Microeconomics Definitions
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Quantity Demanded
The amount of good/service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price in a given period of time
Law of Demand
there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, ceteris paribus
Market Demand
the combination of all the individual demand for a good/service
Quantity Supplied
The amount of a good/service that producers are willing and able to supply at a given price at a given time period
Law of Supply
price and quantity supplied have a positive relationship, ceteris paribus
Producer subsidy
an amount of money paid to the firm by the government for each unit produced
Joint Supply
The output of one good or service increases the output of another, occurs when the supply of 2 goods stem from the same source (beef and leather)
Market
a place that brings producers and consumers together to exchange goods and services
consumer sovereignty
the economic power exerted by the consumers in a market
Equilibrium
in a market occurs when demand = supply
Disequilibrium
in the market occurs whenever there is excess demand/ supply in a market, demand =/= supply
The Price Mechanism
the interaction of demand and supply in a free market. this interaction determines prices which are means by which scarce resources are allocated between competing goods and service.
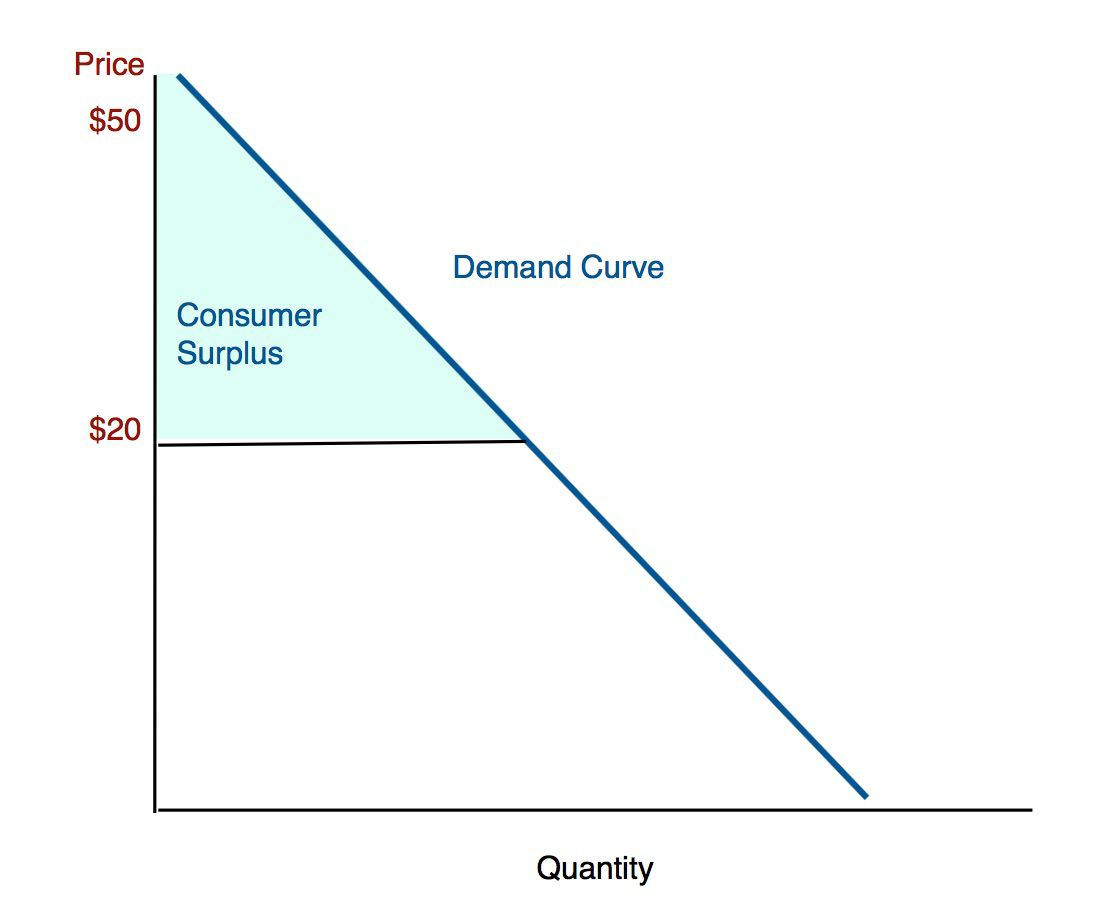
Consumer surplus
the difference between the amount the consumer is willing to pay for a product and the price they paid (between the demand curve and price to equilibrium line)
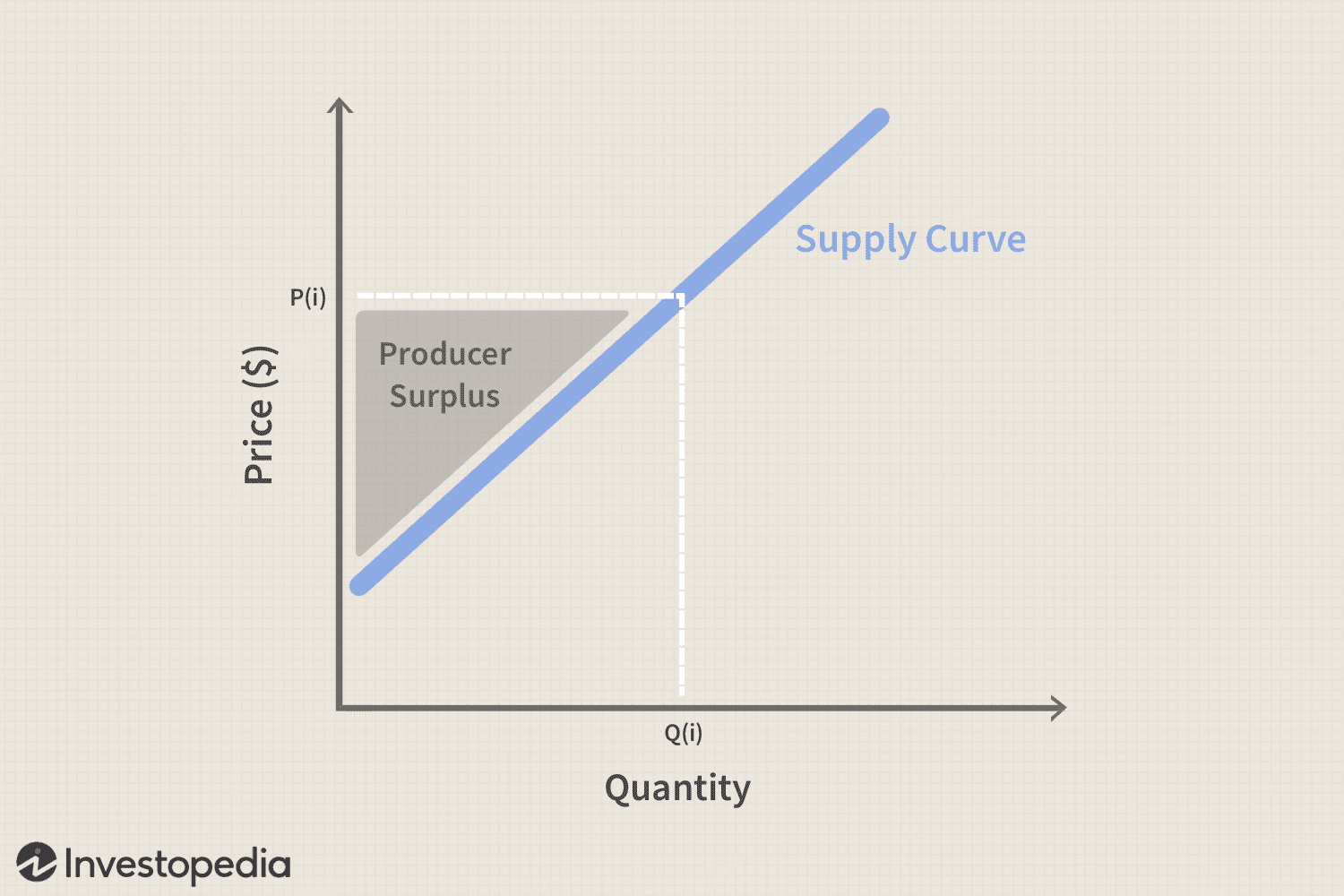
producer surplus
the difference between the amount the producer is willing to sell a product for and the price they actually sell it at (between the supply cure and the price to equilibrium line)
allocative efficiency
Occurs at an output level where marginal utility (marginal benefit MB) is equal to marginal cost MC; Resources are allocated so consumers and producers receive maximum possible benefit, no excess demand or supply. Social optimum when resources are distributed in the most effective and beneficial way.
Productive efficiency
occurs at an output level where average costs are minimized, there is no wastage of scarce resources and a high level factor productivity
Price Elasticity of Demand
A measure of how responsive the change in quantity demanded is a change in price
Total Revenue Rule
In order to maximize revenue firms should increase the price of products that are price inelastic and decrease the price of products that are price elastic
Price discrimination
charging different customers different prices for the same product due to different PEDs
Merit goods
goods/service that are beneficial to society but free market does not produce enough of.
Demerit Goods
goods/service that detrimental to society and free market produces too much of it
Income elasticity of demand
A measure of how responsive the change in quantity demanded is to a change in income
Price Elasticity of Supply
A measure of how responsive the change in quantity demanded is to a change in price
Privatization
the act of transferring an asset from public to private ownership and control
expropriation
taking possession of private property
Progressive tax system
a system that applies higher levels of income tax to higher levels of income
welfare benefits
money paid by the government to people who are ill, poor, or unemployed
Indirect Tax
tax paid on the consumption of goods/ services
specific tax
a fixed tax per unit of output
Ad Valorem Tax
a tax that is a percentage of the purchase price
Subsidies
a producer subsidy is per unit amount of money given to a firm by the government to increase production and or increase the provision of a merit good
price ceilling
a maximum price of a good/service set by the government below the existing free market equilibrium price and sellers cannot legally sell the good/service at a higher price
Price floor
a minimum price of a good/service set by the government above the existing free market equilibrium price and sellers cannot legally sell the good/service for less
Market Failure
When there is a lack of allocative efficiency from the POV of society.
Externalities
external impacts on a third party not involved in the economic transaction between the producer and consumer
Marginal Private Benefit (MPB)
The additional benefit received from the consumption or production (output) of one additional unit of output
Marginal Social Benefit (MSB)
The benefit to society received from the consumption or production (output) of one additional unit of output. It is the sum of the private benefits plus the external benefits
Marginal Private Cost
The additional cost incurred through the consumption or production (output) of one additional unit of output
Marginal Social Cost
The cost to society incurred through the consumption or production of one additional unit of output. It is the sum of the private costs plus the external costs
Socially Optimum Output
The socially optimum output occurs at the level of output where the marginal social benefit (MSB) = marginal social cost (MSC)
Entrepreneurship
the ability to innovate by developing new methods, organizes the 3 other factors of production
Capital
man made factor of production, something that was itself produced eg. machinery; Resources that can produce a future stream of benefits
Labour
human input, the physical and mental effort contributed by people to the production of goods and services
Free good
any good that is not scarce and therefor has no opportunity cost
economic good
a good that is scarce and therefor has an opportunity cost of its consumption
Free rider problem
some goods are non-rivalrous and non-excludable so if provided anyone can use it without paying so firms do not profit from providing them
Common Pool Resources
are those that are non-excludable but are rivalrous in consumption
Private Goods
are goods that firms are able to provide to generate profits, because they are excludable and rivalrous
Public Goods
are goods that are beneficial to society but firms will not provide because of non-excludability and non-rivalry
Complementary goods
Goods or services that are jointly demanded.
Substitute Goods
Goods or services that compete against each other and are hence in competitive demand.
Competitive Supply
The output of one good or service prevents the output of another.
Signalling Function
Provides information to consumers and producers on where resources should be allocated.
Incentive Function
Provides motivation for consumers and producers to change their behavior to maximize profits.
Rationing Function
Ensures scarce goods and services deter consumers by raising prices.
Inferior Goods
Goods with a negative income elasticity (as incomes increase, less will be demanded)
Normal Goods
Goods with an income elasticity between 0 and 1 (as incomes increase, more will be demanded, but less than the proportionate change).
Luxury Goods
Goods with an income elasticity of more than 1 (as incomes increase, more will be demanded, and more than the proportionate change).
Government Failure
Arises when government intervention causes more social costs than benefits.
Carbon Tax
A tax on greenhouse gas emissions that aim to reduce pollution
Tradable Permits
Government-regulated tradable contracts that allow for pollution. They can be traded amongst firms to result in a more socially optimum level.