Genetics exam 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Genetics
Study of hereditary and the variation of inherited characteristics.
Central Dogma
The process in molecular biology that describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein.
Systematics
The branch of biology that deals with the classification of organisms and their evolutionary relationships.
Artificial Selection
Process where humans intentionally breed specific organisms with desirable traits.
Eugenics
The study or belief in improving the genetic quality of the human population, often associated with controversial and unethical practices.
Mitosis
A type of cell division where a single cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells.
Meiosis
A specialized form of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four genetically different haploid cells.
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes that are alike in size, shape, and genetic content.
Locus
The specific physical location of a gene on a chromosome.
Diploid
A cell or organism that has two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
Haploid
A cell that has a single set of unpaired chromosomes.
P53 Protein
A protein that regulates the cell cycle and functions as a tumor suppressor.
Crossing Over
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis, leading to genetic variation.
Chiasmata
The points at which paired chromosomes exchange genetic material during meiosis.
Chi-square Test
A statistical method used to determine if there is a significant difference between expected and observed frequencies.
Mutation
Any heritable change in genetic information.
Cystic Fibrosis Gene Product
The protein involved in the movement of chloride ions across cell membranes, mutations can lead to disease.
Sickle Cell Disease
A genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the gene for hemoglobin, leading to misshaped red blood cells.
What is cell division?
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells.
What are the two main types of cell division?
The two main types of cell division are mitosis and meiosis.
What is the purpose of mitosis?
Mitosis is used for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction, producing identical cells.
What is meiosis used for?
Meiosis is used in the production of gametes for sexual reproduction, resulting in genetic diversity.
What is the role of spindle fibers in cell division?
Spindle fibers help separate chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis, ensuring proper distribution to daughter cells.
What occurs during prophase?
During prophase, chromosomes condense and become visible, and the nuclear envelope begins to break down.
What happens during metaphase?
During metaphase, chromosomes align at the cell's equatorial plane before being separated.
What is the significance of cytokinesis?
Cytokinesis is the final stage of cell division where the cytoplasm divides, resulting in two separate cells.
How does mitosis differ from meiosis?
Mitosis results in two identical diploid cells, while meiosis produces four genetically distinct haploid cells.
What is the role of checkpoints in the cell cycle?
Checkpoints are mechanisms that ensure the cell is ready to proceed to the next phase of the cell cycle, preventing errors.
What is interphase?
Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle where the cell prepares for mitosis by growing and replicating its DNA.
What occurs during prophase in mitosis?
During prophase, chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
What happens during prometaphase?
In prometaphase, the nuclear envelope is completely gone, and spindle fibers attach to kinetochores on the chromosomes.
What occurs during metaphase in mitosis?
During metaphase, chromosomes align along the equatorial plane of the cell.
What is anaphase?
Anaphase is the stage where sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell.
What happens during telophase?
During telophase, the chromosomes de-condense back into chromatin, and the nuclear envelope re-forms around each set of chromosomes.
What is cytokinesis?
Cytokinesis is the process that follows telophase, where the cytoplasm divides, resulting in two distinct daughter cells.
How long does mitosis typically last?
Mitosis usually lasts about one hour, depending on the cell type.
What is the role of the spindle apparatus?
The spindle apparatus is responsible for segregating chromosomes during cell division.
What are sister chromatids?
Sister chromatids are two identical copies of a chromosome, created during DNA replication.
Genetics
Study of hereditary and the variation of inherited characteristics.
Central Dogma
The process in molecular biology that describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein.
Systematics
The branch of biology that deals with the classification of organisms and their evolutionary relationships.
Artificial Selection
Process where humans intentionally breed specific organisms with desirable traits.
Eugenics
The study or belief in improving the genetic quality of the human population, often associated with controversial and unethical practices.
Mitosis
A type of cell division where a single cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells.
Meiosis
A specialized form of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four genetically different haploid cells.
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes that are alike in size, shape, and genetic content.
Locus
The specific physical location of a gene on a chromosome.
Diploid
A cell or organism that has two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
What is a gene?
A gene is a segment of DNA that contains the instructions for building a particular protein or set of proteins.
What is DNA?
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the molecule that carries genetic information in living organisms.
What is RNA?
RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a nucleic acid that plays an important role in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes.
What are nucleotides?
Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA and RNA, consisting of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
What are alleles?
Alleles are different versions of a gene that can produce variations in a trait.
What is a phenotype?
A phenotype is the observable physical or biochemical characteristics of an organism as determined by both genetic makeup and environmental influences.
What is a genotype?
A genotype is the genetic constitution of an individual, which determines a specific characteristic.
What is homologous recombination?
Homologous recombination is the process by which genetic material is exchanged between homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
What is a mutation?
A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that can lead to alterations in phenotype and can be inherited.
What is genetic drift?
Genetic drift is a mechanism of evolution that refers to random changes in allele frequencies within a population.
What is a genotype-environment interaction?
A genotype-environment interaction occurs when different genotypes respond differently to environmental pressures.
What is phenotypic plasticity?
Phenotypic plasticity is the ability of an organism to change its phenotype in response to changes in the environment.
What is natural selection?
Natural selection is the process by which organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
What is a pedigree?
A pedigree is a diagram that depicts the genetic relationships within a family, showing the inheritance of traits.
What is a karyotype?
A karyotype is a visual representation of the chromosomes in a cell, used to assess chromosomal abnormalities.
What are gametes?
Gametes are reproductive cells (sperm and egg) that carry half the genetic information of an individual.
What is fertilization?
Fertilization is the process by which a sperm cell unites with an egg cell to form a zygote.
What is dominance in genetics?
Dominance refers to the relationship between alleles, where one allele masks the expression of another in the phenotype.
What is recessive inheritance?
Recessive inheritance occurs when an individual expresses a trait only when two copies of the recessive allele are present.
What is the role of enzymes in DNA replication?
Enzymes such as DNA polymerase help synthesize new DNA strands by adding nucleotides complementary to the template strand.
What is a chromosome?
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule that contains many genes and regulatory elements.
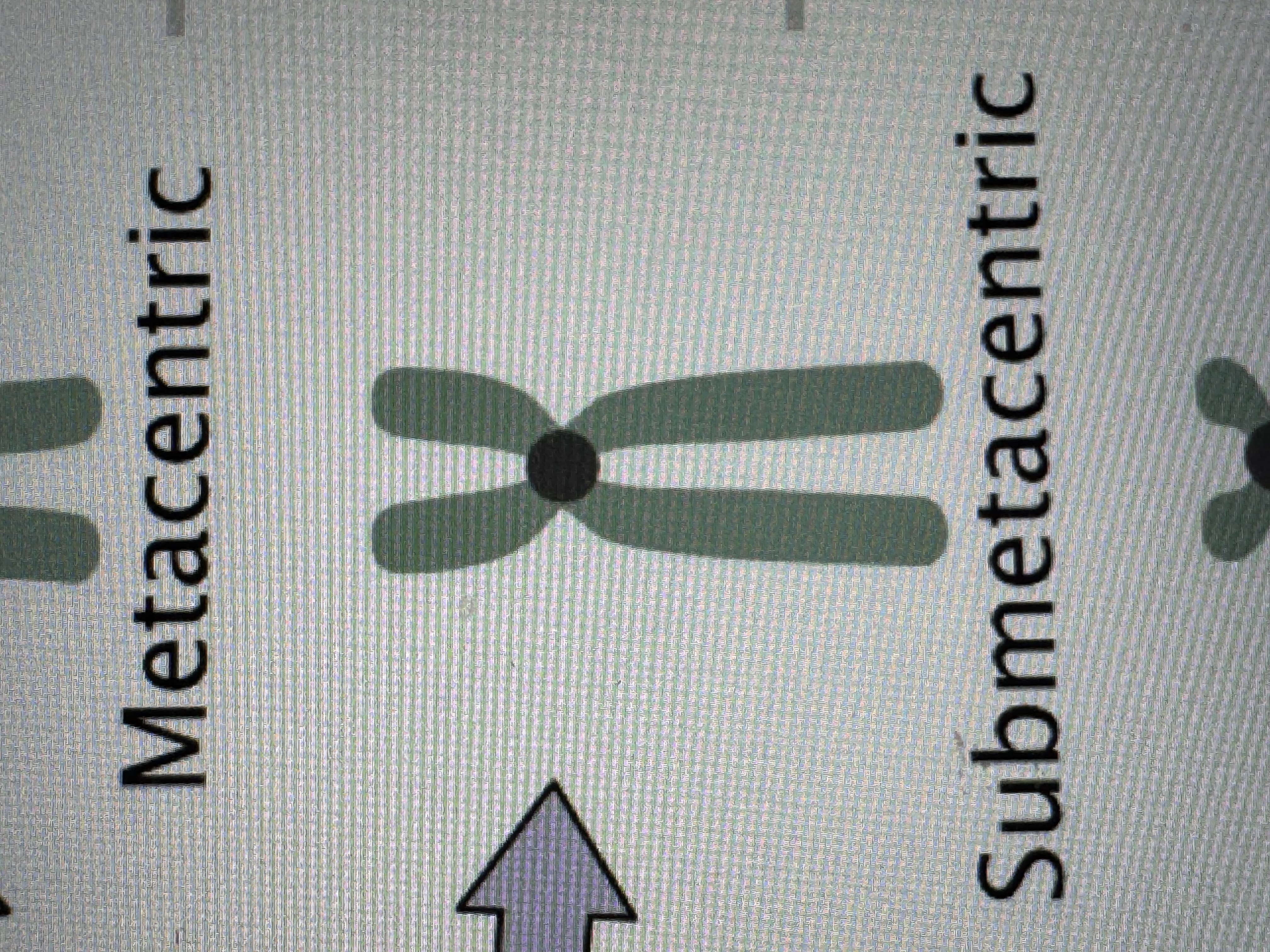
Metacentric chromosome
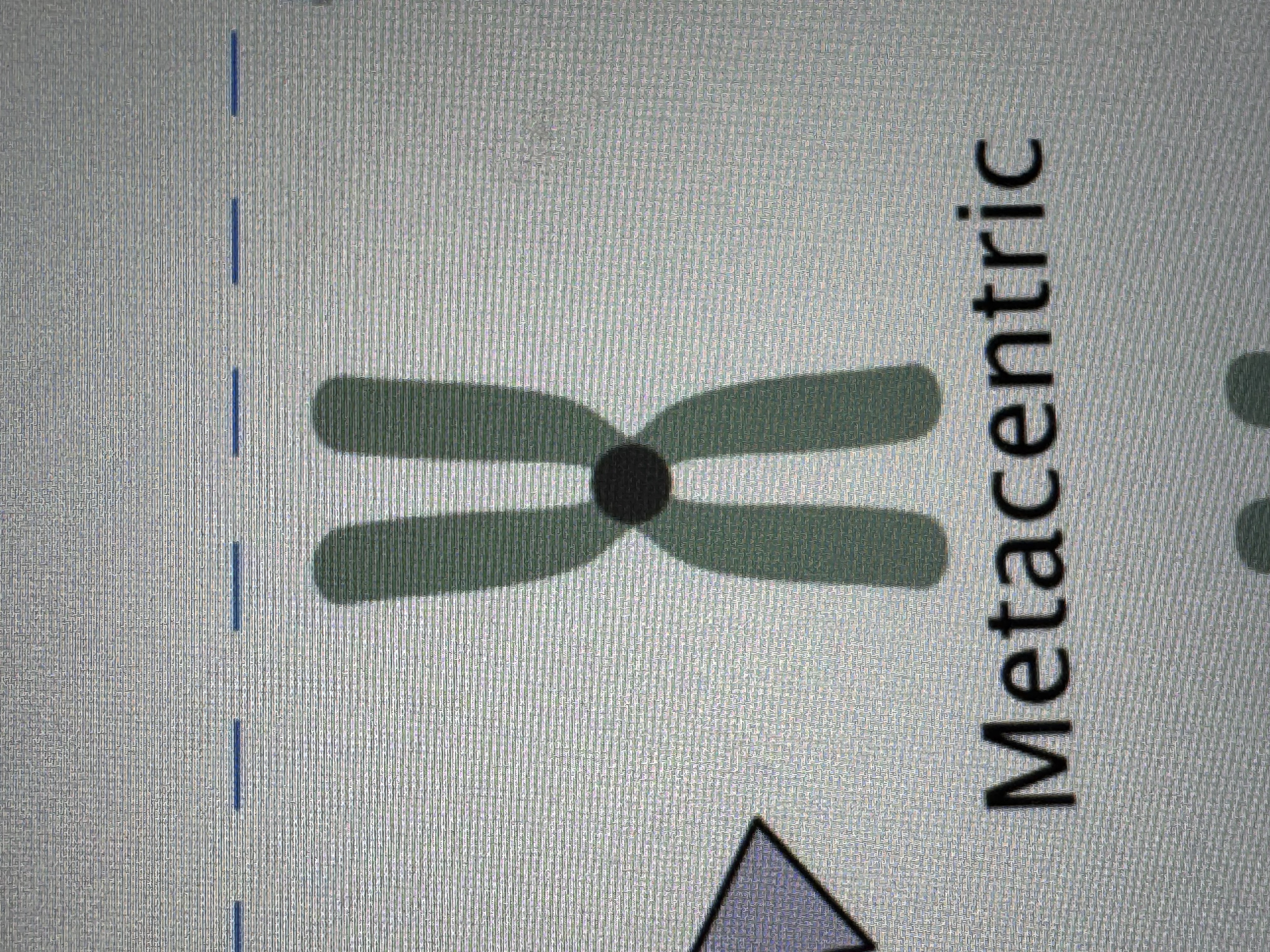
Submetacentric
Acrocentric

Telocentric
