Chapter 14- The Digestive System
1/90
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Pepsinogensin
inactive protein-digesting enzymes
Pepsin
active protein-digesting enzymes; HCl converts pepsinogen to it
Gastrin
(stomach) stimulates the release of gastric juice and stomach emptying; secreted caused by food in stomach (digested proteins) and ACh
Intestinal Gastrin
(duodenum) stimulates gastric secretion and emptying; secreted by food in stomach
Histamine
(stomach); activates parietal cells to secrete hydrochloric acid; secreted by food in stomach
Somatostatin
(stomach/duodenum); inhibits secretion of gastric juice and pancreatic juice and the emptying of stomach and gallbladder; secreted caused by food in stomach and sympathetic nerve fibers
Secretin
(duodenum) increased output of pancreatic juice rich in bicarbonate ions ad bile output by liver; inhibits gastric mobility and gastric gland secretion; secretion by acidic chyme and partially digested foods in duodenum
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
(duodenum) increases output of enzyme-rich pancreatic juice, stimulates gallbladder to expel stored bile, relaxes sphincter of duodenal papilla ot allow bile and pancreatic juice to enter the duodenum; caused by fatty chyme and partially digested proteins in duodenum
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide (GIP)
(duodenum) inhibits secretion of gastric juice nad stimulates insulin release; secreted by food in duodenum
Amylase
in saliva; bicarbonate-rich juice that begins the process of starch digestion
Lysozyme and IgA antibodies
inhibit bacteria
Pancreatic Amylase
breaks down starch in small intestine
Brush border enzymes
in small intestine; dextrinase, glucoaylase, lactase, maltase, sucrase (break down carbohydrates); aminopeptidase, carboxypeptidase, dipeptidase (protein digestion)
Pancreatic Enzymes
trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase; break down large polypeptides into small polypeptides in small intestine
Lingual and gastric lipases
break down unemulsified fats in mouth and stomach
Pancreactic Lipase
breaks down unemulsified fats in small intestine
Renin
second protein-digestine enzyme produced by the stomach to digest milk protein
Digestion occurs in
mouth, stomach, small intestine
What is the main place for digestion and absorption?
Small intestine
Gallbladder
stores and concentrates bile
small intestine
major (chemical) digestive organ; absorbs (nearly all) nutrients
large intestine
dry out the indigestible food residue by absorbing water and to eliminate these residues from the body (feces)
Liver
produce bile
Stomach
stores and breaks down food; churns, mixes, and pummels it; chemical & mechanical digestion
Peristalsis
involuntary; alternating waves of contraction adn relaxation of the longitudinal muscles in the organ wall to squeeze food along the tract
Mastication
chewing; mechanical breakdown of food (first step)
Bile
contains bile salts that physically break down large fat globules into small ones to allow fat-digesting enzymes to work on
Pancreas
produces enzymes that break down all categories of digestible foods; produces hormones: insulin and glucagon
Glycogen
combined glucose molecules and stored in liver
Glucagon
hormone produced by the pancreas to raise blood sugar by stimulating the liver to released glycogen (stored glucose) and produce more glucose (gluconeogenesis)
Glucose
primary source of energy for body
Insulin
hormone produced by the pancreas that allows glucose to be stored in the liver as glycogen
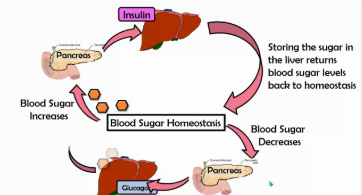
Blood Glucose Levels are high
insulin is released to store excess glucose as glycogen and help glucose enter cells
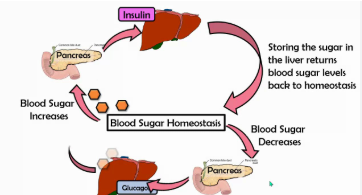
Blood Glucose Levels are low
glucagon signals the liver to release stored glycogen back into the bloodstream
1
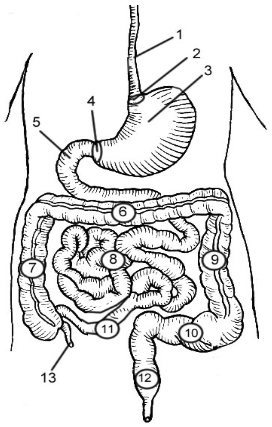
Esophagus
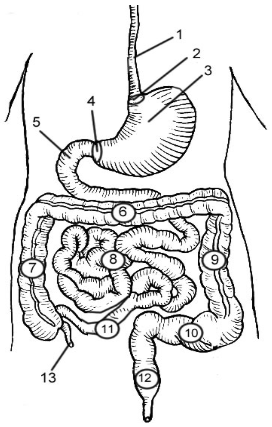
2
Cardioesophageal Sphincter
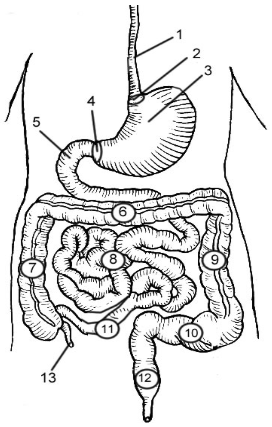
3
Stomach
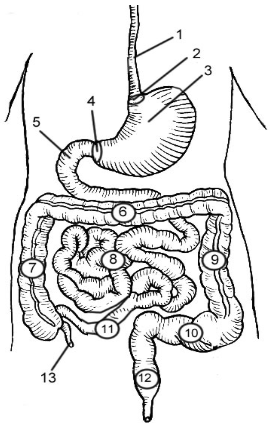
4
Pyloric Sphincter/valve
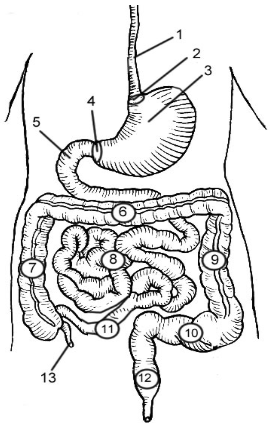
5
Duodenum
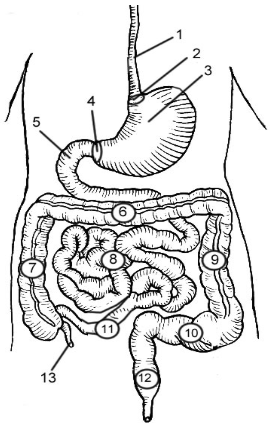
6
Transverse Colon
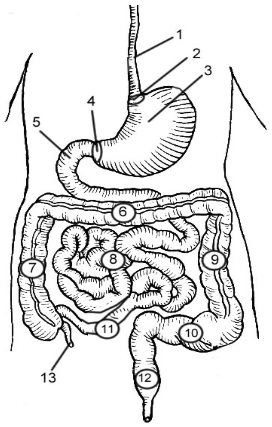
7
Ascending Colon
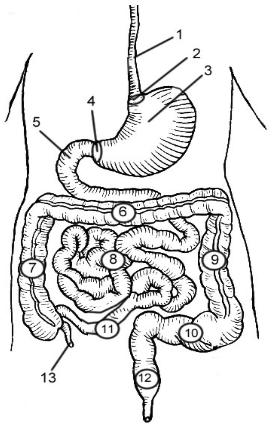
8
Jejunum
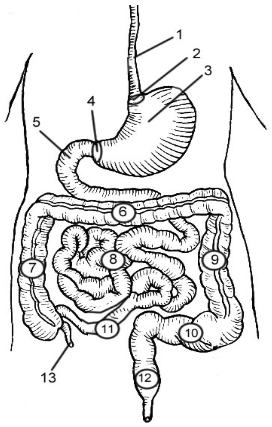
9
Descending Colon
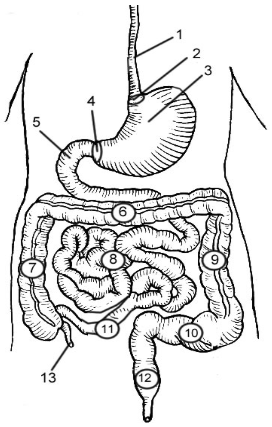
10
Sigmoid colon
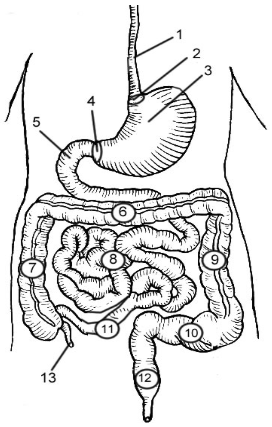
11
Ileum
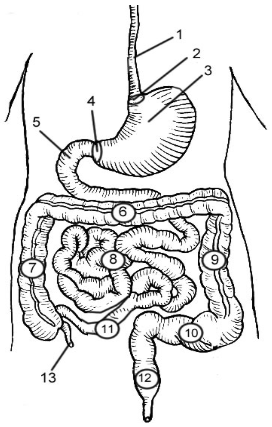
12
Rectum
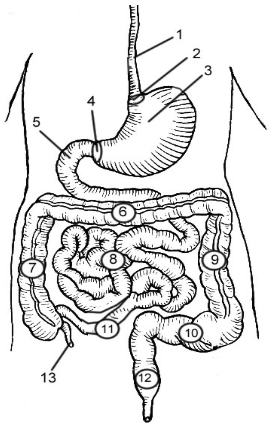
13
Appendix
Irritable Bowel disease
chronic complex intestinal condition that caused inflammation in the digestive tract; possible causes are genetics, environment, or immune; abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, anemia, bowel obstruction
Diverticulitis
mucosa protrudes through the colon walls; diverticula becomes inflamed; pouches form on the wall of the colon
Gastroenteritis
intestinal infection (aka stomach flu); diarrhea, cramps, vomiting, fever
Crohn's disease
chronic inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation in your gastrointestinal tract; probably genetics; diarrhea, cramping, weight loss, fatigue
Ulcerative colitis
chronic inflammation in the large intestine (colon and rectum) so colon damage; abdominal pain, bloody stools, fatigue, frequent bathroom trips
Peptic ulcer
sores that develop in the lining of the stomach or duodenum; from imbalance in gastric juices, bacterial infection, smoking, alcohol abuse; symptoms- heartburn, chest pain, vomiting, weight loss
Dysentery
inflammation of the intestines accompanied by bloody diarrhea; abdominal pain, fever, malaise; from shigella bacteria or amoeba
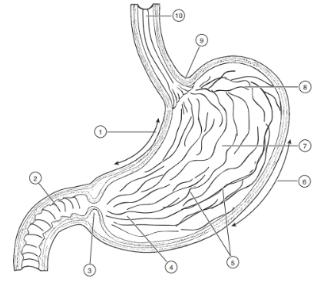
1
Lesser curvature
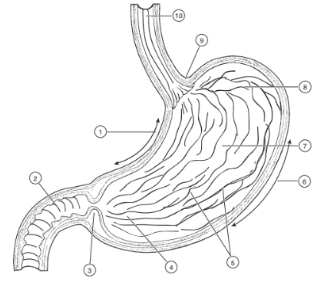
2
Duodenum
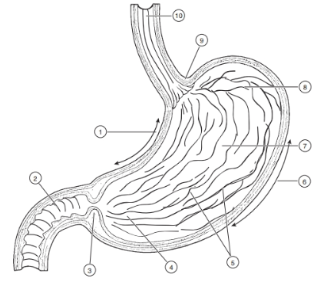
3
Pyloric Sphincter/Valve
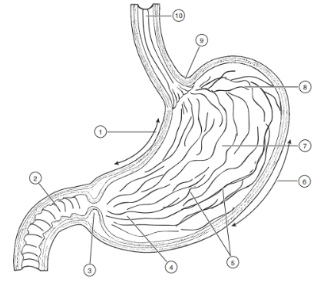
4
Pyloric Region of stomach
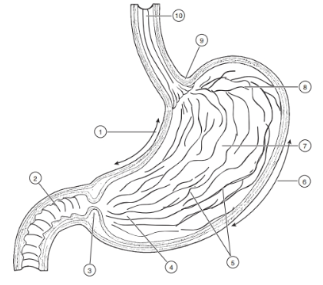
5
Rugae (of mucosa)
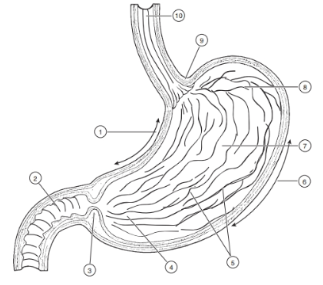
6
Greater Curvature
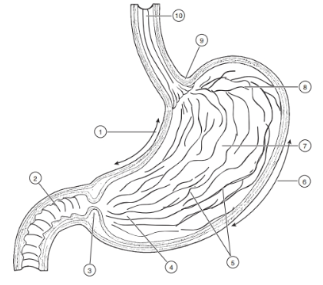
7
Body
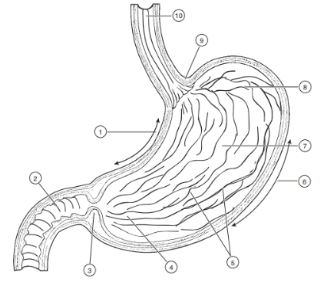
8
Fundus
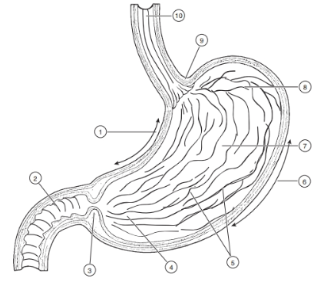
9
Cardioesophageal Sphincter
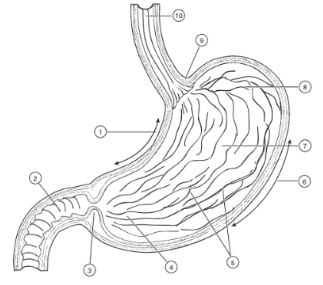
10
Esophagus
Valve opens from esophagus to stomach
Cardioesophageal sphincter
Valve opens from stomach to small intestine
pyloric sphincter/valve
Intestinal villi
increase the surface area of the small intestine; completes the digestion of proteins and carbohydrates in its plasma membrane and absorbs nutrients through the mucosal cells
6 Steps of GI Tract
ingestion, propulsion, mechanical breakdown, digestion, absorption, defecation
Ingestion
food is placed in the mouth
Propulsion
food is propelled from one organ ot the next; ex: swallowing, peristalsis
Mechanical Breakdown
physically fragments food into smaller particles, increasing surface area, prepares food for further degradation by enzymes; ex: segmentation, chewing, churning of food in stomach
Segmentation
moves food back and forth across internal wall of small intestine to propel food through small intestine; mechanical digestion
Digestion
large food molecules are chemically broken down ot their building blocks by enzymes
Absorption
transport of digestive end products from lumen of GI tract to blood or lymph by entering mucosal cells; mainly in small intestine
Defecation
elimination of indigestibel residues and gut bacteria from the GI tract via the anus in the form of feces
Bolus
food that has been chewed and mixed with saliva; formed in mouth
Chyme
food grinded by stomach (liquid); formed in stomach
Gastric Glands
secrete gastric juice components
Chief Cells
make pepsinogen
Parietal cells
produce hydrochloric acid
Mucous neck cells
produce thin acidic mucus
Enteroendocrine cells
make local hormones
Intrinsic factor
required for absorption of vitamin B12
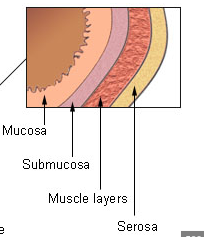
Mucosa
innermost layer of moist mucous membrane lining the lumen of the GI tract
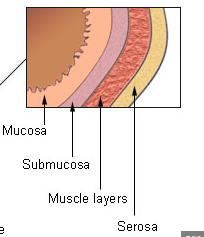
Submucosa
deep to mucosa; made of connective tissue containing blood vessles, nerves, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), lumphatic vessels
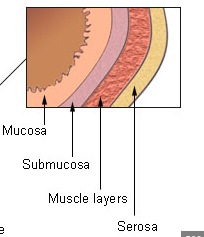
Muscularis externa
smooth muscle layer iwth inner circular layer and outer longitudinal layer
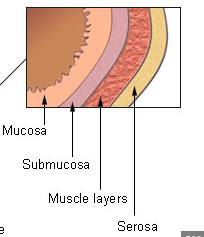
Serosa
outermost layer (aka visceral peritoneum); continuous with parietal peritonem lingin the cavity
Mesentery
double layer of peritoneum
Deglutition
aka swallowing; complex coordinated effort involving the tongue, soft palate, pharynx, and esophagus
Buccal phase
voluntary; occurs in the mouth when the tongue forces the food bolus toward the pharynx
Pharyngeal-Esophageal phase
involuntary; transports food through teh pharynx and esophague controlled by the vagus nerves