PSY 120: Exam 3 Study Guide
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/229
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:26 AM on 11/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
230 Terms
1
New cards
motivation
describes the wants or needs that direct behavior toward a goal
2
New cards
intrinsic motivation
(arising from internal factors); performed because of the sense of personal satisfaction that they bring
3
New cards
extrinsic motivation
(arising from external factors); performed in order to receive something from others
4
New cards
instinct
species-specific pattern of behavior that is not learned
5
New cards
homeostasis
tendency to maintain a balance, or optimal level, within a biological system
6
New cards
over justification effect
the hypothesis that extrinsic motivation can supplant pre-existing intrinsic motivation
7
New cards
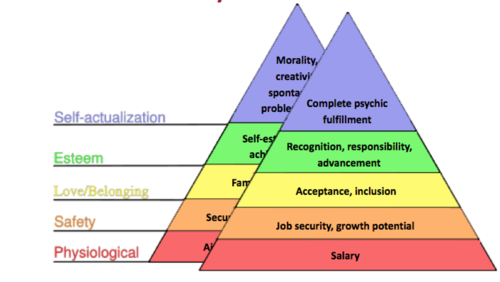
Masclow's Hierarchy of Needs
physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, self-actualization
8
New cards
Drive theory
deviations from homeostasis create physiological needs that result in psychological drive states that direct behavior to meet the need and ultimately bring the system back to homeostasis
9
New cards
primary drive
biological and innate
10
New cards
secondary drive
conditioned and learned
11
New cards
habit
pattern of behavior in which we regularly engage
12
New cards
optimal arousal theory
organisms are motivated to achieve and maintain an optimal level of arousal
13
New cards
self-determined theory
We are motivated by intrinsic goals, and want to feel like we are in control of out destiny
14
New cards
Yerkes - Dodson law
which holds that a simple task is performed best when arousal levels are relatively high and complex tasks that are best performed when arousal levels are lower
15
New cards
approach goals
goals we seek or aspire toward (trying to become good at a sport)
16
New cards
avoidance goals
Goals we want to avoid. (avoiding public embarrassment, financial ruin)
17
New cards
performance goals
performing well in front of others,being judged well
18
New cards
mastery goals
Increasing competence and skills
(Hitting the ball well, even when nobody's watching)
(Hitting the ball well, even when nobody's watching)
19
New cards
approach-aproach conflict
a choice must be made between two attractive goals
20
New cards
avoidance-avoidance conflict
Choice between two appealing activities or goals
21
New cards
approach-avoidance conflict
Choice has both positive and negative outcomes
22
New cards
self-efficacy
One's belief in his or her own ability.
23
New cards
Satiation
fullness; satisfaction
24
New cards
Leptin
satiety hormone
25
New cards
metabolic rate
amount of energy that is expended in a given period of time
26
New cards
set point theory
asserts that each individual has an ideal body weight, or set point, which is resistant to change
27
New cards
overweight
25-29.9
28
New cards
obese
BMI of 30 or higher
29
New cards
morbid obesity
BMI) of 40 or greater
30
New cards
bariatric surgery
surgery specifically aimed at weight reduction
31
New cards
bulimia nervosa
an eating disorder in which a person alternates binge eating (usually of high-calorie foods) with purging (by vomiting or laxative use) or fasting
32
New cards
binge eating disorder
significant binge-eating episodes, followed by distress, disgust, or guilt, but without the compensatory purging, fasting, or excessive exercise that marks bulimia nervosa
33
New cards
distorted body image
individuals view themselves as overweight even though they are not
34
New cards
James-Lange Theory
emotion asserts that emotions arise of psychological arousal
35
New cards
Cannon-Bard Theory
psychological arousal and emotion experience occur at the same time
36
New cards
Schachter-Singer Theory
A theory of emotion that states that both physiological arousal and cognitive appraisal must occur before an emotion is consciously experienced.
37
New cards
polygraph
lie detector
38
New cards
cognitive-mediational theory
theory of emotion in which a stimulus must be interpreted (appraised) by a person in order to result in a physical response and an emotional reaction
39
New cards
basolateral complex
part of the brain with dense connections with a variety of sensory areas of the brain; it is critical for classical conditioning and attaching emotional value to memory
40
New cards
bisexual
emotional and erotic attractions to both same-sexed individuals and opposite-sexed individuals
41
New cards
body language
emotional expression through body position or movement
42
New cards
components of emotion
physiological arousal, psychological appraisal, and subjective experience
43
New cards
cultural display rule
one of the culturally specific standards that govern the types and frequencies of emotions that are acceptable
44
New cards
emotion
subjective state of being often described as feelings
45
New cards
exceitement
phase of the sexual response cycle that involves sexual arousal
46
New cards
facial feedback hypothesis
facial expressions are capable of influencing our emotions
47
New cards
gender dysphoria
diagnostic category in DSM-5 for individuals who do not identify as the gender associated with their biological sex
48
New cards
gender identity
the individual's sense of being male or female
49
New cards
heterosexual
emotional, romantic, and/or erotic attractions to opposite-sex individuals
50
New cards
Plateu
phase of the sexual response cycle that falls between excitement and orgasm
51
New cards
refactory period
time immediately following an orgasm during which an individual is incapable of experiencing another orgasm
52
New cards
resolution
phase of the sexual response cycle following orgasm during which the body returns to its unaroused state
53
New cards
sexual orientation
emotional and erotic attraction to same-sexed individuals, opposite-sexed individuals, or both
54
New cards
sexual response cycle
divided into 4 phases including excitement, plateau, orgasm, and resolution
55
New cards
transgender hormone therapy
use of hormones to make one's body look more like the opposite-sex
56
New cards
anal stage
psychosexual stage in which children experience pleasure in their bowel and bladder movements
57
New cards
analytical psychology
Jung's theory focusing on the balance of opposing forces within one's personality and the significance of the collective unconscious
58
New cards
Archetype
pattern that exists in our collective unconscious across cultures and societies
59
New cards
collective unconscious
common psychological tendencies that have been passed down from one generation to the next
60
New cards
congruene
state of being In which out thoughts about our real and ideal selves are very similar
61
New cards
conscious
mental activity (thoughts, feelings, and memories) that we can access at any time
62
New cards
Contemporized-Themes Concerning Blacks Test (C-TCB)
projective test designed to be culturally relevant to African Americans, using images that relate to African-American culture
63
New cards
Culture
all of the beliefs, customs, art, and traditions of a particular society
64
New cards
defense mechanisms
ego defense mechanism in which a person transfers inappropriate urges or behaviors toward a more acceptable or less threatening target
65
New cards
ego
aspect of personality that represents the self, or the part of one's personality that is visible to others
66
New cards
Five Factor Model
theory that personality is composed of five factors or traits, including openness, conscientiousness, extroversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism- Costa and McRae
67
New cards
genital stage
psychosexual stage in which the focus is on mature sexual interests
68
New cards
Heritability
proportion of difference amount people that is attribute to genetics
69
New cards
Id
aspect of personality that consists of our most primitive drives or urges, including impulses for hunger, thirst, and sex
70
New cards
ideal self
person we would like to be
71
New cards
incogruence
state of being in which there Is a great discrepancy between our real and ideal selves
72
New cards
individual psychology
school of psychology proposed by Adler that focuses on our drive to compensate for feelings of inferiority
73
New cards
inferiorty complex
refers to a persons feelings that they lack worth and don't measure up to others or to society's standards
74
New cards
latency period
psychosexual stage in which sexual feelings are dormant
75
New cards
locus of control
beliefs about the power we have over our lives; an external locus of control is the belief that our outcomes are outside of our control; an internal locus of control is the belief that we control our own outcomes
76
New cards
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
personality test composed of a series of true/false questions in order to establish a clinical profile of an individual
77
New cards
neurosis
tendency to experience negative emotions
78
New cards
oral stage
psychosexual stage in which an infant's pleasure is focused on the mouth
79
New cards
Personality
long-standing traits and patterns that propel individuals to consistently think, feel, and behave in specific ways
80
New cards
phallic stage
psychosexual stage that focuses on the genitals
81
New cards
Projection
ego defense mechanism in which a person confronted with anxiety disguises their unacceptable urges or behaviors by attributing them to other people
82
New cards
projective test
personality assessment in which a person responds to ambiguous stimuli, revealing hidden feelings, impulses, and desires
83
New cards
psychosexual stages of development
stages of child development in which a child's pleasure-seeking urges are focused on specific areas of the body called erogenous zones
84
New cards
Rationalization
ego defense mechanism in which a person confronted with anxiety makes excuses to justify behavior
85
New cards
reaction formation
ego defense mechanism in which a person confronted with anxiety swaps unacceptable urges or behaviors for their opposites
86
New cards
real self
person who we actually are
87
New cards
reciprocal determinism
belief that one's environment can determine behavior, but at the same time, people can influence the environment with both their thoughts and behaviors
88
New cards
Regression
ego defense mechanism in which a person confronted with anxiety returns to a more immature behavioral state
89
New cards
Repression
ego defense mechanism in which anxiety-related thoughts and memories are kept in the unconscious
90
New cards
Rorshach inkblot technique
projective test that employs a series of symmetrical inkblot cards that are presented to a client by a psychologist in an effort to reveal the persons unconscious desires, fears, and struggles
91
New cards
Rotter Incomplete Sentence Blank (RISB)
projective test that is similar to a word association test in which a person completes sentences in order to reveal their unconscious desires, fears, and struggles
92
New cards
selective migration
concept that people choose to move to places that are compatible with their personalities and needs
93
New cards
self-concept
our thoughts and feelings about ourselves
94
New cards
social cognitive theory
Bandura's theory of personality that emphasizes both cognition and learning as sources of individual differences in personality
95
New cards
sublimation
ego defense mechanism in which unacceptable urges are channeled into more appropriate activities
96
New cards
superego
aspect of the personality that serves as one's moral compass, or conscience
97
New cards
TEMAS Multicultural Thematic Apperception Test
projective test designed to be culturally relevant to minority groups, especially Hispanic youths, using images and storytelling that relate to minority culture
98
New cards
temperament
how a person reacts to the world, including their activity level, starting when they are very young
99
New cards
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
projective test in which people are presented with ambiguous images, and they then make up stories to go with the images in an effort to uncover their unconscious desires, fears, and struggles
100
New cards
traits
characteristic ways of behaving