Soft Tissue Sarcomas
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is the most common type of soft tissue sarcoma?
Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma
What is the most important prognostic factor in soft tissue sarcoma?
A) Tumor size
B) Tumor location
C) Tumor grade
D) Lymph node status
C) Tumor grade
What is the overall 5-year survival rate for soft tissue sarcoma?
A) 20-30%
B) 30-40%
C) 50-60%
D) 60-70%
C) 50-60%
What is the recommended treatment for a soft tissue sarcoma that is unresectable?
A) Surgery alone
B) Surgery with adjuvant radiation therapy
C) Surgery with adjuvant chemotherapy
D) Surgery with adjuvant radiation and chemotherapy
D) Surgery with adjuvant radiation and chemotherapy
What is the most common site of distant metastasis for soft tissue sarcoma?
A) Lungs
B) Liver
C) Bones
D) Brain
A) Lungs
What is the imaging modality of choice for evaluating soft tissue sarcomas?
A) Contrast-enhanced CT scan
B) MRI
C) PET scan
D) Ultrasound
B) MRI
What is the most common type of biopsy used for soft tissue sarcoma?
A) Fine needle aspiration biopsy
B) Core needle biopsy
C) Incision biopsy
D) Excision biopsy
B) Core needle biopsy
What is the most common type of sarcoma that arises from the breast?
A) Stromal sarcoma
B) Fibrosarcoma
C) Malignant fibrous histiocytoma
D) Angiosarcoma
D) Angiosarcoma
Route of Metastasis of Sarcomas?
Hematogenous
What is the most common type of soft tissue sarcoma that is associated with a high risk of local recurrence?
A) Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma
B) Gastrointestinal stromal tumors
C) Liposarcoma
D) Myxoid liposarcoma
D) Myxoid liposarcoma
What is the most common type of soft tissue sarcoma that is associated with a high risk of mortality?
A) Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma
B) Liposarcoma
C) Leiomyosarcoma
C) Leiomyosarcoma
All options are indicated for high risks in mortality but most common is Leiomyosarcoma
What is the recommended surgical approach for a patient with a soft tissue sarcoma that has invaded the surrounding neurovascular structures?
A) Radical amputation
B) Wide excision with removal of the adventitia or perineurium
C) Enucleation of the tumor
D) Radical lymphadenectomy
B) Wide excision with removal of the adventitia or perineurium
A 55-year-old patient is diagnosed with a 10 cm soft tissue sarcoma in the thigh. The tumor is located pressed against tissues forming a pseudocapsule. What is the recommended surgical approach?
A) Radical amputation
B) Wide excision with 1-2 cm margins
C) Enucleation of the tumor
D) Surgical re-excision with adjuvant radiation therapy
B) Wide excision with 1-2 cm margins
What is the recommended approach for a patient with a soft tissue sarcoma that has a positive surgical margin (R1 resection)?
A) Observation with close monitoring
B) Adjuvant radiation therapy
C) Surgical re-excision if feasible
D) Adjuvant chemotherapy
C) Surgical re-excision if feasible
Isolated Limb Perfusion was performed after a sarcoma was spotted in the thigh region of a patient. Which vessels are to be isolated in this case?
A. External Iliac
B. Femoral/Popliteal
C. Axillary Vessels
A. External Iliac
Isolated Limb Perfusion was performed after a sarcoma was spotted in the leg region of a patient. Which vessels are to be isolated in this case?
A. External Iliac
B. Femoral/Popliteal
C. Axillary Vessels
B. Femoral/Popliteal
Isolated Limb Perfusion was performed after a sarcoma was spotted in the upper extremities of a patient. Which vessels are to be isolated in this case?
A. External Iliac
B. Femoral/Popliteal
C. Axillary Vessels
C. Axillary Vessels
How is the Isolated Limb Perfusion technique performed?
Inducing high perfusion of TNF-a with Melphalan under hyperthermic conditions → Local Control of tumor
What are the different modes of radiation therapy available for soft tissue sarcomas?
A) External Beam Radiotherapy (EBRT)
B) Brachytherapy
C) Intensity Modulated Radio Therapy (IMRT)
D) All of the above
D) All of the above
What are the potential complications of radiation therapy for soft tissue sarcomas?
A) Wound dehiscence
B) Increased risk for recurrence
C) Pain
D) All of the above
A) Wound dehiscence

A 45-year-old patient is diagnosed with a high-grade soft tissue sarcoma in the thigh. The tumor is resectable, but the patient is at high risk for distant metastases. What is the recommended systemic therapy approach?
A) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy
B) Adjuvant chemotherapy
C) Concurrent chemoradiation
D) Targeted therapy
B) Adjuvant chemotherapy
A 60-year-old patient is diagnosed with an unresectable soft tissue sarcoma in the abdomen. What is the recommended systemic therapy approach?
A) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy
B) Adjuvant chemotherapy
C) Concurrent chemoradiation
D) Targeted therapy
A) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Downsize tumor and observe response
What are the standard chemotherapeutic agents used in the treatment of soft tissue sarcomas?
A) Doxorubicin and ifosfamide
B) Gemcitabine and docetaxel
C) Pazopanib and bevacizumab
D) Both A and B
D) Both A and B
What is the purpose of using neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the management of soft tissue sarcomas?
A) To downsize the tumor and increase the chances of a R0 resection
B) To improve local control
C) To reduce the risk of distant metastases
D) All of the above
A) To downsize the tumor and increase the chances of a R0 resection
What is the purpose of using concurrent chemoradiation in the management of soft tissue sarcomas?
A) To improve local control
B) To enhance the efficacy of radiation therapy
C) To reduce the duration of treatment
D) All of the above
D) All of the above
Concurrent Chemoradiation - is a radiosensitizer (SYNERGISTIC EFFECT)
Decreases treatment time
Quicker control of local disease
Which among these histological types of sarcomas are chemosensitive? (Standard chemotherapy works)
Options:
A. Synovial Sarcoma
B. Pleomorphic Liposarcoma
C. Clear Cell Sarcoma
A. Synovial Sarcoma

Which targeted therapies is commonly used for GIST?
Imatinib
Sunitinib
Sorafenib
TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITORS → TARGETS CD117 (CKIT receptor)
Which of the following targeted therapies is commonly used for Angiosarcoma?
A) Bevacizumab
B) Sorafenib
C) Sunitinib
D) Pazopanib
A) Bevacizumab
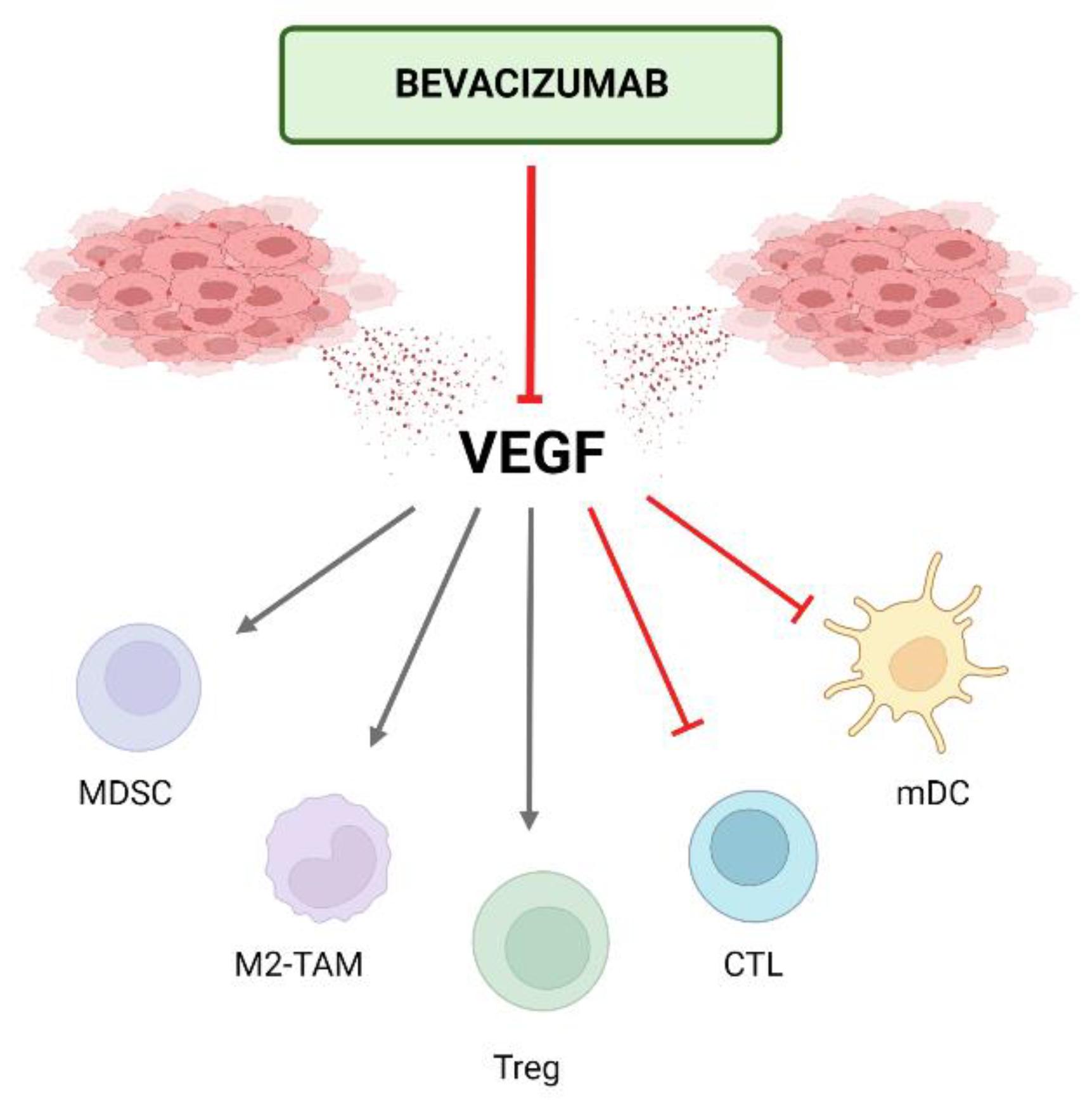
Which of the following targeted therapies is commonly used for hemangioendotheliomas?
A) Imatinib
B) Sunitinib
C) Pazopanib
D) Sorafenib
C) Pazopanib
Angiogenesis inhibitor
targets VEGF receptors