Cell cycle
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Mitosis
Undergone by all somatic cells (body cells)
All somatic cells will have a Diploid number of chromosomes
G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase
Stages of interphase
interphase
Longest cycle in cells life
Time when cell actually grows and divide
g1 phase
Starts right after cell division
What happens?
Cell growth
Organelle duplication
Protein synthesis
Checkpoint monitoring
Preparation for DNA replication
Cell differentiation
Repair and recovery
s phase
Where DNA replication occur
Produces another chromatid after this phase
X form of chromosome is seen after this phase
g2 phase
Preparation for cell division
Nuclear envelope encloses the nucleus
The nucleus contains one or more nucleoli
2 centrosomes have formed by duplication of a single centrosome.
Each centrosome contains 2 centrioles.
Chromosomes, duplicated during S phase, cannot be seen individually because they have not yet condensed.
centrosomes
Are regions in animal cells that organize the microtubules of the spindle.
prophase
Chromatin fibers become more tightly coiled.
condensing into discrete chromosomes
observable with a light microscope.
The nucleoli disappear.
To release the chromosomes into the cytoplasm
Mitotic spindle begins to form
Composed of centrosomes and the microtubules that extend from them.
The radial arrays of shorter microtubules that extend from the centrosomes are called asters
The centrosomes move away from each other, propelled partly by the lengthening microtubules between them.
prometaphase
The nuclear envelope fragments.
The microtubules extending from each centrosome can now invade the nuclear area.
chromosomes have become even more condensed.
A kinetochore, a specialized protein structure, has now formed at the centromere of each chromatid
thus, 2 per chromosome
Some of the microtubules attach to the kinetochores, becoming “kinetochore microtubules,” which jerk the chromosomes back and forth.
metaphase
All chromosomes are aligned at the center
centrosomes are now at opposite poles of the cell
chromosomes have all arrived at the metaphase plate
a plane that is equidistant between the spindle’s two poles.
The chromosomes’ centromeres lie at the metaphase plate.
For each chromosome, the kinetochores of the sister chromatids are attached to kinetochore microtubules coming from opposite pole
Anaphase
is the shortest stage of mitosis, often lasting only a few minutes.
begins when the cohesion proteins are cleaved.
This allows the two sister chromatids of each pair to part suddenly.
Each chromatid thus becomes an independent chromosome.
Two new daughter chromosomes begin moving toward opposite ends of the cell as their kinetochore microtubules shorten.
Because these microtubules are attached at the centromere region, the centromeres are pulled ahead of the arms, moving at a rate of about 1 μm/min.
The cell elongates as the nonkinetochore microtubules lengthen.
By the end of this phase: two ends of the cell have equivalent—and complete—collections of chromosomes.
telophase
Two daughter nuclei form in the cell.
Nuclear envelopes arise from the fragments of the parent cell’s nuclear envelope and other portions of the endomembrane system.
Nucleoli reappear.
The chromosomes become less condensed.
Any remaining spindle microtubules are depolymerized.
Mitosis, the division of one nucleus into two genetically identical nuclei, is now complete.
cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm is usually well under way by late telophase, so the two daughter cells appear shortly after the end of mitosis.
In animal cells, this involves the formation of a cleavage furrow, which pinches the cell in two.
checkpoint
when the cell undergoes cell cycle we have what we call the?
If there is a cell that produced an abnormality, but was not caught at the ________, it will go on and on in the cycle, and that cell maybe abnormal.
That cell maybe producing harmful proteins, this is one way cancer develops
meiosis
Sex cells undergo?
prophase 1
Each chromosome pairs with its homologous.
crossing over also called genetic recombination
The DNA molecules of non sister chromatids are broken (by proteins) and are rejoined to each other.
chiasmata
Prophase 1 : Meiosis
Each homologous pair has one or more X-shaped regions called?
this is where the crossovers have occurred.
chromatids
we count chromosomes by the number of?
tetrad
Prophase 1 : Meiosis
the homologous chromosomes pair up with each other and form a unit called?
It is called as this because its units have 4 chromatids
synapsis
Prophase 1 : Meiosis
The process during which the homologous chromosomes pair up with each other is called?
chiasma
Prophase 1 : Meiosis
In synapsis (pair up of homologous chromosomes), they will get a little closer together and they will be called as?
synaptonemal complex
Prophase 1 : Meiosis
The protein complex is called as the?
With the help of this, the 2 chromatids will swap material, and now this is what we call ass crossing over
recombinant
Prophase 1 : Meiosis
Moving forward to meiosis 2, all the chromatids gets separated into different gametes
Everything that is happening in this chromosome is also happening to the others
Now we can see that we get 4 different gametes
2 of them we call as?
because they have a combination of alleles
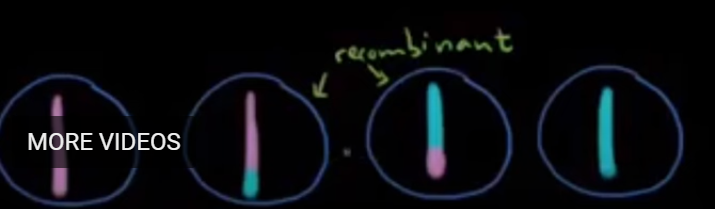
genetic variability
Genetic recombination increases?
metaphase 1
The alignment in here is by homologous pairs, unlike in metaphase in mitosis.
By this time, the spindle fibers are attached to the kinetochores
anaphase 1
the homologous pairs will be separated
but you will not be separating them by chromatids yet.
But rather you will be separating them into separate chromosomes.
telophase 1
Meiosis
same with telophase in mitosis, you form a nuclear envelope.
since you didin’t actually pull the chromatids apart.
you pull them apart to the sides, now after T1;
you will only get ONE HALF
therefore after this phase, the no. of chromosomes in the cells are just HAPLOID
prophase 2
Meiosis
nuclear envelope will dissapear
centromeres and the spindles form
In late prophase 2, chromosomes are still composed of 2 cromatids
metaphase 2
Meiosis
chromosomes will line up in the center like mitosis, in a single fine, no longer in homologous pairs anymore
anaphase 2
Meiosis
breakdown of proteins holding the sister chromatins together
start moving towards opposite poles as individual chromosomes
telophase 2 and cytokinesis
Meiosis
4 new nuclei are made and 4 new haploid cells form
diploid
both egg and sperm cells come form special mother cells that are ______ - meaning they have two sets of chromosomes
oogoniium
Female Side (Egg Cell Development)
The mother cell of the egg
still diploid, not ready to divide yet
primary oocyte
Female Side (Egg Cell Development)
Grows form the oogonium
gets big because it needs to give most of the cytoplasm to the egg
now ready for meiosis 1
meiosis 1
Female Side (Egg Cell Development)
Divides into
Secondary oocyte (haploid) - gets most of the cytoplasm
First polar body (haploid)- a small cell that wont be used
meiosis 2
Female Side (Egg Cell Development)
Secondary oocyte divides into:
ootid (haploid) - this becomes the ovum (egg)
second polar body (haplod)- again wont be used
ovum
Female Side (Egg Cell Development)
ootid turn into? - the final egg cell
spermatogonium
Male side (Sperm Development)
The mother cell of sperm
Each one can produce 4 sperm
diploid
Primary spermatocyte
Male side (Sperm Development)
Grows from spermatogonium
Gets ready for meiosis 1
diploid
meiosis 1
Male side (Sperm Development)
Divides into 2 secondary spermatocytes
haploid
Male side (Sperm Development)
Each secondary spermatocyte divides into 2 spermatids
haploid
Totaling = 4 spermatids
spermatozoa
Male side (Sperm Development)
Spermatids become ?