Monohybrid Crosses
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Phenotype
Determined by genotype and is the result of proteins produced
Different alleles cause
different sequences
Amino acids are made up by?
different proteins
Codon is? Start and stop codons?
3 base pairs of mRNA that code for an amino acids (triplet codes). Start and stop codons signal the start and end of protein synthesis
A reading frame is
a sequence of codons
Genetic Code Characteristics
Redundant: all but 2 amino acids have a > 1 codon
Unambiguous: one codon = only one amino acid
Non-overlapping: codons read one at a time
Nearly universal: all codons specify the same amino acids in all organisms
Conservative: if >1 codon for an amino acid, first two bases are usually the same
Point Mutation
One or a small number of base changes, examples
Chromosome-level mutations
Larger in scale
Missense mutation
Changes an amino acid
Silent mutations
No changes (due to redundancy)
Frame shift mutations
Shifts reading frame, altering meaning of all subsequent codons
Nonsense mutations
Changes codon to stop codon
Most point mutations are neutral or-
Deleterious
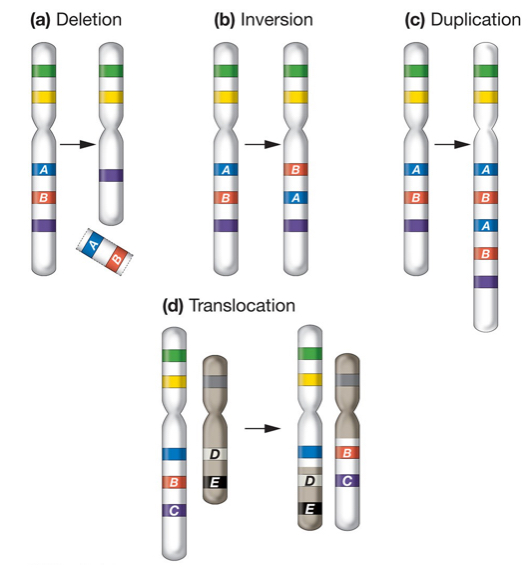
Chromosome level mutation
-Can change chromosome number or structure
-Can be beneficial, neutral, or deleterious
Dr. Esther Miriam Zimmer Lederberg
American microbiologist
Dr. Christine Nüsslein Volhard
German biologist who did research on early embryonic development with fruit flies. She won the Nobel Prize

Transcription
RNA Polymerase vs. DNA Polymerase
Three main steps of transcription
Initiation, elongation, termination
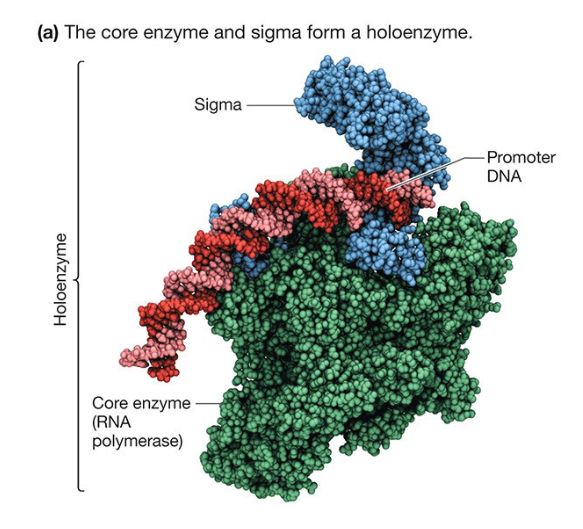
Sigma
Find the DNA and promote
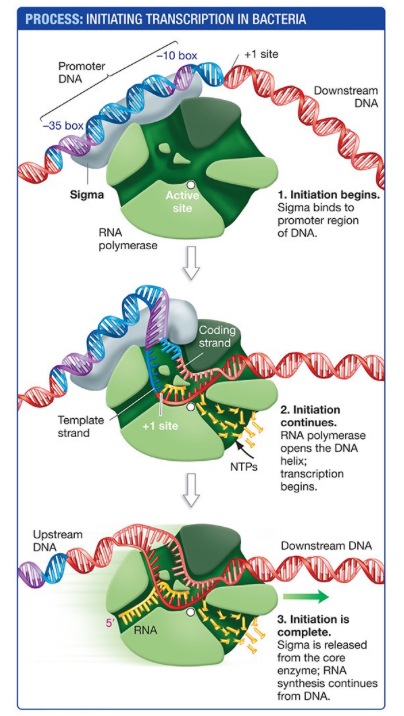
Initiation
RNA polymerase opens double helix, transcription bubble, template threaded through active site. Incoming bases diffuse to active site, complementary base pairing.
Why are promoters needed?
Sigma can’t bind without the special locations of the promoters (-10, -35)
Instead of Helicase, what opens up the helix?
RNA Polymerase
Bacteria ctive site has what type of chemical reaction in Initiation?
Where condensation reaction
During bacteria Elongation, RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template until when?
Until it runs into a transcription-termination
During bacteria Termination what structure to separate the transcript from the RNA polymerase?
Hair pin
Bacteria summary
Eukaryote Summary
During Splicing what’s the difference between exons and introns?
Exons are coding regions and introns are non-coding regions
Spliceosome
Splits away the introns
What is added after splicing? How do they help?
A cap and a tail.
Cap
Helps ribosomes bind and protects from degradation
PolyA Tail
Needed for translation, protects from degradation. Also dissembles RNA like hairpin, termination signal
Translation is ?
a conversion from one language to another
In translation, ribosomes what?
Synthesize proteins
In eukaryotes is transcription and translation physically separated or no?
Physically separated
What does a tRNA Adapter do?
-Holds amino acids
-Interacts with mRNA stand
-Transfer amino acid to growing polypeptide strand
-The Anticodon = matches codon of mRNA
What does an anticodon do?
Matches codon of mRNA
Dr. William Augustus Hinton
Graduated Harvard in 3years, wrote the textbook on syphilis and helped develop the Hinton Flocculation test for it.
Operon
set of coordinately regulated bacterial
genes, transcribed together into one mRNA
LacI
Continuatively active gene (always turned on). It’s a repressor gene.
lacZ
Dr. Roger Kornberg
How are genes regulated in eukaryotes?