Veterinary Diagnostic Procedures
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover essential diagnostic procedures related to veterinary care including ear cytology, fecal examination, blood analysis, and urinalysis.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
How do you prepare a mite slide for ear cytology?
Wipe significant chunks on the side of the slide, add a drop of mineral oil, place a coverslip on the sample, and examine using a 10x objective.
What should you note on the swab for ear cytology?
Color, texture, and presence of significant chunks.
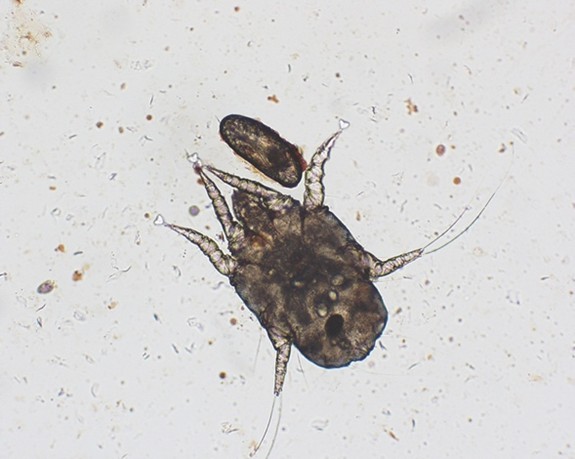

What is the scientific name for dogs and cats' ear mite?
Otodectes cynotis.
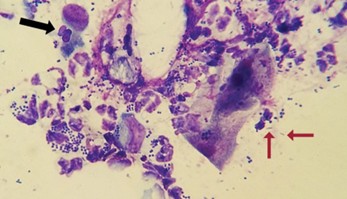
What types of microorganisms can be found on a microorganism slide?
Cocci (strepto, staphylo), rods (Pseudomonas or proteus), and yeast (Malassezia).
What does the '+' sign indicate when quantifying organisms on a slide?
indicates 1-2 organisms seen per high power field (HPF).
What is the first step in performing a direct fecal smear?
Take a very small amount of fresh feces on a tongue depressor and put it onto a microscope slide.
What do you do if the feces is diarrhea while performing a gross fecal exam?
Use 2 teaspoons of feces instead of 1.
What must be added to feces before mixing if performing a gross fecal exam?
Fecasol until the feces are covered.
What is the normal brown color associated with on a fecal exam?
Normal feces consistency.
What should you note regarding blood in a fecal sample?
Distinguish between fresh (bright red) and digested (dark red) blood.
What are the normal PCV values for canines?
37%-55%.
How do you perform a total protein (TP) measurement?
Break the PCV tube at the etching point and dab it on the refractometer; read the value with light.
What is the normal TP value range for canines, felines, and equines?
5.5-7.5g/dL.
How do you perform a hemoglobin count?
Load blood into a hemocytometer, mix with saponin, and apply a cover glass before reading the value.
What is the normal hemoglobin level for felines?
9-15 g/dL.
What do you do when performing a blood smear?
Invert the blood tube, draw blood into hematocrit tubes, and spread blood on a slide at a 30-to-45-degree angle.
What is the normal platelet count for canines?
2.5-5x10^6 thrombocytes/uL.
What indicates thrombocytopenia?
A panic value of under 25,000 thrombocytes/uL.
What is anisocytosis in RBC morphology?
A variation in RBC sizes.
What does polychromasia indicate?
The presence of an abnormally high amount of immature RBCs.
What RBC morphology is associated with IMHA?
Spherocytes.
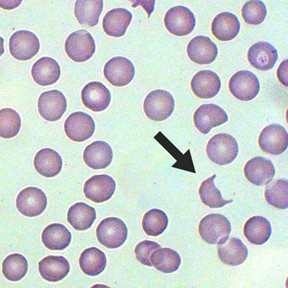
What abnormalities can cause schistocytes?
Diseases damaging circulating blood, like hemangiosarcoma, DIC, and iron deficiency.
How do you perform a dipstick urine exam?
Place a drop of urine onto the dipstick at each box, tap off excess, and read the values.
What is a common cause of hematuria?
Presence of RBCs in urine.
What does bilirubinuria indicate?
Liver disease or intravascular hemolysis.
What is the normal color for urine in a gross exam?
Light yellow to amber.
What urine specific gravity indicates healthy kidneys?
Normal canine: 1.015-1.045; normal feline: 1.020-1.060.
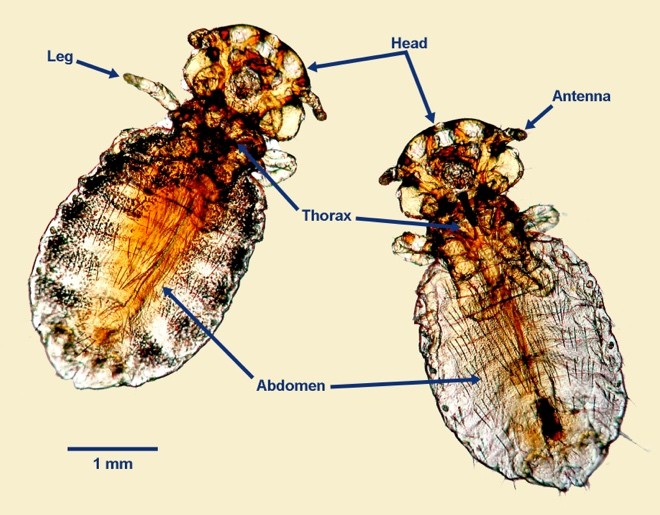
What are chewing lice classified as?
Mallophaga.
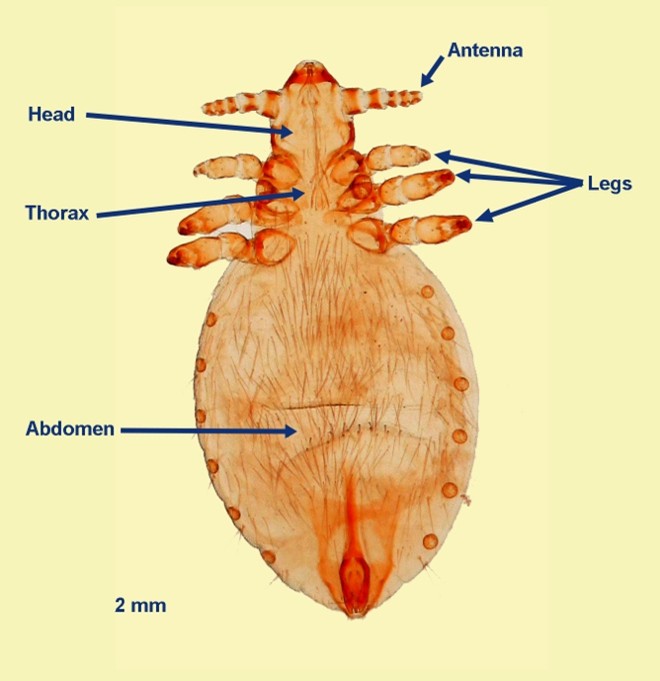
What are sucking lice classified as?
Anoplura.

What is an example of a hard tick?
Ixodid.

What is an example of a soft tick?
Argasid.
What nematodes can be identified in a fecal exam?
Hookworm (Strongyloidea), whipworm (Trichuroidea), roundworms (ascarids).
What might indicate the presence of hyperproteinemia in a blood sample?
Rouleaux formation.
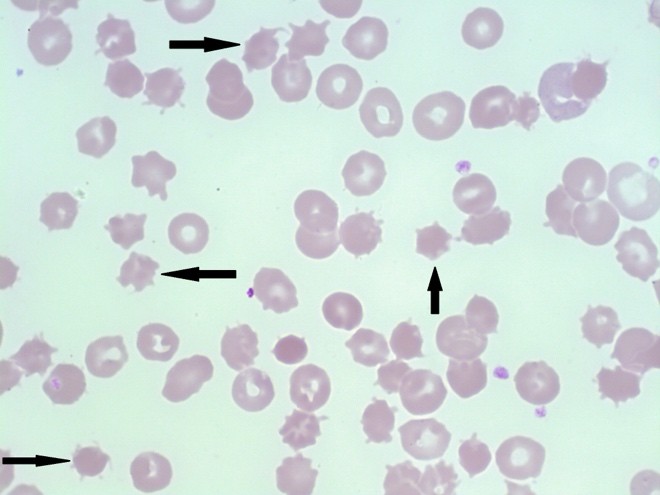
What cellular variation might suggest liver disease in RBC morphology?
Acanthocytes.
What must be done after centrifuging a urine sample?
Take off the supernatant and flick the bottom of the tube to suspend the sediment.
What does the presence of hyaline casts in urine indicate?
May be normal in low numbers, but other casts are not normal.
What is the purpose of adding dye to the urine sediment exam?
To enhance visibility of significant structures under the microscope.