BIOMI 2900: Lecture 37 Review Problems
1/17
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What do lymphoid precursor cells differentiate into?
B or T cells in the Bone marrow or Thymus
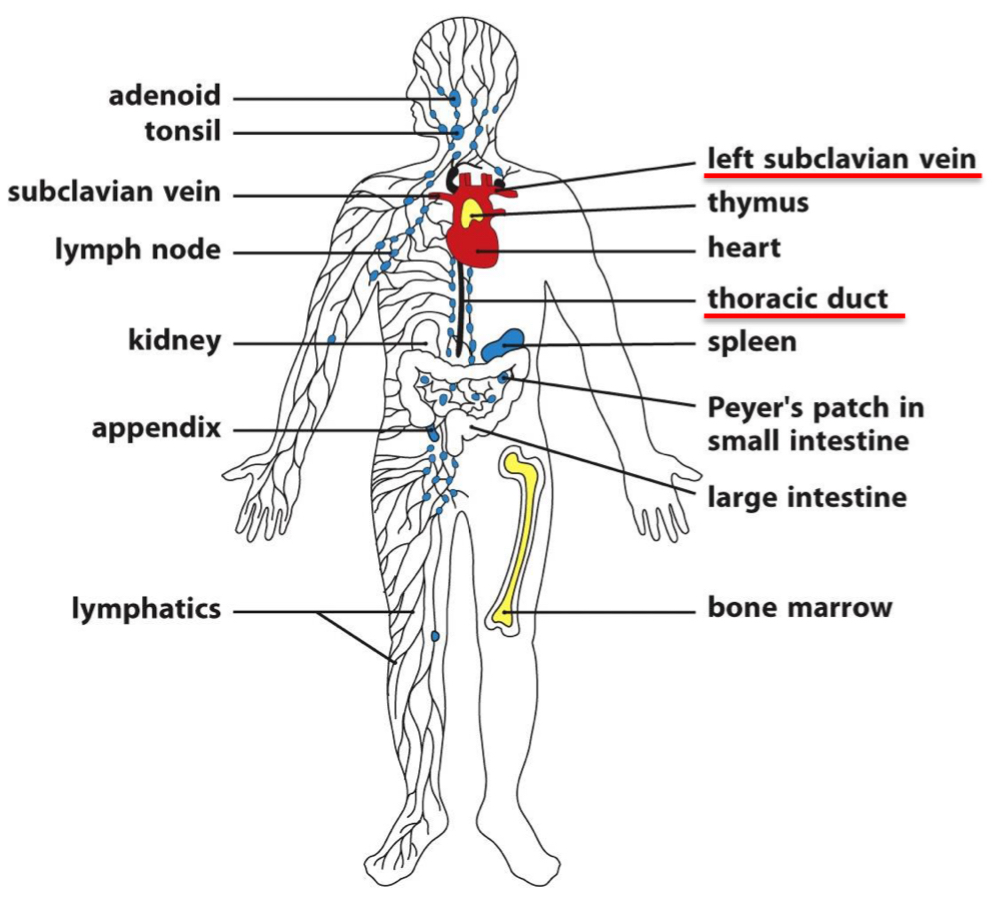
Where are immature (naïve) lymphocytes carried to? At these locations, what can they interact with and cause?
Carried to peripheral lymphoid organs (in blue)
These are locations where they can interact with specific antigens → maturation
What response do T and B cells have?
T lymphocytes (T cells), cell-mediated response
B lymphocytes (B cells), humoral responses (antibody)
What does the adaptive immunity exhibit
Specificity, tolerance, memory
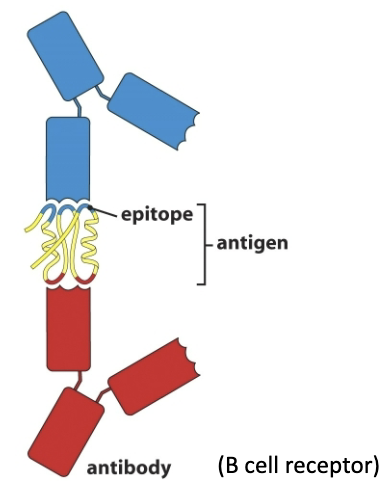
Define the following: antigen, epitope
Antigen: a compound (e.g. protein) recognized as foreign, this recognition activates a lymphocyte and leads to an adaptive immune response
Epitope: tiny portion of an antigen that interacts with and is recognized by a T- or B-cell receptor
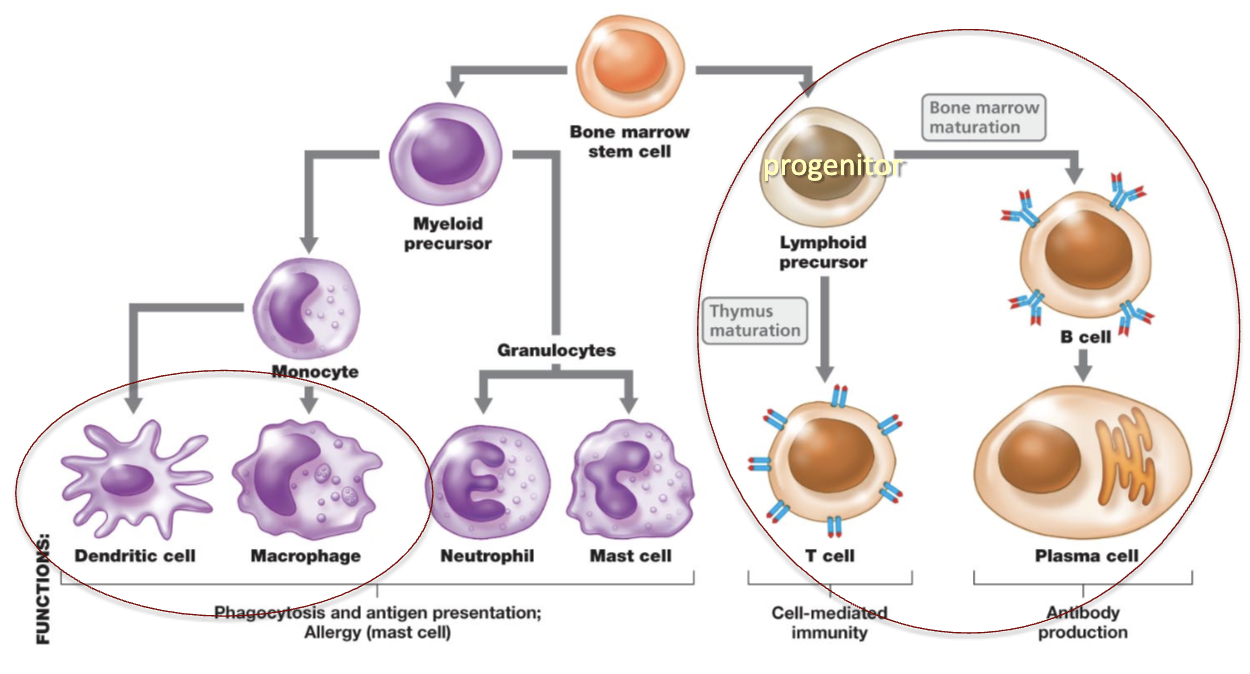
What are the cells of the immune system?
Dendritic cell, macrophage
Lymphoid precursor, B cell, T cell, Plasma cell
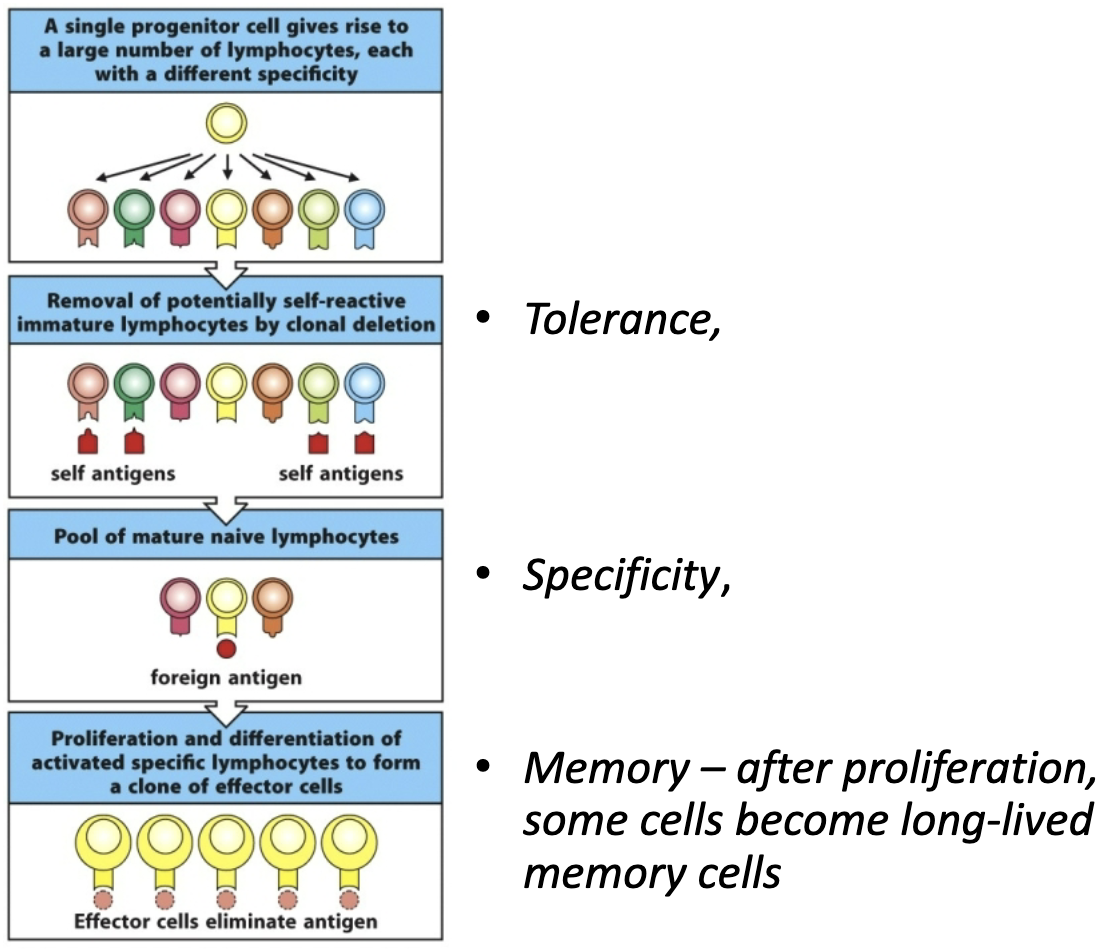
What are the steps to “proliferation and differentiation of activated specific lymphocytes to form a clone of effector cells”? What does memory refer to?
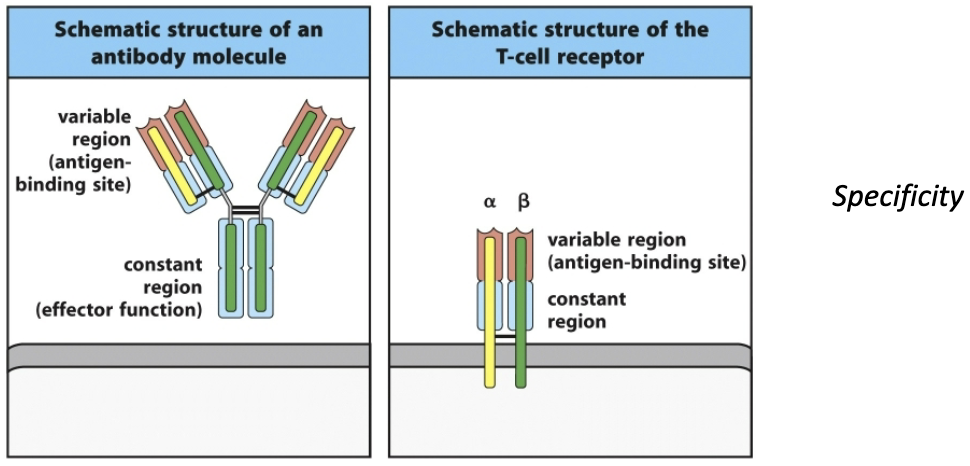
What do T-cell receptors and B-cell receptors all have? What is the variability generated by?
T-cell receptors and B-cell receptors all have a variable region: amino acid sequence in this pocket varies from one lymphocyte to another
The variability is generated by genetic changes in the cell as it develops and provides the capacity of each TCR or BCR to recognize unique epitopes
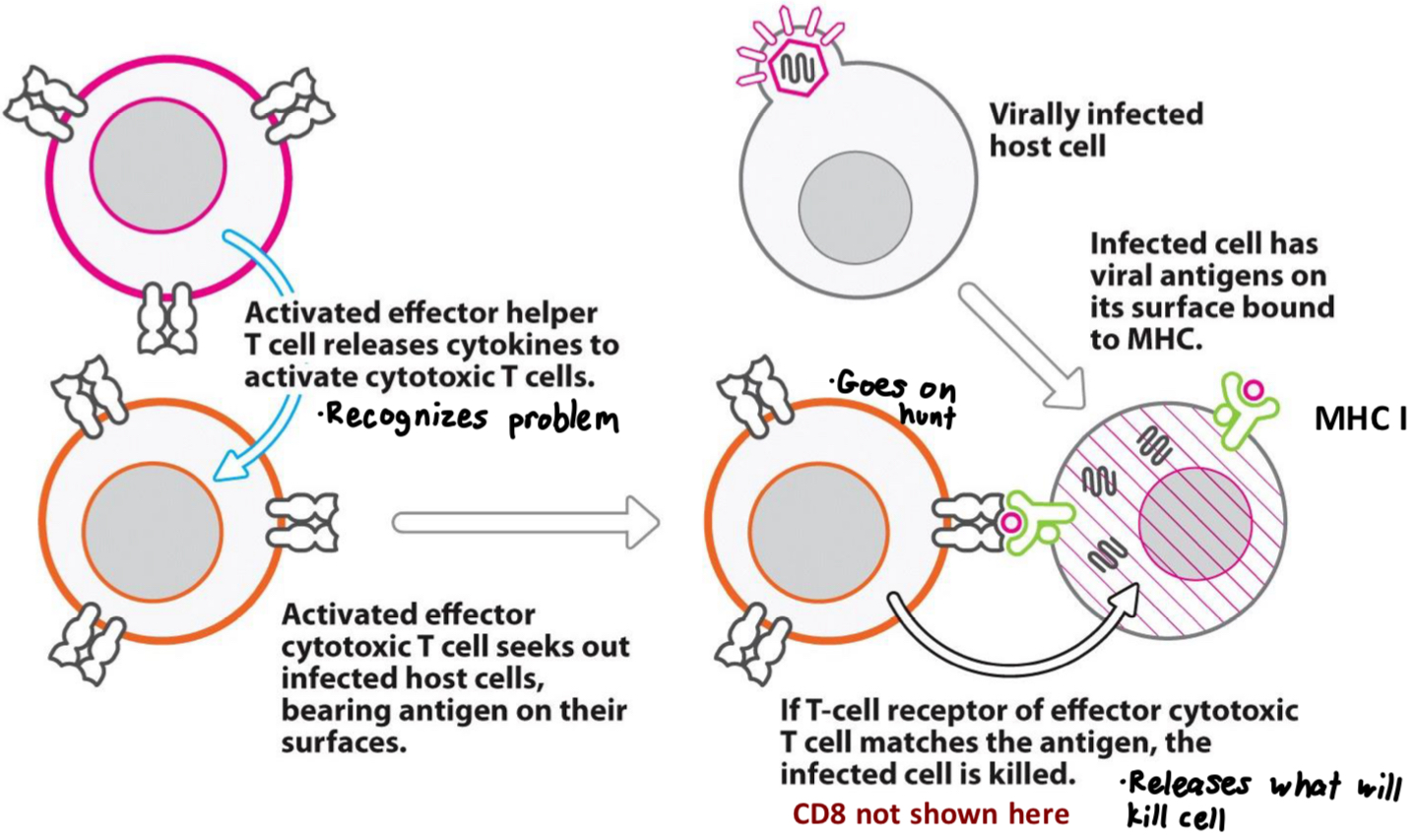
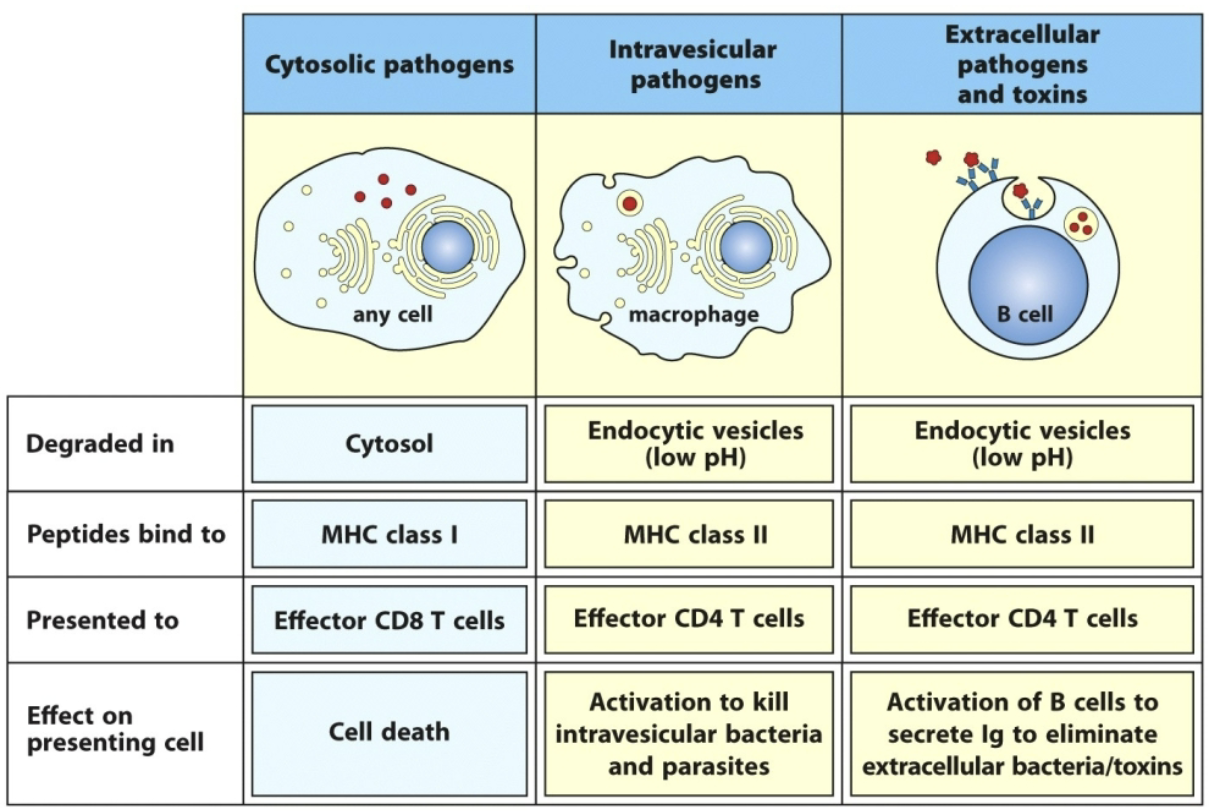
What is the target for cell-mediated immunity? Where are peptide antigens displayed? What is the ultimate effector?
Target: infected host cells (primarily viral infections)
Peptide antigens are displayed on the surface of the infected cell using MHC I
Ultimate effector: cytotoxic T cells that bind antigen displayed on MHC I and kill infected cell
What is the target for humoral immunity? Where are peptide antigens displayed? What is the ultimate effector?
Target: bacteria that have invaded tissues, and other extracellular threats (toxins)
Peptide antigens are displayed on the surface of phagocytic cell by MHC II
Ultimate effector: antibodies produce by B cells when they differentiate into plasma cells
What is MHC?
Major Histocompatibility Complex
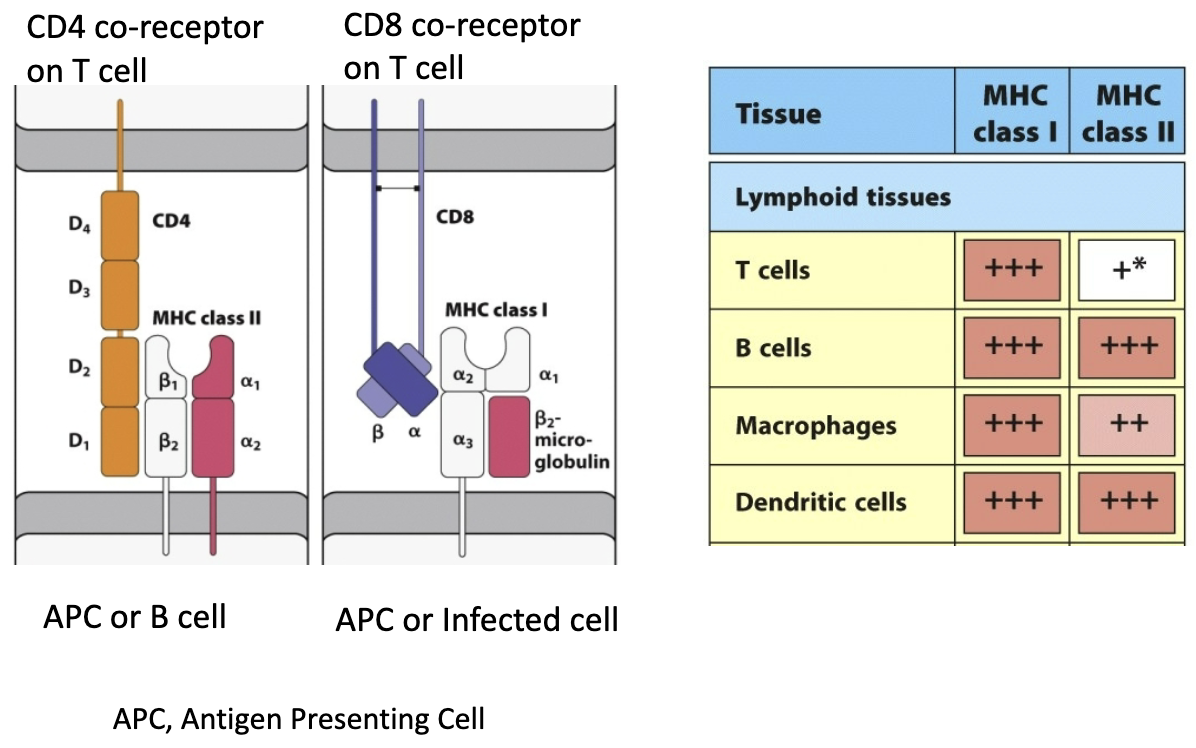
What can phagocytic cells become? What is MHC II?
Antigen presenting cells
MHC II: Major Histocompatibility Complex II
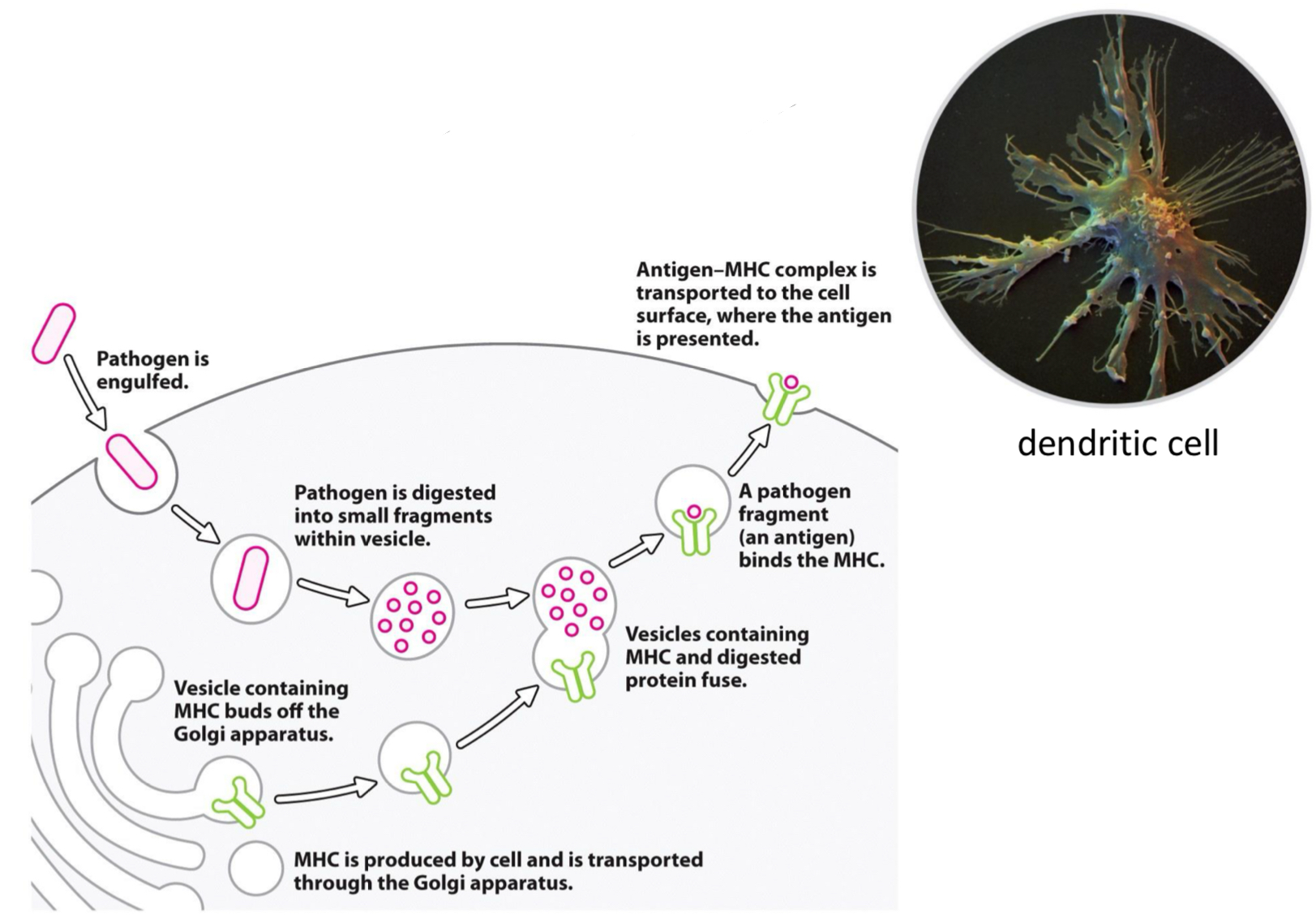
For the following, where are they degraded, where do peptides bind to, what are they presented to, and what is the effect on presenting cells: cytosolic pathogens, intravesicular pathogens, extracellular pathogens and toxins
Steps for T-helper cell activation
An APC displays an antigen on the MHC II receptor protein on the cell surface. It also produces signals to attract naïve T cells.
A helper T cell with a receptor that recognizes the antigen is activated. This effector T cell divides (some become memory T cells)

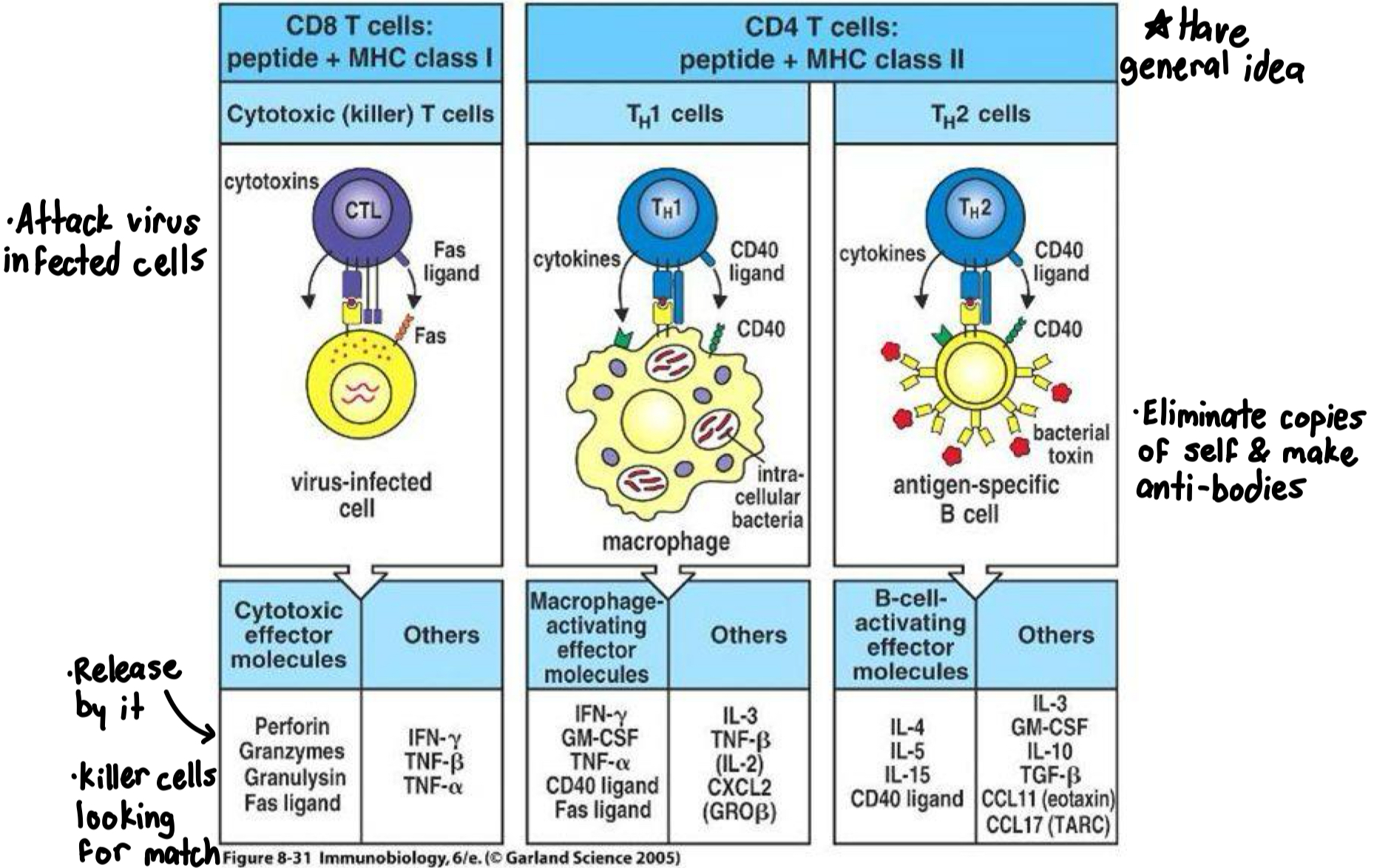
What are effector molecules produced by T cell subsets?
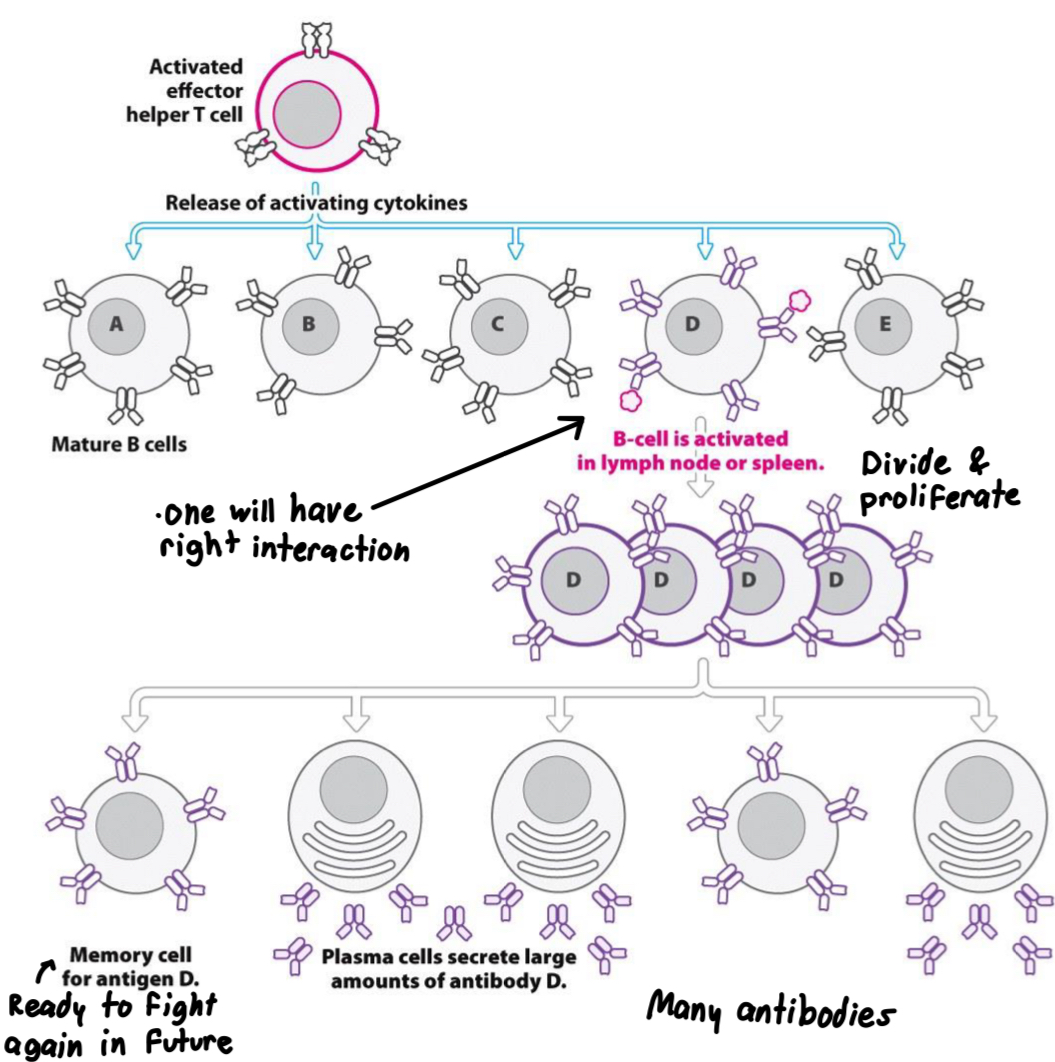
Steps for B cell activation
Effector T helper cell releases cytokines to activate B cells
B cells that recognize an antigen begin to divide (clonal expansion)
Most differentiate into plasma cells, which produce antibodies, some become memory B cells
NOTE: some B cells can be activated directly (engulf invading path)
What are the three major ways antibodies (immunoglobulins) clear an infective agent?
Neutralization (bind & prevent binding to anything else)
Opsonization (tag pathogen & tell immune system to digest it)
Complement activation (interact with complement system and lyse)
What happens in cell-mediated immunity?
Activated effector T8 Cells release cytokines to activate Cytotoxic T Cells