Gross Anatomy - Urinary
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
b. Left popliteal vein
Which of the following is NOT a direct tributary of pin no. 1?
a. Left gonadal vein
b. Left popliteal vein
c. Left suprarenal vein
d. None of the above
b. L1-L2
Pin no. 2 is a direct lateral branch of the abdominal aorta at which vertebral level?
a. L2-L3
b. L1-L2
c. T12-L1
d. T11-T12
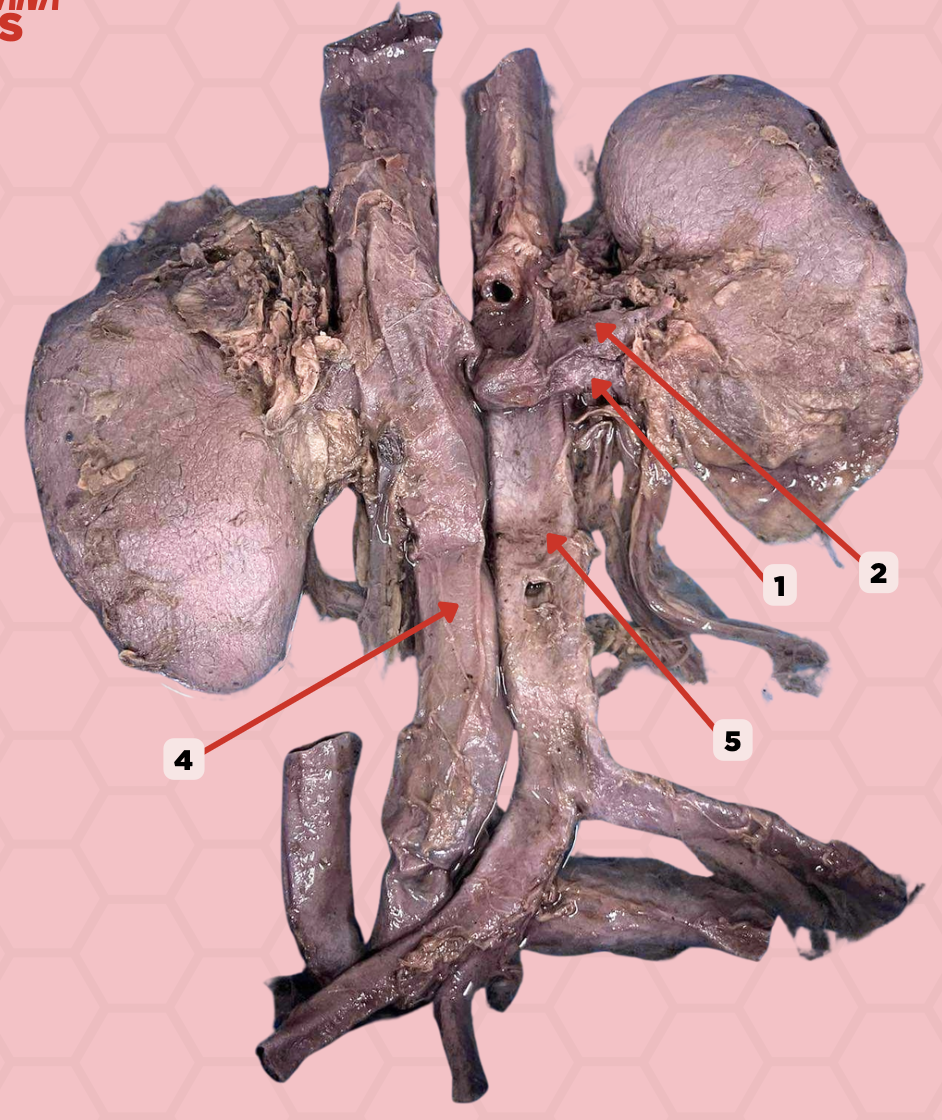
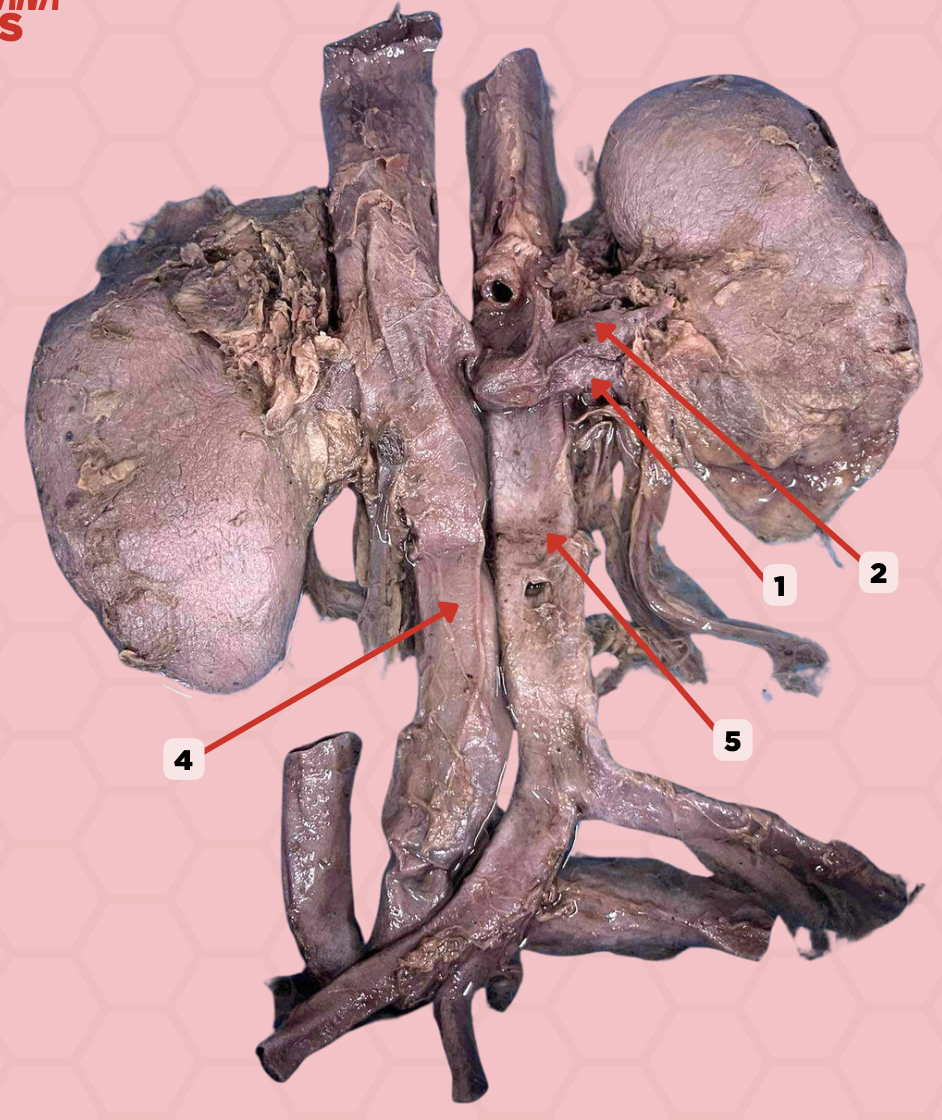
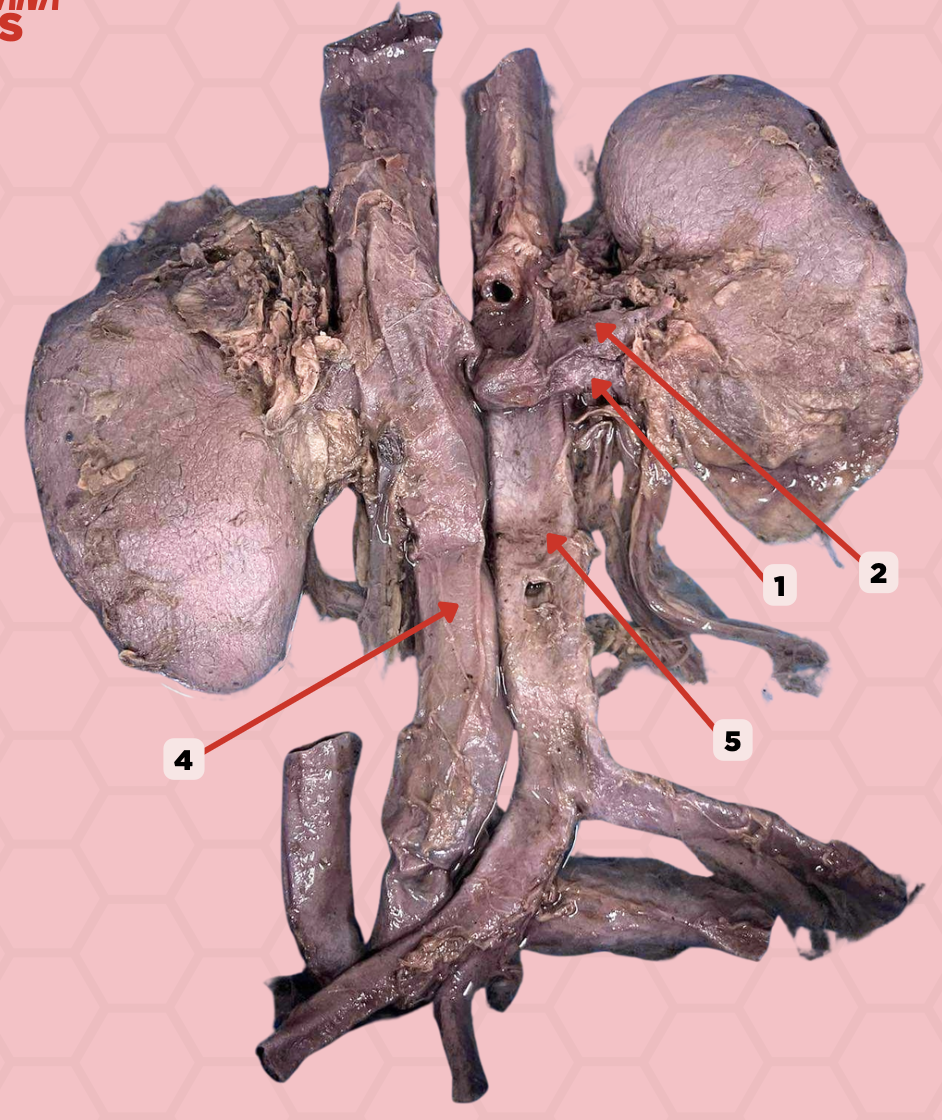
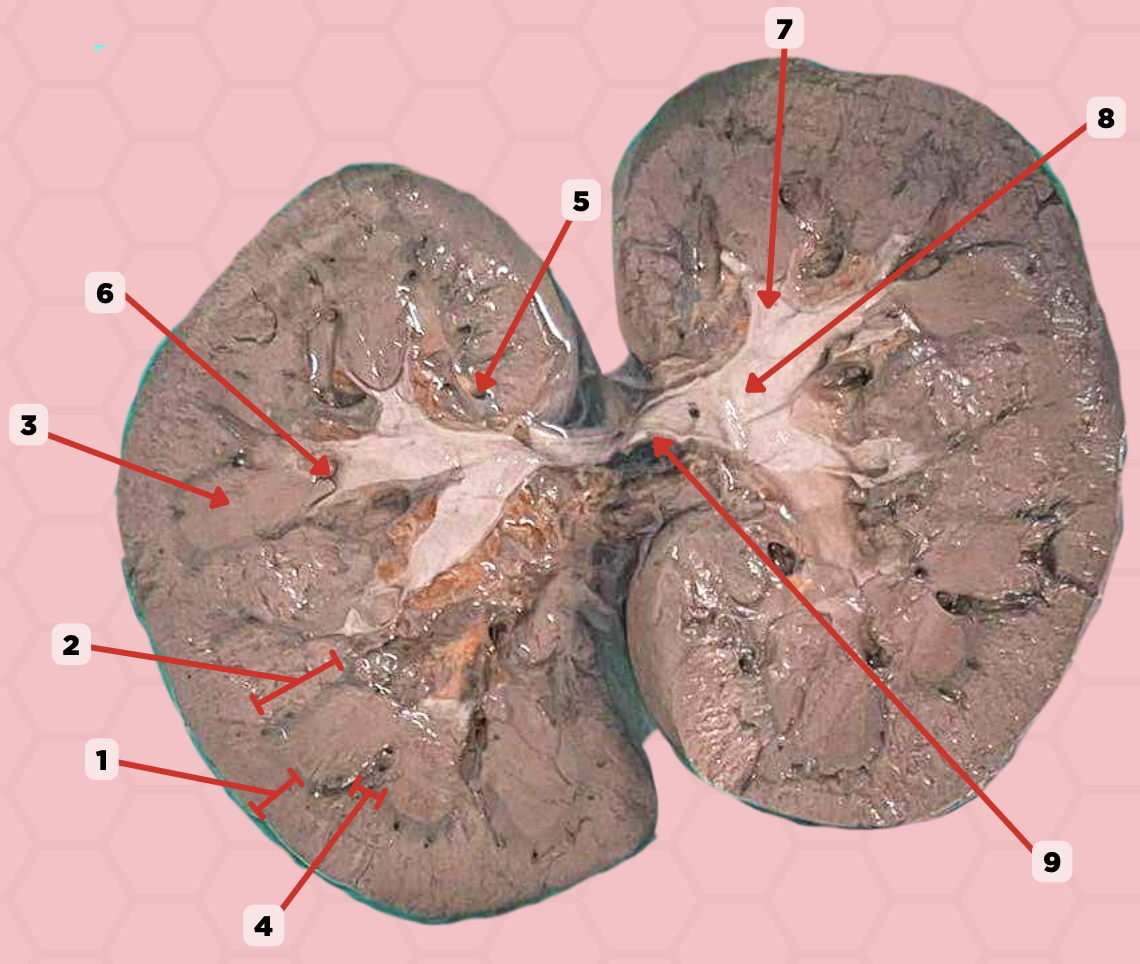
Renal Vein
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
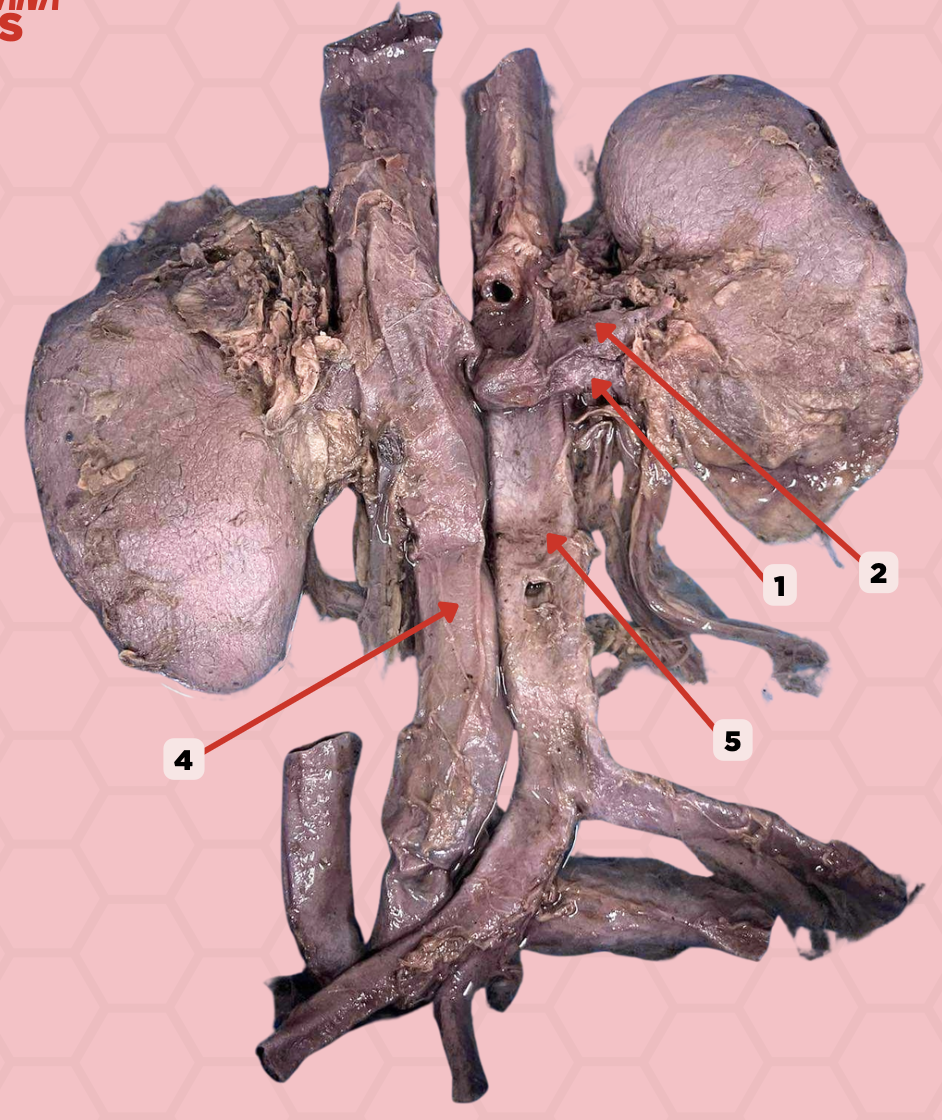
Renal Artery
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
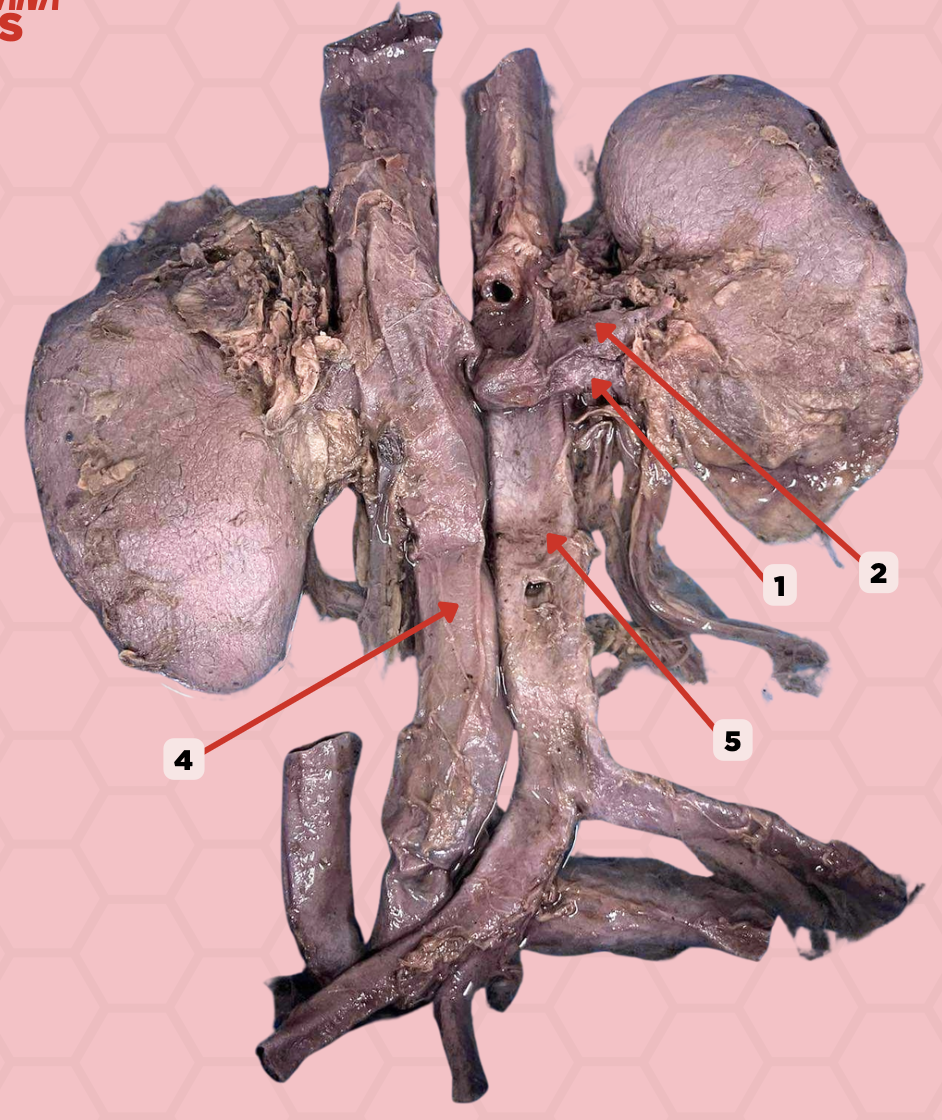
Inferior Vena Cava
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
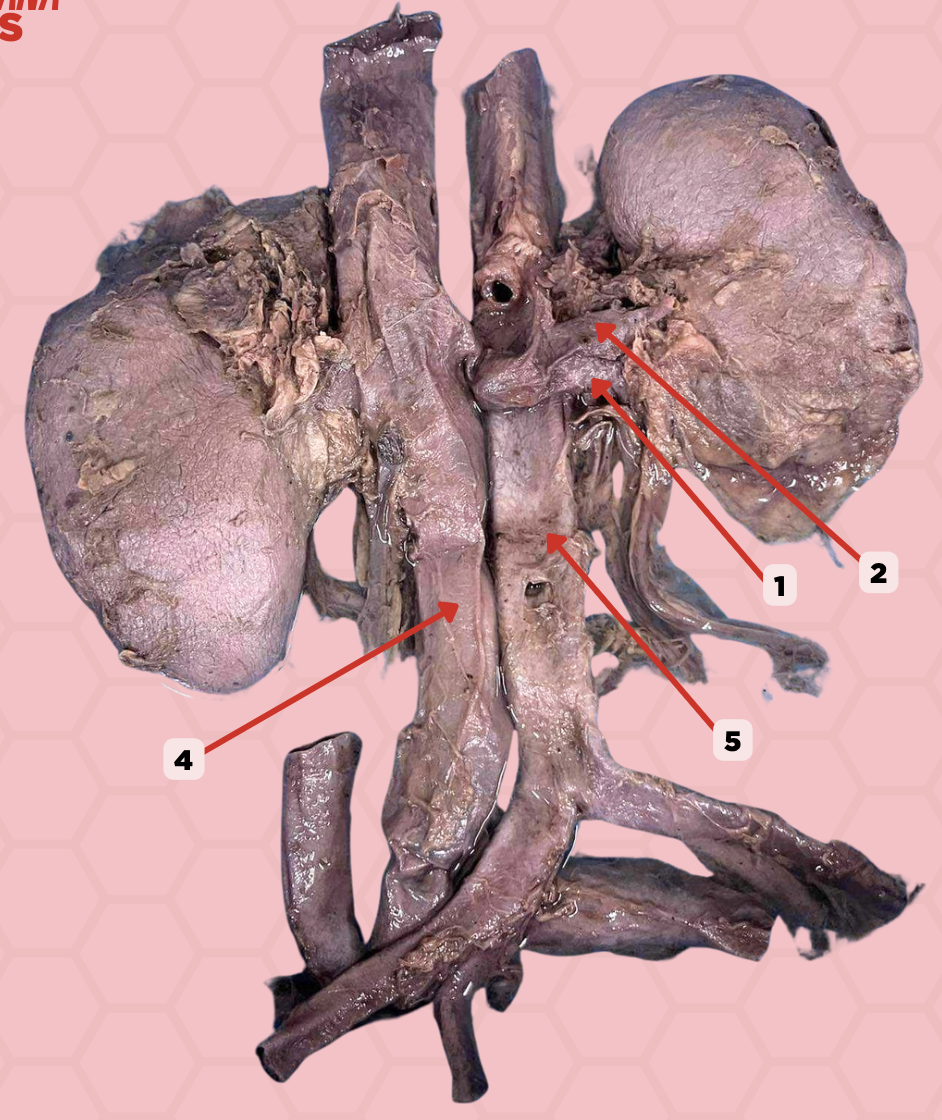
Abdominal Aorta
Identify the structure labeled as 5.
c. five
How many branches will pin no. 2 have as it approaches the hilum of the kidney?
a. nine
b. seven
c. five
d. three
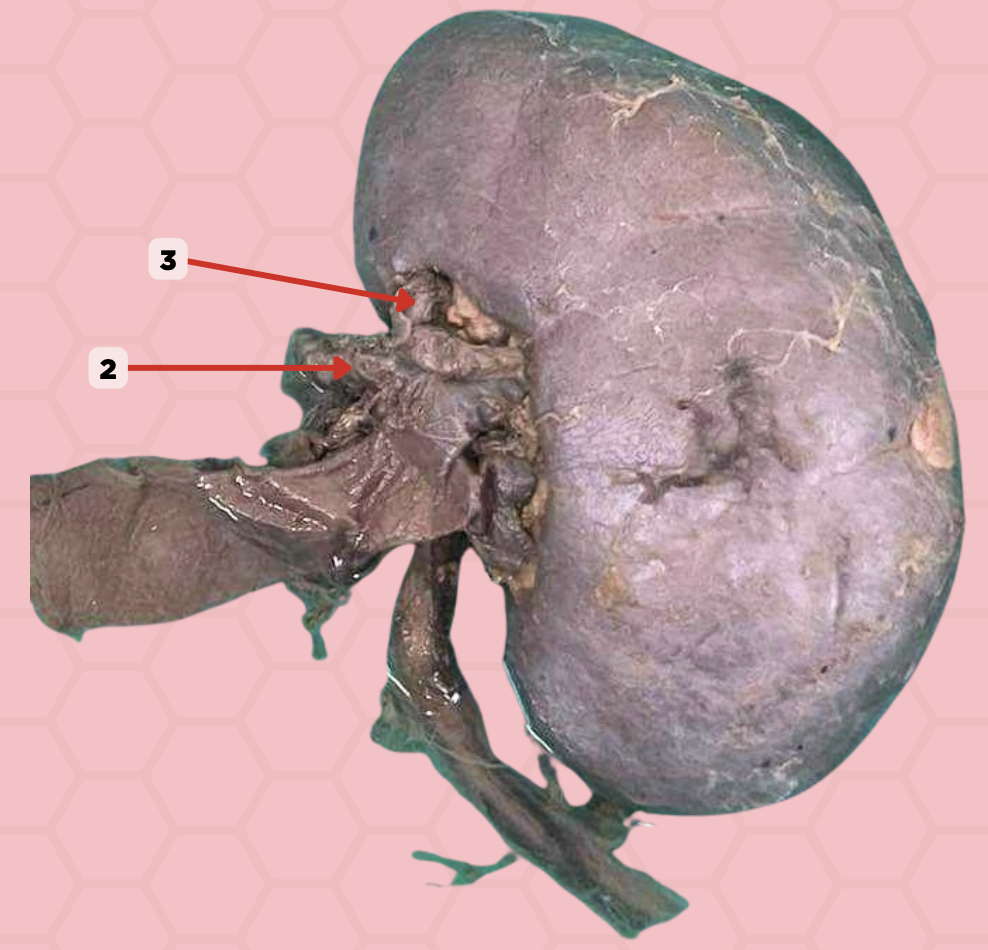
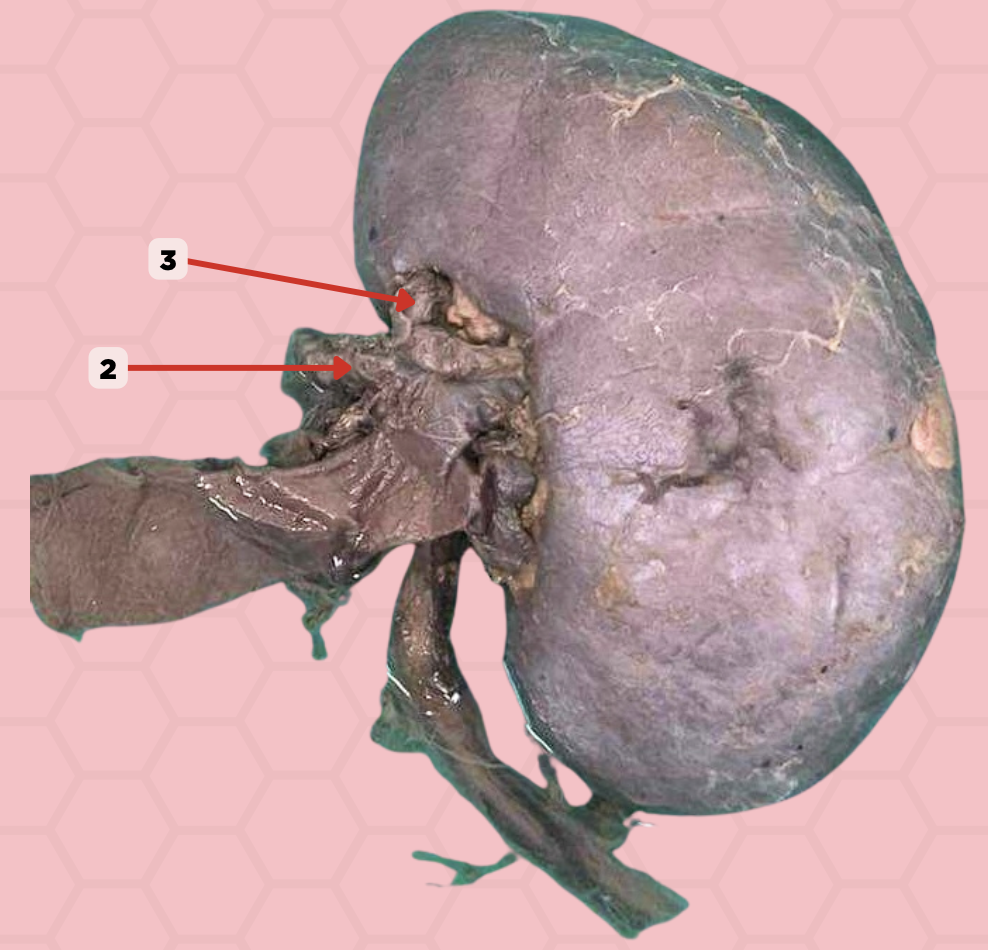
Hepatic Artery
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
Segmental Artery
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
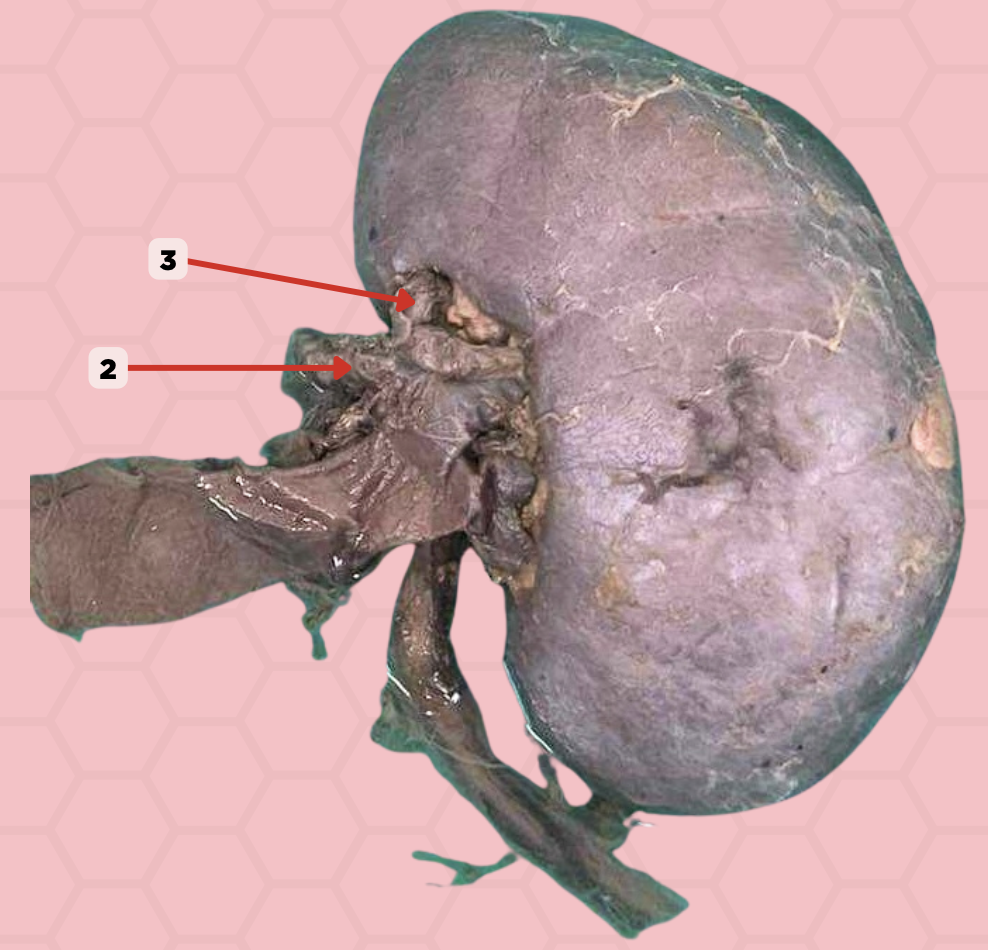
a. Interlobar arteries
What are the direct branches of pin no. 3?
a. Interlobar arteries
b. Interlobular arteries
c. Efferent arterioles
d. Afferent arterioles
Segmental Artery
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
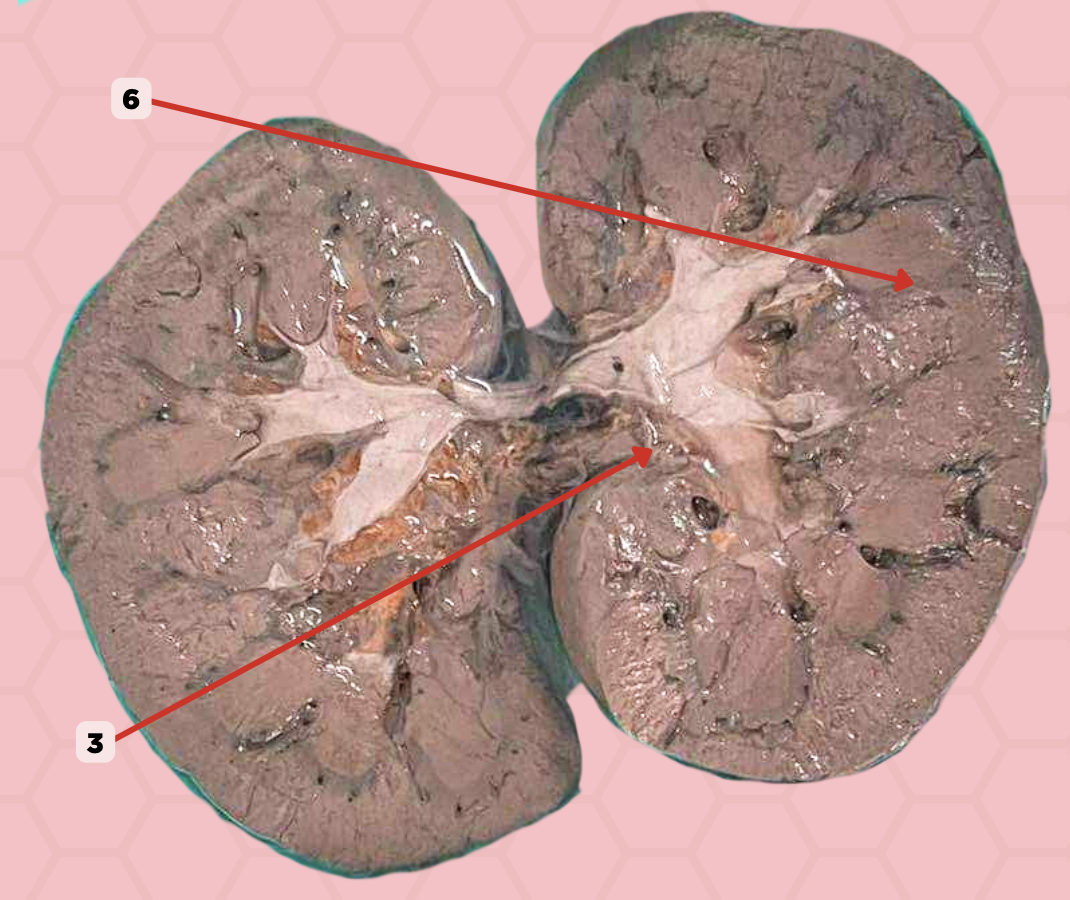
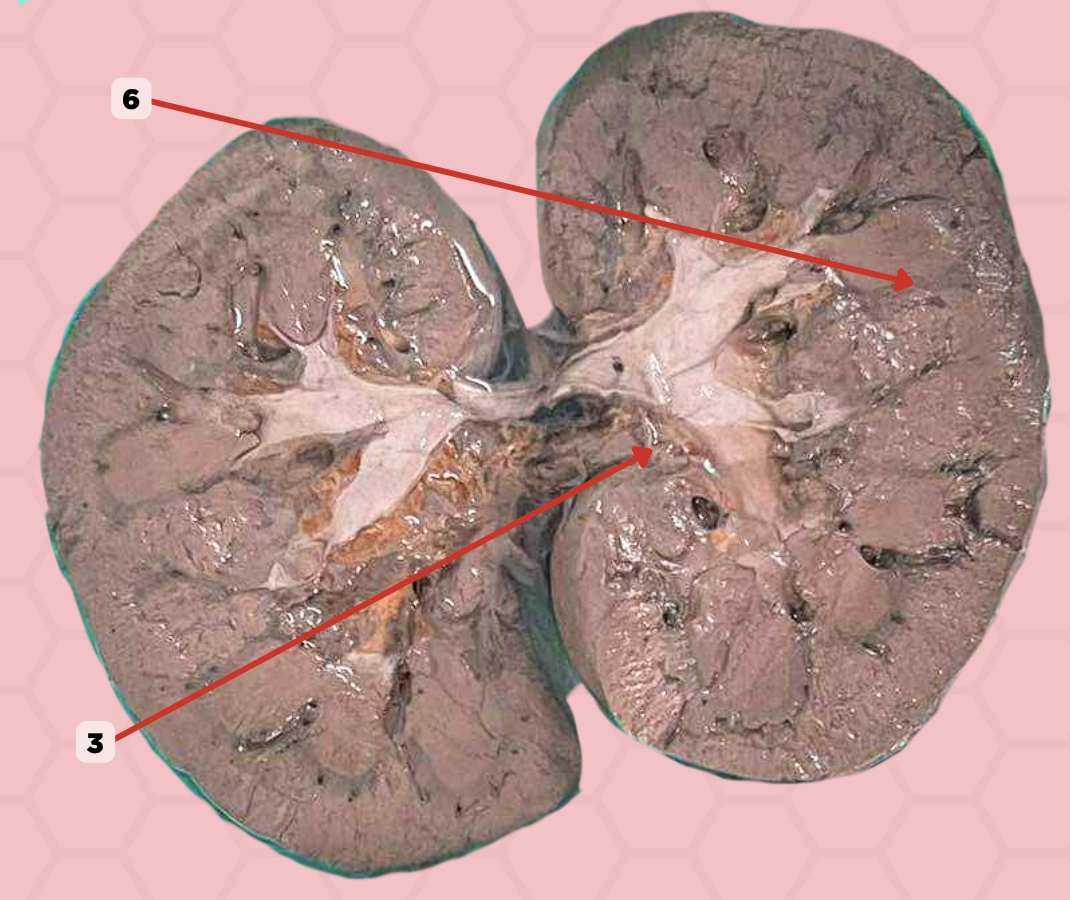
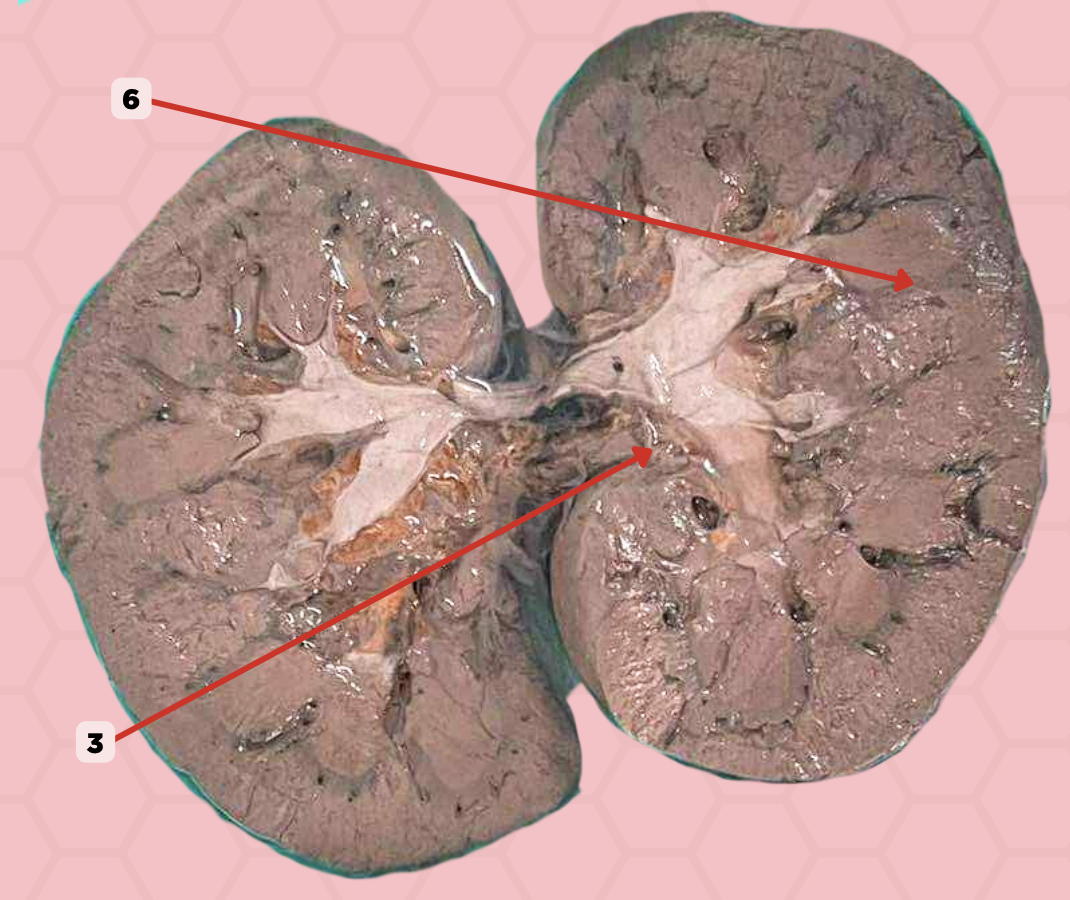
Interlobar Artery & Vein
Identify the structure labeled as 6.
Widened Mediastinum
When Mediastinum > 6-8 cm. Caused by: Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm/Dissection of Ascending and Proximal Descending Aorta, Traumatic Aortic Rupture
Tumors in the Mediastinum
Superior Mediastinum. Large veins on the right side. Potential dead space on the left side (where tumors tend to project)
Trachea
25 cm from the incisor teeth and 30 cm from the nostrils. Functional importance: Cough Reflex. Pathological importance: Useful Landmark
Neck Infections
Found in the anterior mediastinum. Very narrow space continuous via the superior mediastinum with the pretracheal space of the neck
Portal Hypertension
Cirrhosis of the Liver → Dilated and Open Channels of Portocaval Anastomosis → Creates Esophageal Varices → Hematemesis
Hematemesis
Vomiting of Blood
Acid-Peptid Esophagitis
Esophageal Pain carried by sympathetic fiber to T4 and T5
Esophageal Constrictions
Sites for: Swallowed foreign bodies, strictures, perdilection for carcinoma, difficult to pass an esophagoscopy/gastric tube
Transverse Pericardial Sinus
Surgeons put thumb → Aorta and fingers → Sinus. Ligatures can pass into the transverse sinus to control hemorrhage or to secure cannulas placed in the great vessels
Aneurysm (Adjacent Lung Consolidation)
Displacement or loss of definition of Aortic Knuckle. Left lateral edge of the aorta. Arches backwards over left main bronchus and pulmonary vessels
Enlargement of Lymph Nodes
Can be seen in x-ray in the aorta-pulmonary window. Normally points towards aorto-pulmonary window between the Aortic Knuckle and the Left Pulmonary Artery
Right Paratracheal Stripe
If thickened > 3 mm, may represent pathology. Thin white stripe. Normally found from the level of the clavicles to the azygos vein at the right edge of the trachea
Cardiothoracic Ratio (CTR)
Cardiac size vs Thoracic width (%). Cardiac size - lateral width of heart. Thoracic width - lateral width of ribcage
Ventricle Enlargement
When CTR is >50%. Right ventricle - big main pulmonary artery. Left ventricle - big aorta. Case: Normal Heart when CTR >50%. Pregnant women, Obesity, and Ascites
Ascites
Accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity
Jugular venous distention, Distant heart sounds, Hypotension
What are the beck’s triad?
Pericardial Tamponade
Most common signs are dyspnea and tachypnea. Rapid pericardial effusion. Severe respiratory distress: Agitation, Tachycardia, Hypotension. Patients at risk: Metastatic cancer, History of mediastinal rotation, End-stage renal disease, Tuberculosis, Traumatic injury, With recent cardiac surgery
Pericardiocentesis
Emergency procedure for pericardial tamponade. Aspirate fluids that restore normal cardiac function and peripheral perfusion
a. Suprarenal gland
What structure does the pin no. 5 accommodate?
a. Suprarenal gland
b. Kidney
c. Lung
d. Diaphragm
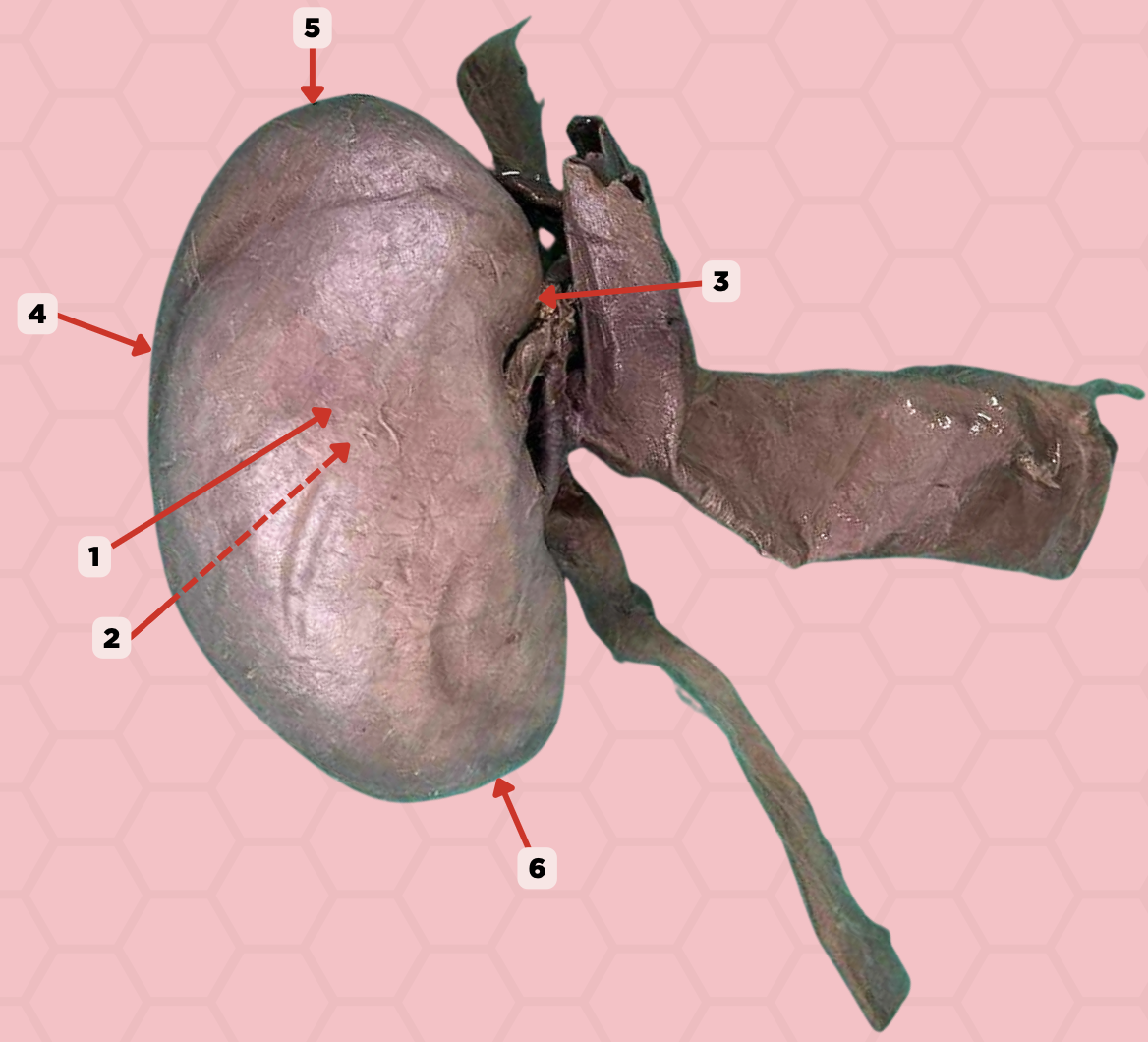
a. Iliac crest
What is the palpable surface landmark that is a finger breadth superior to pin no. 6?
a. Iliac crest
b. 12th rib
c. Sternum
d. L1 vertebra
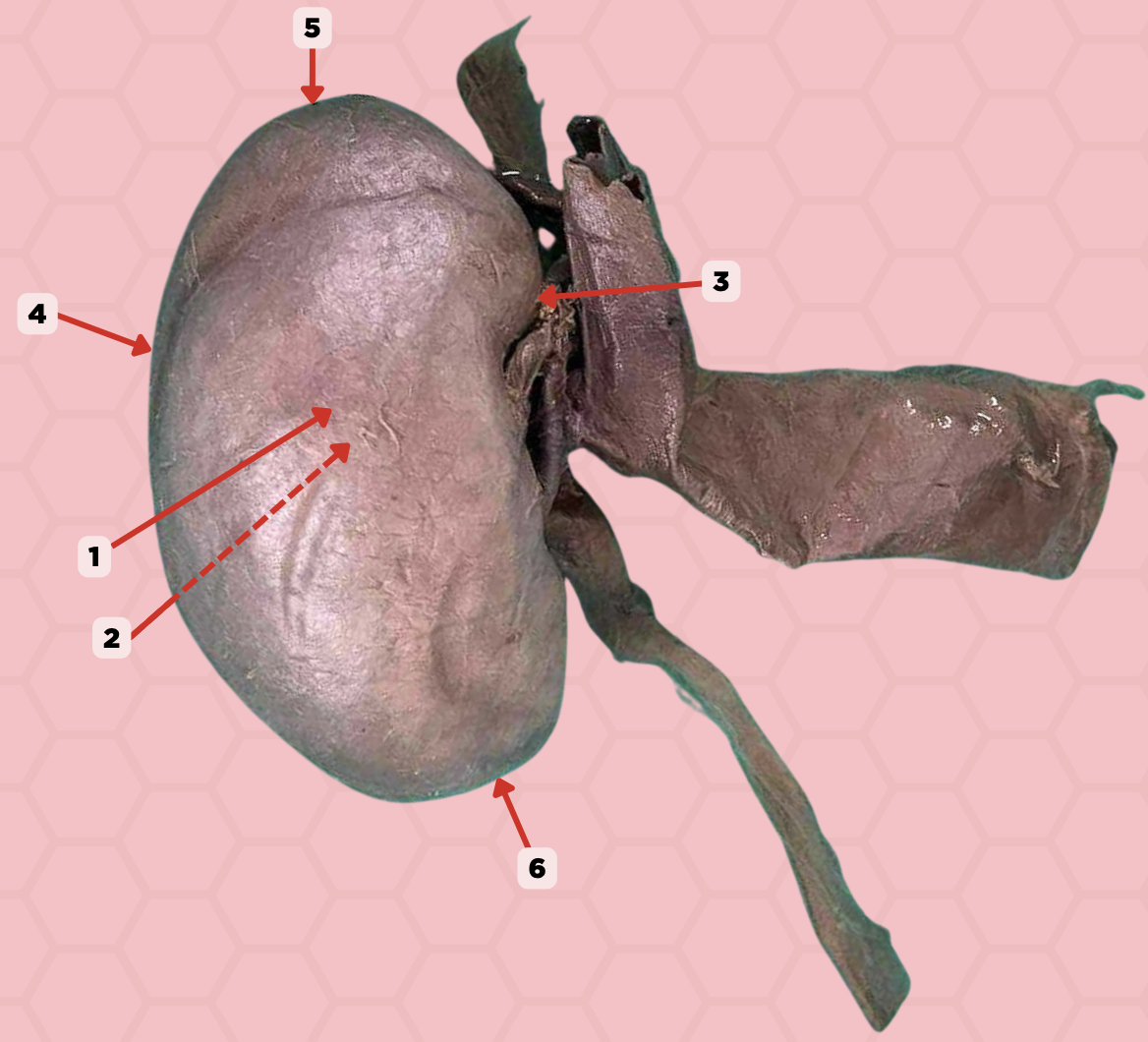
Anterior Surface
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
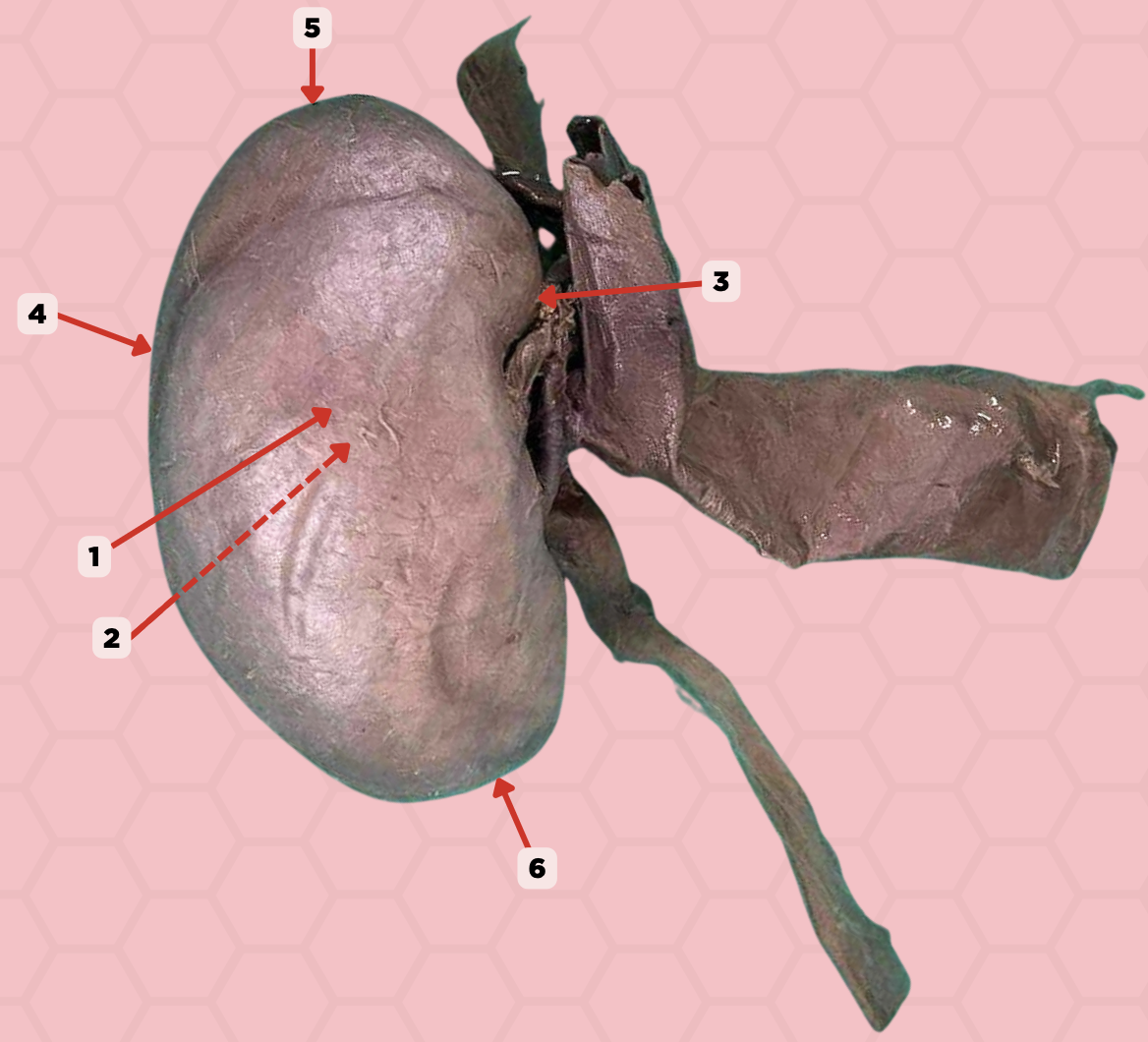
Posterior Surface
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
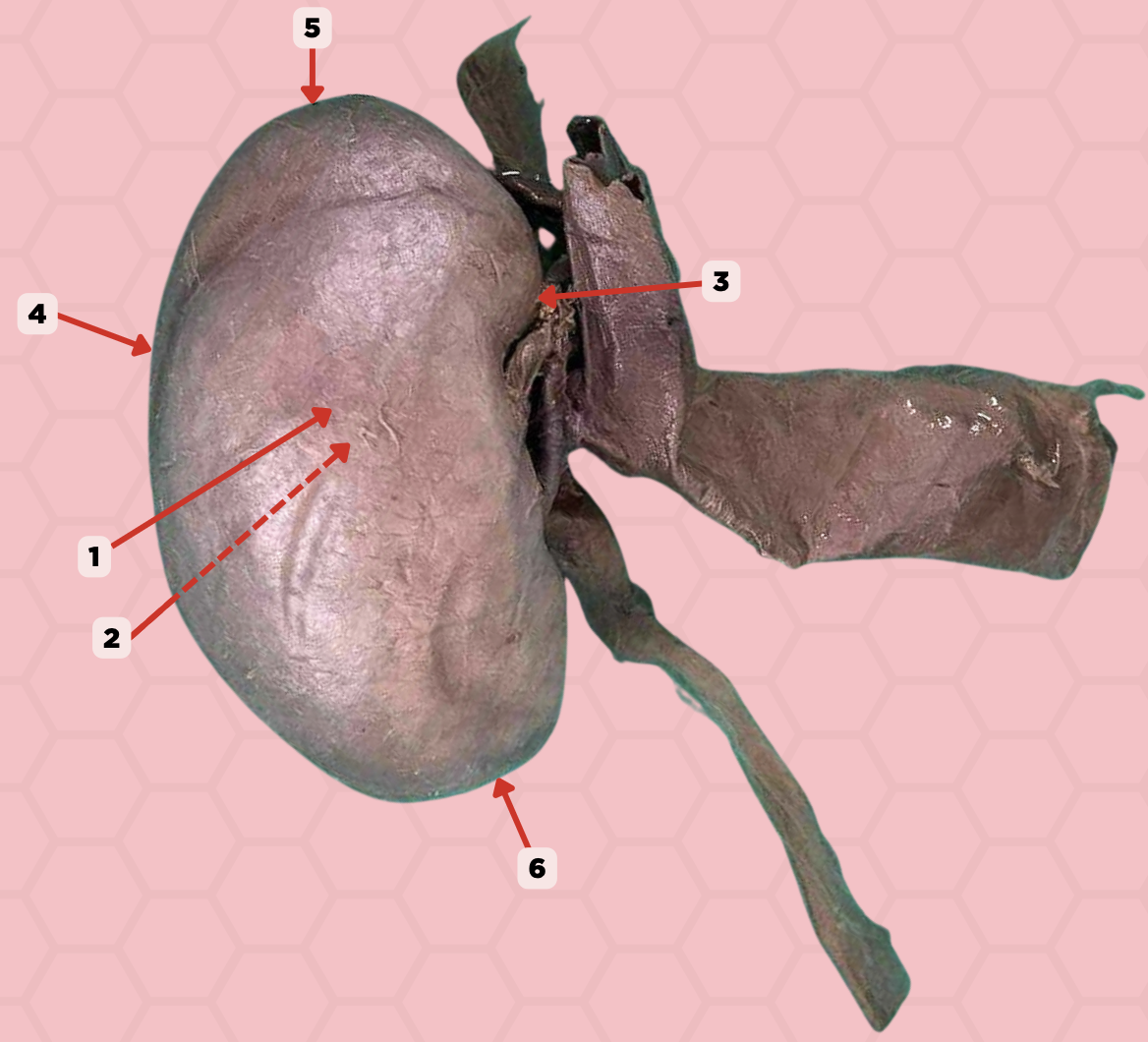
Medial Margin
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
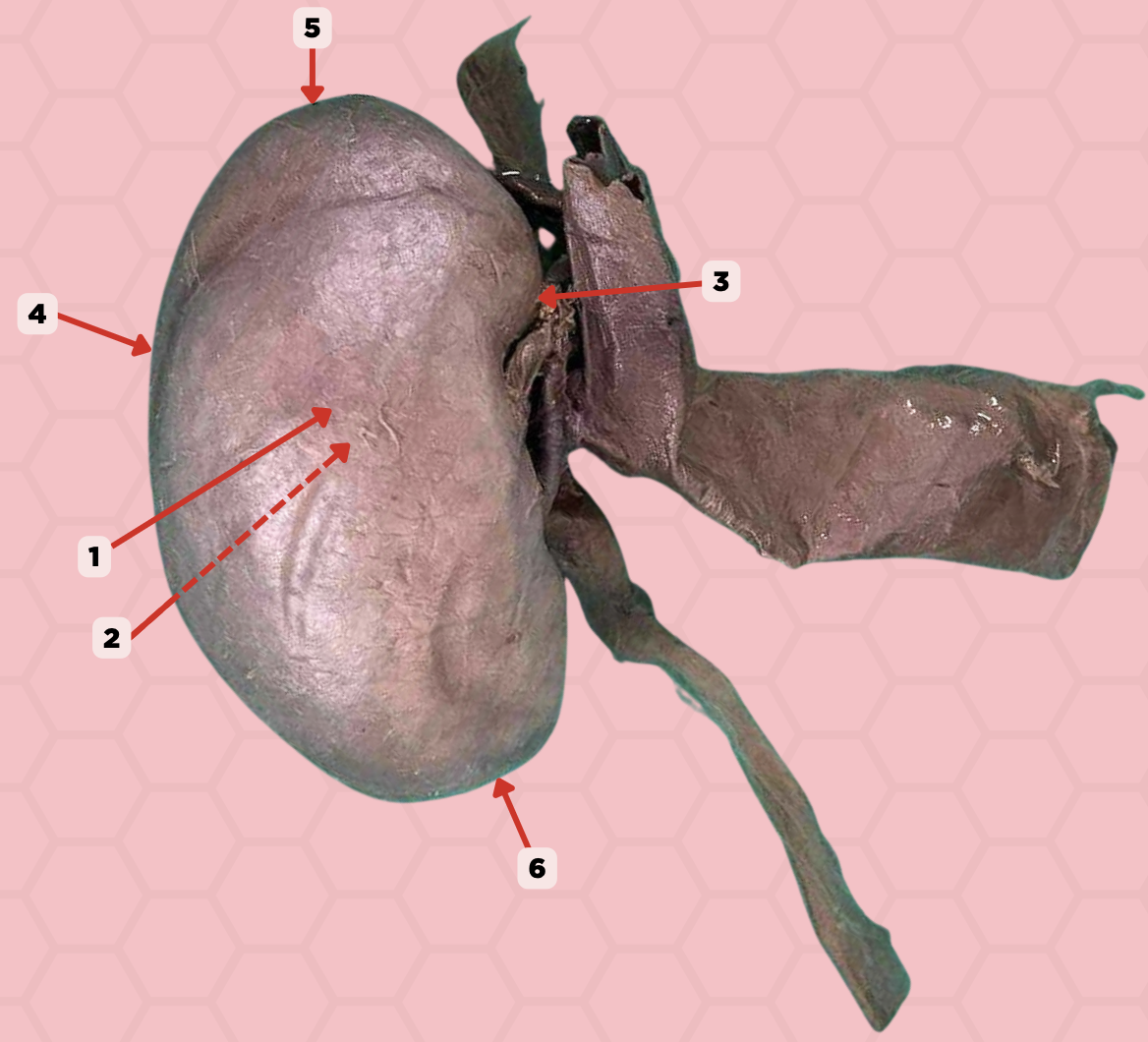
Lateral Margin
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
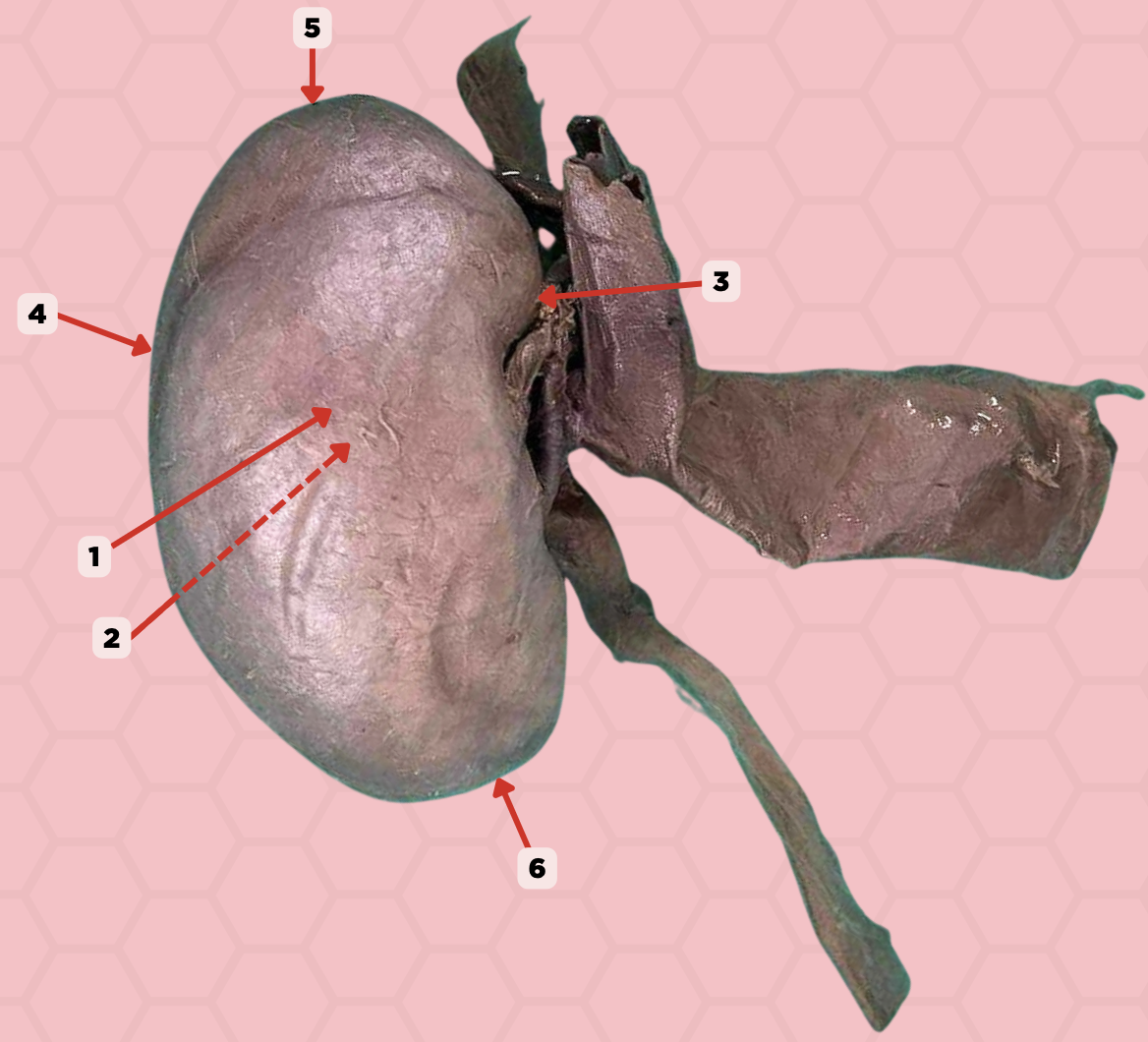
Superior Pole
Identify the structure labeled as 5.
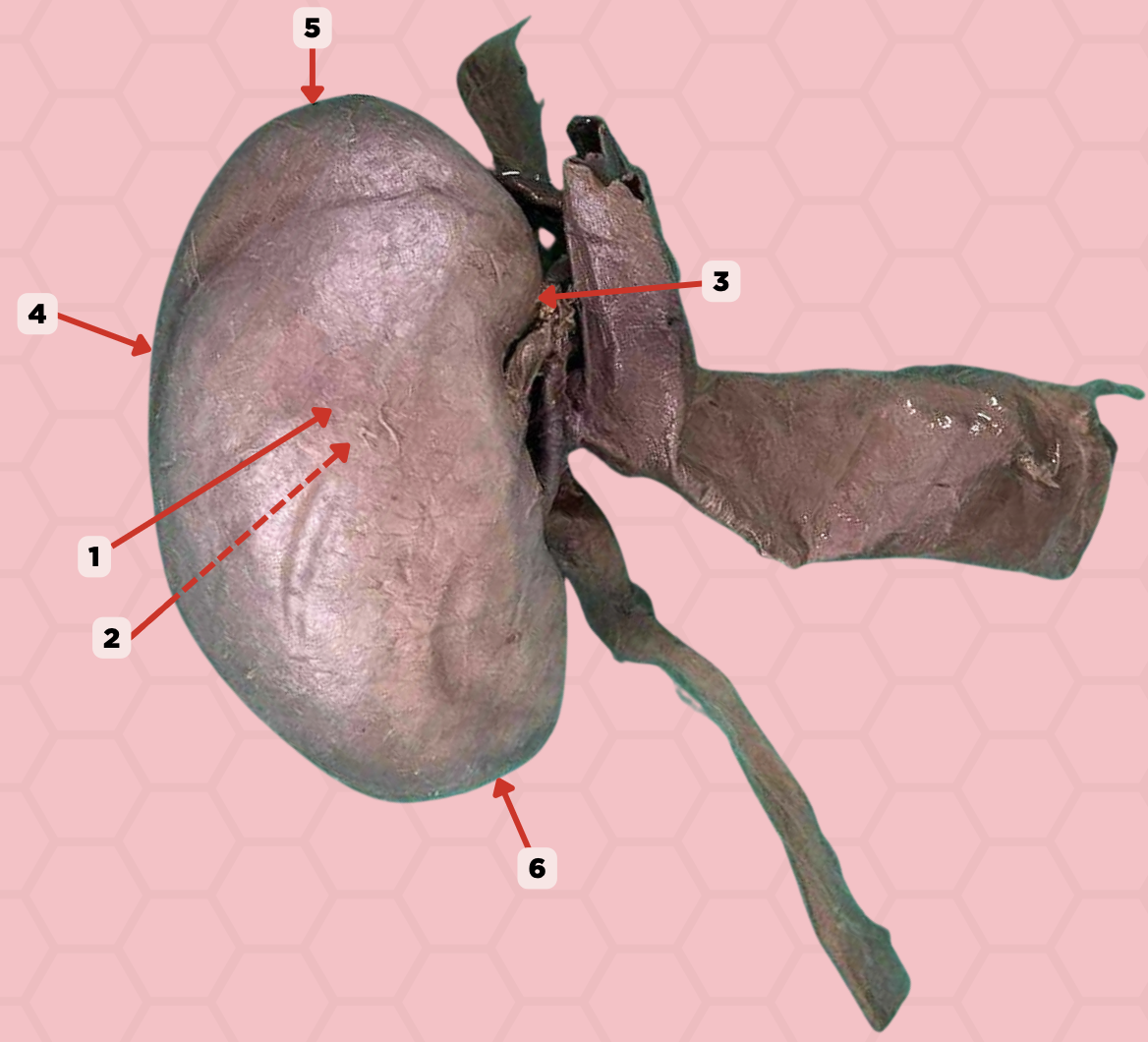
Inferior Pole
Identify the structure labeled as 6.
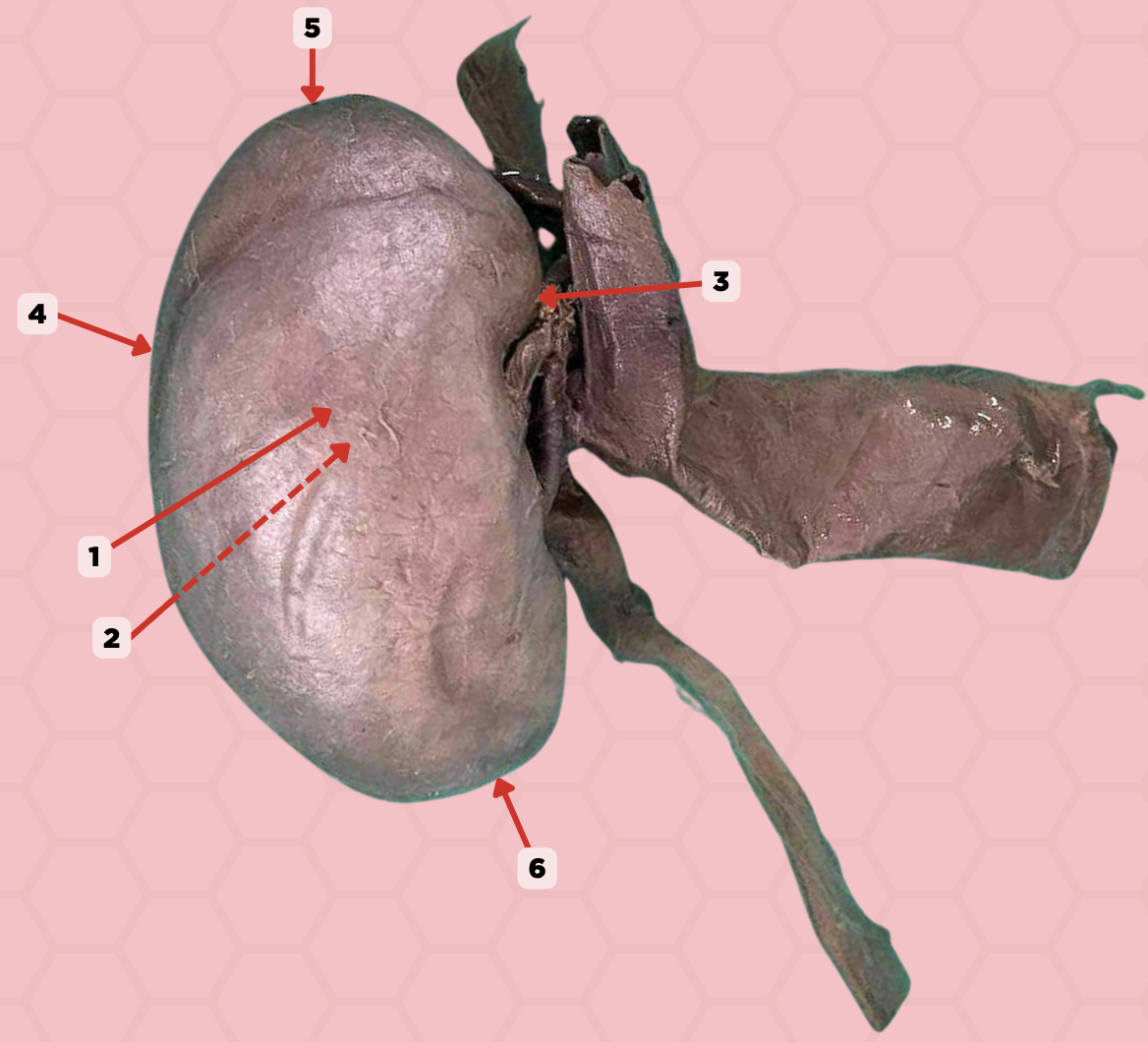
a. pin 6
The tips of which pinned structure empties urine into the minor calyx.
a. pin 6
b. pin 3
c. pin 5
d. pin 9
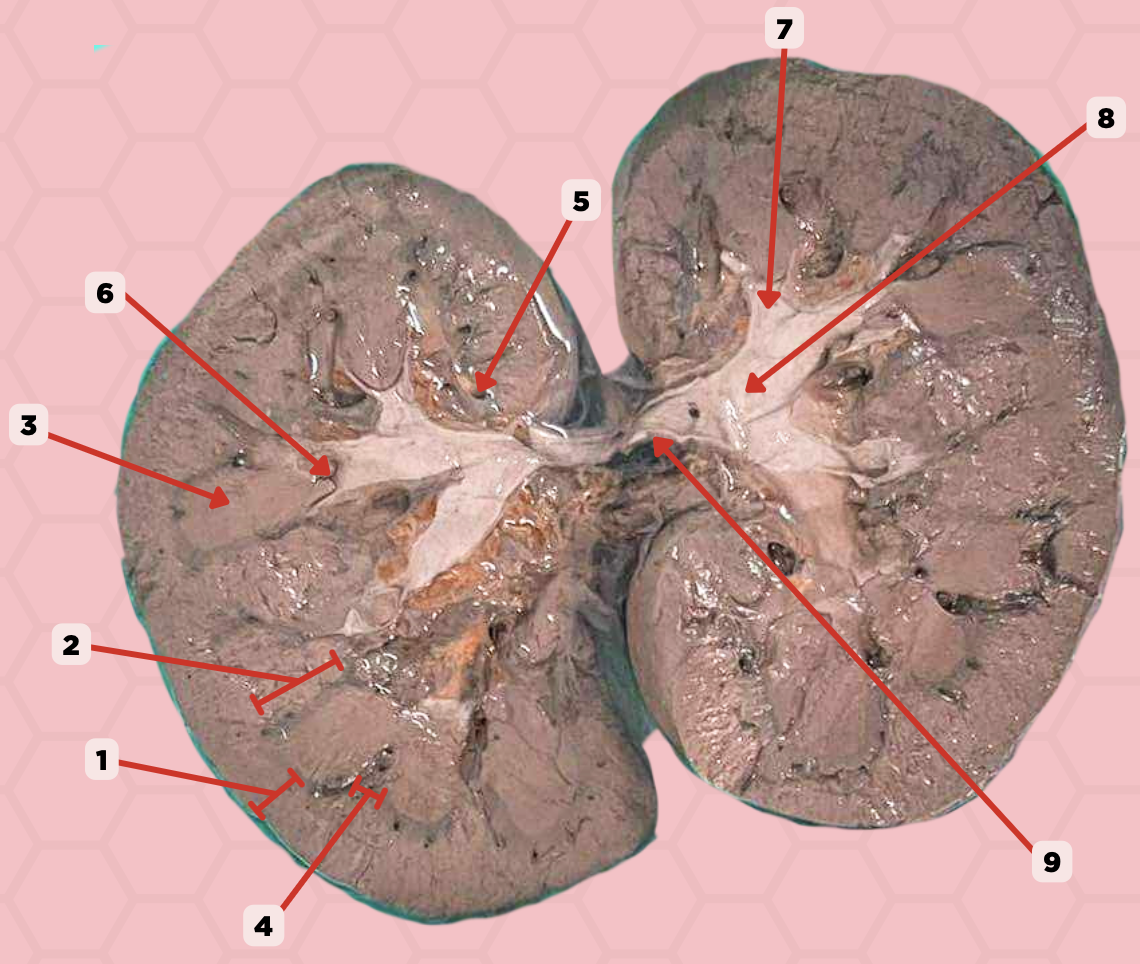
c. minor calyces
Pin 8 is formed by converging of 2 to 3 ____?
a. renal pyramids
b. major calyces
c. minor calyces
d. renal columns of Bertin
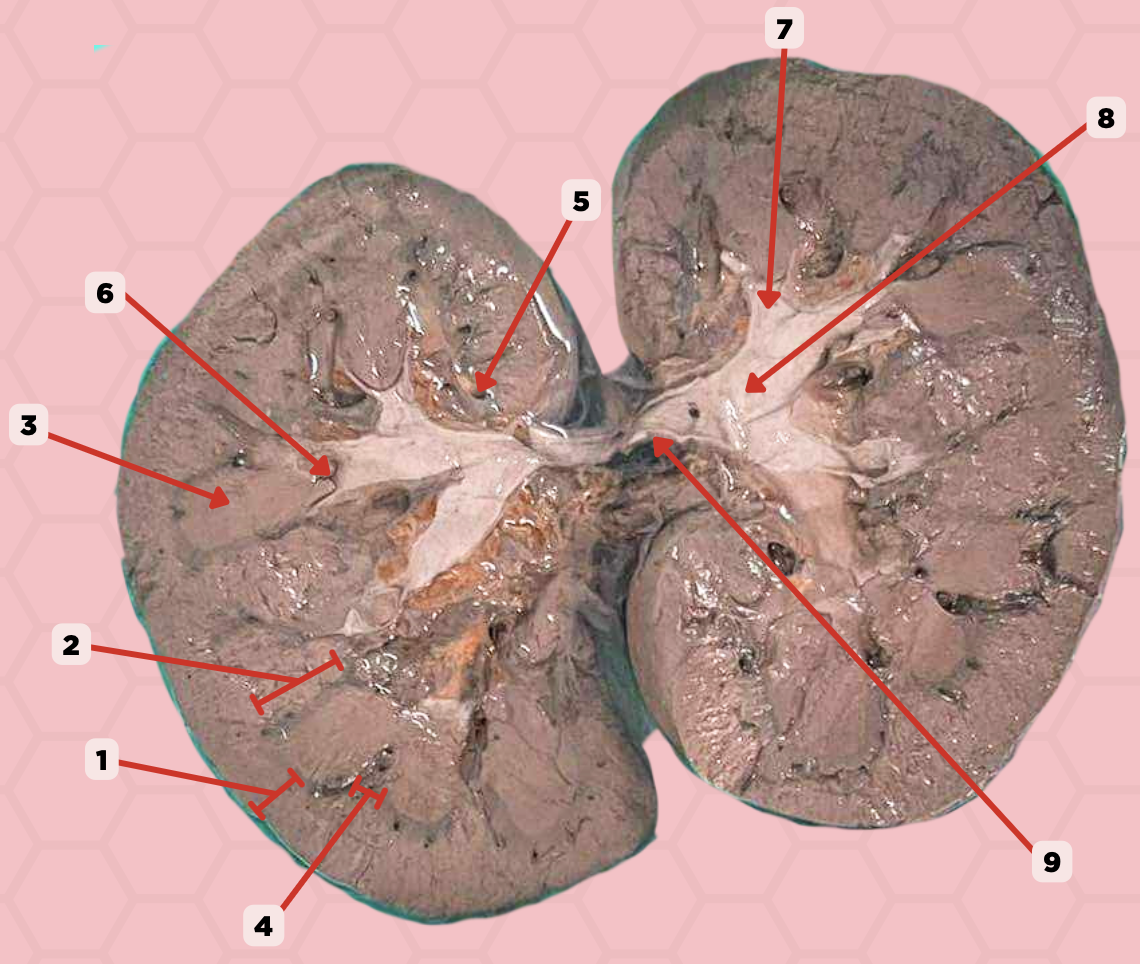
c. arcuate arteries
What blood vessel will course along the base of pin 3 and provide small branches called the cortical radiate arteries?
a. segmental arteries
b. interlobular arteries
c. arcuate arteries
d. interlobular vein
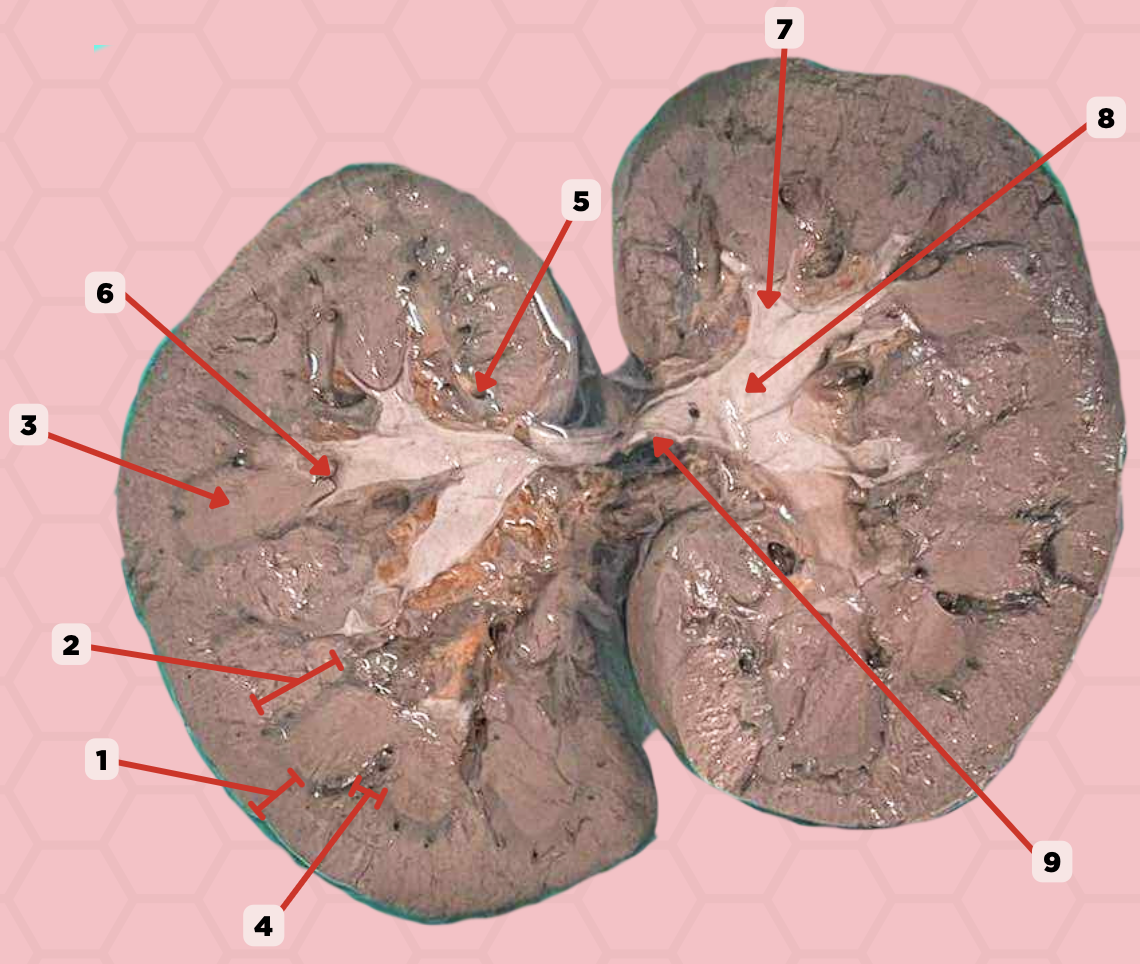
b. pin 9
Which pinned structure will be called ureter as it exits the hilum of the kidney
a. pin 8
b. pin 9
c. pin 7
d. pin 5
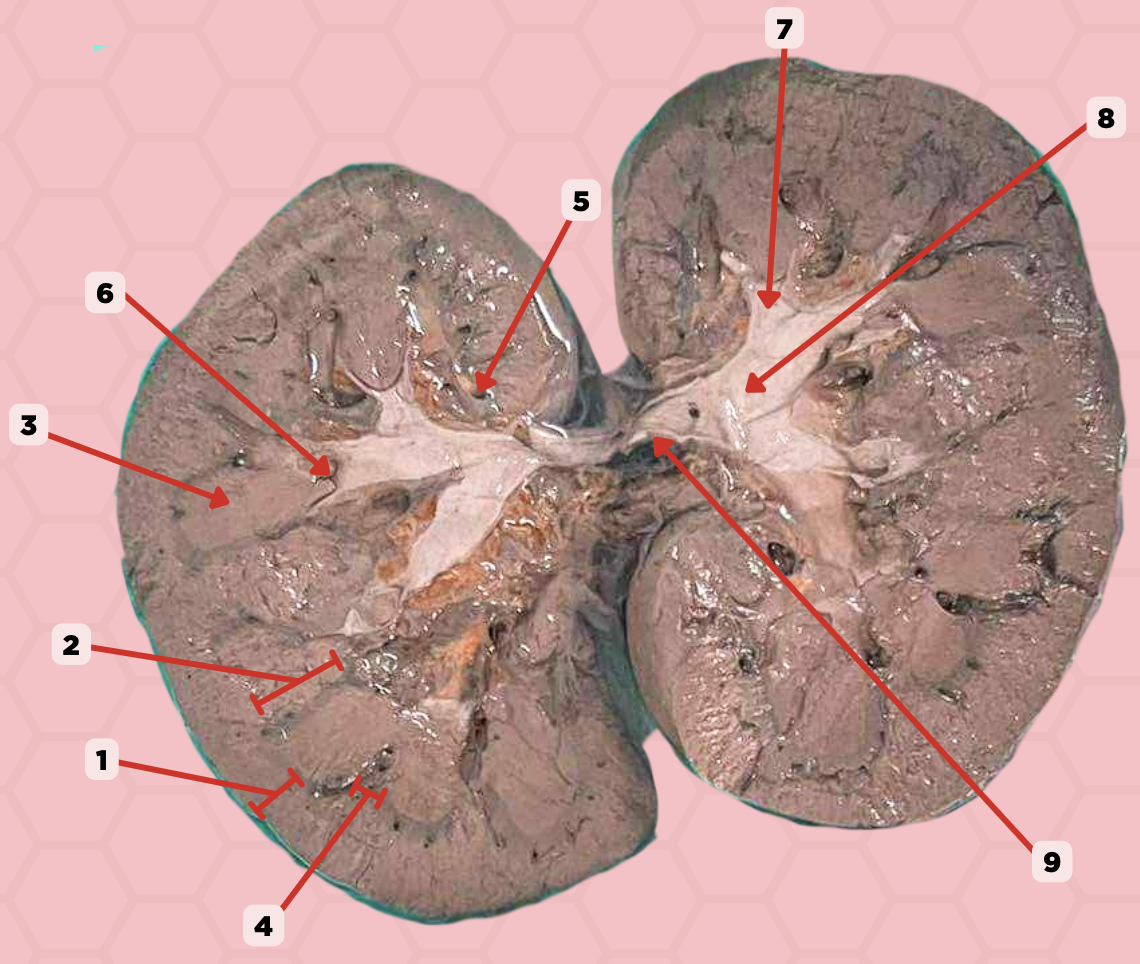
Renal Cortex
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
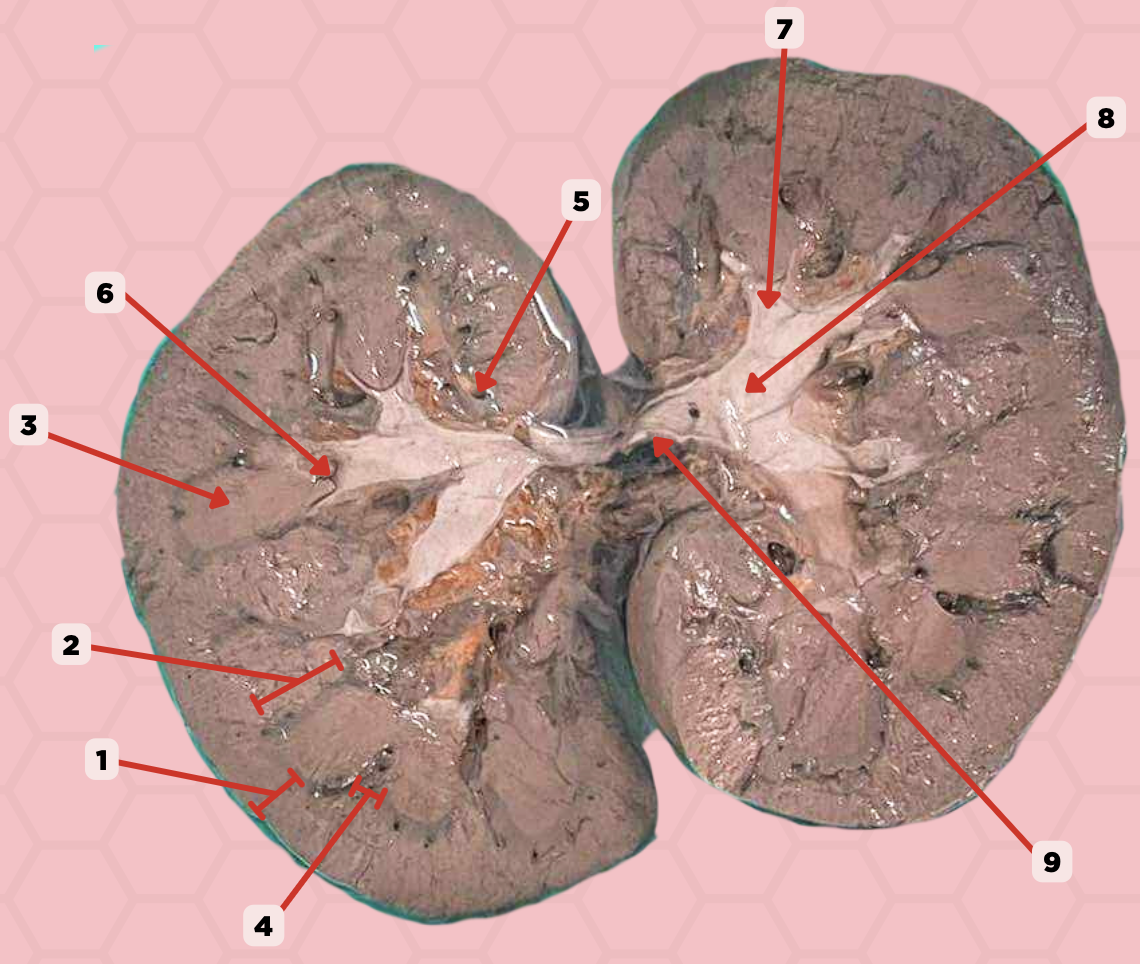
Renal Medulla
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
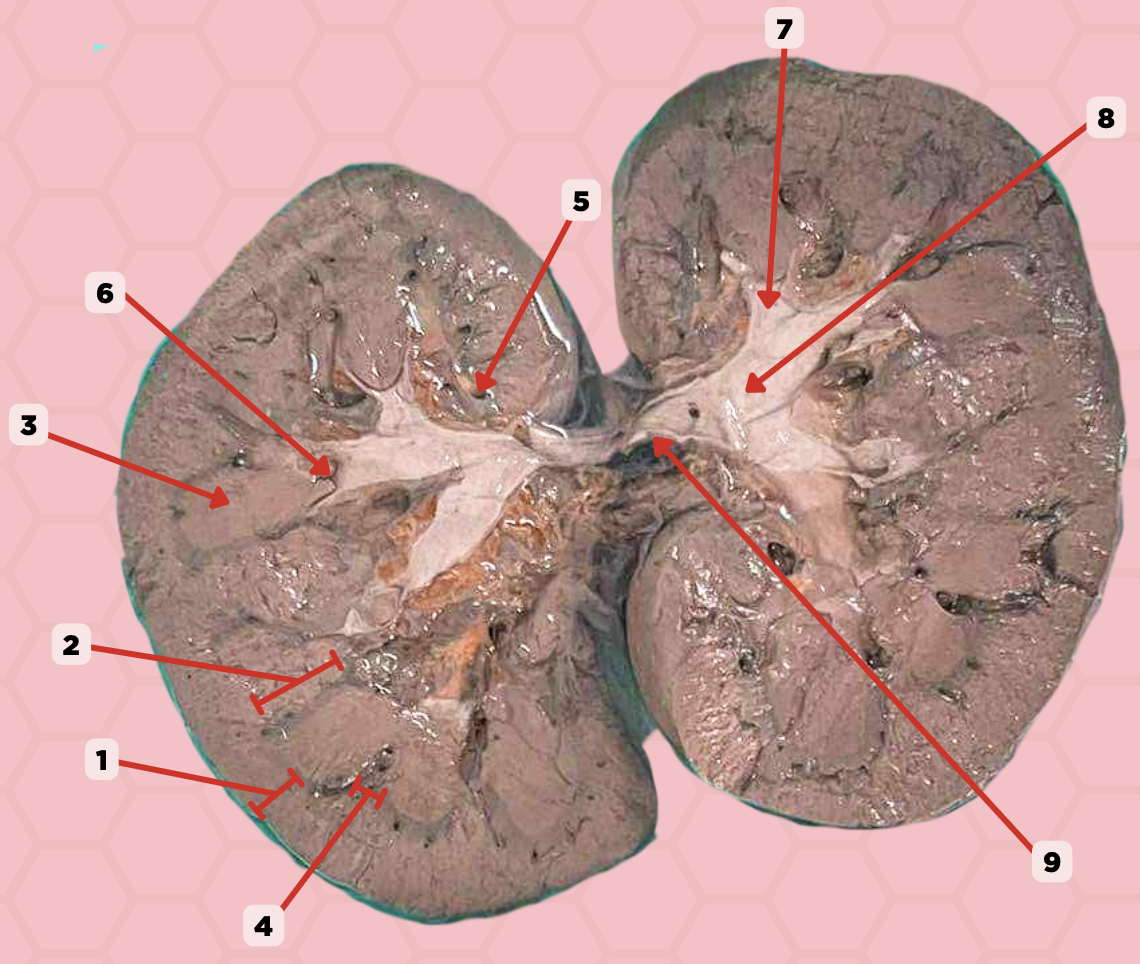
Renal Pyramids
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
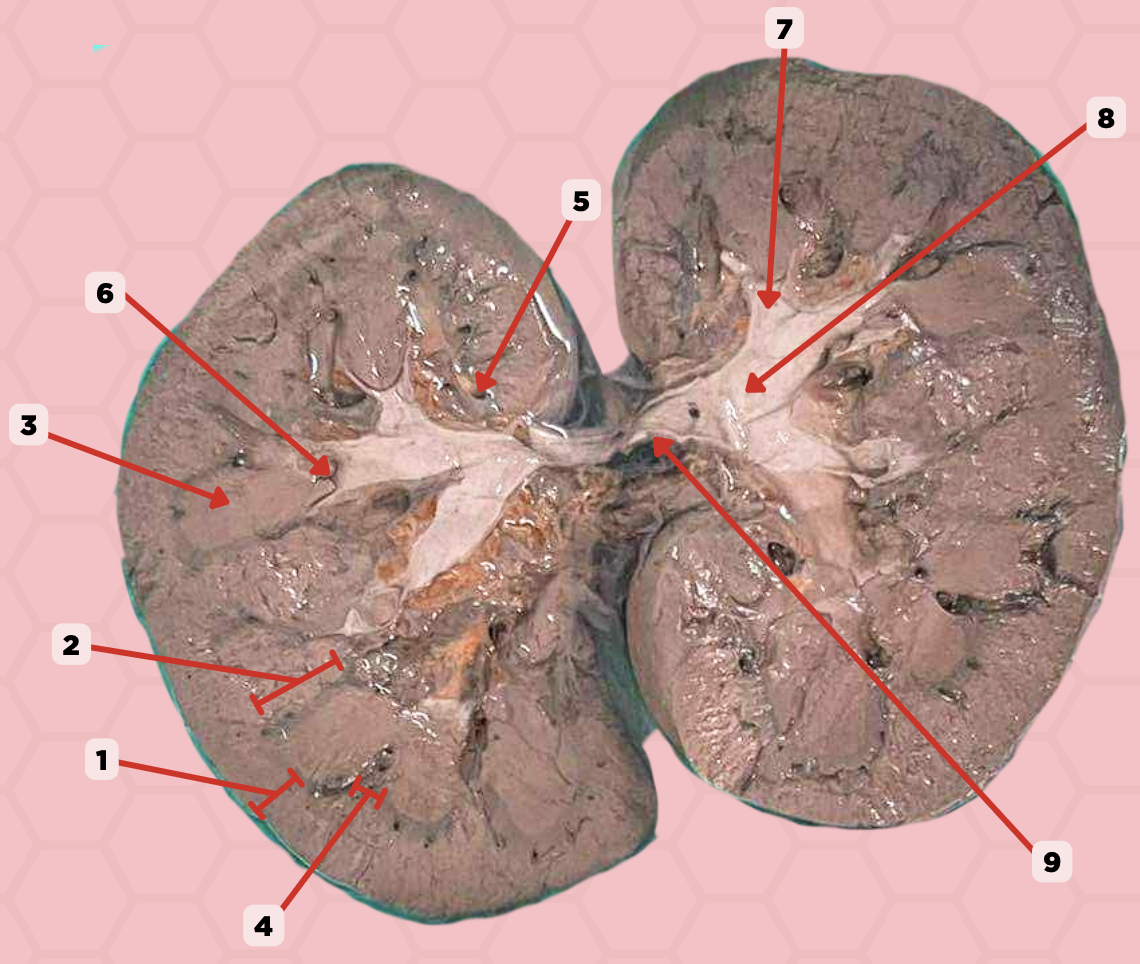
Renal Columns of Bertin
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
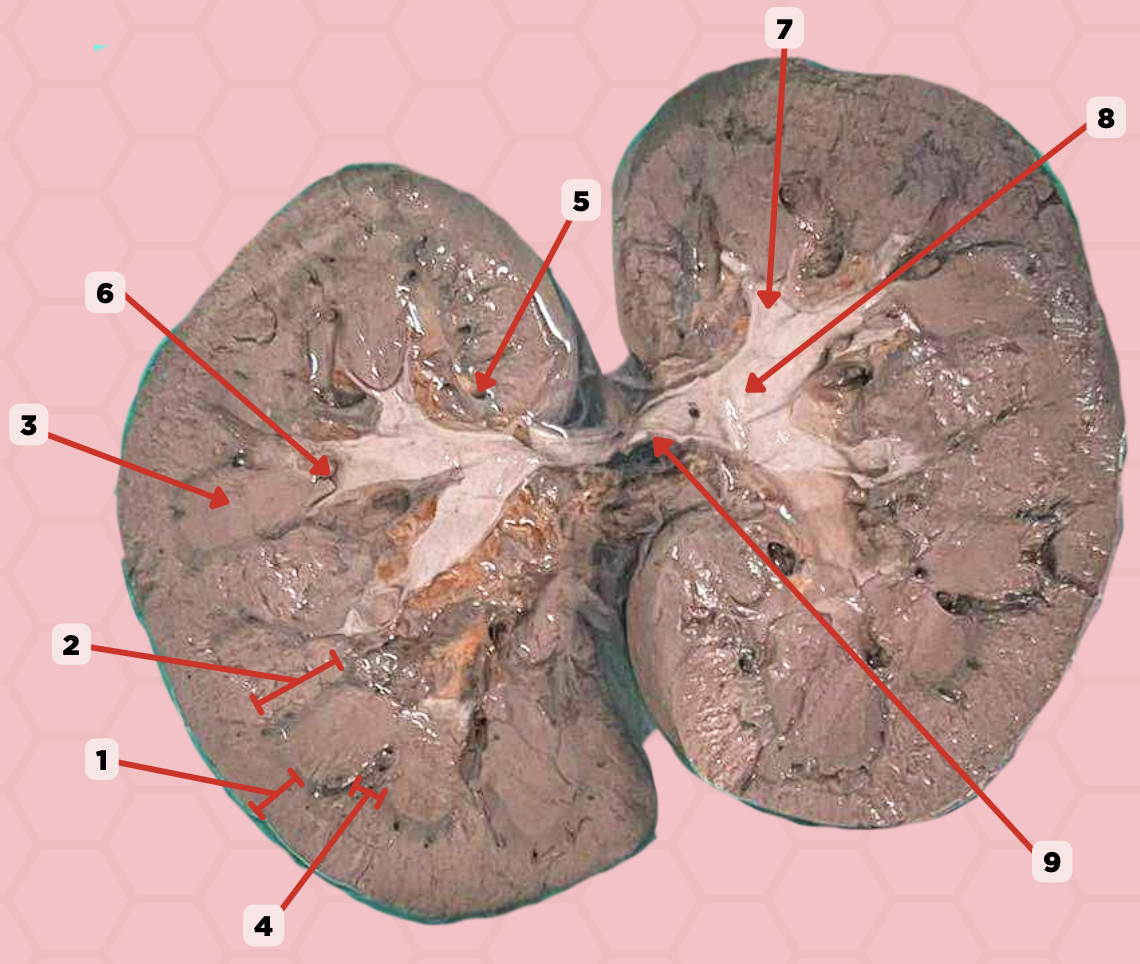
Renal Sinus
Identify the structure labeled as 5.
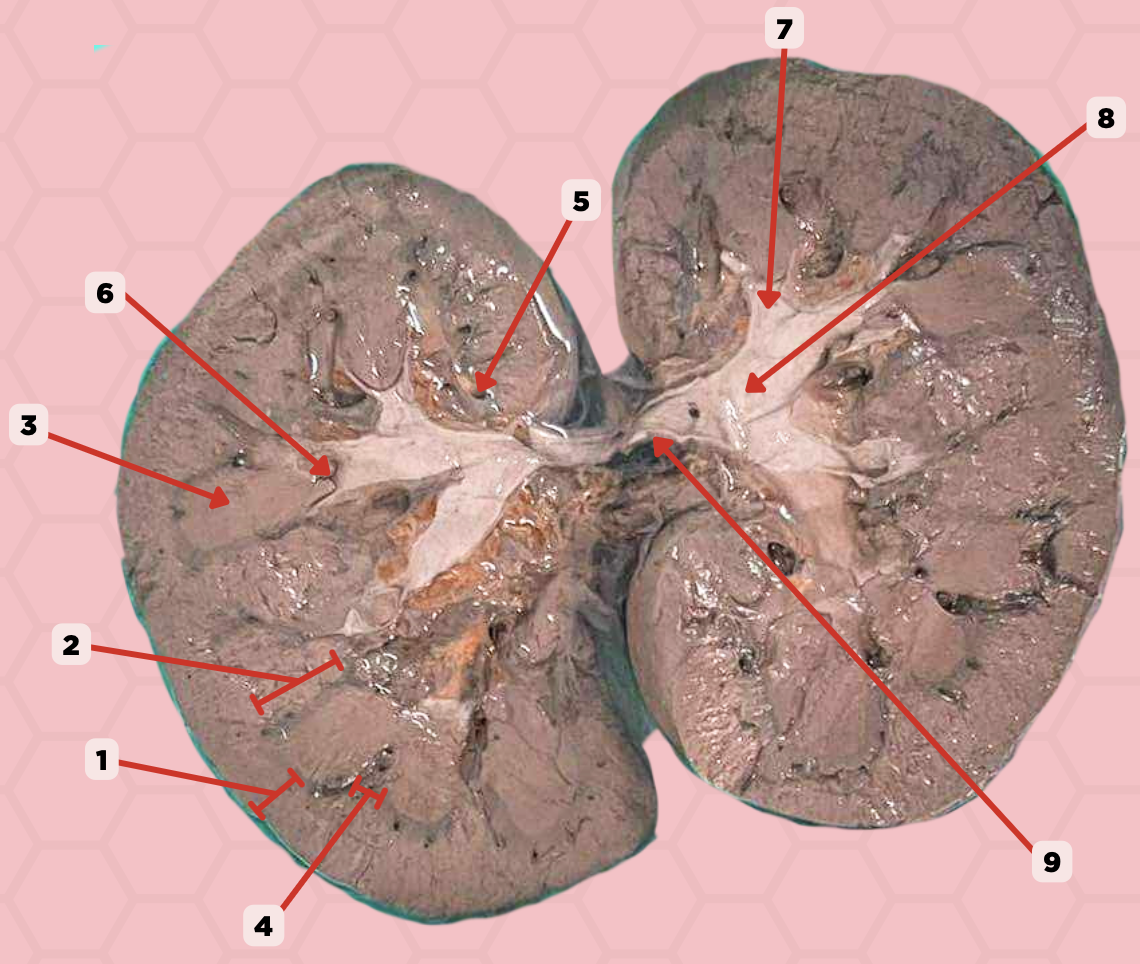
Renal Papilla
Identify the structure labeled as 6.
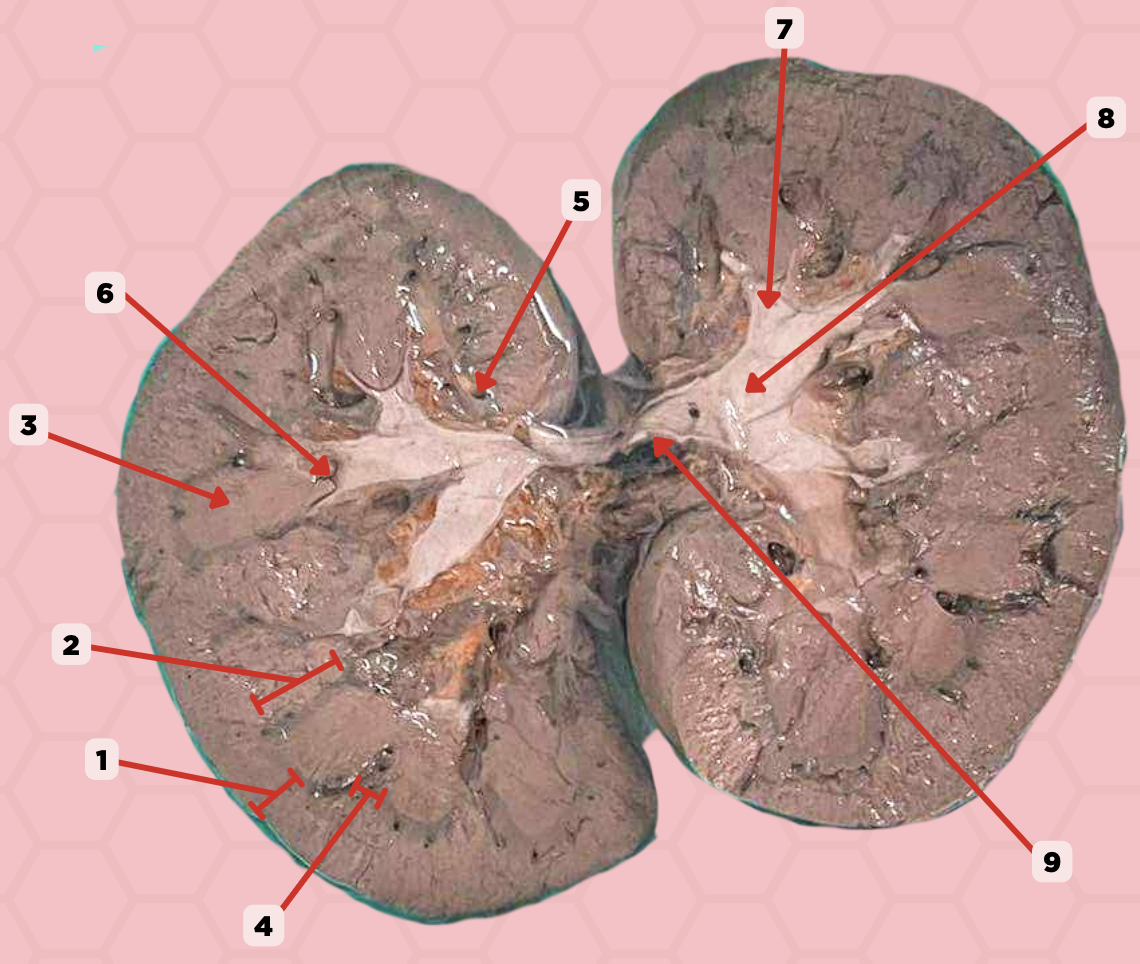
Minor Calyx
Identify the structure labeled as 7.
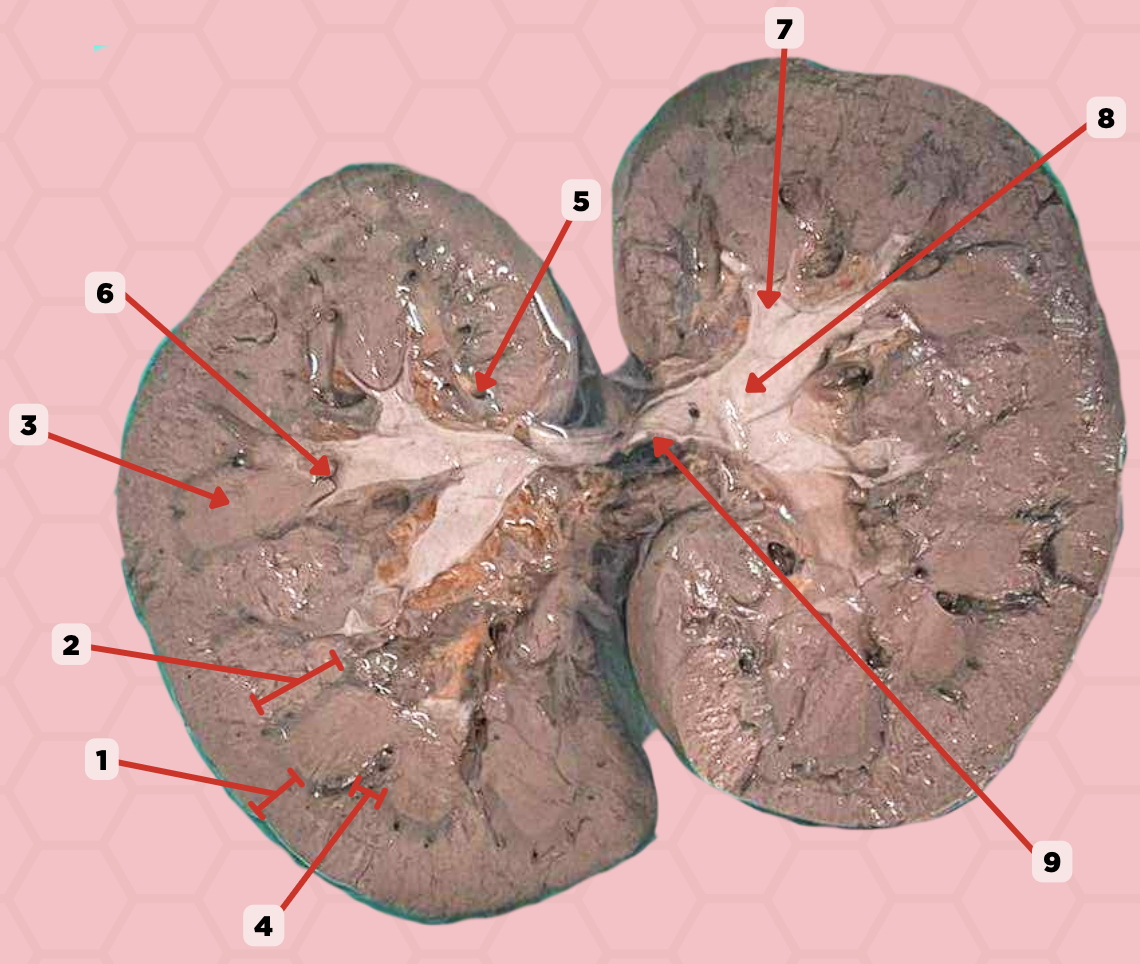
Major Calyx
Identify the structure labeled as 8.
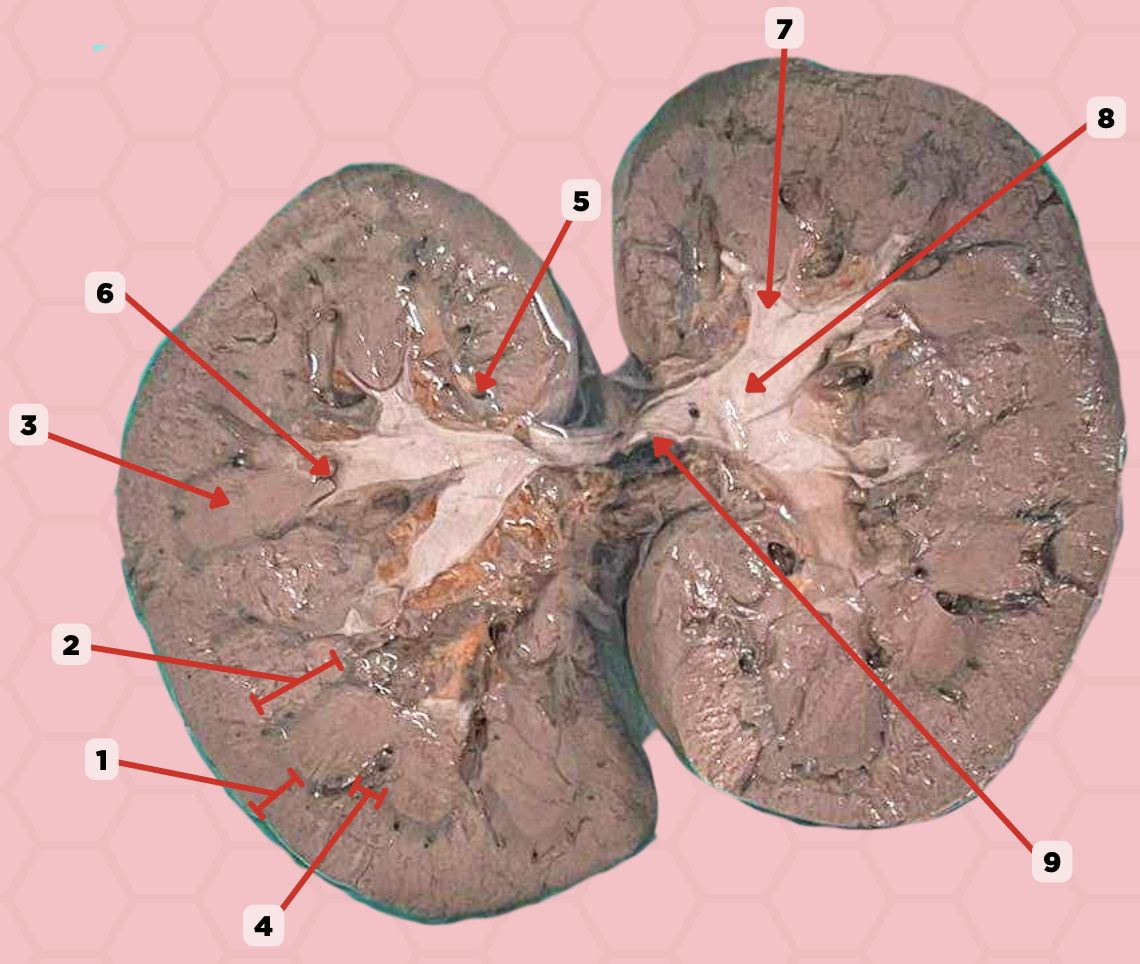
Renal Pelvis
Identify the structure labeled as 9.
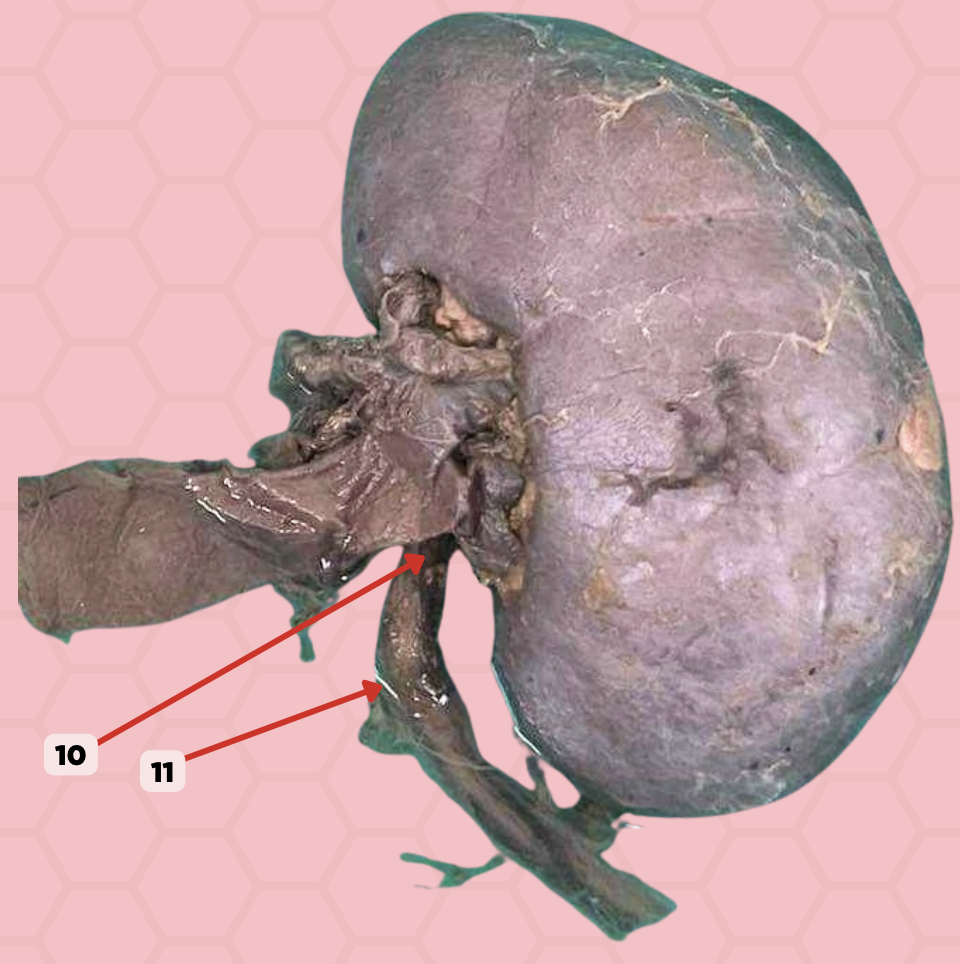
a. uretero-pelvic junction
A patient complains of pain at the Hypogastric area below the umbilicus or the lumbar area. Pinned structure 11 is likely affected. Which constriction site is it?
a. uretero-pelvic junction
b. pelvic brim
c. vesico-ureteric junction
d. vesico-pelvic junction
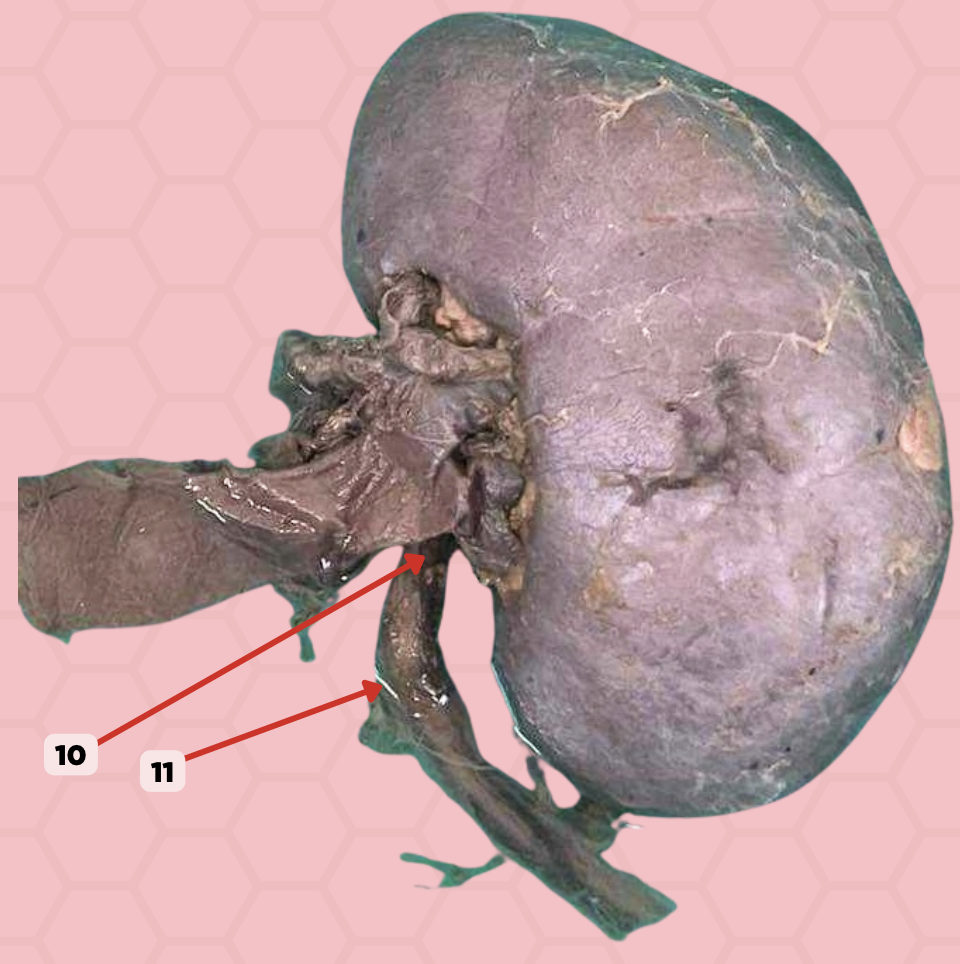
d. bilateral tubular organ
Pinned structure 10 is a ?
a. bilateral alveolar organ
b. unilateral alveolar organ
c. unilateral tubular organ
d. bilateral tubular organ
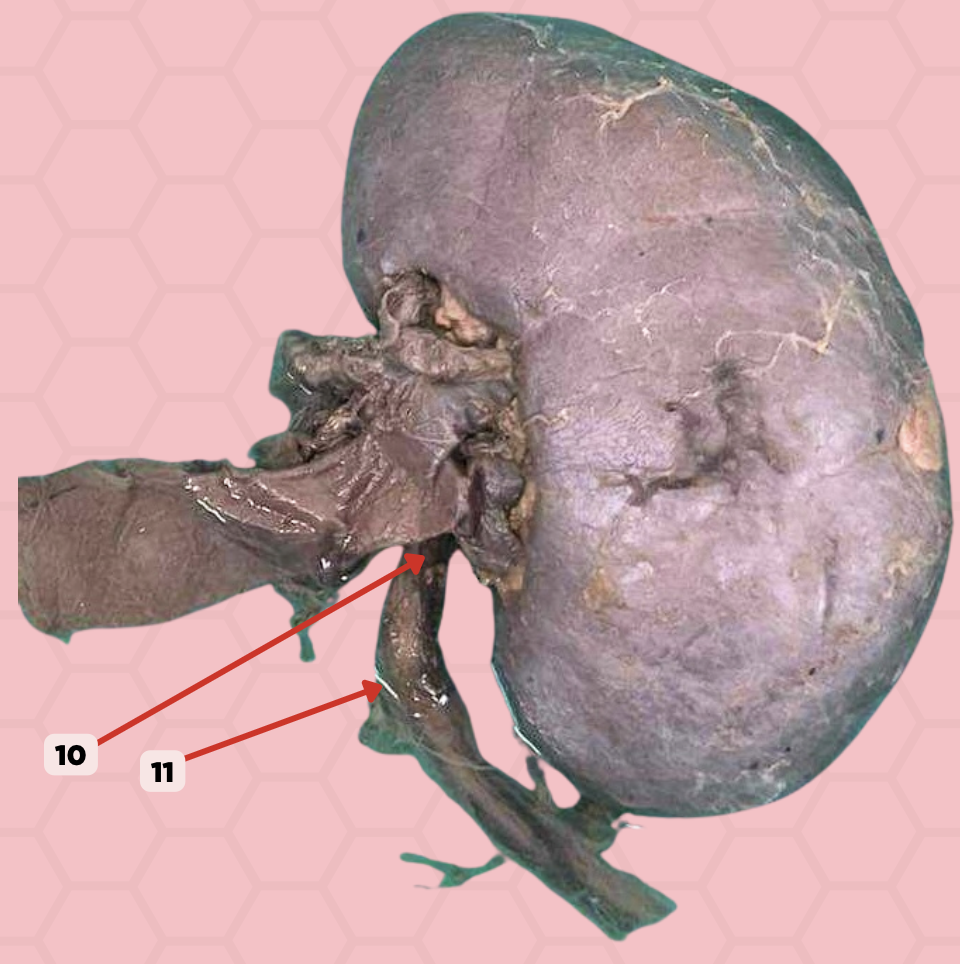
Ureter
Identify the structure labeled as 10.
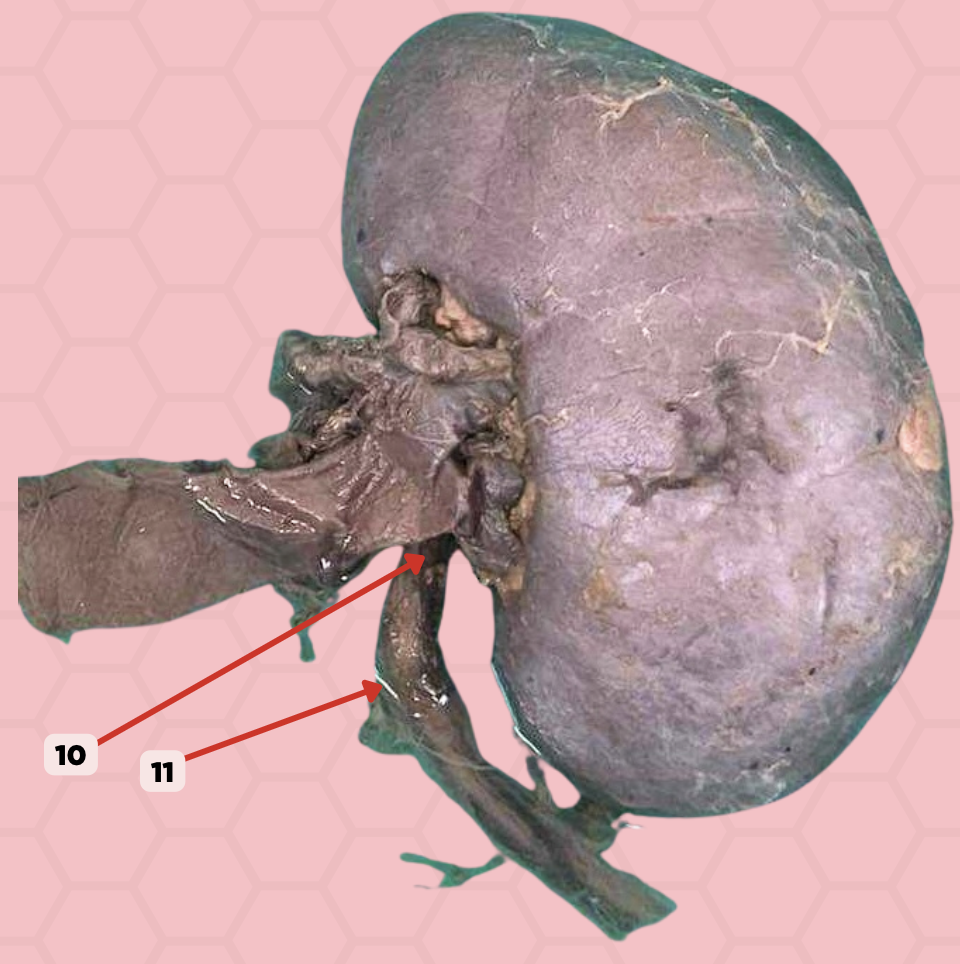
Ureteropelvic Junction
Identify the structure labeled as 11.
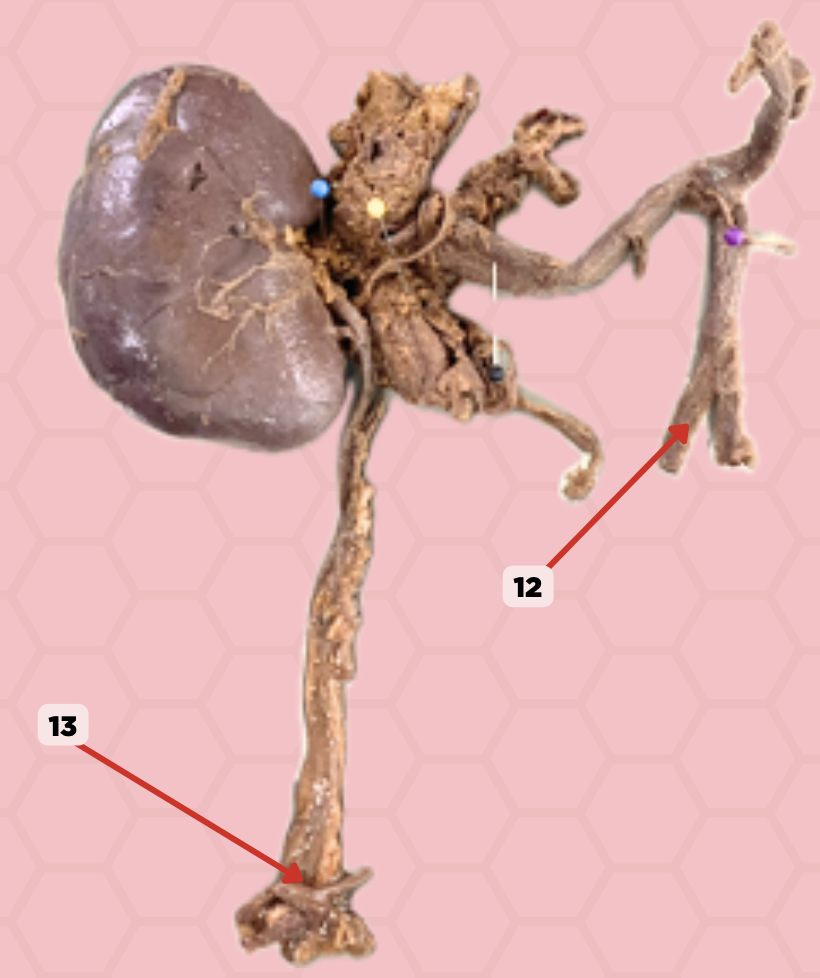
b. 2nd constriction site
Pin No.12 is responsible for causing which constriction site of the ureter?
a. 1st constriction site
b. 2nd constriction site
c. 3rd constriction site
d. 4th constriction site
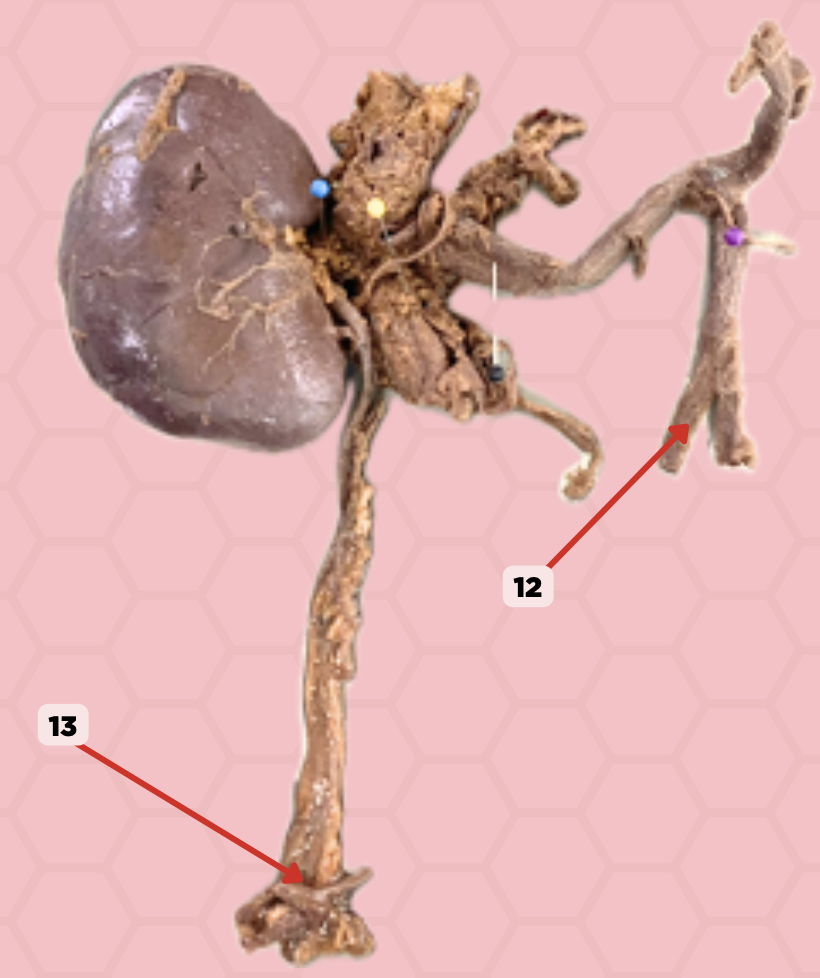
c. Groin area
Should a kidney stone be lodged in the area Pin No. 13, where would the pain present?
a. Hypogastric area below the umbilicus
b. Lumbar area
c. Groin area
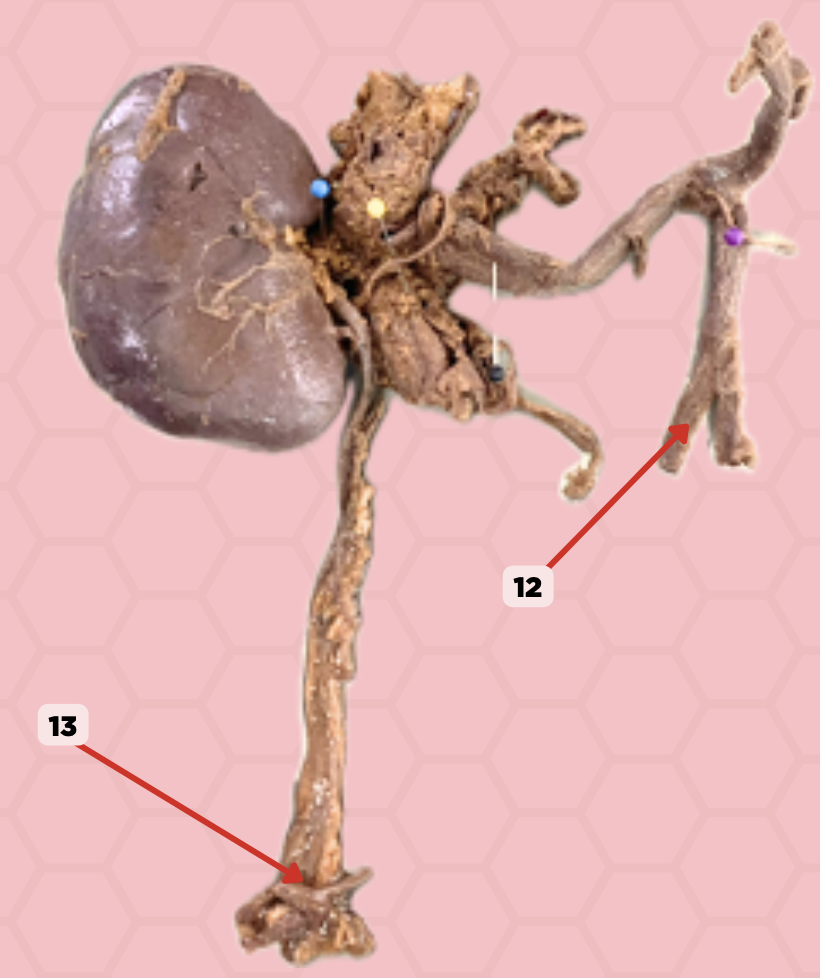
b. Ureterolithiasis
What is the general term for the condition where stones are found lodged in the area of Pin No. 13?
a. Nephrolithiasis
b. Ureterolithiasis
c. Cholelithiasis
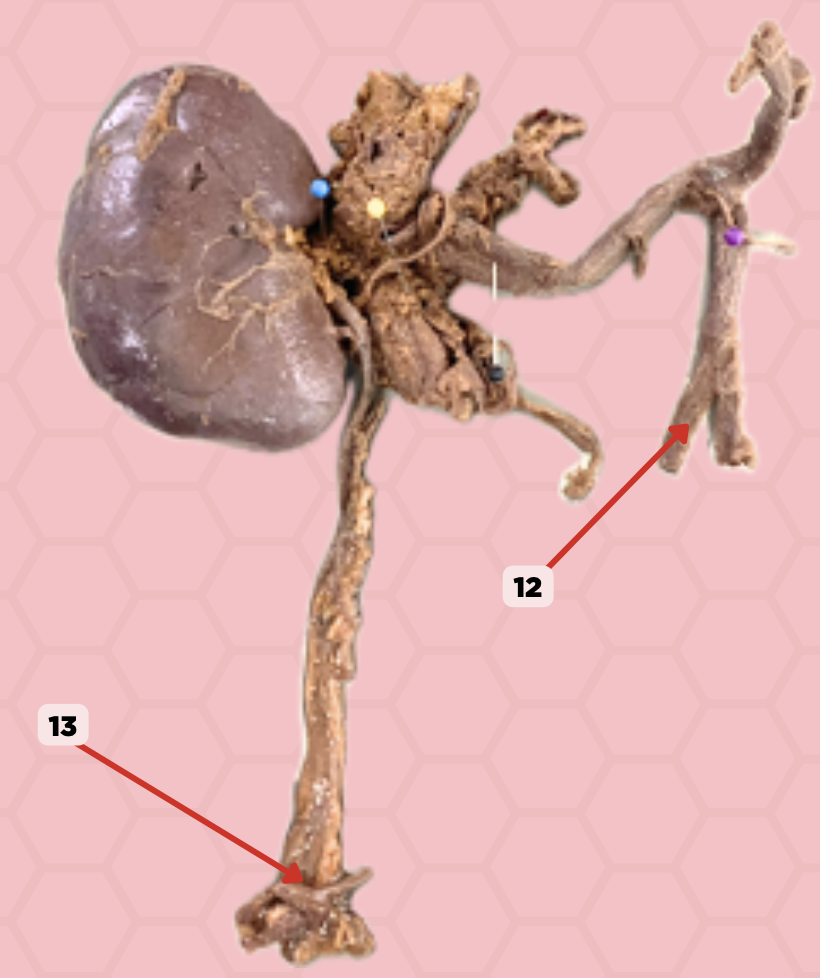
External Iliac Artery (Pelvic Brim)
Identify the structure labeled as 12.
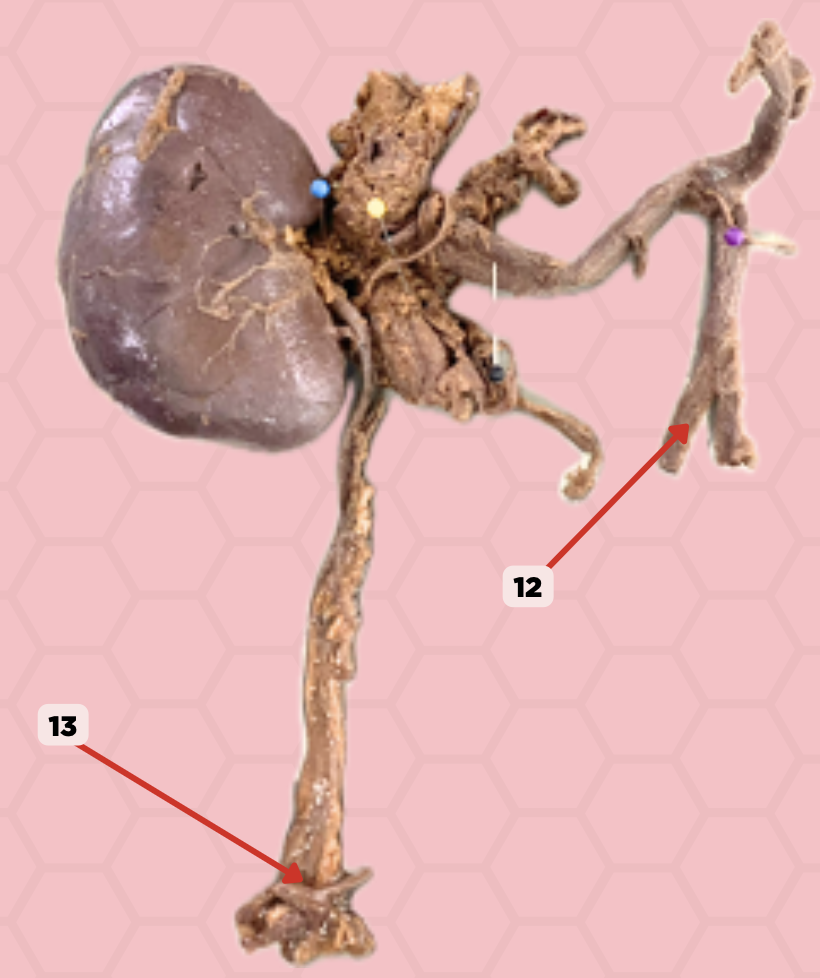
Vesicoureteric junction
Identify the structure labeled as 13.
Right Renal Artery
This renal artery is longer and lower.
Left Renal Artery
This renal artery is longer and lower.
Brodel’s Line
Plane located in the posterolateral aspect of the kidney that is less vascular
Superior (Apical), Anterosuperior, Anteroinferior, Inferior (Basal)
What are the branches of the anterior branch of the renal artery?
Anterior and Posterior
What are the two main branches of the renal artery?
Abdominal Aorta → Renal Artery → Anterior and Posterior Segmental Arteries → Interlobar Arteries → Arcuate Arteries → Cortical Radiate Arteries → Afferent Arterioles → Glomerular Capillaries → Efferent Arterioles
Trace the blood supply of the kidneys starting from the abdominal aorta.
Suprarenal Vein, Gonadal Vein, Ascending Lumbar Vein
What are the three branches of the left renal vein?
Inferior Vena Cava → Renal Vein → Interlobar Vein → Arcuate Vein → Cortical Radiate Vein
Trace the venous drainage system of the kidneys starting from the inferior vena cava
Diarrhea
Pain felt from visceral peritoneum that is stimulated by stretching and chemical irritation. Offending agents will cause irritation int GI tract as a result of toxins being present, causing formation of gas or watery stool that will eventually cause stretching. Poorly localized pain. Relieved when you start passing out offending agents.
Stab Wounds
Pain felt from the parietal peritoneum. Parietal peritoneum has the same blood and nerve supply as the abdominal wall and is sensitive to laceration, heat, or cold. Pain will mainly be localized
Appendicitis
Early disease process: periumbilical discomfort (midgut pain) secondary to distention of the appendiceal lumen that affects the visceral peritoneum. Pain often begins in the center of the abdomen (or periumbilicus). Pain progresses to localized RLQ pain and tenderness as the inflammation becomes transural and involves the parietal peritoneum.
Kidney Stones
Pain in the flank area/lumbar area. Kidney stones may dislodge or obstruct the flow of urine
Ureterolithiasis
If the stones are located within the ureter, it is now called?
Ureteropelvic Junction
Pain and clinical presentation will depend on the level at which the stone is obstructed: hypogastric area below the umbilicus or the lumbar area
Distal part of ureter
Pain and clinical presentation will depend on the level at which the stone is obstructed: groin area
Bilateral Renal Agenesis
From overexpression of WT1. A newborn is lacking one or both kidneys
Wilm’s Tumor
From underexpression of WT1. Two foci of masses are found on the superior and lateral aspects of the kidney
Polycystic Kidney Disease
Formation of multiple cysts. Caused by: 2 genes remain activated after the 12th week of AOG, and the fetal urine inside the nephron will start to collect, pool, remain inside the unit, and can proceed to inadvertent ballooning.
Ren Arcuatus
Horseshoe Kidney. Usually diagnosed by incidental findings, as it provides neither signs nor symptoms.