(3) Theories of Personality (manual)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
personality
unique way in which each individual thinks, acts, and feels throughout life
character
value judgments made about a person’s morals or ethical behavior
temperament
the biologically innate and enduring characteristics with which each person is born (irritability or adaptability)
Psychodynamic Perspectives: Sigmund Freud
raised in Europe (Victorian Age) = Sexual Repression
Freudian
there were layers of consciousness in the mind
Freudian: The mind was divided into three part
preconscious
conscious
unconscious
preconscious mind
memories, information, and events of which one can easily become aware
conscious mind
one’s current awareness
unconscious mind

Divisions of the Personality
Id, Ego, Superego
Id
completely unconscious, pleasure-seeking, amoral part of the personality that exists at birth
contains all the basic biological drives
pleasure principle
“if it feels good, do it”
Ego
“I”
part of the personality that develops out of need to deal with reality (conscious, rational, logical)
Superego
“over the self”
moral center of personality (conscience)
How do the three parts of the personality work together?
id: makes demands
superego: puts restrictions on how to meet demands
ego: come up with plan that quiets id and satisfies superego
defmech: denial
refusal to recognize threatening situation
defmech: repression
pushing threatening situations out of conscious memory
defmech: rationalization
making up acceptable excuses for unacceptable behavior
defmech: projection
placing one’s own unacceptable thoughts onto others
defmech: reaction formation
forming an emotional reaction opposite from actual thought
defmech: displacement
expressing feeling to a substitute target instead of the real target
defmech: regression
childlike pattern
defmech: identification
trying to become like someone else
defmech: compensation
make up for areas lacking by being superior in other areas
defmech: sublimation
turn socially acceptable to socially acceptable
stages of personality development
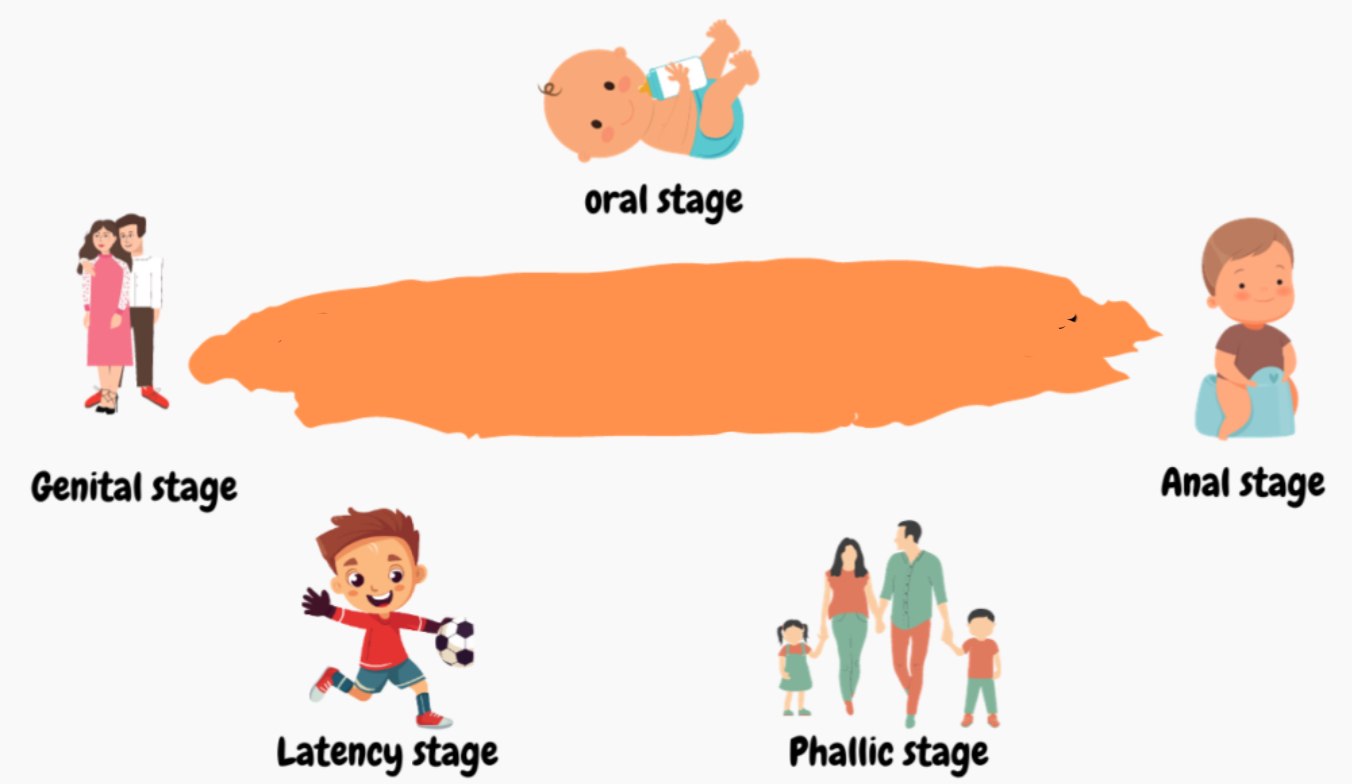
oral stage
first 18 months
erogenous zone: mouth
conflict: weaning
overeating
anal stage
18-36 mos
erogenous zone: anus
conflict: toilet training
anal expulsive: destructive and hostile
anal retentive: stingy, stubborn, excessively neat
phallic
3-6 yrs
erogenous zone: genitals
conflict: awakening sexual feelings
Oedipus/Electra Complex: child develops a sexual attraction to the opposite-sex parent and jealousy of the same-sex parent
latency
6yrs to puberty
children grow and develop intellectually, physically, and socially but not sexually
genital
puberty onwards
represented the final process in Freud’s personality theory, as well as the entry into adult social and sexual behavior
neo-freudian
focus on the impact of the social environment
Carl Justav Jung
disagreed with Freud about the nature of the unconscious mind
Archetypes
anima/animus
shadow
persona
anima/animus
feminine man, masculine woman
shadow
dark side of personality “devil”
persona
personality shown to the world
Alfred Adler
people all develop feelings of inferiority when comparing themselves to the more powerful, superior adults in their world
firstborn children
overachievers
feel inferior once those younger siblings get all the attention
middle children
feel superior over the dethroned older child while dominating younger siblings
younger children
feel inferior because they are not allowed the freedom and responsibility of the older children
Karen Honey
“womb envy” — men felt the need to compensate for their lack of child-bearing ability by striving for success in other areas
Erik Erikson
emphasis on the social relationships that are important at every stage of life
Personality (behaviorist lens)
nothing more than a set of learned responses or habits
social cognitive learning theorists
emphasize on the importance of both the influences of other people’s behavior and of a person’s own expectancies on learning
social cognitive view
learning theory that includes cognitive processes such as anticipating, judging, memory, and imitation of models
Reciprocal Determinism
Environment
Behavior
Personal/Cognitive
Self-efficacy
a person’s expectancy of how effective his or her efforts to accomplish a goal will be in any particular circumstance (not the same concept as self-esteem, which is the positive values a person places on his or her sense of worth)
high self-efficacy
more persistent, expect to succeed
low self-efficacy
tend to avoid challenges, expect to fail
Julian Rotter
concept of locus of control, the tendency for people to assume that they either have control or do not have control over events and consequences in their lives
Internal in locus of control
people who assume that their own actions and decisions directly affect the consequences they experience
External in locus of control
people who assume that their lives are more controlled by powerful others, luck, or fate
2 factors influencing a person’s decision to act in a certain way
expectancy
reinforcement value
expectancy
person’s subjective feeling that a particular behavior will lead to a reinforcing consequence
reinforcement value
individual’s preference for a particular reinforcer over all other possible reinforcing consequences