Biology Unit 9 - Ecology
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Last updated 9:09 PM on 5/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
Producers
photosynthetic organisms
2
New cards
Secondary consumers
usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers {Ex: Fox eating a rabbit}
3
New cards
Tertiary consumers
carnivores that eat other carnivores. {Ex: Owls eating snakes}
4
New cards
Apex consumers
Organisms at the top of the food chain
5
New cards
Grazing food web
has plants or other photosynthetic organisms at its base, followed by herbivores and various carnivores
6
New cards
Detrital food web
a base of organisms that feed on decaying organic matter, including decomposers and detritivores
7
New cards
Gross primary productivity
The rate at which photosynthetic producers incorporate energy from the Sun
8
New cards
Net primary productivity
the energy that remains in the producers after accounting for these organisms’ respiration and heat loss.
9
New cards
Biomagnification
the increasing concentration of persistent, toxic substances in organisms at each successive trophic level.
10
New cards
Biogeochemical cycle
the recycling of inorganic matter between living organisms and their nonliving environment
11
New cards
hydrosphere
the area of Earth where water movement and storage occurs {lakes, rivers, oceans}
12
New cards
Subduction
Carbon sediments from the ocean floor are taken deep within Earth / the movement of one tectonic plate beneath another.
13
New cards
Dead zone
an area in lakes and oceans near the mouths of rivers where large areas are periodically depleted of their normal flora and fauna
14
New cards
Fallout
Sulfer falling directly from the atmosphere
15
New cards
Biome
Large scale community of organisms, primarily defined on land by the dominant plant types that exist in geographic regions of the planet with similar climatic conditions.
16
New cards
Resistance
The ability of an ecosystem to remain at equilibrium in spite of disturbances
17
New cards
Resilience
The speed at which an ecosystem recovers equilibrium after being disturbed
18
New cards
Trophic level
Energy level / its position in the food chain or food web.
19
New cards
Primary consumers
The organisms that consume the producers are herbivores {Ex: Grasshopper eating grass}
20
New cards
Carbon cycle
nature's way of reusing carbon atoms, which travel from the atmosphere into organisms in the Earth and then back into the atmosphere.
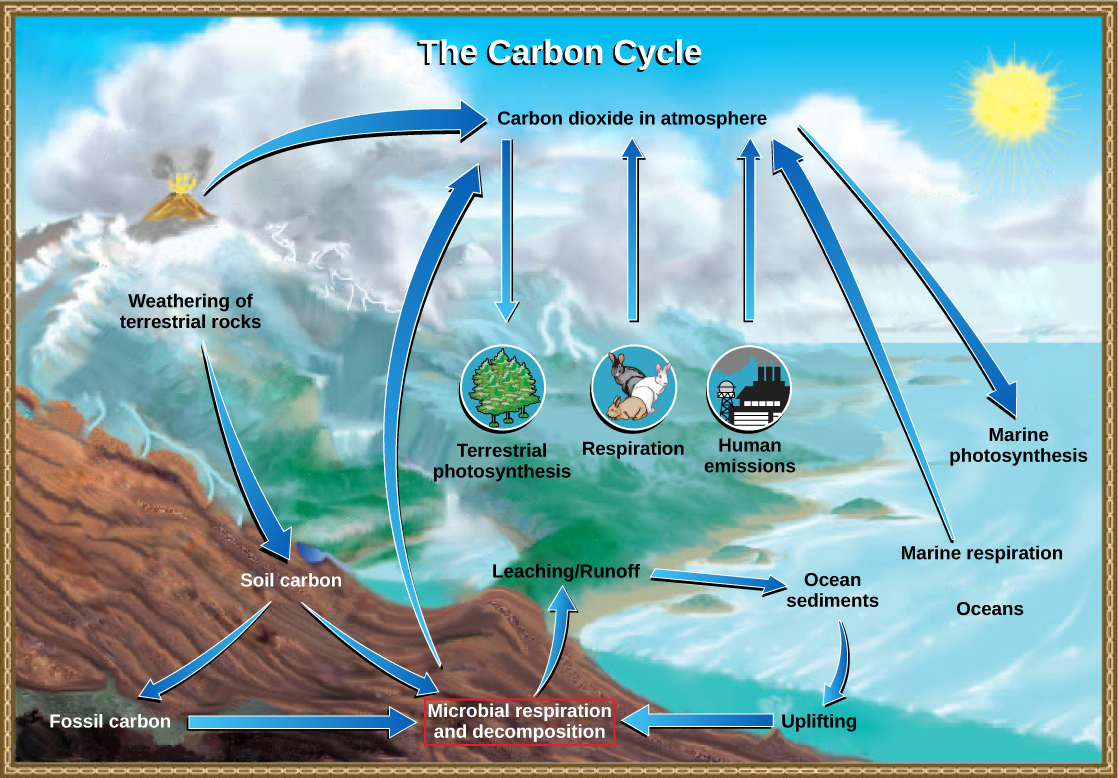
21
New cards
Water cycle
the path that all water follows as it moves around Earth in different states
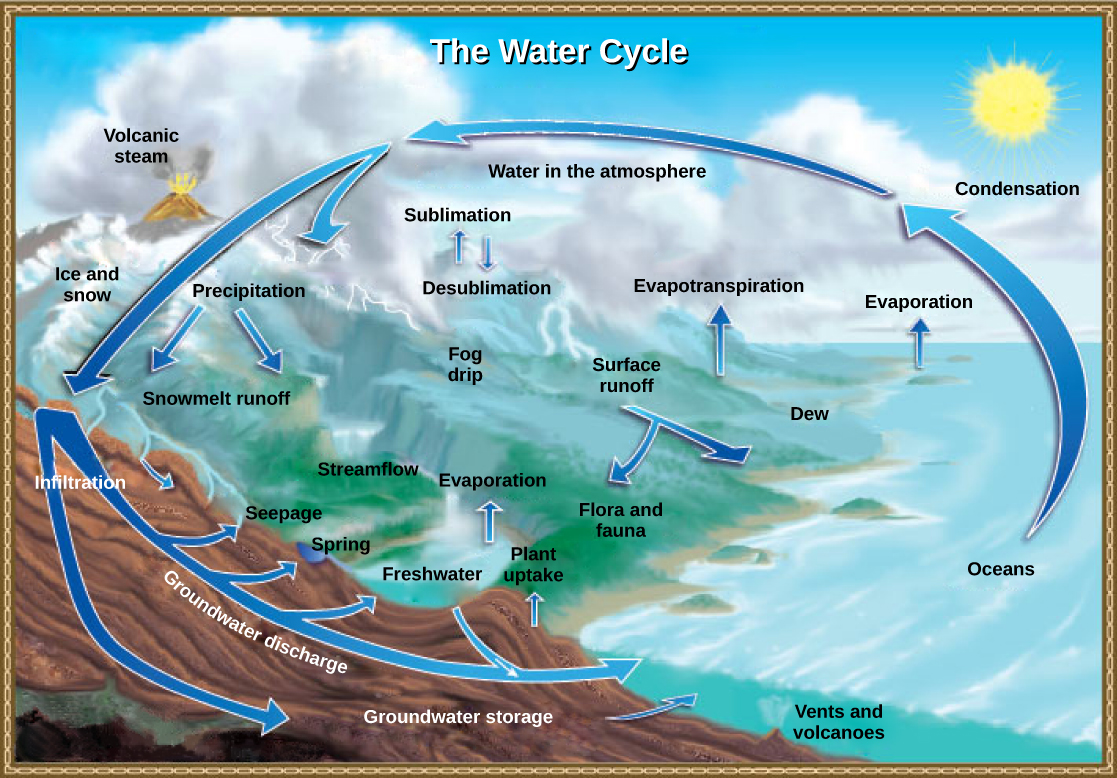
22
New cards
Nitrogen cycle
how nitrogen moves between plants, animals, bacteria, the atmosphere, and soil in the ground.
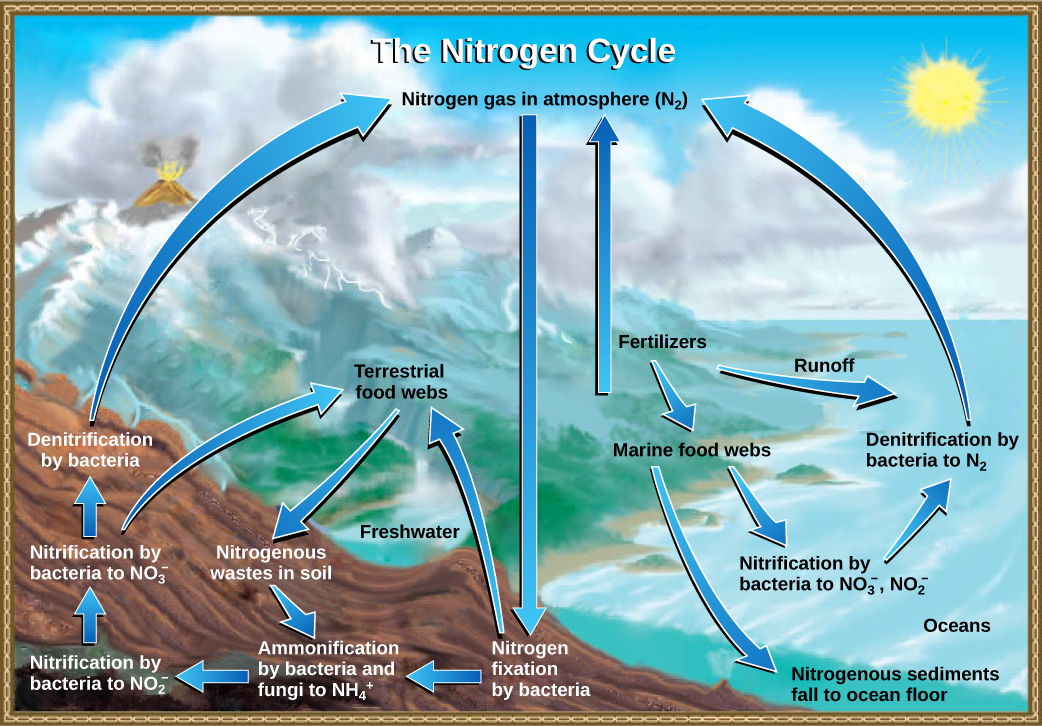
23
New cards
Phosphorus cycle
the movement of phosphorus from the rocks where it's found into the environment and, finally, into the plants and animals that need it.
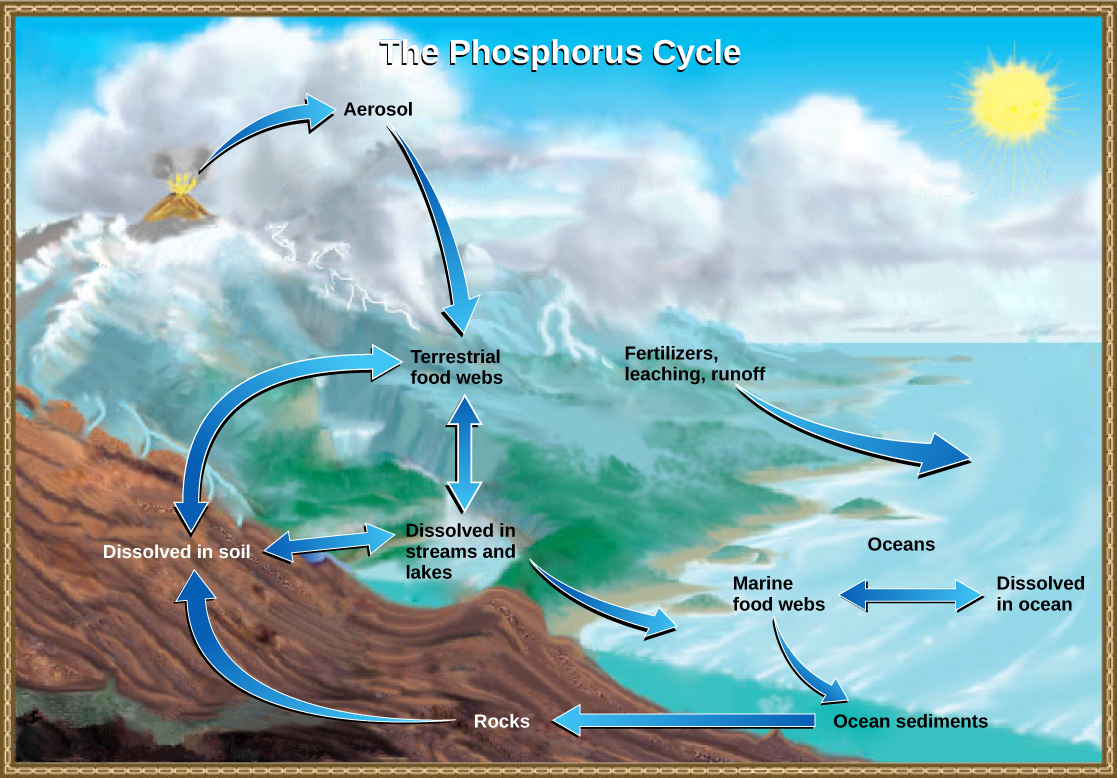
24
New cards
Sulfur cycle
the movement of sulfur through the geosphere and biosphere.
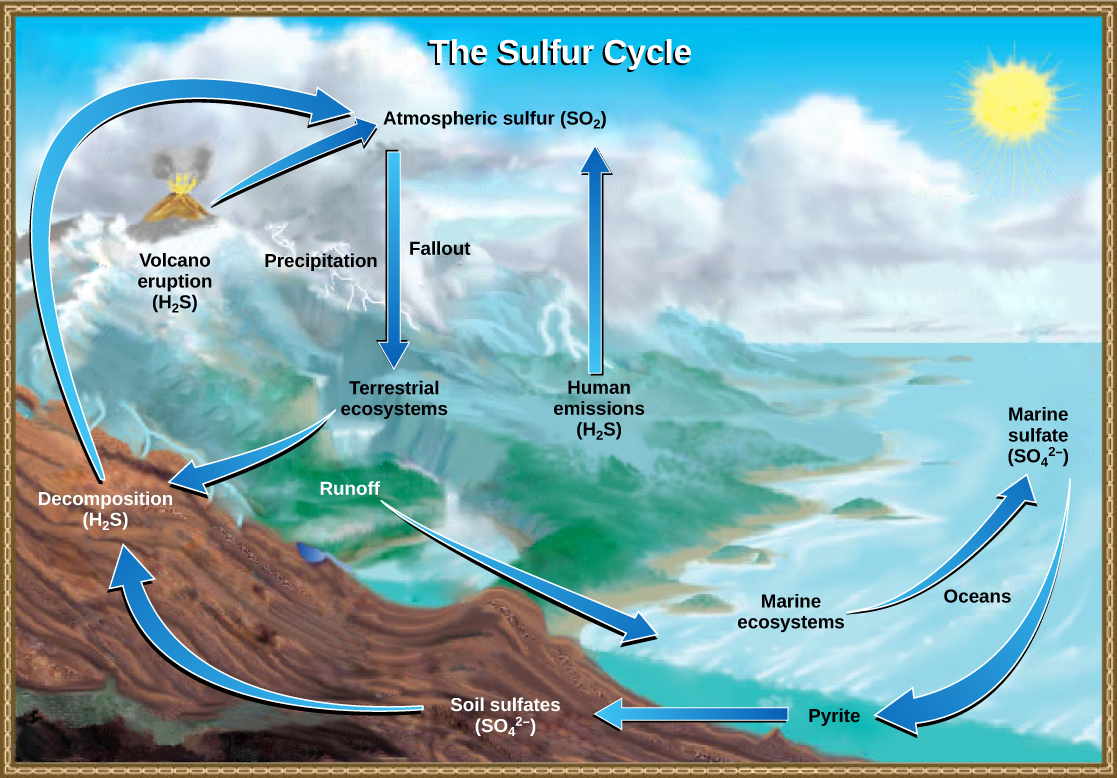
25
New cards
Autotroph
an organism that can produce its own food using light, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals.
26
New cards
Heterotroph
an organism that consumes other organisms in a food chain.
27
New cards
Carbon sink
anything that absorbs more carbon from the atmosphere than it releases
28
New cards
Carbon Source
burning of fossil fuels like gas, coal and oil, deforestation and volcanic eruptions.
29
New cards
Carbon store
fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, oil shale, and carbonate based sedimentary deposits like limestone.
30
New cards
Nitrogen fixation
When nitrogen is taken from its molecular form (N2) in the atmosphere and converted into nitrogen compounds useful for other biochemical processes. {triple covalently bonded nitrogen → animals and plants can’t break it down}
31
New cards
Denitrification
Bacteria breaking down triple covalently bonded nitrogen and releasing it back into the atmosphere for organisms to use.
32
New cards
Eutrophication
a natural process that results from accumulation of nutrients in lakes or other bodies of water. (algae bloom)