Work energy and power and materials
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
How is work done defined in physics
Work done = force x distance moved in the direction of the force
What are the units of work done
Nm or joule
1j = 1Nm
How is energy defined
Work done = energy transferred
How do you calculate work done is the force applied is at an angle to the direction in which the object moves
W= Fx cos θ
Derive an expression relating power to constant speed v
Power = force x velocity
Define power in words
Power is the rate of work done
Give two alternative units for power
(J/s) or (W)
1W = 1J/s
What is gravitational potential energy
The capacity for doing work as a result of an object's position in a gravitational field
Why does Ep=mgh only work for objects in a uniform field
This equation assumes that the gravitational field is uniform, meaning the force of gravity is constant throughout the objects motion
Give an example in which GPE and KE are exchanged
As an object falls it's GPE decreases and it's KE increases
mgh = 1/2 mv2
What is kinetic energy?
the energy an object has due to its motion
How it's kinetic energy calculated
Kinetic energy = 1/2 x mass x velocity 2
What are the 2 general classifications of energy for systems with mass
* kinetic energy is the energy due to the moment of an object
* Gravitational Potential energy is the energy due to the position of an object in the Earth is gravitational field
State the principle of conservation of energy
In a closed system, energy cannot be created or destroyed but only transferred from one form to another.
What does the term potential mean
hidden or stored
Give two examples of potential energy
* Gravitational potential energy- energy of an object due to its position in a gravitational field
* Elastic potential energy- energy stored in an object as a result of reversible change in its shape
What is energy
the capacity to do work
J
Is energy scalar or vector?
scalar- magnitude but no direction
What is a tensile force
A force produces an extension of the object.
what is a compressive force
A force that reduces the length of an object.
State hooke's
The extension of the spring is directly proportional to the force applied. This is true as long as the elastic limit of the spring is not exceeded
what does spring constant (force constant) tell you about the spring
This is a measure of the stiffness of a spring. A spring with a large force constant is difficult to expand and you would refer to it as a stiff spring
Explain what elastic limit means
The maximum stress that a material can withstand without undergoing permanent deformation
explain what plastic deformation means
The permanent change in shape of a material when subjected to a stress or force beyond its elastic limit
how can you determine the elastic potential energy stored in a stretched elastic material from the force extension graph
Area under a force - extension graph = work done
The work done on the spring is transferred to elastic potential energy within the spring. This energy is fully recoverable because of the elastic behaviour of the spring
if you double the extension of spring what happens to the energy stored
E is directly proportional to extension squared so doubling the extension quadruples the energy stored
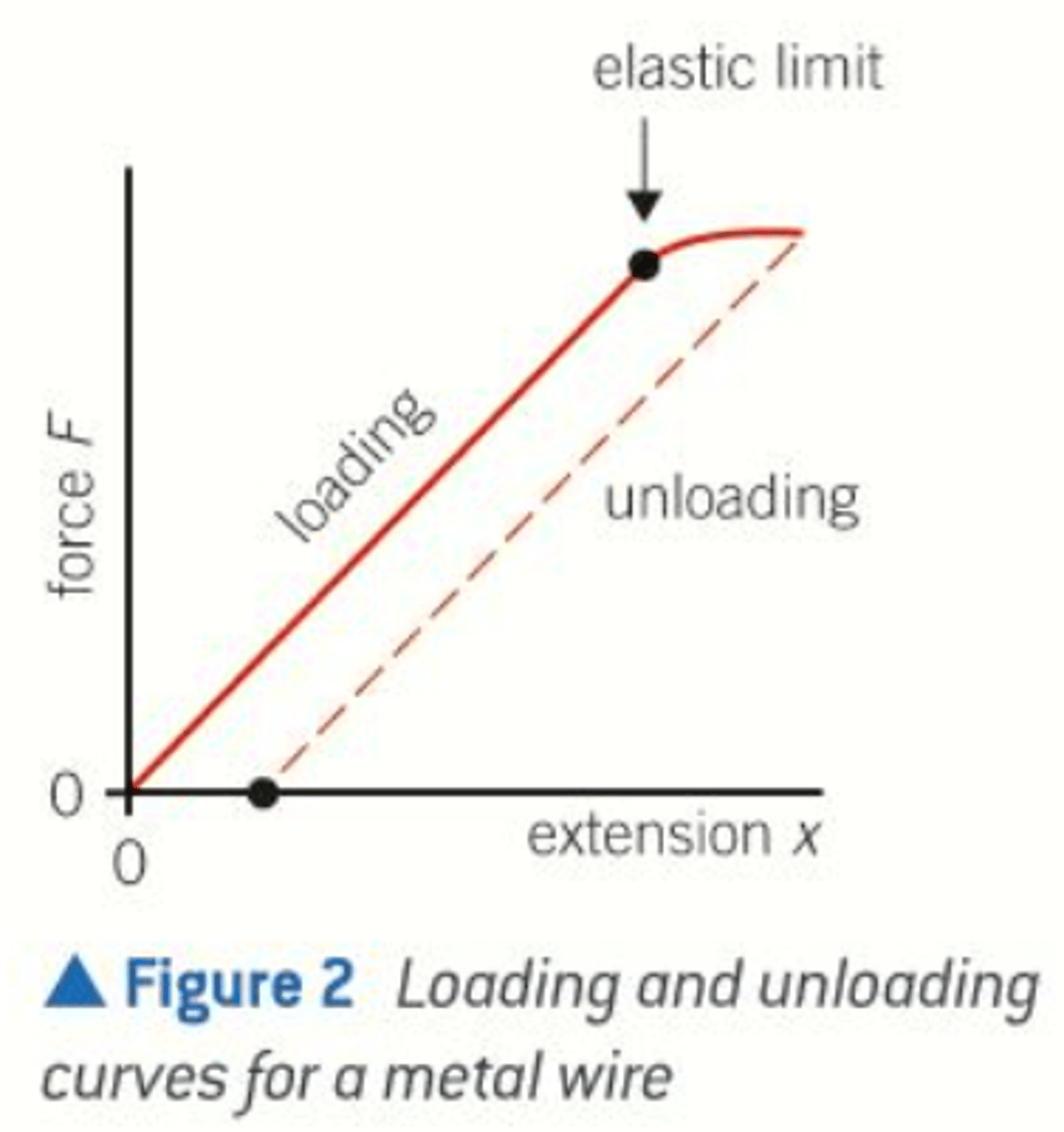
sketch a force extension curve for a metal
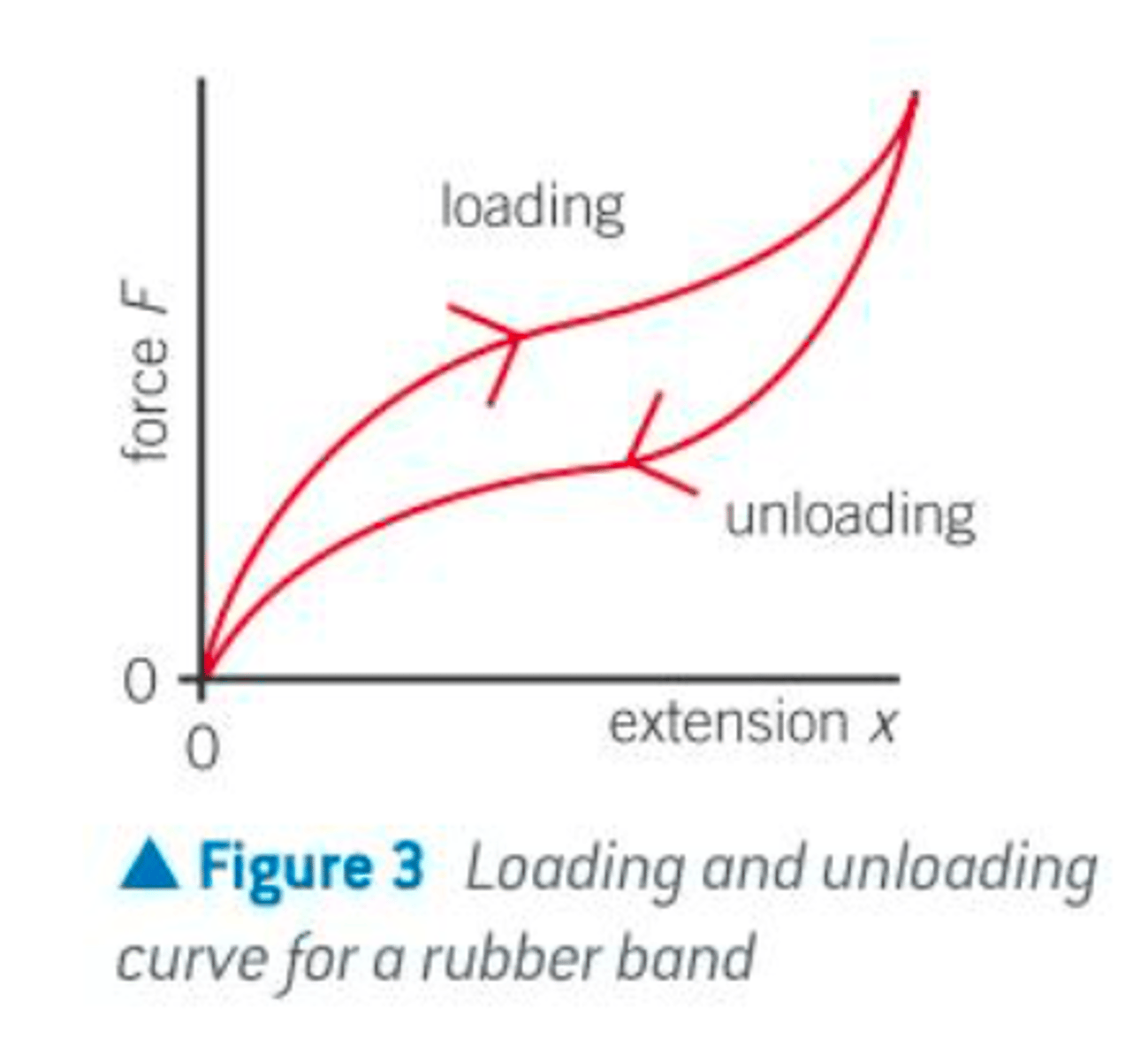
sketch a force extension curve for a rubber band
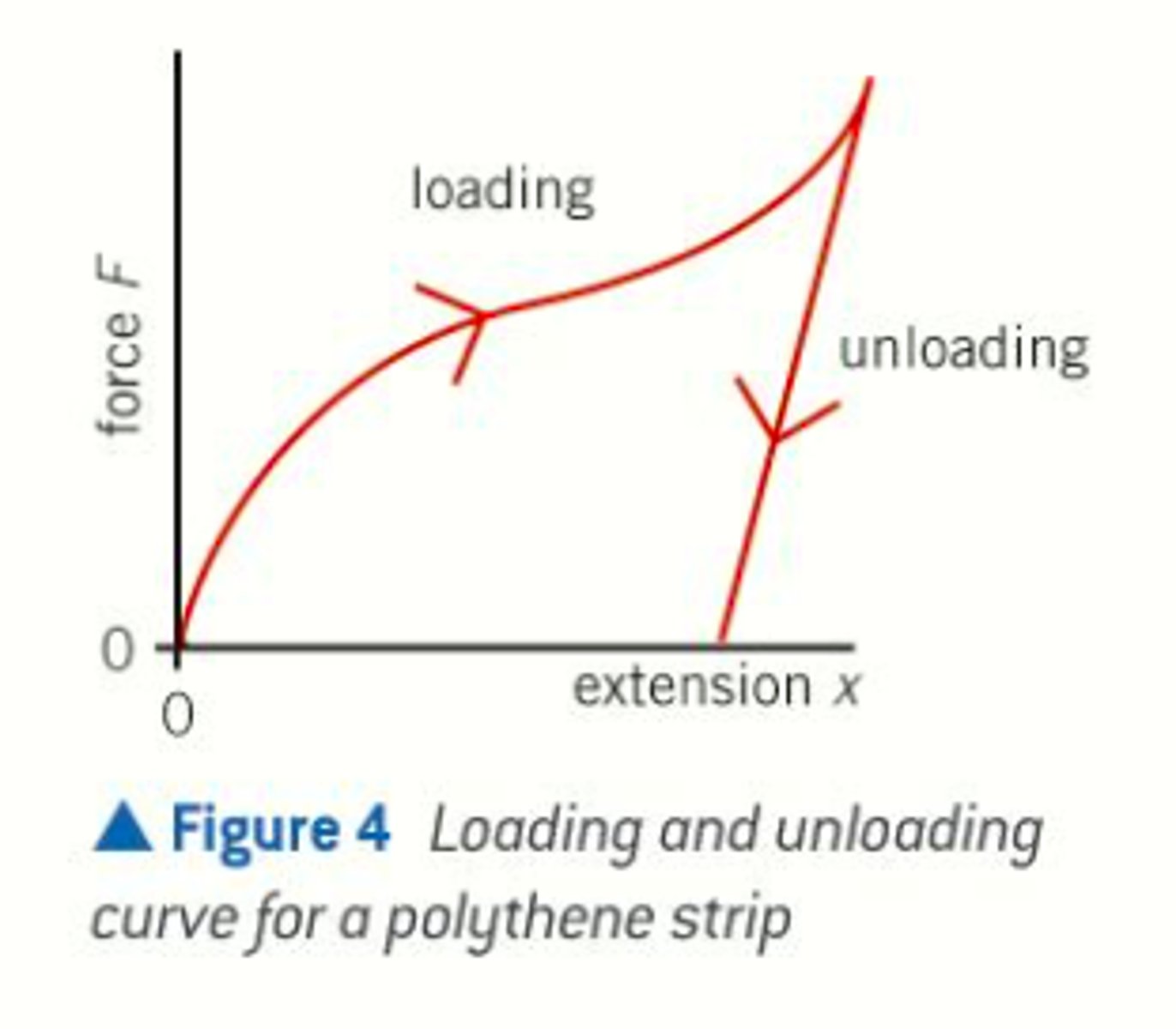
sketch a force extension curve for polythene
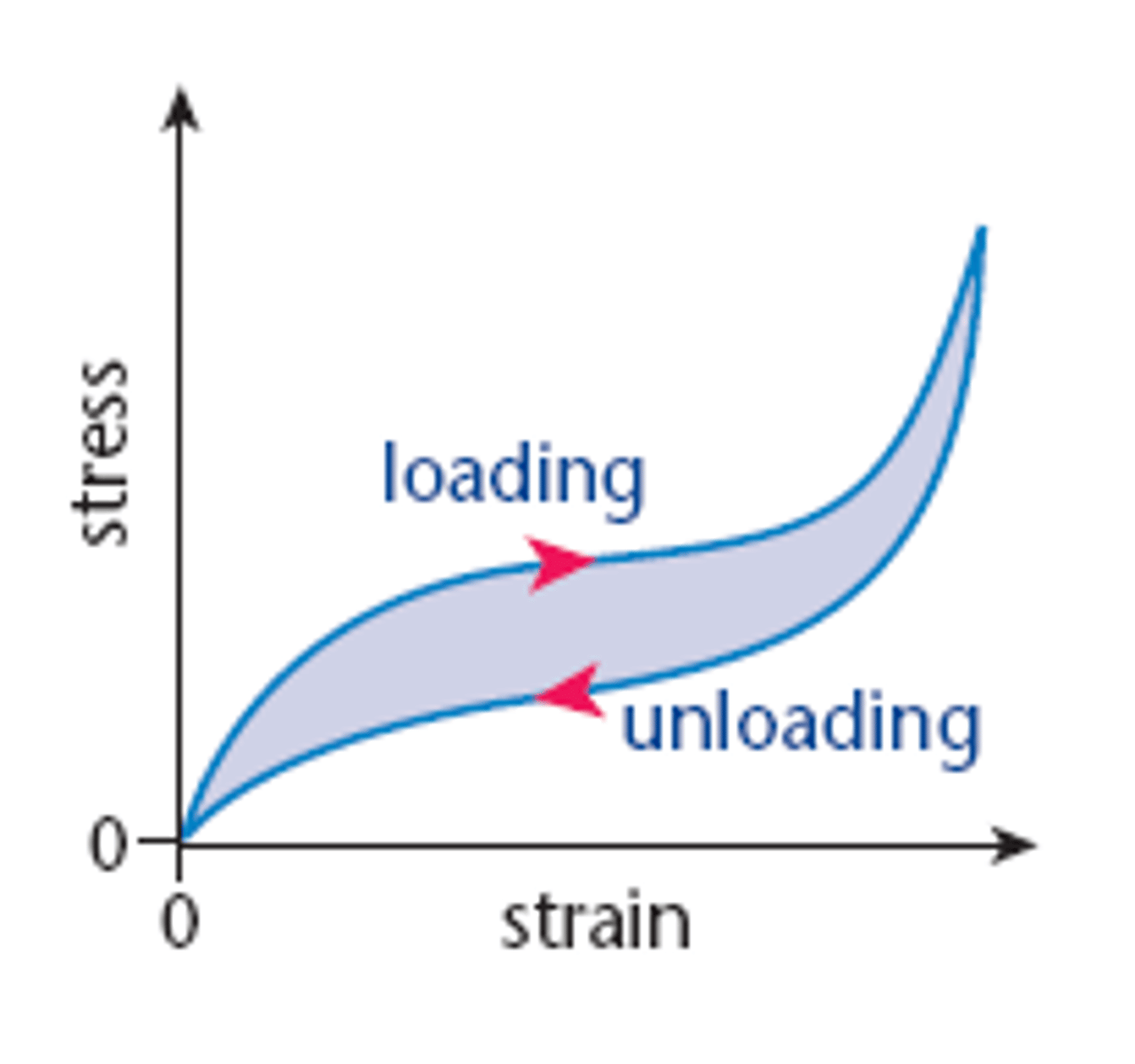
what is a hysteresis loop
The loop formed by the loading and unloading curves
how can you determine the thermal energy lost to the surrounding from a force extension graph
The area under a force extension graph is equal to work done. More work is done when stretching a rubber band than is done when its extension decreases again. Thermal energy is released when the material is loaded then unloaded, represented by the area inside the hysteresis loop
describe the molecular structure of a rubber band
rubber bands do not obey Hooke's law. The rubber band will return to its original length after the force is removed - elastic deformation - but the loading and unloading graphs are both curved and are different.
define tensile stress in words
the force applied per unit cross sectional area of the wire
tensile stress equation
force/cross sectional area
units of tensile stress
units pascals
define tensile strain in words
the fractional change in the original length of the wire
tensile strain equation
Extension / original length
what are the units of tensile strain
no units
what is meant by ultimate tensile strength
this is the maximum stress that a material can withstand when being stretched before it breaks
define young's modulus in words
within the limit of proportionality, stress is directly proportional to strain. The ratio of stress to strain for a particular material is constant and is known as its Young Modulus, E
state the equation for young modulus
tensile stress/ tensile strain
what are the units of young's modulus
Nm^-2 or Pa
(same as stress)
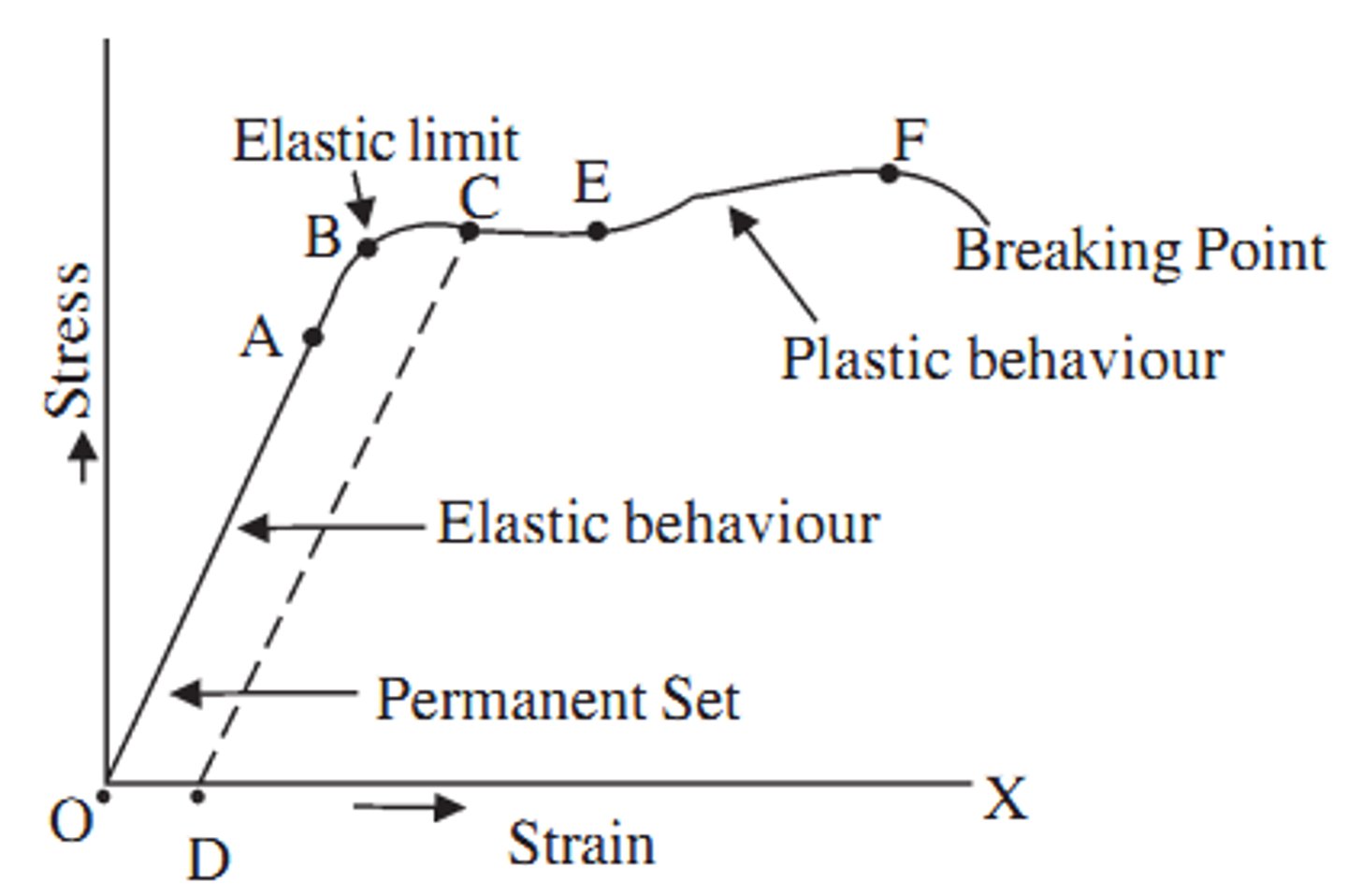
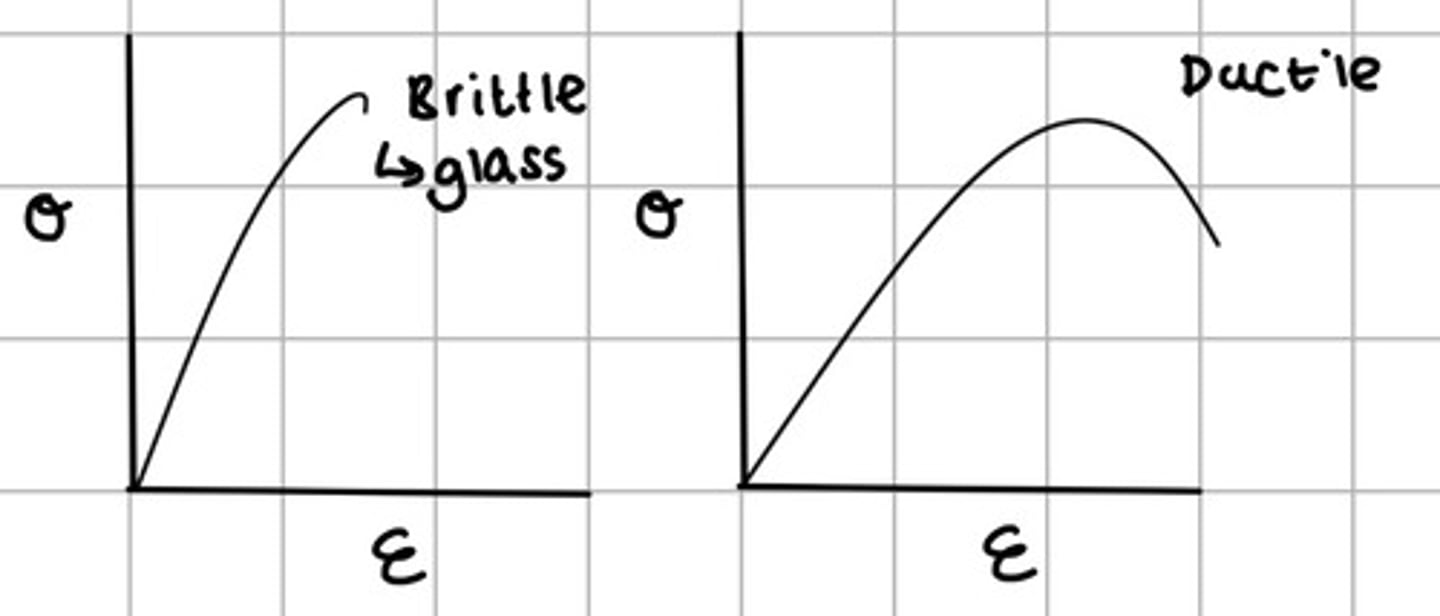
sketch a typical stress strain graph for a ductile material
sketch a stress strain graph for a brittle material
sketch a stress strain graph for rubber
rubber shows elastic behaviour
sketch a stress strain graph for polythene
Polythene shows plastic behaviour
what is a polymeric material
materials that consist of long molecular chains. These behave differently depending on their molecular structure and temperature
what is meant by limit of proportionality
the value of stress or force beyond which stress is no longer proportional to strain
what is a yield point on a stress strain graph
where the material extends rapidly. This part of the curve is typical of mild steel but may be absent from other ductile materials
whats the difference between ultimate tensile strength and breaking strength
the material eventually snaps as its breaking point. The stress value at the point of fracture is known s the breaking strength of the material