AP Physics C Mechanics Equations to MEMORIZE
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
J = ∆p = F∆t
Impulse-Momentum Theorem
(impulse, J is measured in unit seconds)
W = ∆E
Work-Energy Theorem
vf² = vi²+2a(xf-xi)
vi² = vf²-2a(xf-xi)
Kinematic equation solving for Vf without t
Fg = mg
The Force of Gravity or Weight of an object
Δx = 1/2(vf +vi)Δt
The fourth Uniformly Accelerated Motion equation
Fg⊥ = mgcos θ & Fgll = mg sin θ
The components of the force of gravity parallel and perpendicular on an incline where θ is the incline angle
0 - 2
General range for coefficients of friction
ΔEsystem = ∑T
The general equation relating the change in energy of the system to the net energy transferred into or out of the system.
W = ∑ΔKE
Work energy theorem -always true.
Wfriction = ΔME
Nonconservative forces 1 -only true when there is no energy added to or removed from the system via a force.
MEi = MEf
Nonconservative forces 2 -only true when there is no energy added to or removed from the system via a force and there is no work done by a nonconservative force.
Fx =−dU/dx
The equation which relates a conservative force and the potential energy associated with that force -Force is the derivative of potential energy with respect to displacement
That every derivative is ____
That every derivative is an integral and every integral is a derivative.
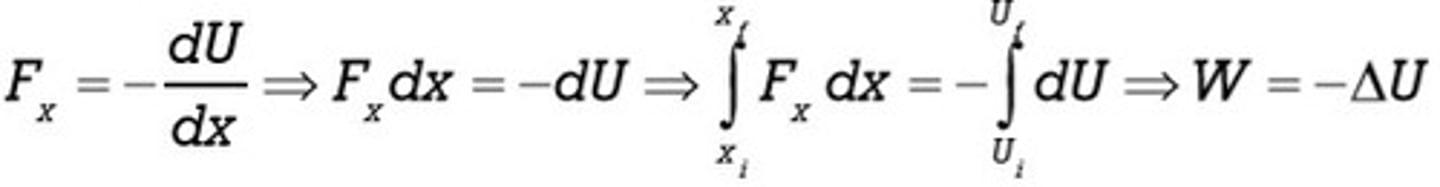
∑->Pi = ∑->Pf
Conservation of Momentum. It may seem obvious, however, you need to remember when it is valid.
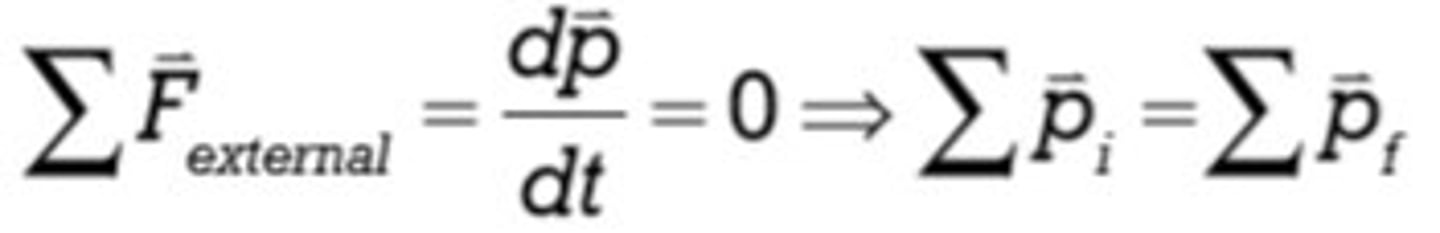
∑->Li = ∑->Lf
Conservation of Momentum. It may seem obvious, however, you need to remember when it is valid.
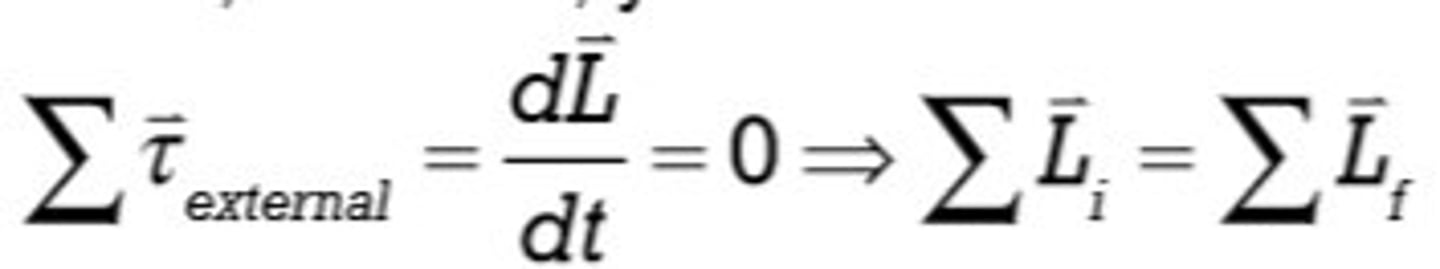
rcm = (1/mtotal)*∫*rdm
The center of mass of a rigid object with shape (do not confuse with moment of inertia I=∫r²dm)
ρ = m/∀ & λ = m/L
Volumetric Mass Density and Linear Mass Density
s = rΔ θ & at = r α
Arc length and tangential acceleration. vt = r ω is on the equation sheet, so it is easy to get to the other two.
Vcm = Rω & acm = R α
The velocity and acceleration of the center of mass of a rigid object which is rolling without slipping. Easy to remember from the previous equations.
360° = 2 π radians
1 revolution (conversion factor)
(ω f)² = (ω i)² + 2 α Δ θ & Δ θ = 1/2 (ω i + ω f) Δt
Uniformly Angularly Accelerated Motion equations
d²x/dt² = − ω²x
The condition for simple harmonic motion
vmax = A ω
The maximum velocity during simple harmonic motion
amax = A ω²
The maximum acceleration during simple harmonic motion
x(t) = Acos(wt+θ)
v(t) = -Awsin(wt+θ)
a(t) = -Aw²cos(wt+θ)
Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration of Simple Harmonic Motion
->Fr =−b->v & ->Fr = 1/2 D ρ Av²
Don't memorize -Resistive force equations. The problem will specify to use ->Fr = 1/2 D ρ Av² and give you that equation OR tell you the drag force is "proportional to" the velocity, which means ->Fr = -b->v
746 watts = 1 hp
Don't Memorize -Conversion will be provided
G =6.67×10−11 N⋅m² kg²
Don't memorize -reference the "Table of Information" and the page of general math formulas on the AP Physics equation sheet
vcm = ∑(mivi)/∑(mi) & acm = ∑(miai)/∑(mi)
Don't memorize -know how to derive. velocity and acceleration of the center of mass of a system of particles. Simply take the derivative with respect to time once or twice of the position of the center of mass of a system of particles to get these equations.
????????????vterminal = √[(2mg)/(DρA)]
???????????Don't memorize -Terminal Velocity (p is density)
WFa = Gmomp/Rp
Don't Memorize -Binding Energy
Vescape = √[2GmEarth/REarth]
Don't memorize (on calculator) -Escape Velocity
?????MEtotal = −Gmomp/2r
??????Don't Memorize -Total Mechanical Energy of an *Orbital* Object (mp is mass of planet)
T² = [4π2/Gmp]r³
Don't Memorize -Kepler's Third Law of periods: Kepler's constant describes the relationship of a planets period to its radius.
v (t) = −A ω sin(ωt+φ)
Velocity in simple harmonic motion
a (t) = −A ω² cos(ωt+φ)
Acceleration in simple harmonic motion
I = Icm+mD²
The parallel axis theorem
Icm = mR²
Uniform Hoop or thin cylindrical shell about its cylindrical axis
Icm = 1/12 mL²
Moment of inertia [center of mass] for Uniform Thin and Long rod about center axis
Icm = 1/2mR²
Moment of inertia [center of mass] for Uniform Solid cylinder or disk about its cylindrical axis & Moment of inertia for a Hoop around its diameter (not symmetric)