INTRO to DIGITAL TECH
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
OR gate
Output is 1 only when one or both of its inputs are 1
Output is 1 only when both of its inputs are 1
Nand
Sequential Logic
A circuit producing outputs based on present and past inputs to store info (at least one bit).
Combinational Logic
Circuit output only dependent on present combinational input values
What are the two edges
Rising edge and falling edge
What does a rising and falling edge do?
Signals transitions between high and low state
What does a falling edge indicate?
A signal turning off, becoming false
What does a rising edge indicate?
A signal turning on, becoming true
Rising edge
Low to high state
Falling edge
High to low state
What happens in a clock flip flop?
The output only changes when there is an edge on the clock input
Edge triggered 1
output doesn’t change unless theres a specified edge signal
Edge triggered 2
Edge is rising or falling
Edge triggered 3
The input with a triangle symbol indicates the clock input
When the D clock’s active edge occurs
Q takes the value of D
When there is no activity in D clock edge
Q keeps previous value
TRUE OR FALSE: All digital sys with synchronous logic have a system clock
True
TRUE OR FALSE: Sys clocks usually produced by an oscillator is a regular square wave signal
True
Asynchronous Inputs
Change the output immediately to a set value, without waiting for the clock.
Negative edge trigger JK Flip flop
REVIEW
What are the two Asynchronous inputs called?
Preset and Clear
Preset input forces output to what value?
Q=1
What is the meaning of Q in flip flops?
The main output
Clear input forces output to what value?
Q=0
What is this?
Asynchronous table condictions REVIEW
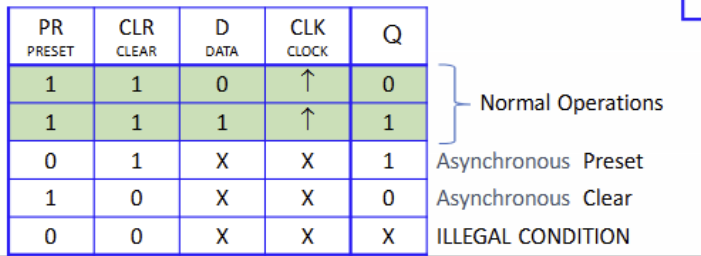
What indicates that signals are active low
The circles on the inputs ( The 0 on the signal causes the set or reset to occur)
TRUE OR FALSE: No clock edge is necessary for the set or reset to take effect
TRUE
A negative edge-triggered D flip-flop responds to asynchronous timing signals like preset (PRE) and clear (CLR)
What is the difference between synchronous and asynchronous inputs?
Asynchronous changes the output immediately while
Synchronous changes the output only when the clock (or control signal) is active.
ACTIVE means
High or Low
MSI
One chip contained the combinational logic to handle data
MUX
take several input signals and send only one of them to the output.
What are the mux sizes
┌────────────┐
D ─▶│ │
CLK▶│► │
└─────Q──────┘
Synchronous
┌────────────┐
D ─▶│ │
CLK▶│► │
CLR▶│o │
└─────Q──────┘
Asynchronous
┌────────────┐
J ─▶│ │
K ─▶│ │
CLK▶│► │
└─────Q──────┘
Synchronous
┌────────────┐
D ─▶│ │
CLK▶│►o │
└─────Q──────┘
Falling edge
┌────────────┐
D ─▶│ │
CLK▶│► │
PR▶ │o │
└─────Q──────┘
Asynchronous
When does overflow occur
When ADDING 2 positives give a negative or 2 negatives give a positive
What indicates sign in sign bit system
1 = negative 0 = positive
A circuit that adds three bits and generates a sum and carry-out is know as a
Full adder
A circuit that adds two bits and generates a sum and carry-out is know as a
Half adder
When does overflow occur?
Results of binary addition and subtraction can’t be represented is too larger or small to fit in number of bits
Overflow in Binary addition
When you add two positive numbers but end up with a negative
Overflow in Binary subtraction
When you subtract two negative numbers but end up with a positive
If number being added has different signs
No overflow
If both numbers added have same signs
Overflow
If subtracted and signs are different its overflow because
The result has the same sign as the number being subtracted
Number being subtracted
Subtrahend
State Machines
Finite State Machine
A device that traverse through a predetermined sequence of states in order
How many states is a Finite Machine given?
One state
What is the finite machine state called?
Current state
What is it called when something changes from one state to another after a triggering event or condition?
This change is called a transition.
What defines a particular Finite State Machine (FSM)?
An FSM is defined by a list of its states and the triggering condition for each transition.
Are state machine synchronous or asychronous?
Synchronous
Synchronous Sequential Circuit
A circuit whose output depends on its past and current inputs
How is a state represented?
Q’s or flip-flops outputs
The state is represented by the Q’s or flip-flop outputs.
States are encoded as one-hot (only one flip-flop is ‘1’ at a time).
With n flip-flops, there are n possible states.
For n states, n flip-flops are needed.
The next state is determined by the inputs and the current state.
Embedded systems
Any system that includes a programmable computer
What are the three major components of a microprocessor?
How do embedded systems differ form Pcs?
ES has a specific application that is known at design time, Not programmable by the end of user, Optimized for fixed run-time requirements
How do PCs differ from embedded systems?
PCs have a broad class of applications , Programmable by the end
CPU is logical
True
Moore’s Law
Every two years the power of computers double while staying the same price
Microprocessor
has CPU, ROM, RAM, has 3000 bits of memory, 5000 transistors, and 128 bits of access memory
Mircoprocessor (CPU)
The Brains of the computer
What can the CPU do?
Only what the program says it can do as it has no independent thinking
Digital Systems
A large state machine with a predefined logical and mathematical operation built in
M