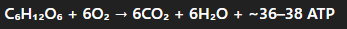AP Bio - Cellular Energetics
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
First law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed; it can only be transformed from one form to another
Second law of thermodynamics
Energy transfer leads to more disorder (entropy)
Exergonic reaction
A type of chemical reaction that releases energy, typically in the form of heat, resulting in products with lower energy than the reactants
Note: delta G in the photo is the amount of energy released
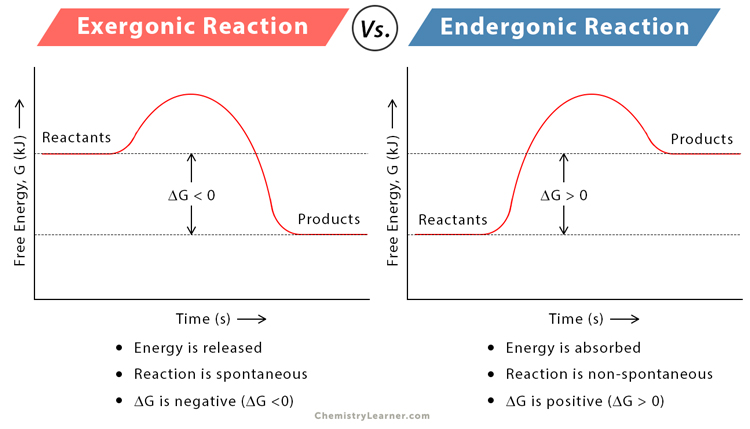
Endergonic reaction
A type of chemical reaction that absorbs energy, resulting in products with higher energy than the reactants
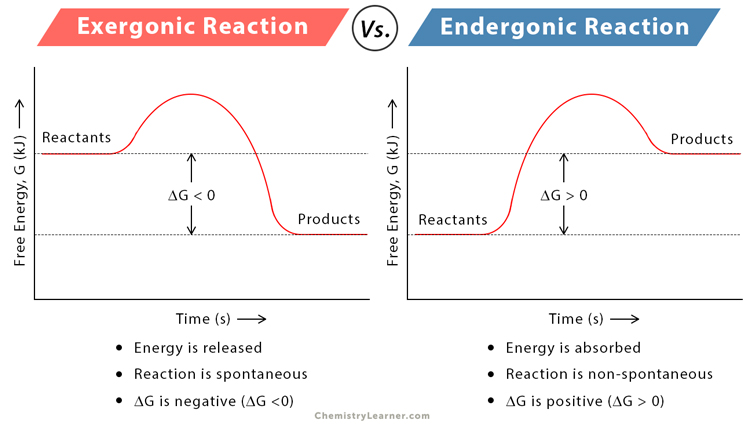
Transition state
The state of a chemical reaction in which the reactants are converted to products, kind of a hybrid between the two
Activation energy
The minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction, allowing reactants to reach the transition state
Enzymes are biological catalysts that…
Speed up reactions by lowering the required activation energy to reach the transition state
True or false: Enzymes change the energy of the starting point or ending point of the reaction
False, they do not change energy, only lower the required activation energy
Each enzyme of catalyzes ____ type of reaction
one (aka enzyme specificty)
Enzyme-substrate complex
Substrate binds to enzyme’s active site to form the enzyme-substrate complex. This complex stabilizes the transition state and facilitates the conversion of substrate into product.
The structure of a substrate must be compatible with the active site, meaning…
It must fit properly, allowing the enzyme to effectively catalyze the reaction. Charge must also be compatible.
Are enzymes reused?
Yes
Enzymes Do/Dont’s
Do:
Increase rate of reaction by lowering activation energy
Form temporary enzyme-substrate complexes
Remain unaffected by reaction
Don’t:
Change the reaction
Make reactions occur that would not occur otherwise
Induced-fit mechanism
Enzymes undergo a conformational change upon substrate binding to better fit the substrate, enhancing their ability to catalyze reactions.
Cofactors
Organic molecules, inorganic molecules, and ions that assist enzymes in their catalytic activity, often essential for enzyme function.
What happens when an enzyme is denatured?
The temp (typically above 42 C) gets too high, causing the enzyme to lose its three-dimensional structure and function.
Is denaturization reversible?
Generally, denaturation is irreversible, but some enzymes may regain function if conditions return to normal.
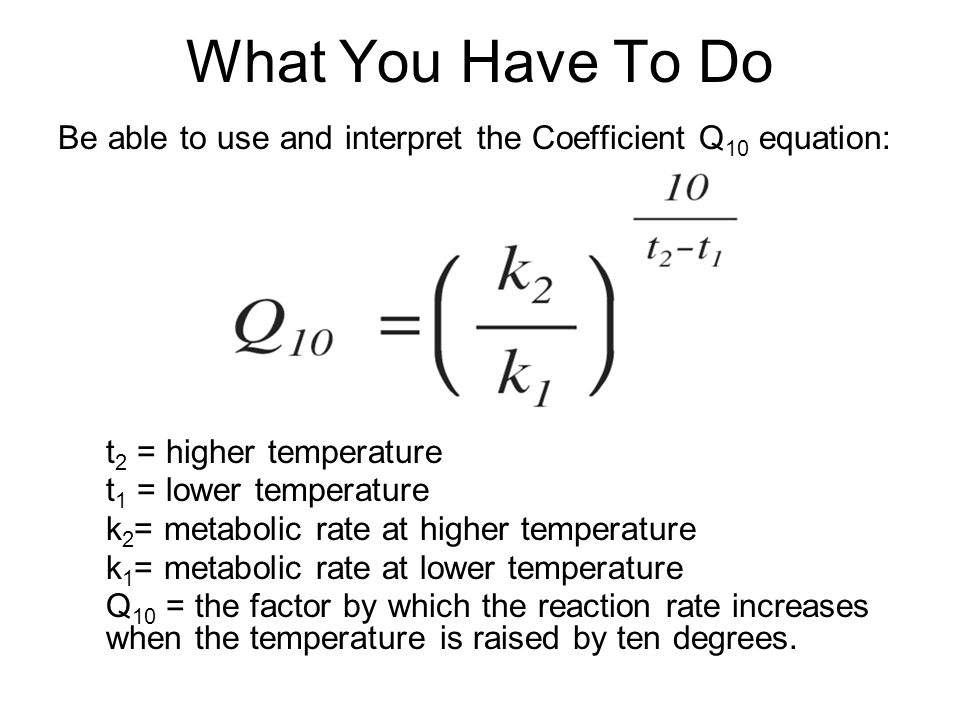
The higher Q10 is, the more…
temperature dependent the reaction is
Note: formula in image is given on the exam
Enzymes operate at an optimal pH, if it’s in an incorrect pH what happens?
Hydrogen bonds are disrupted, causing the structure of the enzyme to be altered
Saturation point
The point at which an enzyme's active sites are fully occupied by substrates, leading to a maximum reaction rate
Cells can control enzymic activity by…
regulating the conditions that influence the shape of the enzyme
Allosteric sites
specific regions on an enzyme that can bind molecules, resulting in a change in enzyme activity or confirmation
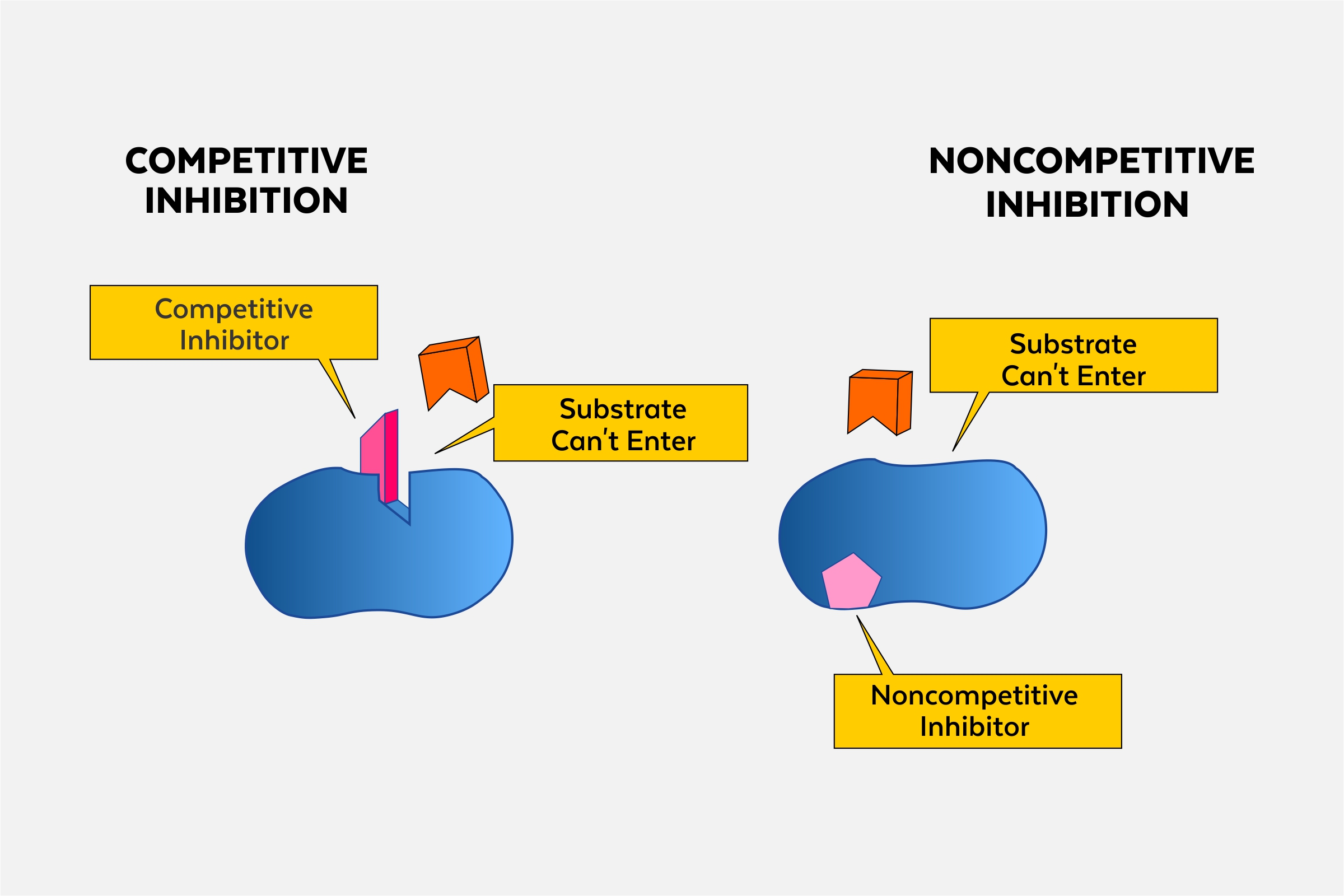
Competitive inhibition
the process where a molecule similar to the substrate competes for the active site of an enzyme, reducing its activity.
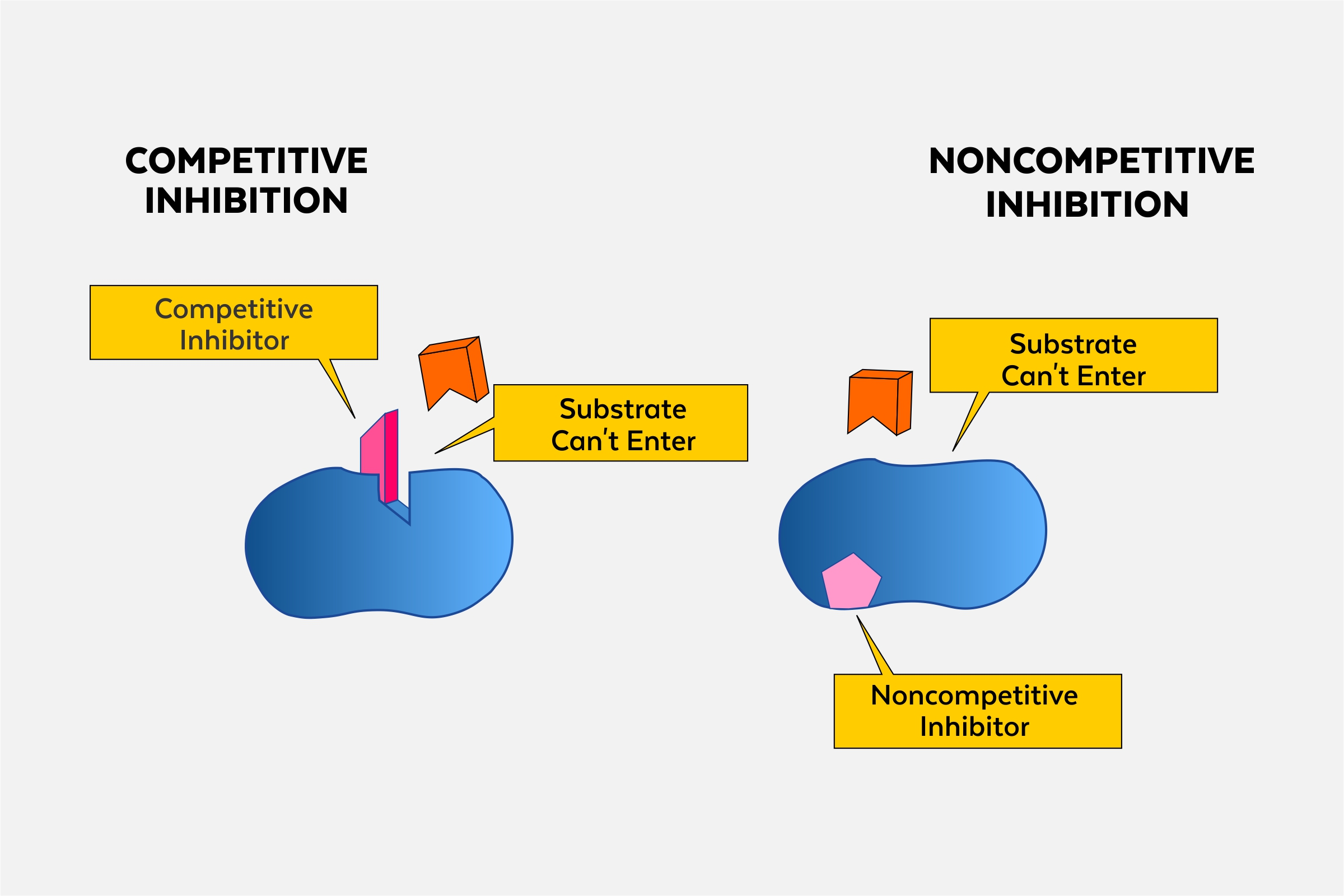
Allosteric inhibitor
a molecule that binds to an allosteric site on an enzyme, decreasing its activity by inducing a conformational change. (noncompetitive)
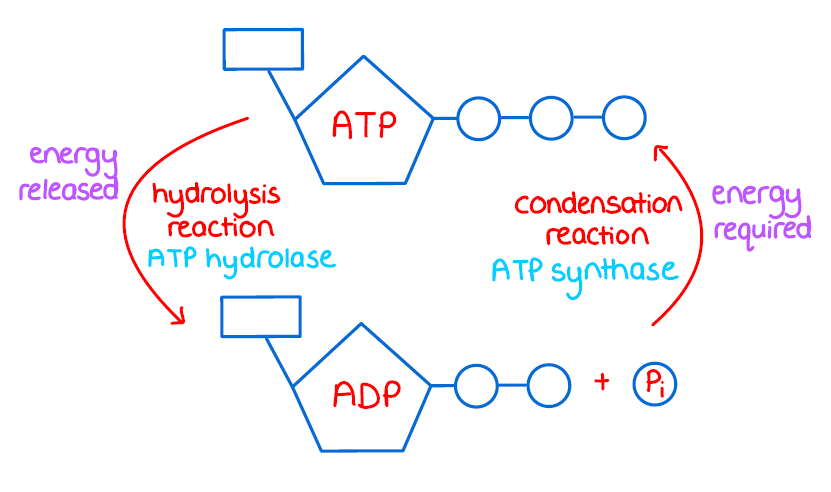
ATP Hydrolysis
the process of breaking down ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate, releasing energy for cellular functions
Sources of ATP
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis
Photosynthesis reaction
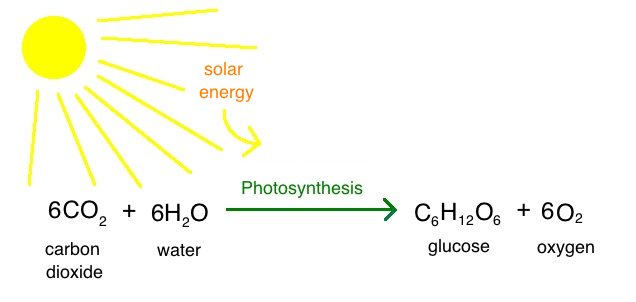
Prokaryotic photosynthesis contributed to…
Production of oxygen in the atmosphere
Laying the foundation for eukaryotic photosynthesis to occur
Chloroplast structure
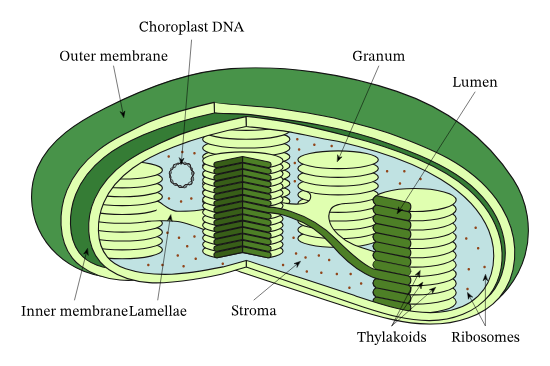
Thylakoid function
The thylakoid is where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur, utilizing sunlight to produce ATP and NADPH.
Photosystem I
is a protein complex in the thylakoid membrane that plays a key role in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, using light energy to produce ATP and NADPH.
Photosystem two
is a protein complex in the thylakoid membrane that works alongside Photosystem I in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, absorbing light energy to drive the production of ATP and NADPH by splitting water molecules.
Photophosphorylation
is the process of generating ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate using the energy derived from light during photosynthesis.
Light reaction steps
Sunlight is captured and sent to photosystem II
Activated electrons are captured by P680
Electrons are passed to primary acceptor
Electrons are passed to the electron transport chain, photolysis occurs
Protons are pumped into the thylakoid lumen establishing a proton gradient
Electrons leave photosystem II to photosystem and pass through a second electron transport chain
ATP is produced through ATP synthase
NADP+ is reduced to NADPH
Light independent reaction
The series of biochemical reactions that occur in the stroma of chloroplasts, using ATP and NADPH from the light reactions to convert carbon dioxide into glucose, primarily through the Calvin cycle
Where do light dependent and light dependent reactions occur?
Light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes, while light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle) take place in the stroma of the chloroplasts.
Link between light dependent and light independent reactions
Neither can produce CO2 alone
Light depend reactions produce ATP and NADPH, which are used in light-independent reactions to synthesize glucose
Cellular respiration reaction