AQA GCSE History: Medieval Medicine
1/149
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
Miasma
A noxious or poisonous atmosphere. People believed this was created by putrid smells and/or sin.

Privies / Latrines
Other words for toilets (non-flushing in the Medieval Era)

Guilds
Set and checked standards for traders. They would fine producers if their quality dropped.

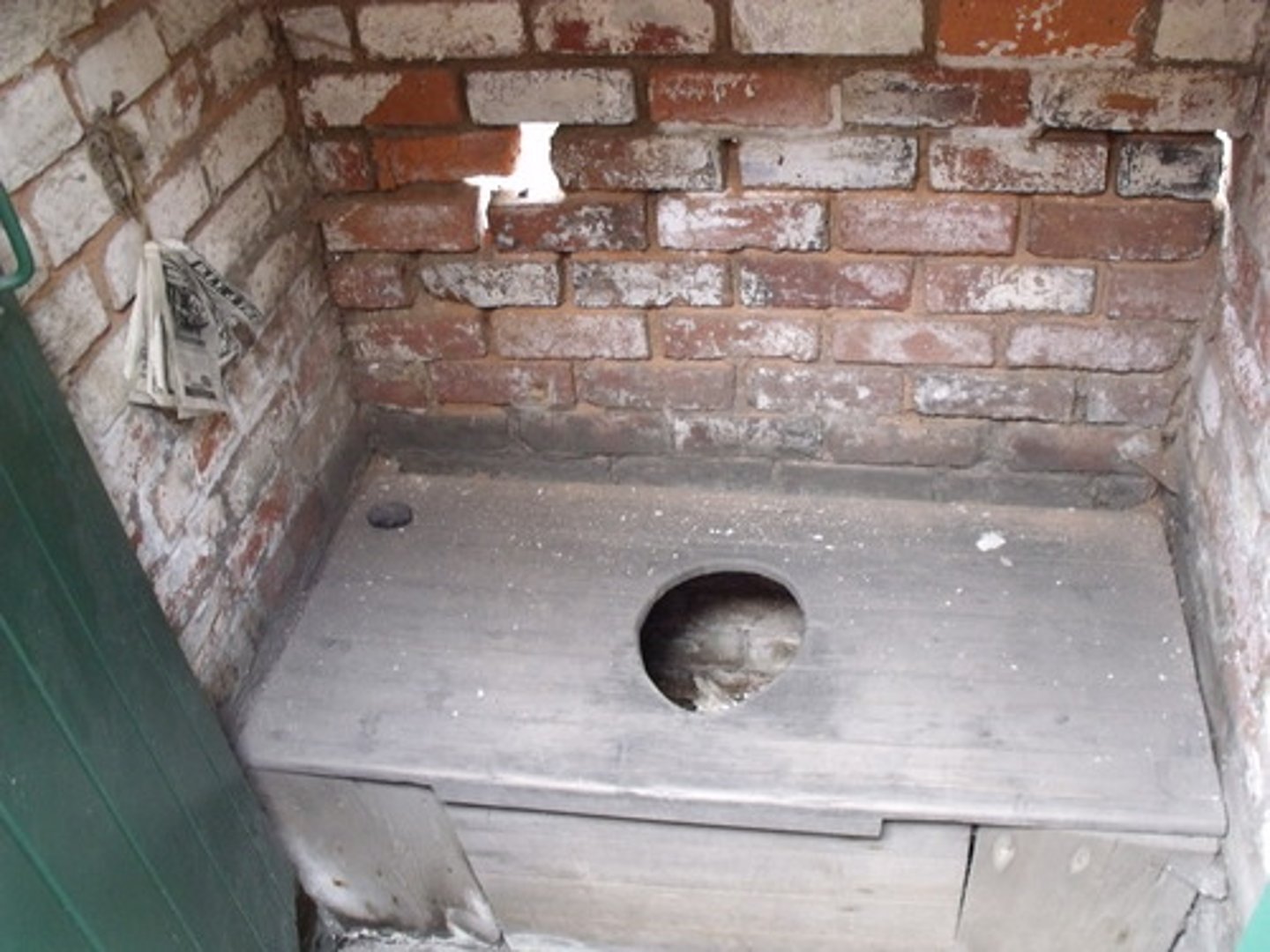
Cesspit
A place where many people emptied their human waste (feces), if they didn't empty it on the street.
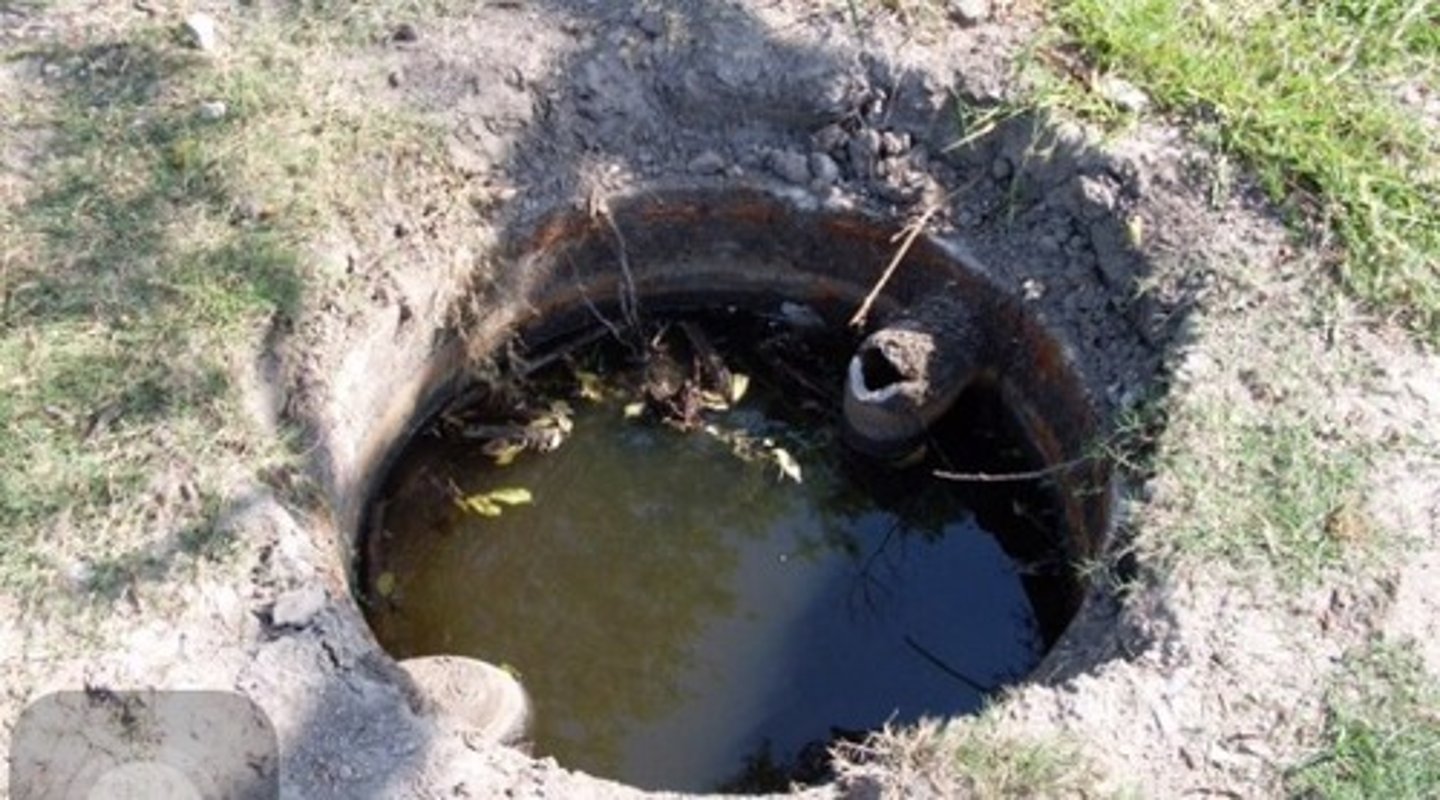

Gongfermers
Person who cleans out cesspits. They earned a good wage and formed their own guild.
Public Latines
Public toilets built in many cities such as Hull, Winchester, London and Leicester

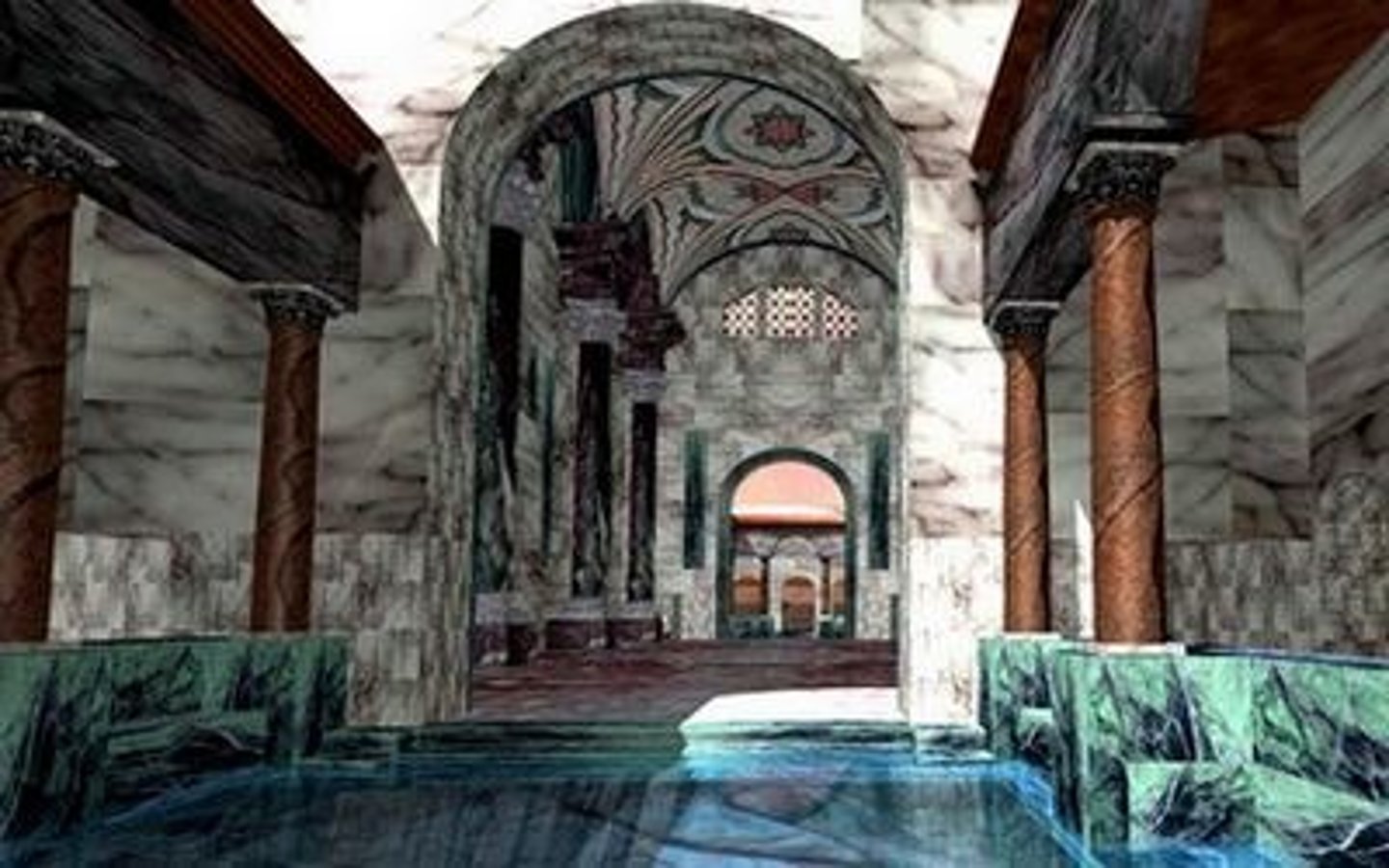
Stews
Public bathhouses where people could pay to have a bath. They also served as brothels. Were closed during plague years ie) London 1417

Lord Mayor
Head of the civic government of London. Usually a wealthy townsman and guild member.

Juries
Groups of cooks and food sellers that would judge and punish people selling 'putrid' or 'corrupt' food.

Carlisle
A town where money had to be spent on town defences against the Scottish, meaning Public Health was very poor
Coventry
Introduced 12p fines for those who didn't clean the street, waste dumps were set up at 4 locations on the outside of the town and waste (latrine and junk) dumping in the River Sherbourne was banned

York
Given orders to clear filth from the streets by Edward I during his wars with the Scots.

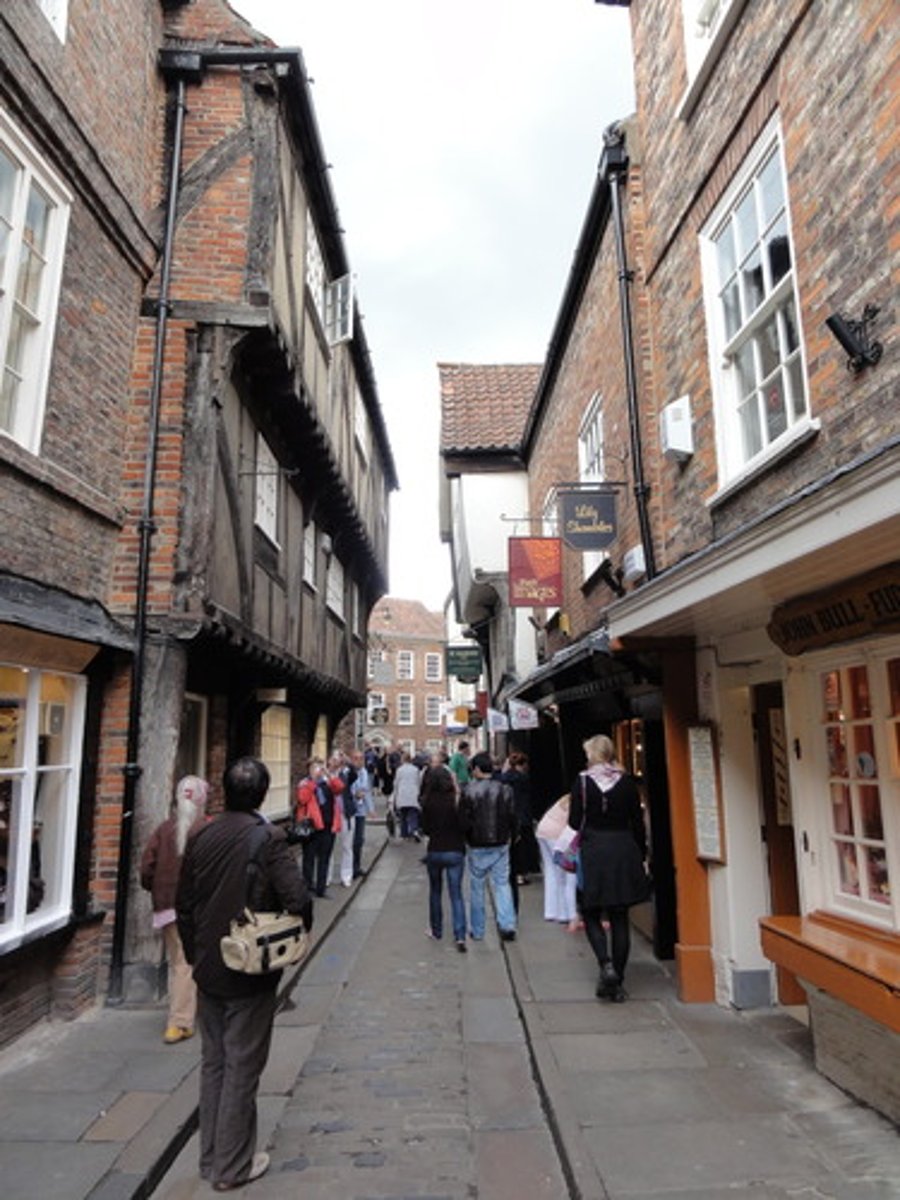
The Shambles
A narrow medieval street in York. The top floors overhang the street to make more indoor space. Lots of butchers, bakers etc. worked on streets like this. Not good in times of disease because they were cramped and full of food waste.

Bristol
Had many by-laws moving dungheaps, lepers and prostitutes to the outskirts of the town - similar to Coventry

London
Edward III gave an order in 1349 that "faeces and other filth" should be removed from London and that the city should be "cleansed from all odour".

London Conduit (1247)
The first major water supply for a town in England since the Roman Era. A huge lead pipe brought 'clean' water from out of town. The River Thames was basically a cesspit
Dick Whittington
Lord Mayor of London in the 1390s and early 1400s. He gave money in his will for drainage systems and a public latrine seating 128.
White Book
A list of regulations about keeping people healthy in London. Written down in 1419 due to the death of many officials in a plague outbreak.

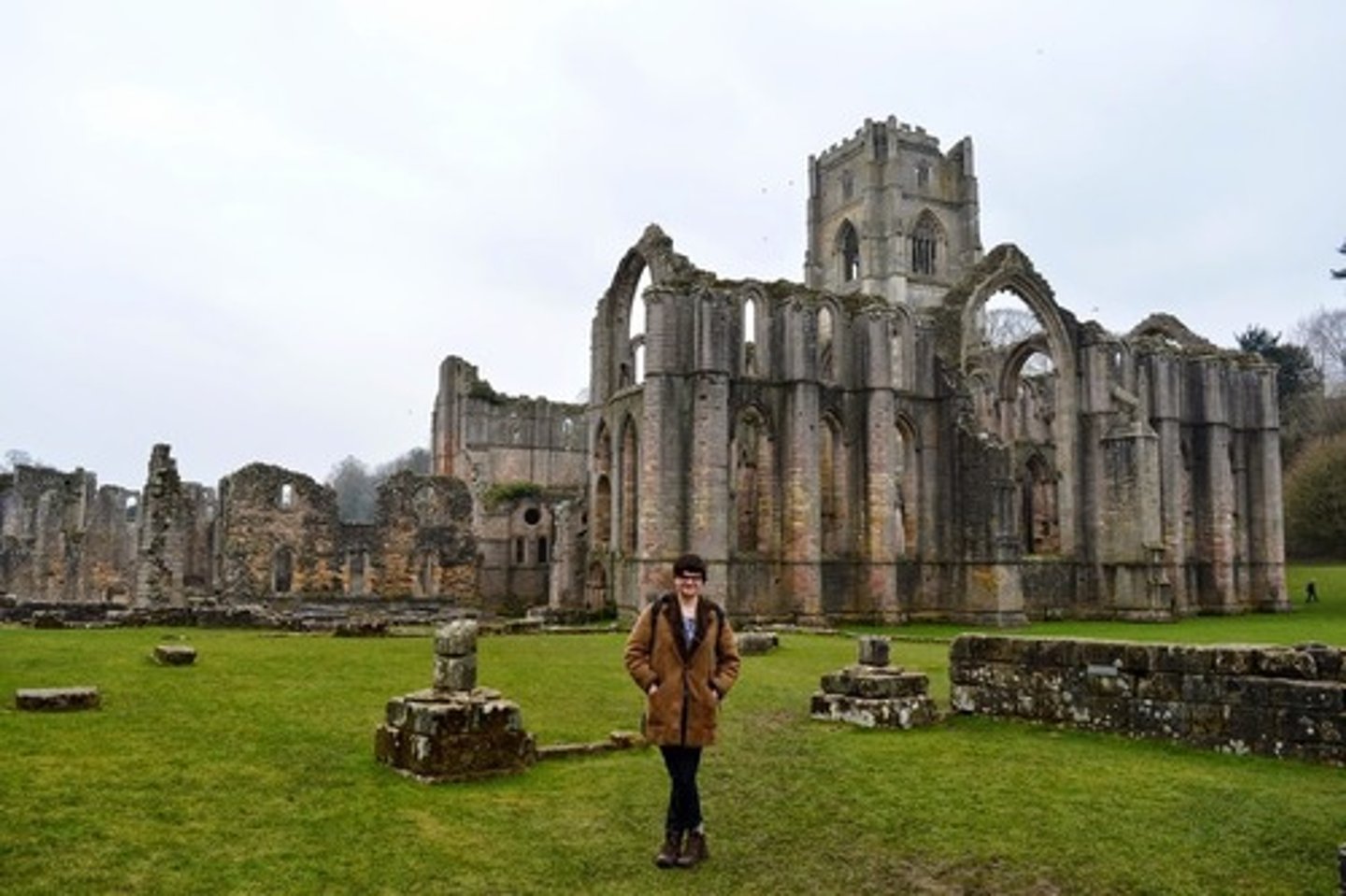
Fountains Abbey
Had an infirmary for the sick, blocks of latrines, and pure spring water carried in pipes.

Prestige
Wealthy citizens of towns received status and a good reputation for funding public health improvements. Many thought it was their Christian duty

Physic Garden
A place in a monastery where plants were grown. Herbs would be sold in the towns and the money used to buy luxury goods like aniseen, wine, liquorice and olive oil. The monks lived well

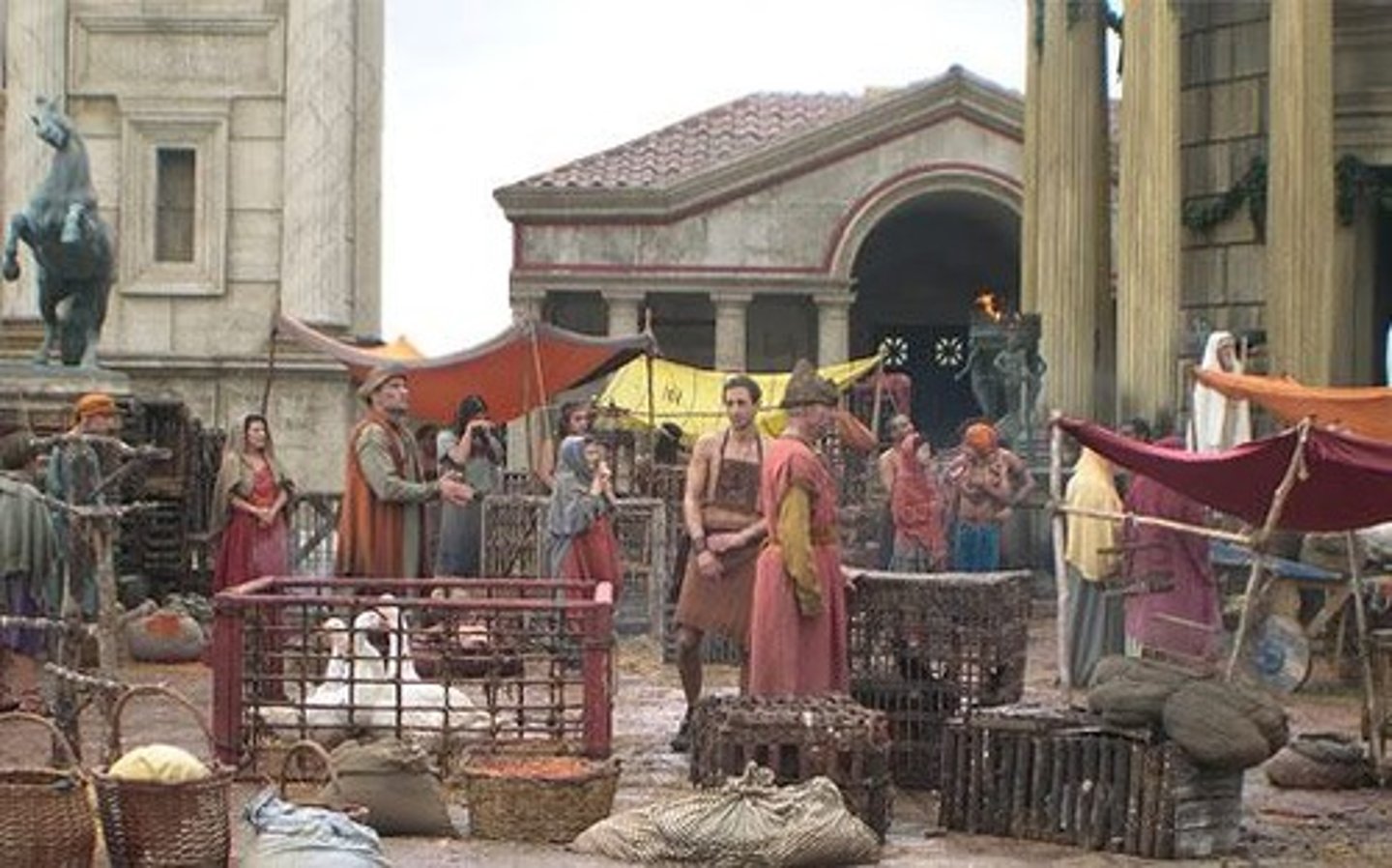
Market
Where goods and services were bought and sold in a town. Usually once or twice a week. Lots of animal carcasses and waste left behind.

Fragrant gardens
In the towns people with gardens grew flowers to get rid of miasma, as they thought it caused diseases. These flowers were used in posies and pomanders

Posies and pomanders
Masks or objects full of fragrant flowers and herbs. The aim of carrying these was to ward off miasma

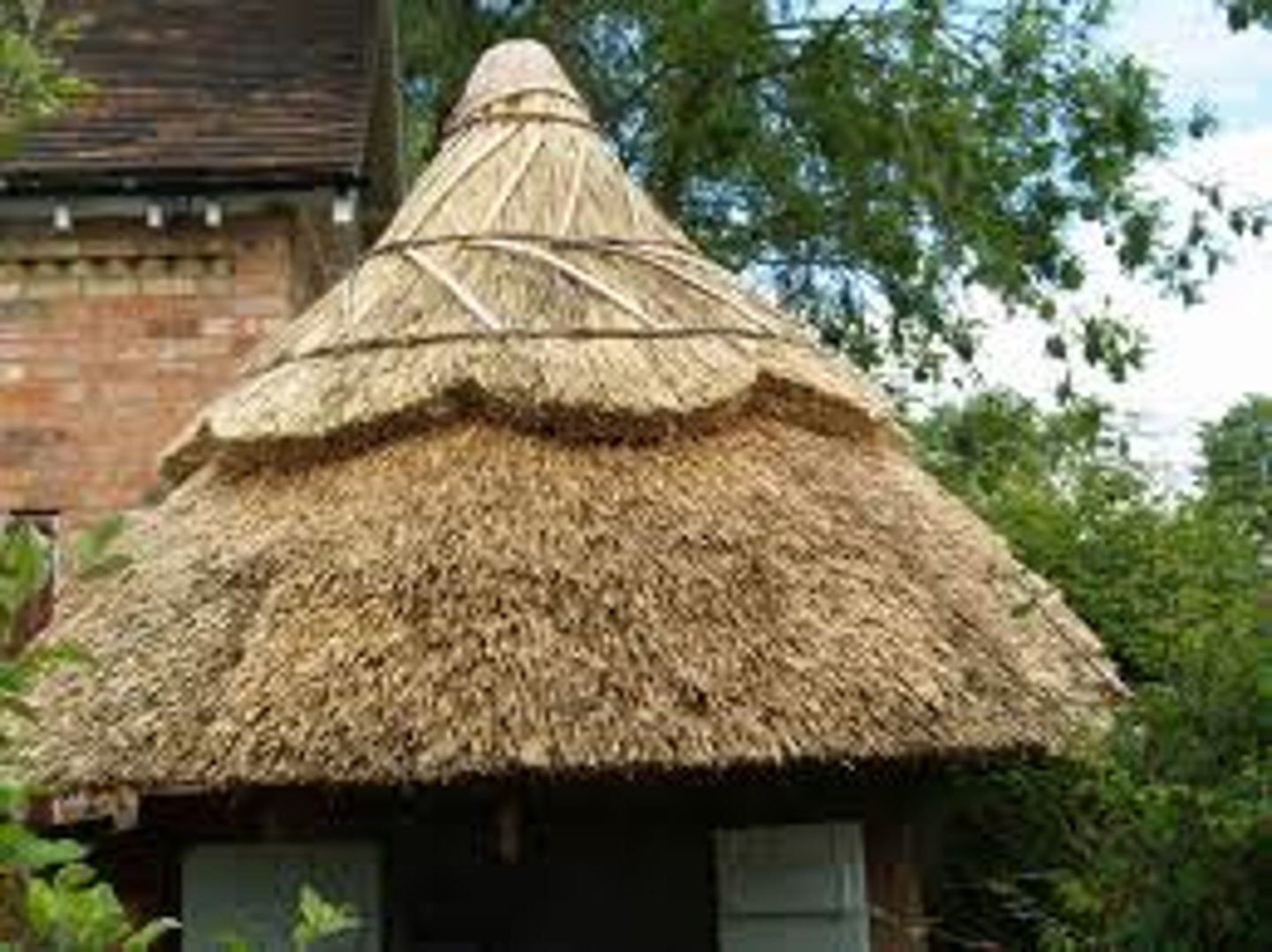
Thatched roofs
Roofs made of layers of thick straw or reeds. Rats made their nests in them. This was terrible in times of Plague

The Black Death (1348-49)
The deadliest pandemic in History, thought to have killed 75-200m people worldwide. In England it killed approximately 1/3 of the people in the countryside and upto 1/2 people in towns
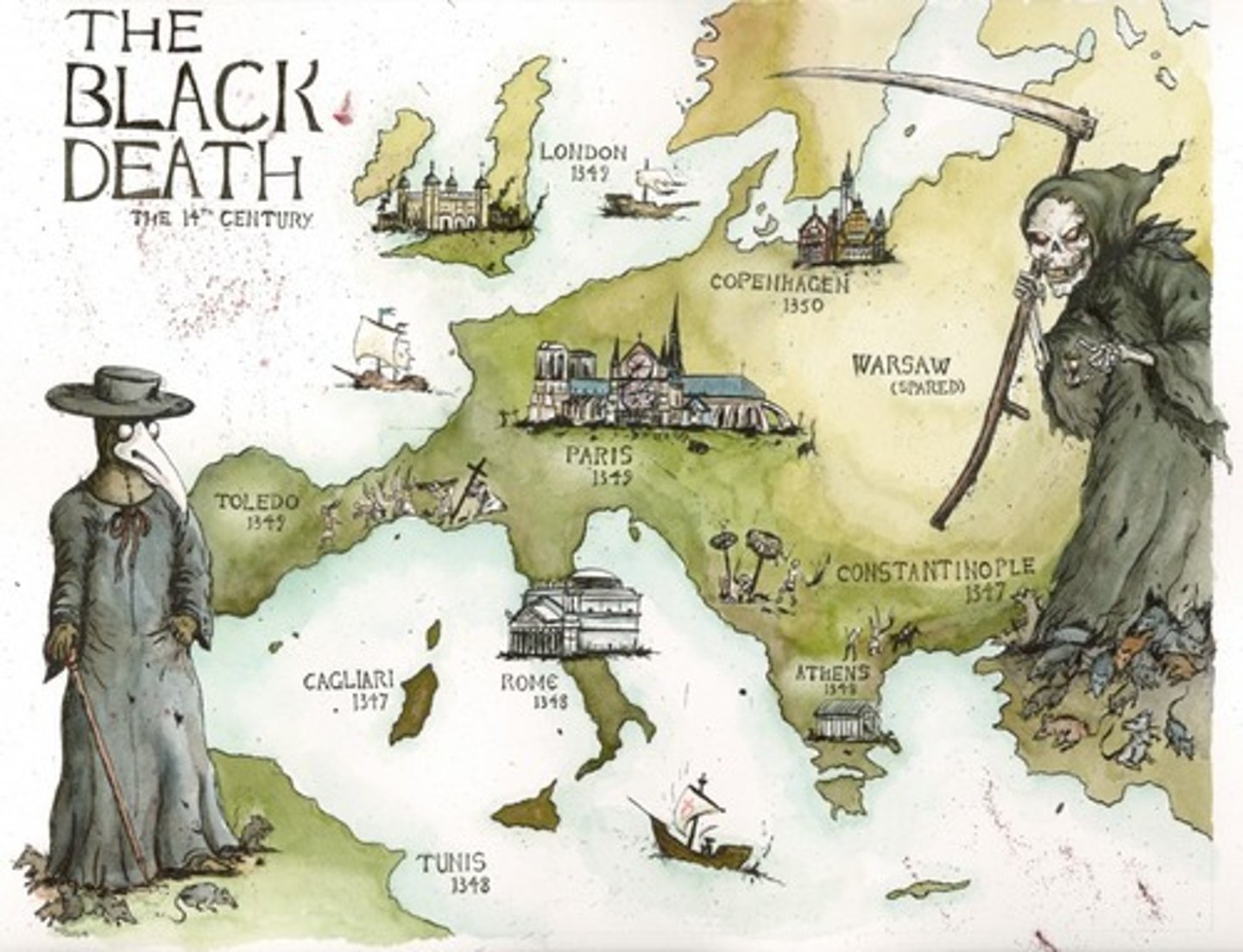
Actual cause: Bad harvests in 1347/48 (Black death?)
The public wasn't as strong due to malnourishment, meaning they were more likely to catch it or get terrible symptoms

Actual cause: Trade routes
The trade ships carried the disease from places like China which already had Black Death. Rats and people from the ships and possibly cargo carried germs.
Actual cause: Bubonic plague strains
The most common version of the plague. Spread by fleas carrying the bacteria from rats to humans

Buboes
Huge blisters, full of puss, that formed around the glands of the infected people (armpits, crotch, under neck and elsewhere)
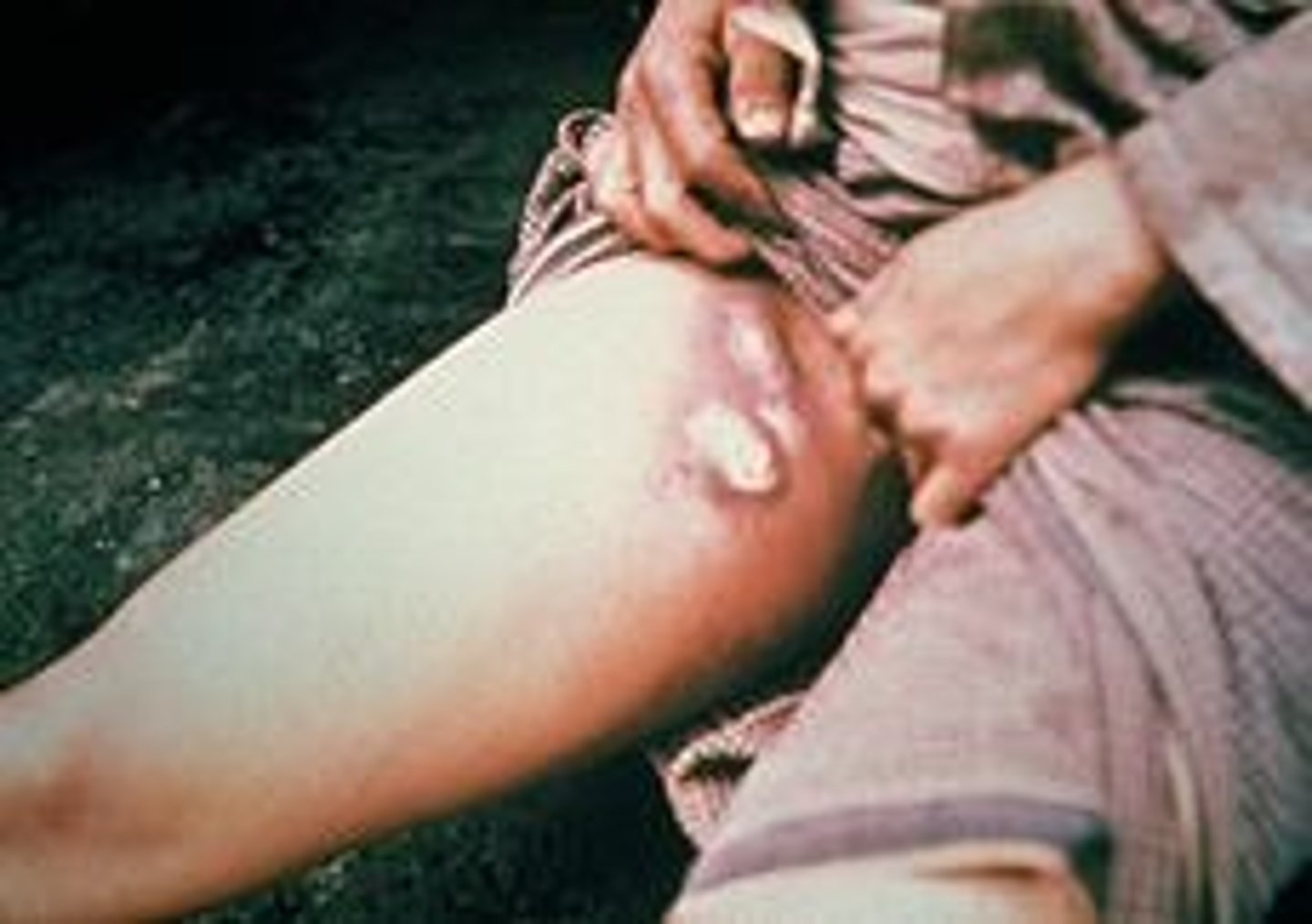
Actual cause: Pneumonic plague
An airbourne version of the same disease which was even more deadly and killed in less than 3 days. Around at the same time
Ideas about cause: Religion
God's punishment for the world's sins. There was a huge earthquake in China in 1347 and many thought that was a punishment from God. Also, many questioned their own sins.

Ideas about cause: Astrology
3 years before Black Death there was unusual alignment of planets. Believed to be a sign on something wonderful or terrible to happen

Ideas about cause: Miasma
Bad miasma coming from the fumes from volcanic eruptions.

Ideas about cause: The Jews
Many blamed Jewish people, accusing them of poisoning water supplies. Anti-Semitism in an earlier form.

Prevention: Religous
The Church told people to pray regularly. Some people wandered around the streets in groups whipping themselves (known as self-flagellation.)
Prevention: Escaping
Many people escaped the plague and got as far away from it as possible. However, often they had been infected but were not ill so they spread the disease to where they moved to.
Prevention: Miasma
People carried posies or fragrant herbs to drive away the bad airs. The theory was they were breathing in good air and not bad air.
Prevention: Quarantine
Local governments tried to quarantine (isolate) infected houses. It didn't work because they couldn't enforce it and the Church insisted that people still attended Church.

Prevention: Effective measures
Clean the streets more (as ordered by Edward III in London), avoid those with the plague already and don't have too much sex (they thought the excitement would give you the Black Death, but it was more likely prostitutes and contact with many men)
Treatments: Religious
Asking God for forgiveness through prayer or confessing your sins. Many prayed, made donations to the Church and tried doing more good deeds
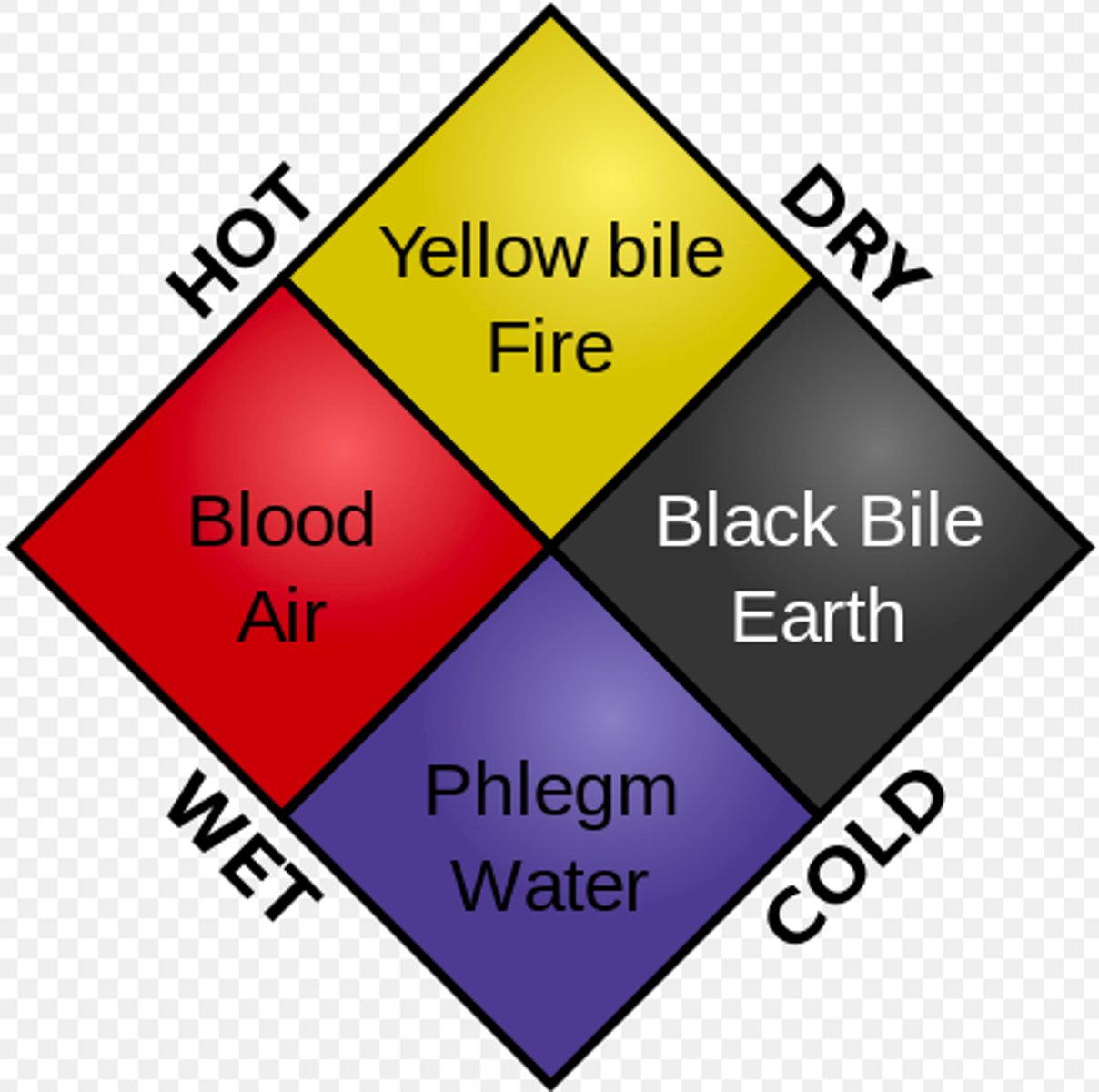
Treatments: 4 Humours
At the beginning of outbreak physicians tried normal treatments but these didn't help. People then turned to religious or radical treatments.
Treatments: Herbal Remedies
Strong smelling herbs, like aloe myrrh believed to have cleansing properties. Apothecaries sold remedies but many of them were mixed at home and made into posies

Treatments: Miasma
People believed lighting a fire or boiling vinegar would drive of the bad air on sick people.

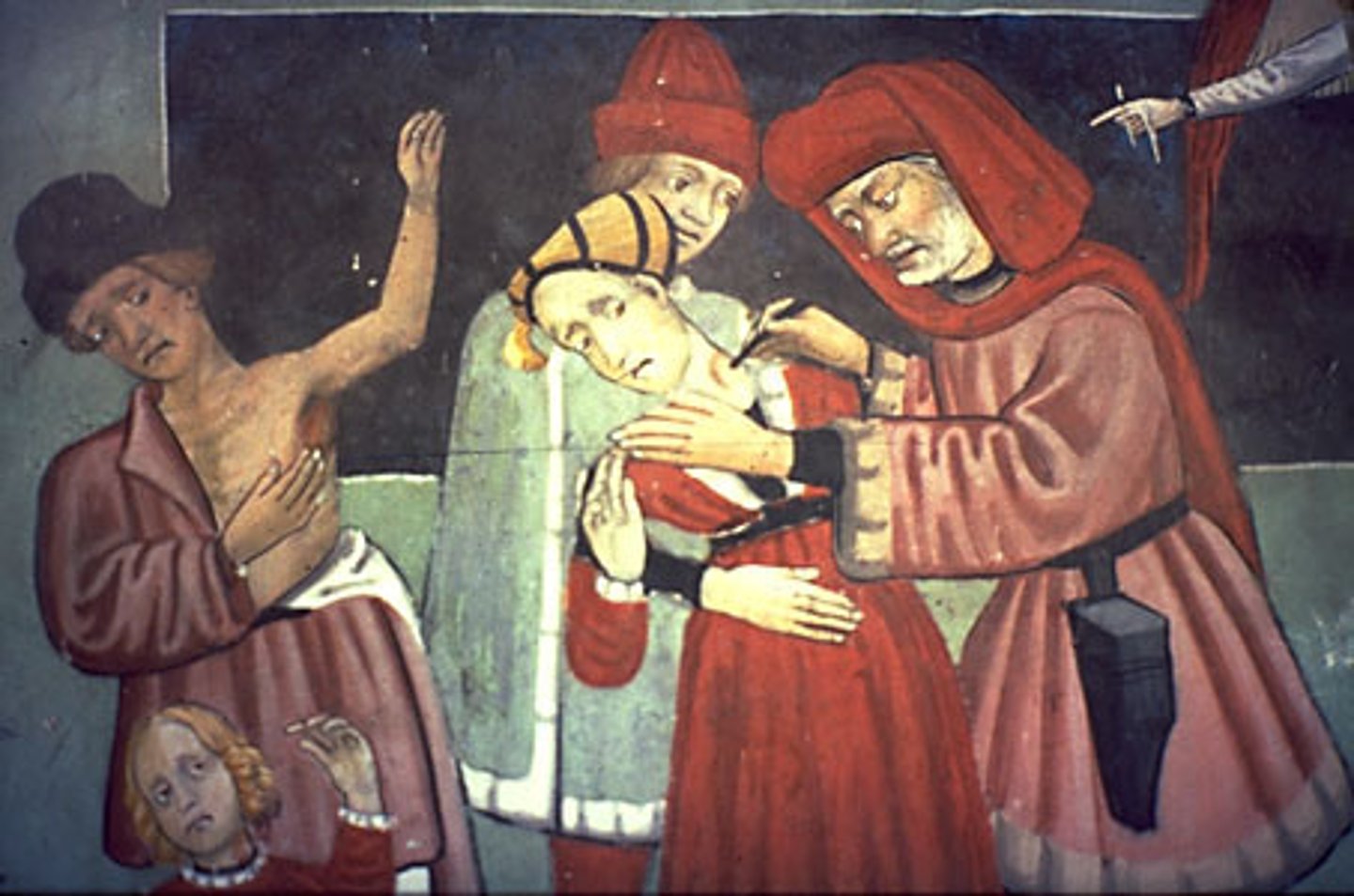
Treatments: Surgery
Sometimes barber surgeons would lance (cut open) the buboes, squeezing out all of the pus. Occasionally this helped the victim survive.
Pious / Devout
Committed to religion. Medieval society in Britain was very Christian and many believed the teachings of God and that Heaven and Hell were real.

Deliverance
Praying to got to save you from disease, illness or other bad events

Indulgences
Could buy passage to heaven by making large donations/offerings to the Church

Pilgrimage
A Pilgrimage is a journey to a holy place or shrine undertaken as a spiritual quest to obtain supernatural help or as a form of penance for sins. A pilgrim is one who undertakes a pilgrimage.

Holy Wars
Some historians have claimed that the church's encouragement of the Crusaders moved funds away from hospitals and health towards wars.

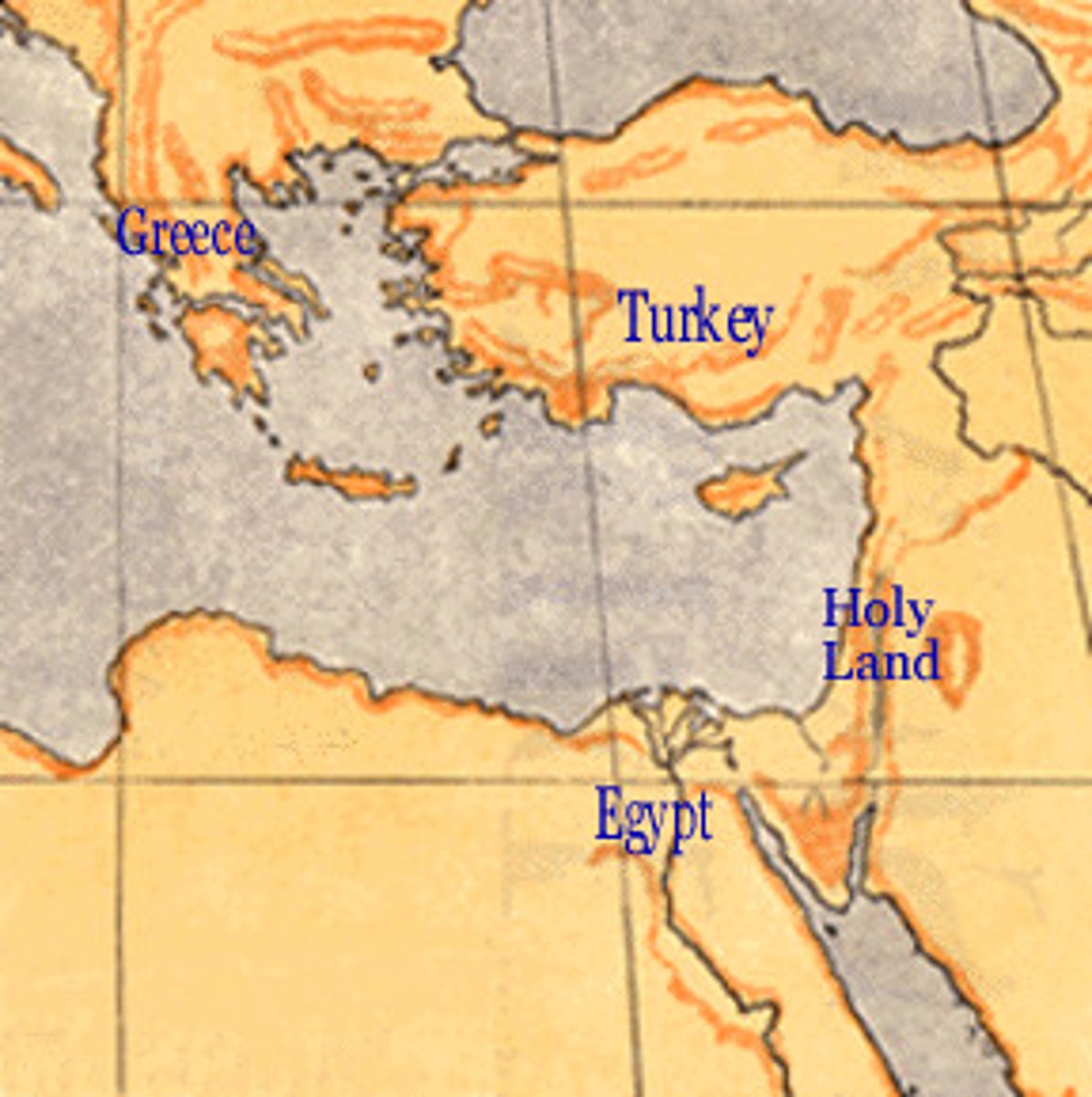
The 'Holy Land'
Travelling on a Crusade to take over modern day Palestine/Israel in the name of Christianity. Contains places of holy significance like Bethlehem and Jerusalem. This was seen as the ultimate pilgrimage
St John of Bridlington
Made a saint (canonised) for his work at Bridlington Priory in 1404. He was known for being generous, holy and rumours about his miracles travelled far and wide. A site of pilgrimage, especially for sailors and women in labour.

Desecration
The belief that cutting up a persons body prevented them entering Heaven. This is why the Church banned dissections, and this prevented progress or challenge.
Roger Bacon
A monk and lecturer at Oxford Uni who was arrested and removed from his positions for questioning Galen's work and the word of the Church - 1277

Christian Duty
Many monasteries were used to care for the sick and ill, as it was seen as a holy thing to do
University schools of medicine
The church set up over 160 of these around Europe in the 12th/13th centuries to teach physicians in a way which centred around the 4 humours
Stagnation
When very little progress or change happens. The church caused stagnation in medical ideas during the Medieval Era

Islam
Is a monotheistic (single god) that teaches that Mohammad is the messenger of Allah (God)

Muslim
Someone who follows Islam and worships Allah

Prophet Muhammed
Seen as Allah's representative on earth in Islam. Related to medicine because in the Qur'an (Islamic bible) he wrote 'For every disease, Allah has given a cure' and many Islamic doctors saw it as their duty to find these cures.

Quran
The holy book of Islam (the equivalent of the bible)

Avicienna / Avi Senna (980-1037)
An Arabic doctor who translated the works of Greece and Rome into Arabic, allowing Arabic doctors to understand Western Medicine. Also wrote the 'Book of Healing' and the 'Canon of Medicine', discovered 760 different drugs, and diagnosed the conditions of anorexia and obesity.
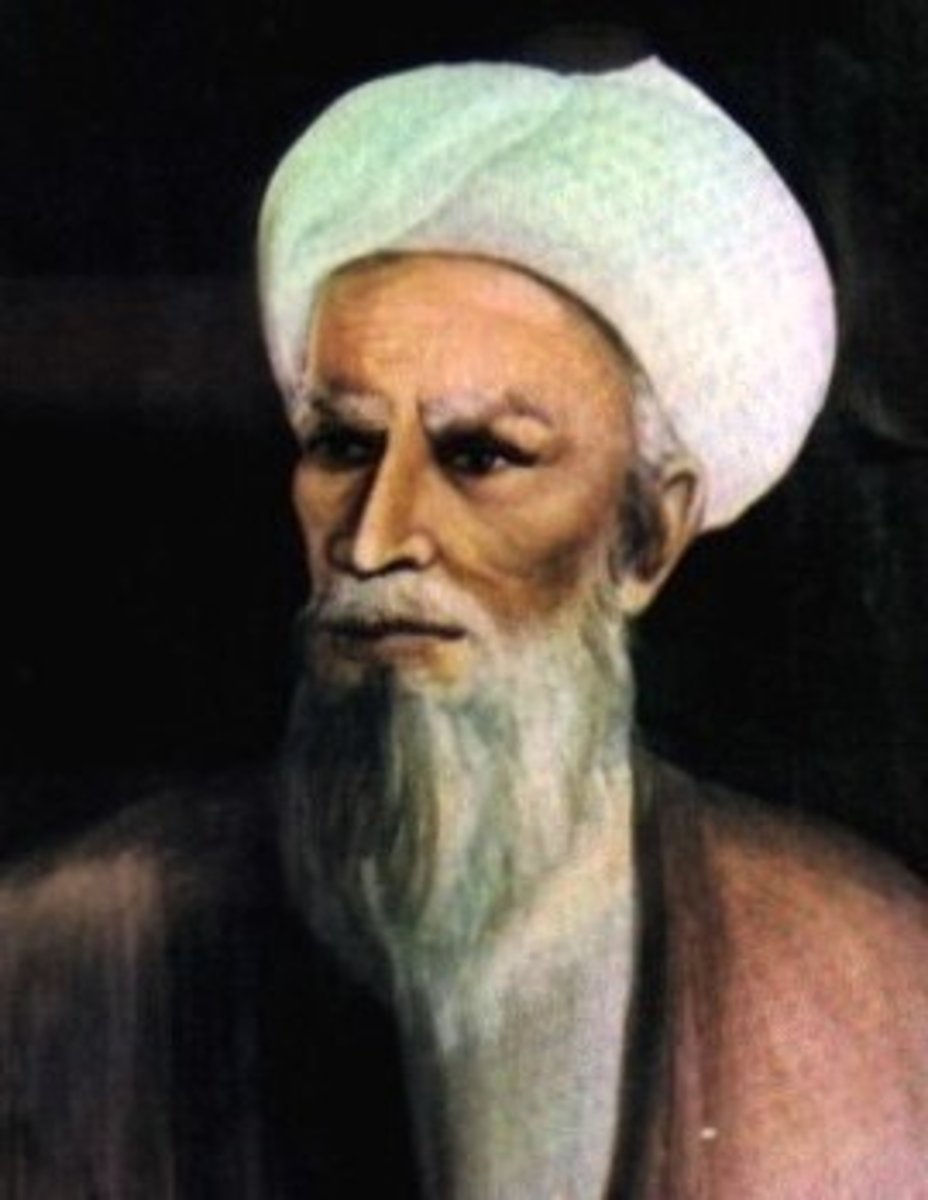
Rhazes (860-932)
An Influential Arabic doctor who wrote over 150 books, including the first known description of the symptoms of Smallpox and challenged the works of Galen in his book 'Doubts about Galen'

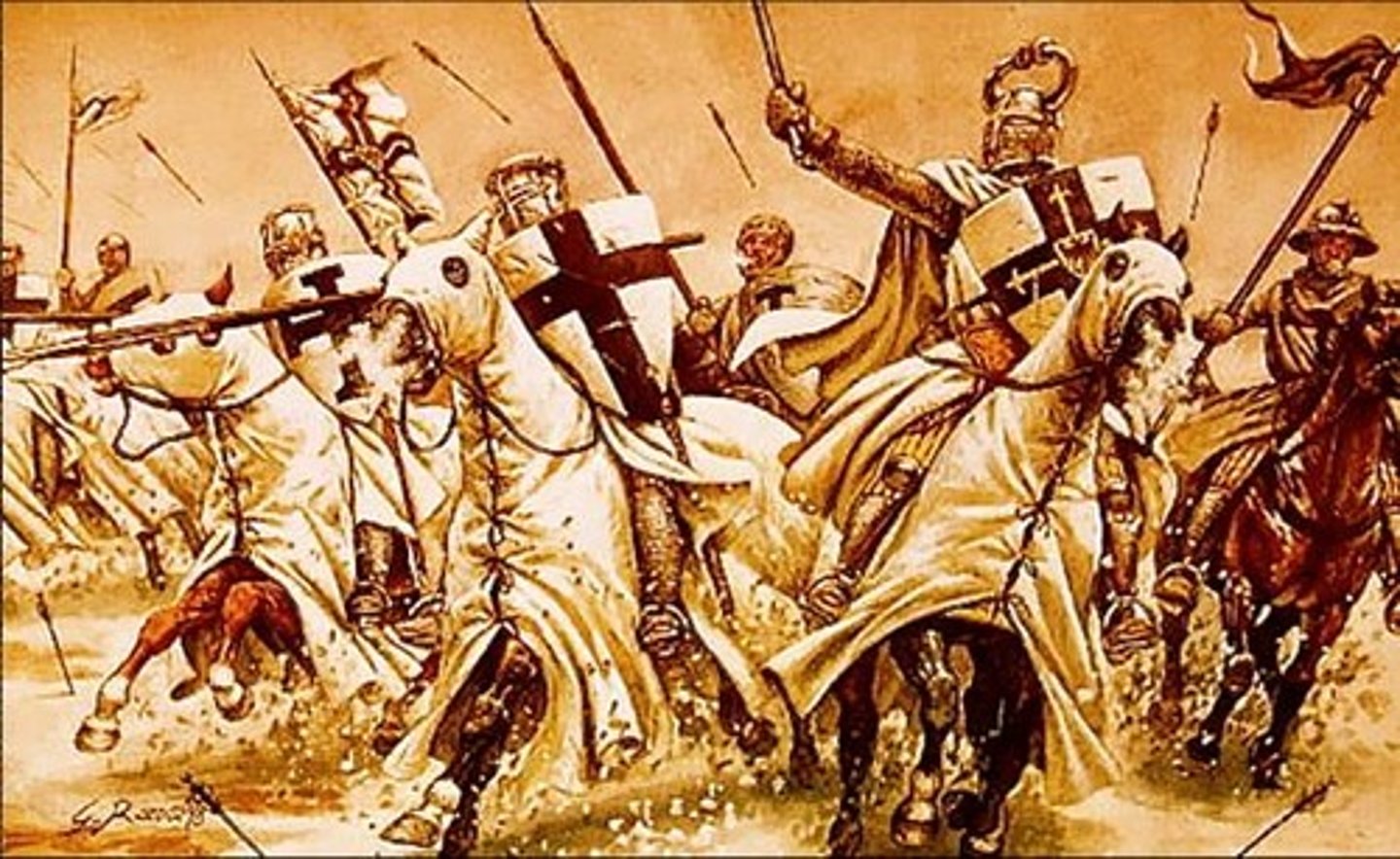
Crusades (1096-1270)
Holy wars were undertaken by European Christians to "free" the Holy Land from Muslim rule. The Crusades helped understanding of the anatomy

Ibn al-Nafis
In the 13th century, Ibn Al-Nafis claimed Galen was wrong thinking that blood was produced in the liver and that it fuelled the body. The thought (correctly) that blood passed through the heart via the lungs. However, Islam banned human dissection too, so he couldn't prove this until the 17th century, due to William Harvey's work

Communication void
When ideas were not spread easily. In the Medieval Era ideas from the Middle East didn't reach Britain due to lack of translation, no printing press and the restrictions of the Church

House of Wisdom
Otherwise known as the Grand Library of Baghdad (Iraq), it was the largest medical library in the world during the medieval era.

University of Padua and Bologna
The only medical universities where doctors from Christian countries may have come into contact with Islamic ideas
Islamic Hospitals
Were far more developed than Christian hospitals because they had pharmacies, lecture rooms, libraries and actively sought to treat patients as opposed to just care ie) they had isolation units for people with contagious illnesses

Hospitality
Welcoming travellers or pilgrims, where the word 'hospitals' came from

Monastery
Abbeys and priories which were associated to the English Church (Roman Catholic). Housed monks / nuns and supported communities throughout England.
Care not cure
The majority of hospitals in the Middle Ages just looked after people, but did not treat them. They were MOSTLY places where people to go to die, in care, or become well, in care.

Endowment
Charitable donation used to set up and run a hospital
Prayer
A spirutual communication with God. Typical "treatment" in a medieval hospital

Almoner
Gave food to the poor

Almshouses
Set up to provide a home for the old and help for those who couldn't find work

Abbot
Head of the monastery who directed all of the monks

Monk
Monks spent a lot of time praying or completing educated work

Novice
A trainee monk. They often did labouring or work on the grounds of the monastaries.
Poverty, Chastity, Obedience
3 vows/rules all monks or nuns had to agree to. Poverty (give up all posessions), chastity (no sex, marriage or children) and obedience (obey the orders of God)
The Black Death
When the bubonic/pneumonic plague killed between 75-200m people globally, between 1348-49

Monastic responsibilities
Follow vows, help the poor and sick, shelter travellers and educate people
Monastic orders
Benedictine, Cistercians, Augustinians - differents types of monks doing things in a slightly different way

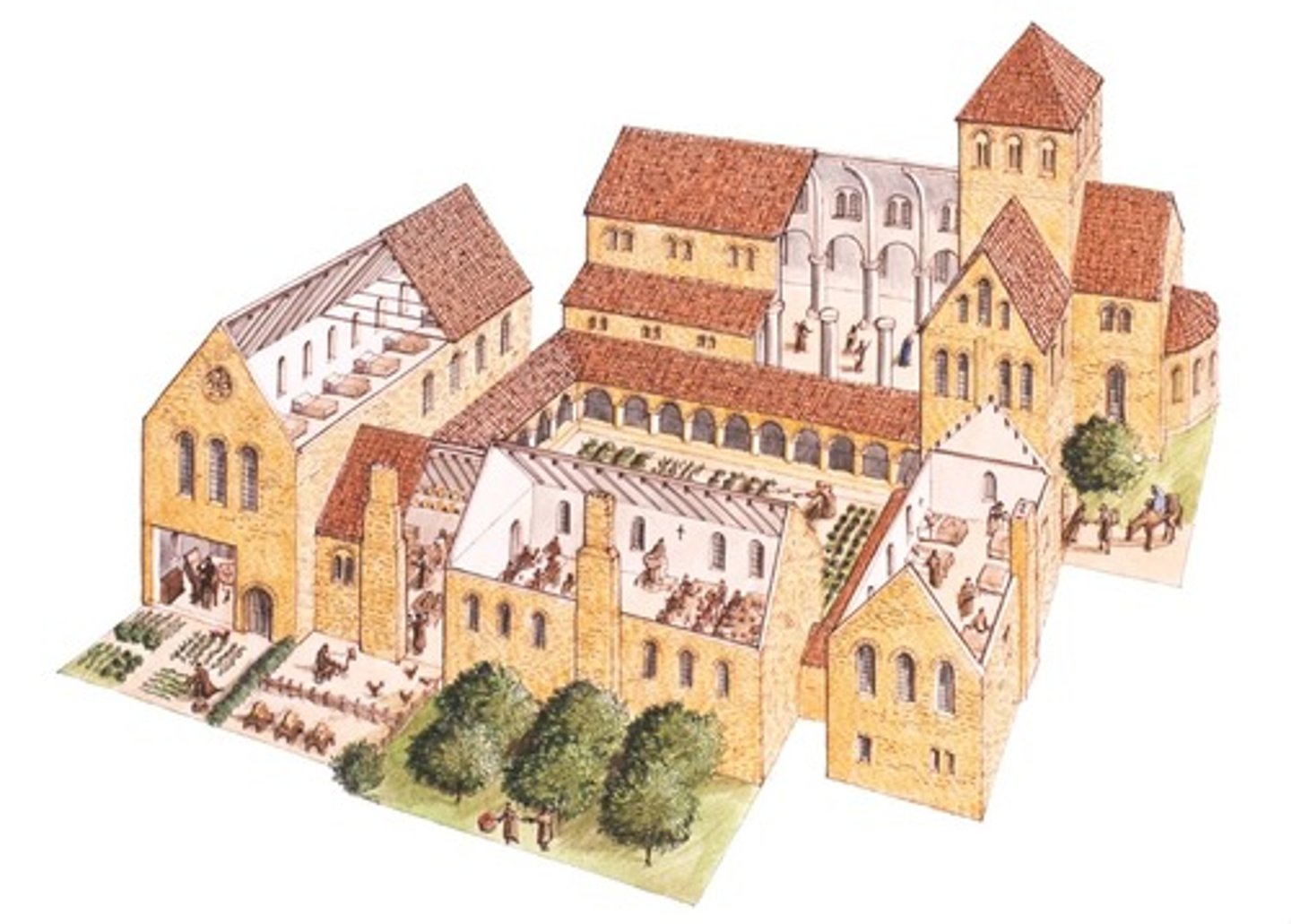
Monastery buildings
Church, almonry, cloisters, refectory, infirmary, dormitory, scriptorium, fruit and veg garden, fields
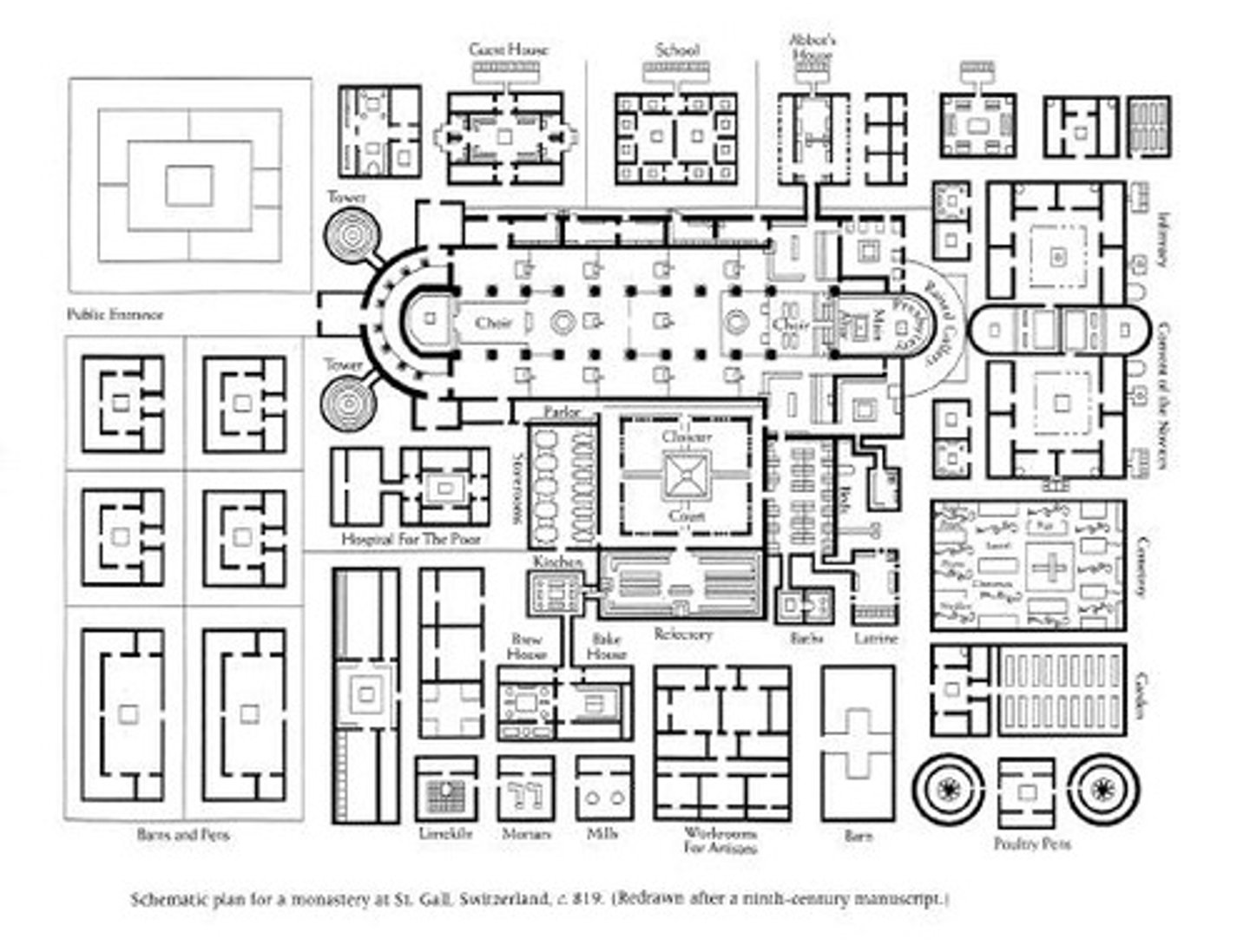
Principal monks
Abbot, infirmarian, sacristan, almoner
New orders
Friars were founded, wandered around preaching and looking after poor and sick, most important were Dominicans (black friars) or Franciscans (grey friars)
Purgatory
A halfway house between Heaven and Hell that is like Hell, but only temporary until sins have been paid for. Only exists in the Catholic Church.
St Giles Hospital
A hospital in Norwich, named after a saint linked to the infirm, lepers and nusring mums, was set up. Bishop Giles had left everything he owned to fund it and got support from others to fund it as payment for his sins, in the hope he would pass through Purgatory more quickly

Soutra
A location on the main road from England to Scotland where a hospital set up by Augustine monks existed that shows clear evidence of herbal remedies - challenging the idea of 'care, not cure'
Lazar
Leper houses, usually outside the city/town in order to keep them away from other people

Hospital of St John
This hospital in Bridgewater did not allow lepers, lunatics, pregnant women, young children or anyone who had a known contagious disease

St Bartholomew's Hospital
Set up in London in 1123, it was the first specialised in the treatment of poor, pregnant women
St Mary of Bethlehem Hospital
Established in 1247, specialised in the treatment of 'poor and silly persons'

Barber Surgeon
A man, who underwent 6 months training, that did surgical operations and cut the hair of his patients

Dissections
Cutting apart a dead body to discover more about how it works. Banned by the Church.
Infection
When a wound isn't treated with anything to kill bacteria. The bacteria infects the wound and can lead to death
Cauterising
Using hot iron pressed against a wounded area to seal the wound through burning the flesh dry

Hole Saw
A tool used to create a neat hole in the skull of patients with a headache (only the best had them)

John Bradmore
A surgeon who created the Bradmore screw (a special tool which can grip and pull things) to remove an arrow head from the skull of Prince Henry (later Henry I)
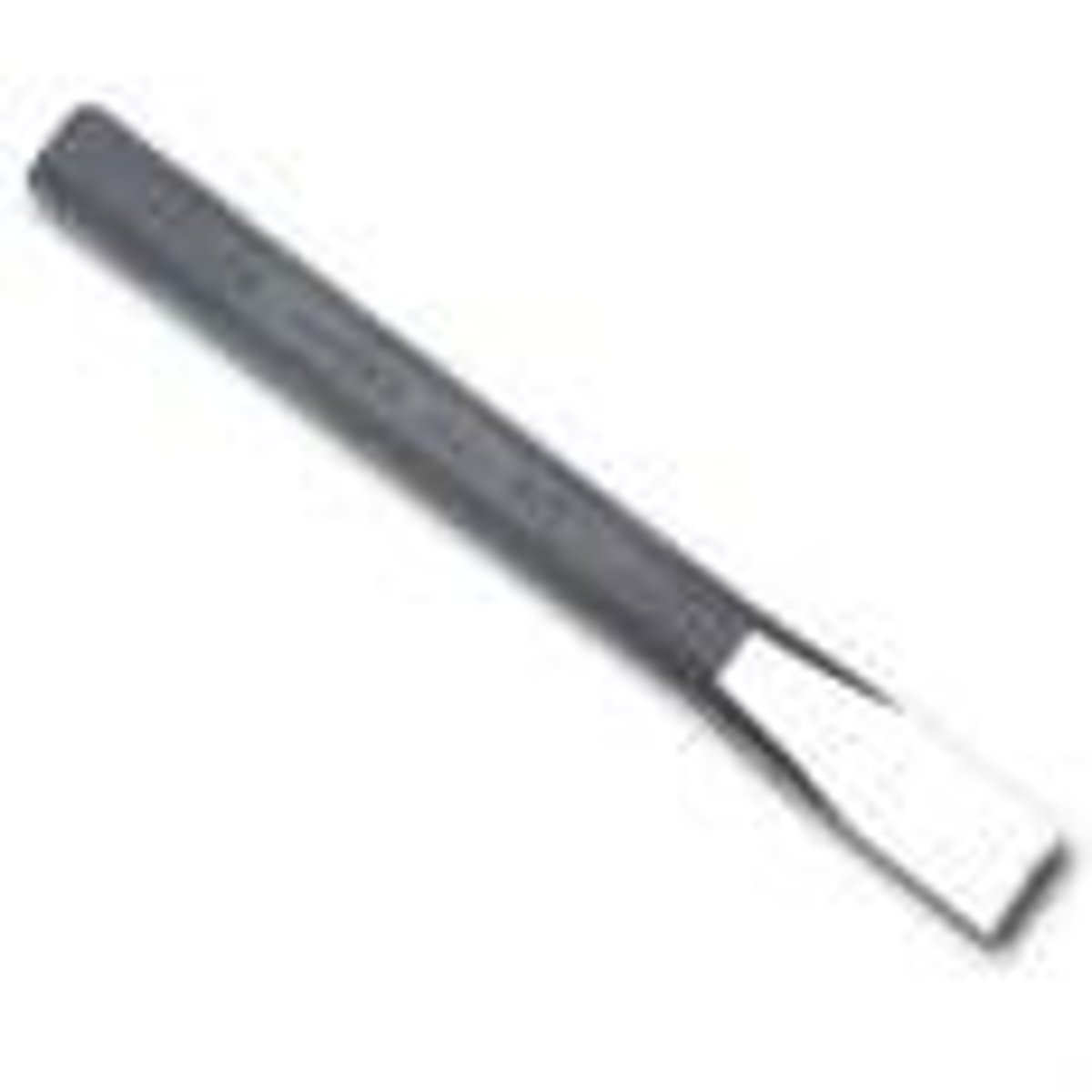
Chisel
A tool used to make a hole in the skull of a patient with a headache
