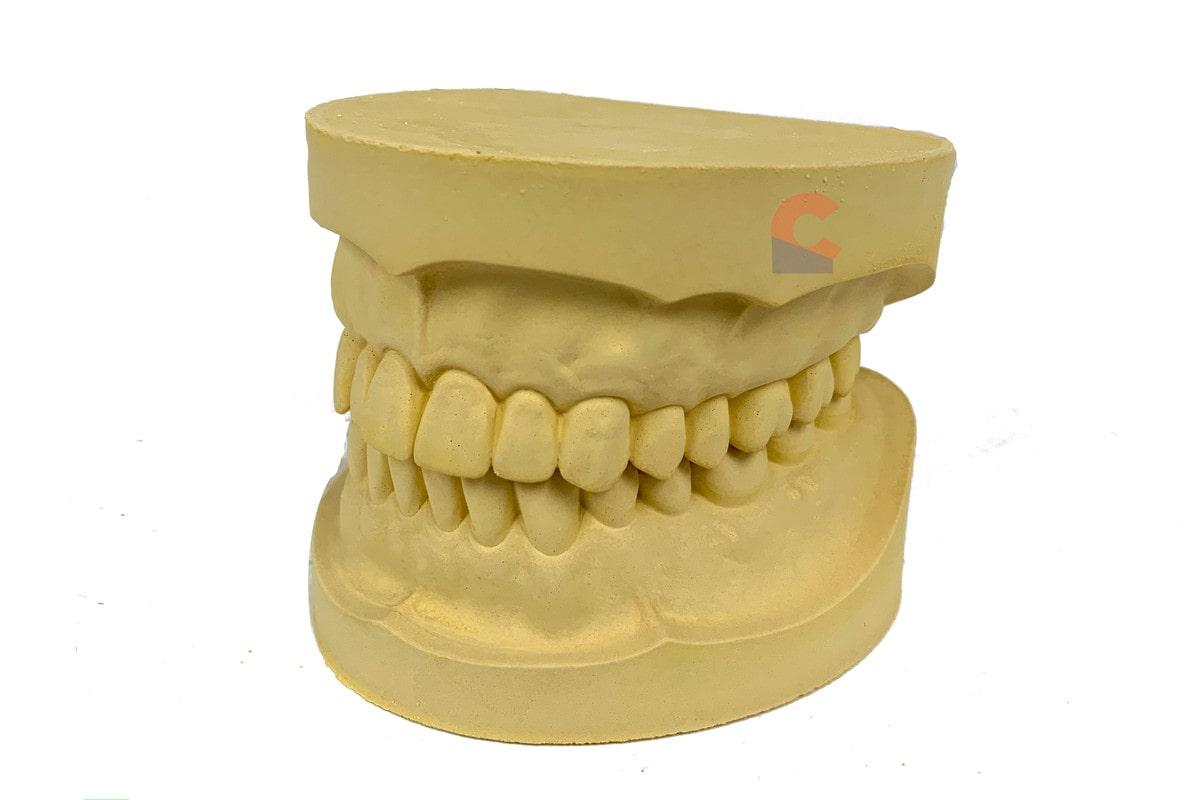
What is a Cast?
A positive model made from an impression, used to study or create restorations.
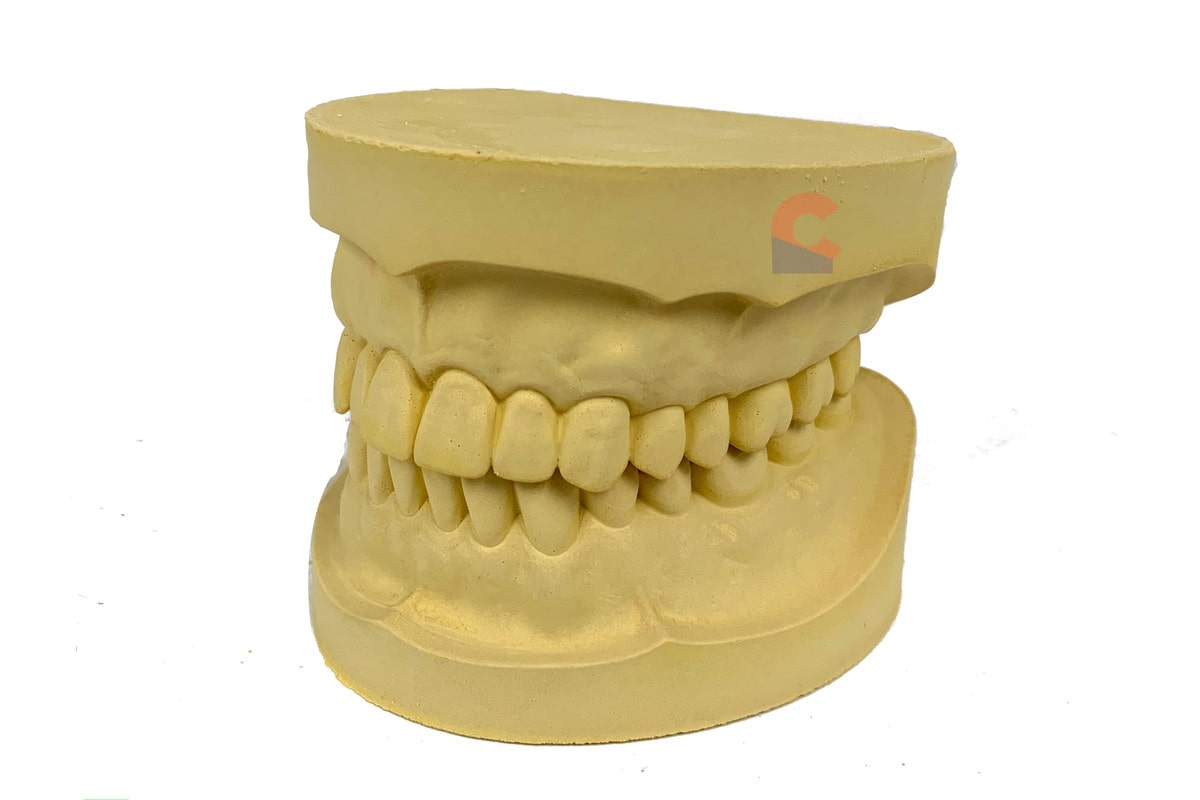
What is this?
A cast
What is a Die?
A highly accurate replica of a single tooth, used for making crowns or inlays.
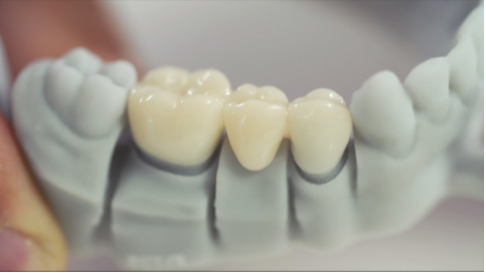
What is a Study Model?
A cast made to examine a patient’s mouth for diagnosis, treatment planning, or patient education.
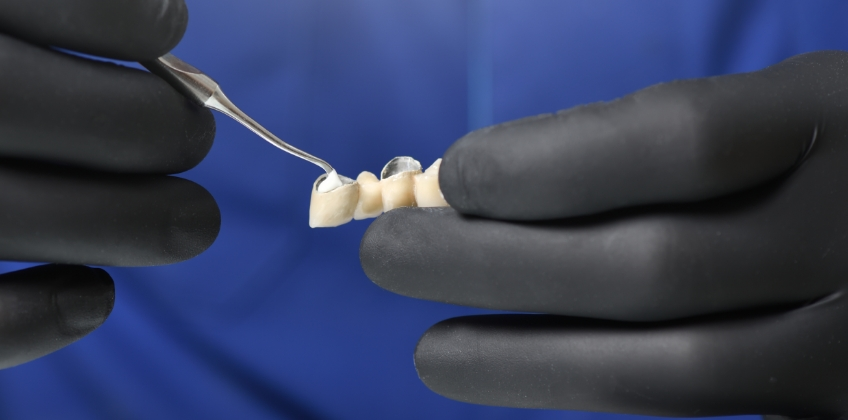
What are Cements?
Materials used to glue restorations, protect the pulp, or fill spaces under restorations.
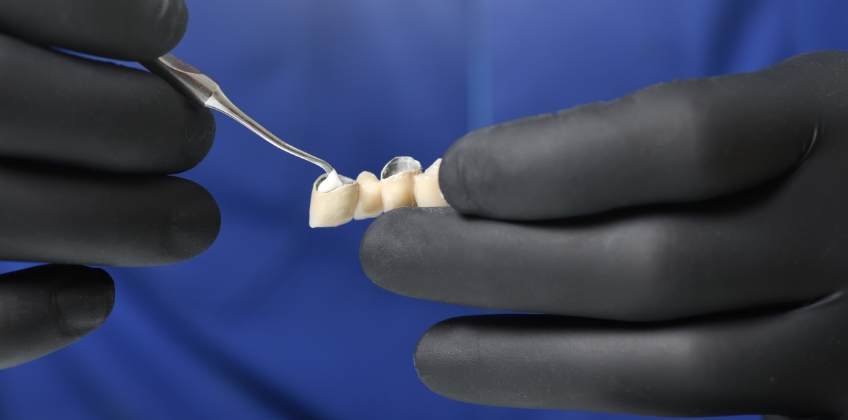
What is a Luting Agent?
A dental cement used to glue a restoration (like a crown or inlay) to a tooth.
Holds restorations in place
What is a Liner?
A thin protective layer placed on the tooth to shield the pulp from irritation.
Thin layer of material to protect the pulp
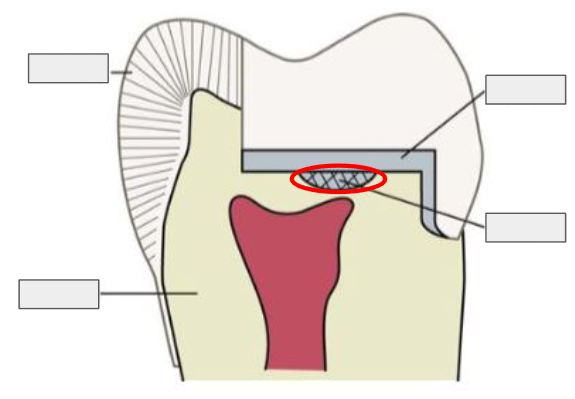
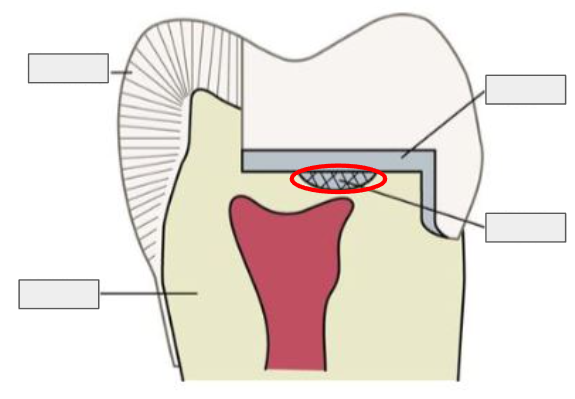
What is this?
A liner
What is a Base?
A thicker layer of material under a restoration that provides thermal protection and support.
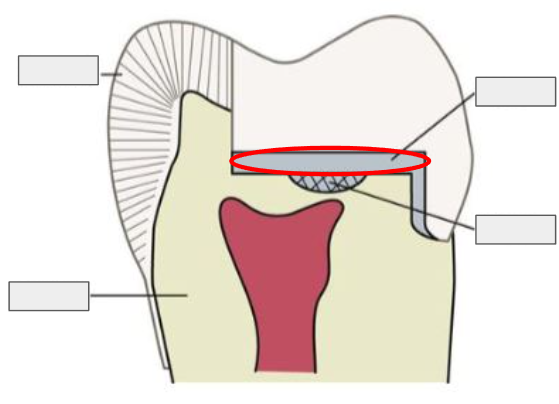
What is this?
The base
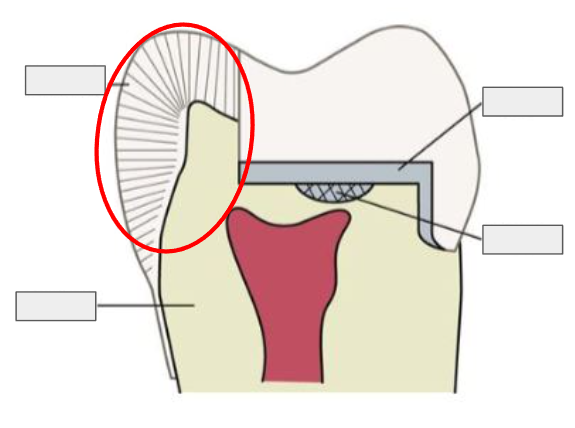
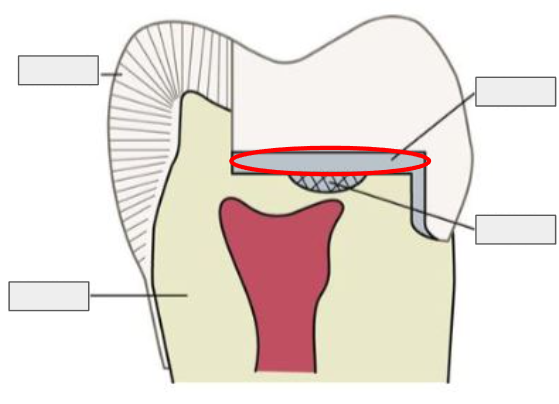
What is this?
Enamel
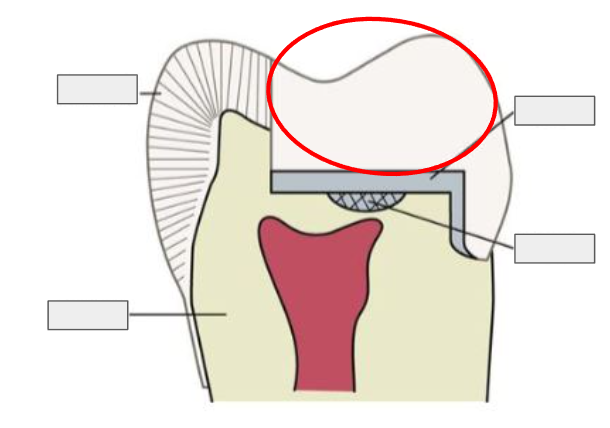
What is this?
Restoration
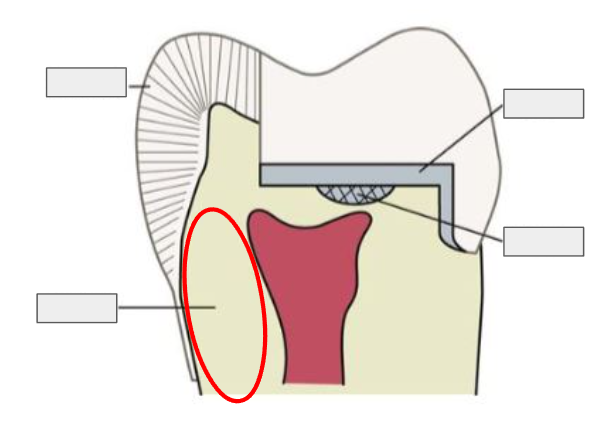
What is this?
Dentin
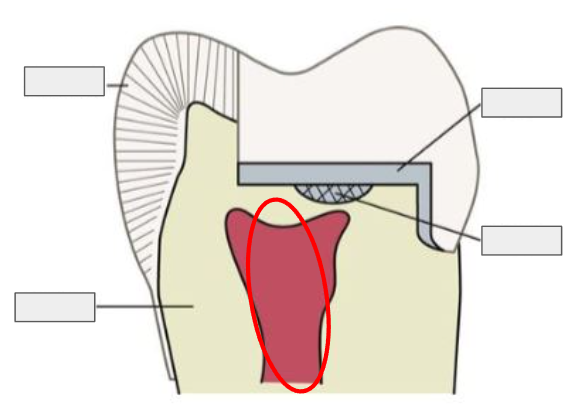
What is this?
Pulp
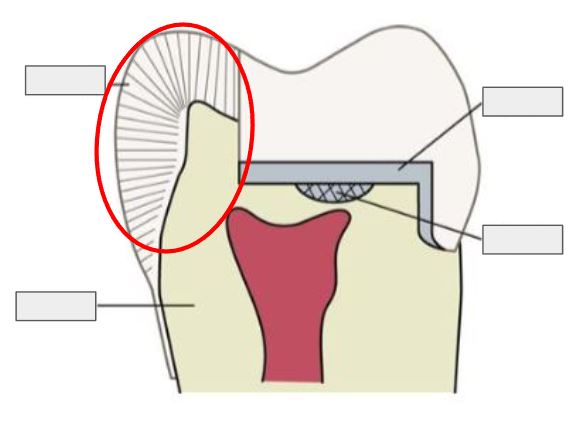
What is Enamel?
The hard, outer layer of a tooth; it’s the strongest substance in the body and protects the tooth.
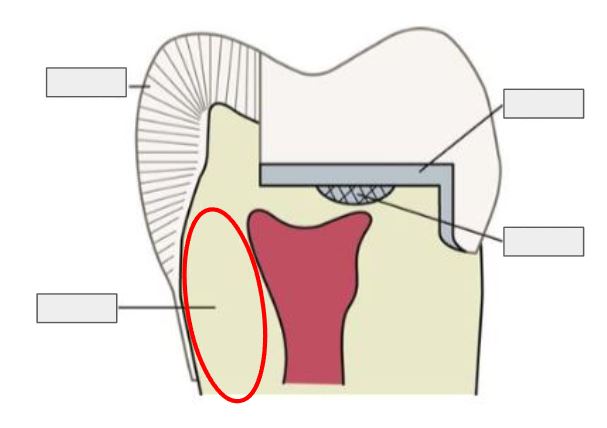
What is Dentin?
The layer under enamel; it’s softer, yellowish, and carries sensations to the pulp.
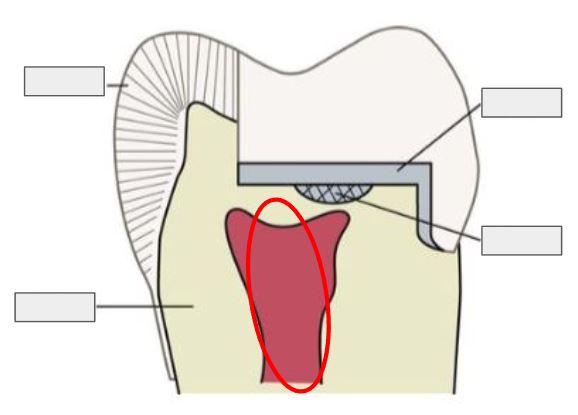
What is Pulp?
The innermost part of the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels, keeping the tooth alive.
What are Temporary Materials?
Short-term materials used until a permanent restoration is placed (e.g., temporary crowns or fillings).
What are Preventive Materials?
Materials that protect teeth from disease or decay, like fluoride and sealants.
What are Polishing Agents?
Materials used to smooth and shine teeth or restorations after procedures.
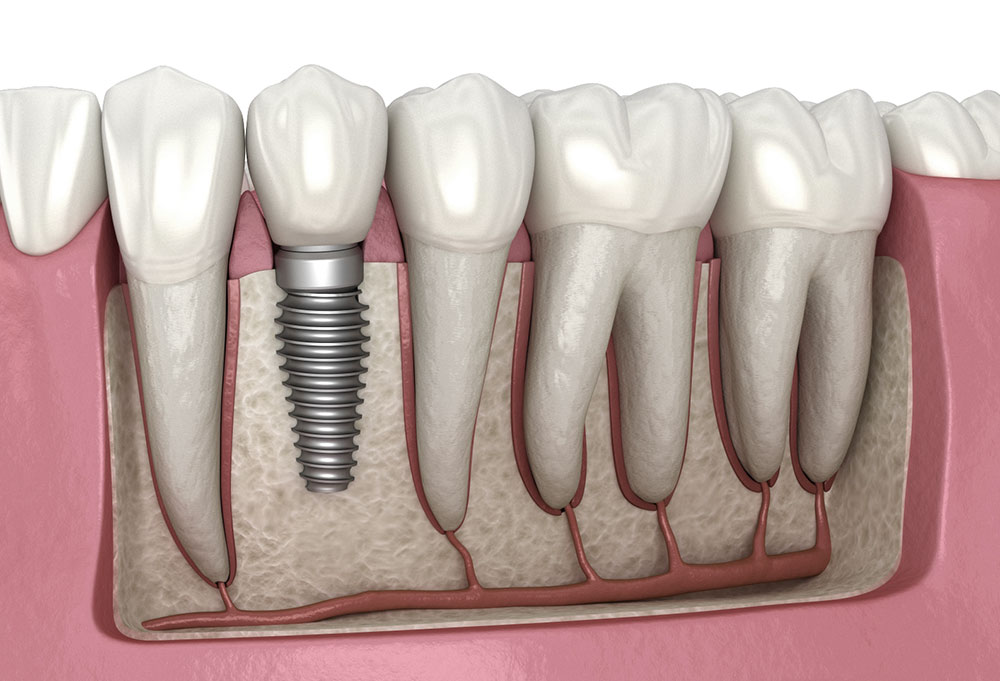
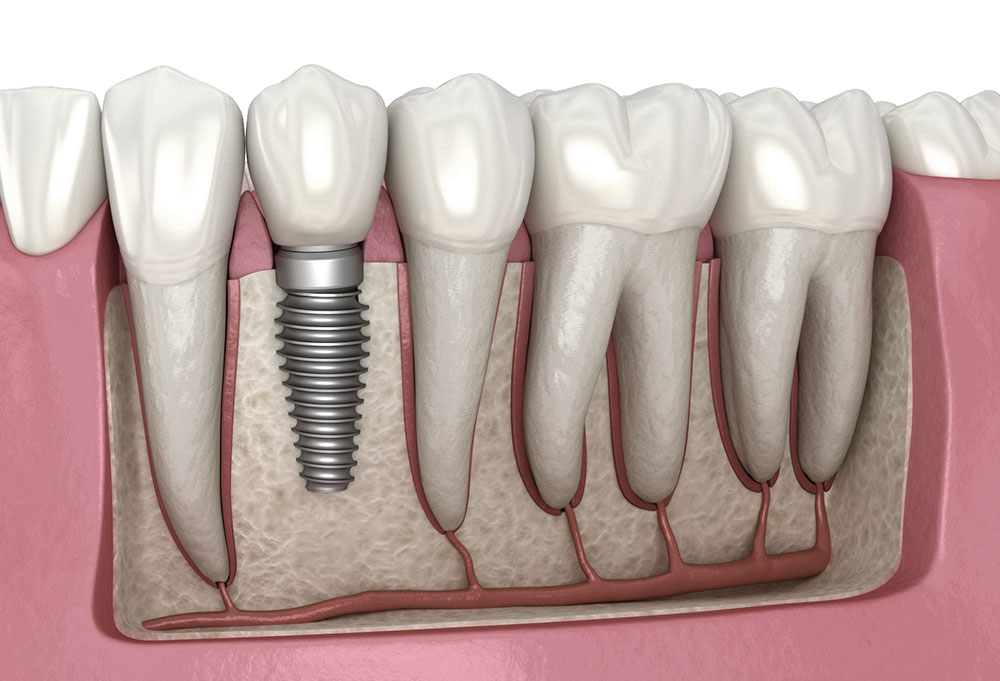
What are Implants?
Metal posts (usually titanium) placed in the jawbone to replace tooth roots and support restorations.
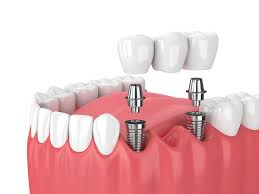
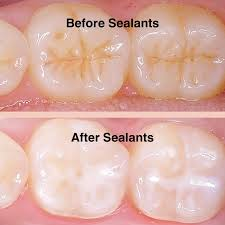
What are sealants?
Thin protective coatings placed on the chewing surfaces of back teeth to prevent cavities.
What are Specialty Materials in dentistry?
Special-use materials like brackets, bands, elastics, sutures, desensitizing agents, paper, waxes, and gutta-percha.
What does Long-Term “Permanent” mean for dental materials?
Materials designed to stay in the mouth for many years, like crowns or implants.
What are Temporary Materials?
Materials meant to last only a short time, like temporary fillings or crowns.
What are Interim Materials?
Medium-term materials used while waiting for a permanent restoration, lasting longer than temporary ones but not forever.

What does OSHA stand for?
Occupational Safety and Health Administration

Who does OSHA protect?
Employees
What is PPE?
Personal protective equipment
What are some important things that OSHA covers?
PPE, infection control, hazard communication
When is OSHA training required?
Within 2 weeks of employment
Annual updates
Whenever a new product is introduced
If something is moved to a secondary/new container _____ is required.
Labeling
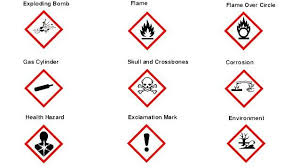
What are OSHA Pictograms?
Standard safety symbols on chemical labels that show specific hazards, like flammability, toxicity, or corrosion.